Global History Midterm (in progress)
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
Great Chain of Being
Aristotelian idea that society is build upon hierarchy
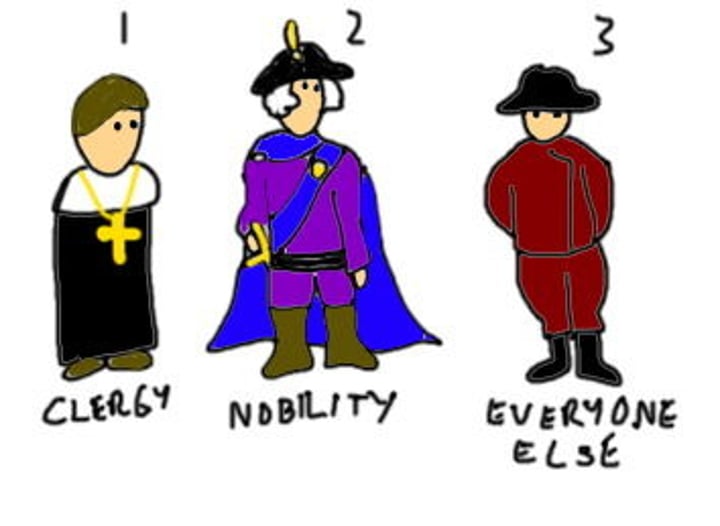
3 Classes of Estates
Clergy, Aristocracy, Everyone else
Development from a monarchy to central state relied on emergence of...
Central Administration and Standing Armies
Reason of State
idea that what's good for the state is good for the king
Serfdom
a system which workers are considered as a part of the land
Guilds
groups made up of similar people and workers which helped formed a local government. they elected officials and decided citizenship.
Economic Traditionalism
people value time over money and want to maintain the standard of living with as little effort as possible
Idealogy provides models for...
how the world works and why the world works
Physical Environment
the physical places we live and exist
Geopolitics
idea that states interact differently based on their localities
Social Structure
looking at categories of difference and categories of community
Categories of Difference
race, class, gender, sexuality, & religion
Categories of Community
citizenship & religion
Political Economy
The study of how we make and distribute stuff
Ideology
a set of interconnected ideas that purport to explain everything necessary to understand and act
Difference between pre-modern and modern idealogies
pre-modern assumed that a larger force shaped reality, while modern assumes that humans make the world.
Whiggish History
looking at history with the idea in mind that the present is the goal
Eschatological History
looking at history with the idea that the end is coming and will redeem the fallen present
Liberalism
the idea that all humans are created equal. idea that everyone has equal access to basic rights of life, liberty, and property
Liberal Paradox
equality can only exist at a level of minimal humanity. focus on equality of opportunity, not outcome
Democracy
core belief that the people should be self governing. idea of popular sovereignty
Democratic Paradox
the democratic claim is that the people govern, when really their representatives do
Challenges for Popular Sovereignty
representation and who gets to be "the people"
Divine Right
the old model of rule, where the ruler was seen to have authority that derives directly from god
Challenges to Divine Right
emergence of rationalism and wars of religion which created pressure to centralize the state
Leviathan (Hobbes)
political work which described human nature as rational, equal, and self-preservative which leads to desire for infinite power. presented idea that human state of nature is miserable and that a sovereign should have absolute power.
Problem with Hobbes' theory in Leviathan
re-justified absolute monarchy, just without God's influence
Second Treatise of Government (Locke)
political work which presents human nature in a similar light as Hobbes. presents idea that state of nature is peaceful and prosperous and that we must have a limited sovereign with a social contract.
Problem with Locke's theory in Second Treatise
since the job of the sovereign is to protect the wealthy, the poor rebel as they are marginalized
Discourse on Inequality (Rousseau)
political work which describes human nature as animalistic. presents state of nature as dumb, poor, and happy, and therefore need a social contract and sovereign to act as the General Will of society.
Problem with Rousseau's theory in Discourse on Inequality
there is no way for dissidents or minorities to object against the General Will
Age of Revolution
Period of political upheaval beginning roughly with the American Revolution in 1775 and continuing through the French Revolution of 1789 and other movements for change up to 1848. Brought about due to new ideas surrounding rule and democratic powers.
Western Exceptionalism
idea that Europeans were different and better than the rest, reaching, far back in history
Problem with Western Exceptionalism
underestimates pre-modern civilizations, especially in Asia and the Islamic world, while overestimating European advantages at the same time.
How did the Americas fall to Europe?
demographic collapse due to disease and genocide
How did Africa fall to Europe?
North Africa Islamized while the rest of Africa became involved in the slave trade
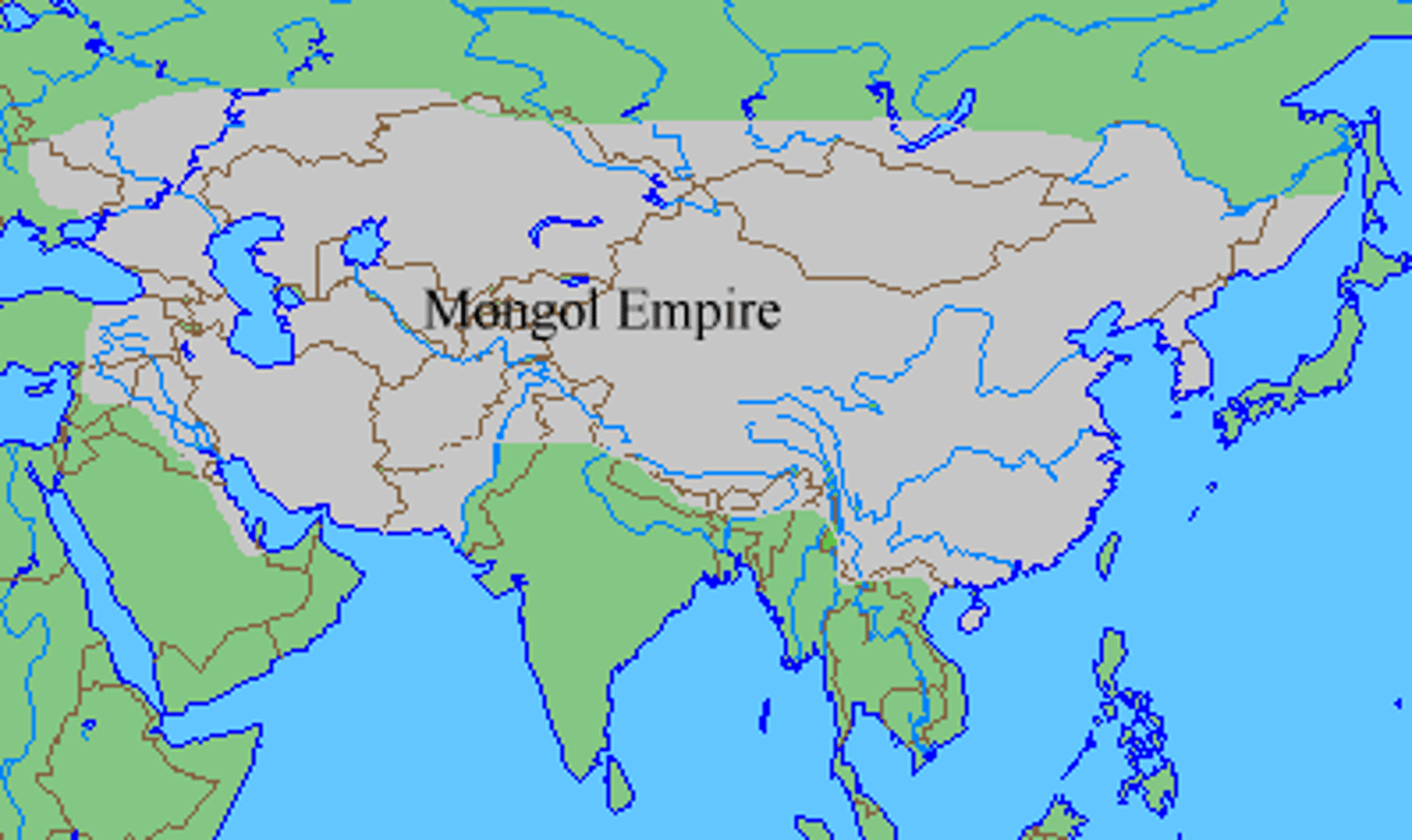
Mongol Empire
an empire founded in the 12th century by Genghis Khan, which reached its greatest territorial extent in the 13th century, encompassing the larger part of Asia and extending westward to the Dnieper River in eastern Europe.
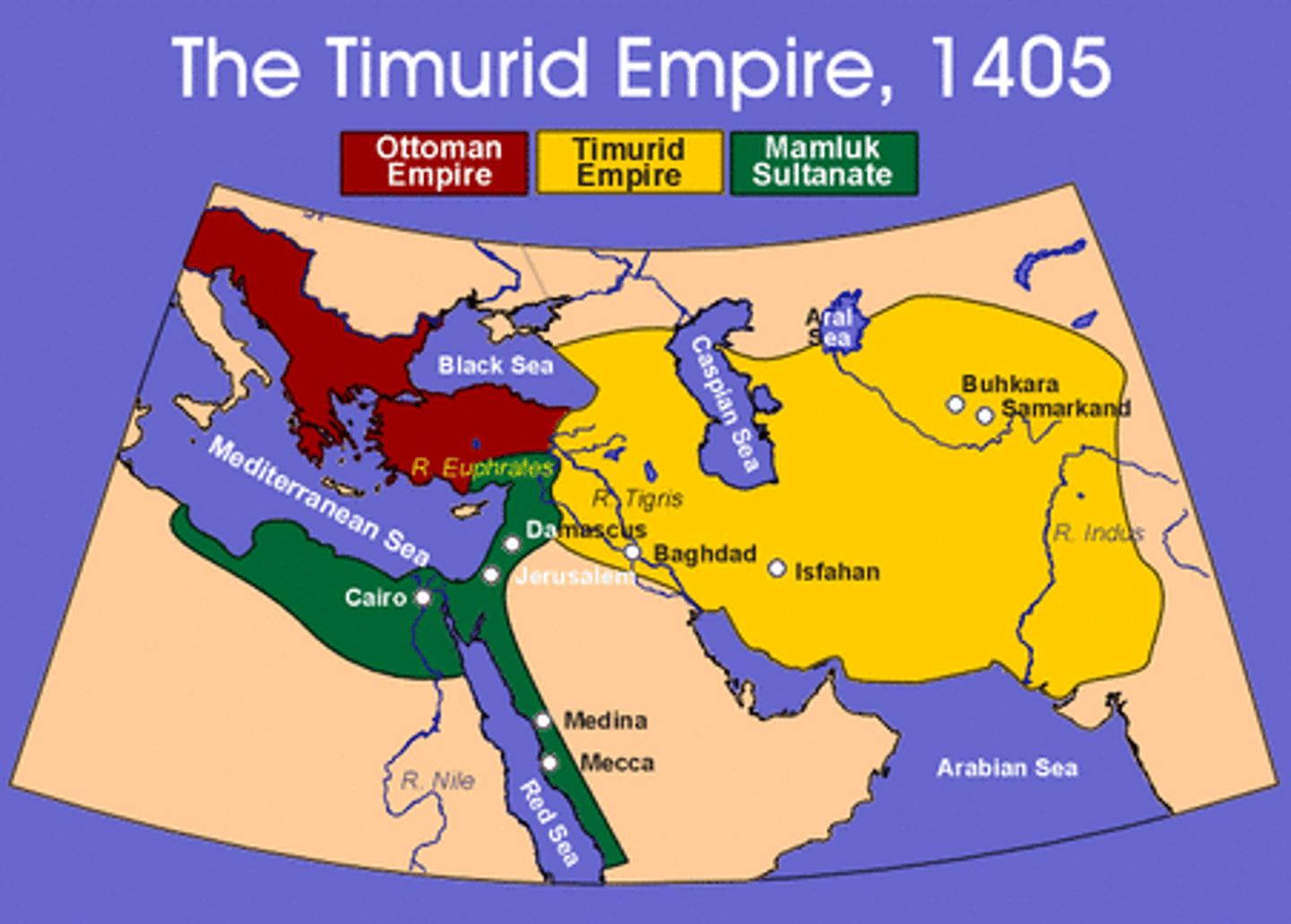
Timurid Empire
Turkic Empire founded by Timur as a mix of Turko-Mongolian and Persian groups
Steppe Empires
Eurasian nomadic empires which were highly dynamic and expansionist. heavily reliant on trade and largely cavalry based.
Limits of Steppe Empires
personal rule and nomadic nature meant very little institution building. in order to durably rule it would have to culturally assimilate and become less nomadic
What led to the end of the cycle of Steppe Invasions?
shift to gun powder weapons brought end to steppe military superiority and technological improvement and location among Eurasian trade routes made them vulnerable to Bubonic Plague
Siege of Vienna
failed attempt by Ottoman Empire to invade Europe. was the farthest Westward advance into Central Europe of the Ottoman Empire.
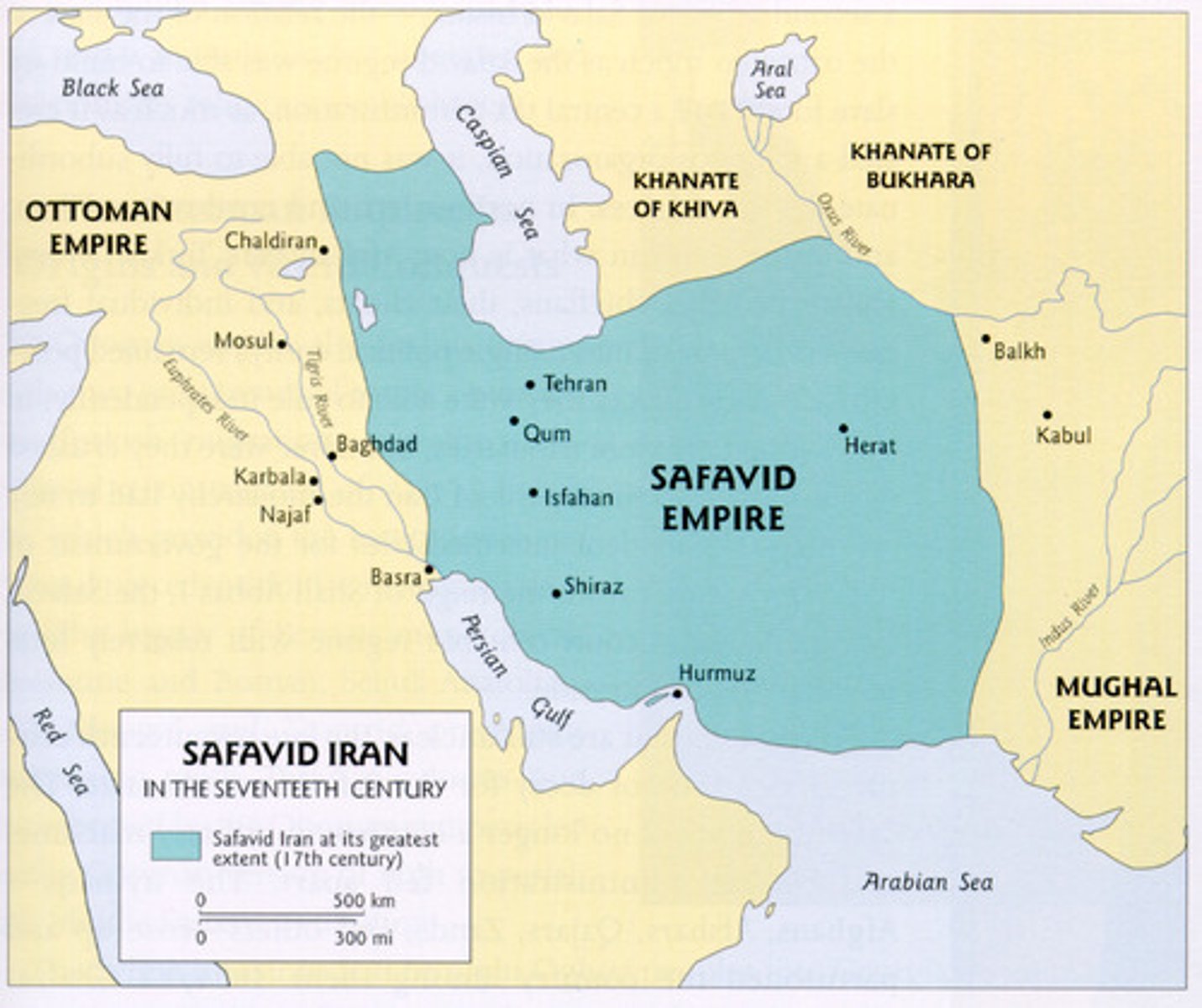
Safavid Empire
Shi'ite Muslim dynasty that ruled Iran between 16th and 18th centuries
French System
framework created by Louis XIV which governed European interstate relations from 1750-1815. It was rooted in a balance of power system and created French alliances
How did the French System help maintain the Eurasian Equilibrium?
protected the Ottomans from the Russians and protected India from the British
What 4 wars destroyed the French System?
7 Years War, American War of Independence, Russo-Ottoman War, and the French Revolutionary & Napoleonic Wars
7 Years War
global war with fronts in North America, India, & Europe. starts in North America with British wanting to expand more.
7 Years War in Europe
Frederick the Great of Prussia sees war in North America as an opportunity to gain territory in Europe while France is busy and can't protect neighbors.
7 Years War in North America
Battle of Fort Necessity sent a message to British & French that war over North America is imminent. French eventually defeated and British capture some colonies.
Diplomatic Revolution of 1756
Major reversal of diplomatic alliances. Great Britain reversed its alliance with Austria and forged a relationship with Prussia, causing France to join with Austria to check Prussian power.
7 Years War in India
France ally with Mughal Empire to try to conquer British territory for trade. French are still defeated, effectively ending their presence in India outside of a few trading posts.
Results of 7 Years War
French overseas empire reduced to Caribbean, French balance of power in Europe ends, Britain controls North America & more power in India, Russia is free to take on Ottomans without worry about the French and their allies
Proclamation Line
British line which prohibited further westward expansion by colonies due to concerns about potential war with Native Americans
Winners of the American War of Independence
Americans and the British, as it frees them of costly North American commitments and allows them to focus on India
Losers of the American War of Independence
Native Americans, as the Northwest Ordinance opens American push into the west & native land, and France, as they do not get Canada or India back and are in massive debt
Causes of Russo-Turkish War
Polish revolt due to Russian control paired with Russian expansion
Results of Russo-Turkish War
Peace treaty which grants Russia control of Crimea, partitions of Poland, Ottoman decline, as they no longer have sole possession of the Black Sea and are plagued by revolts across their European lands.
French Revolution
a tax revolt due to French fiscal crisis resulting from 7 Years War and the American War of Independence. led to development of constitutional monarchy, then series of republics, and eventually an empire under Napoleon.
Results of French Revolution
Napoleon failed to create French hegemony and undo the results of the previous 50 years. Confirmed British naval dominance for next century
How did the period of revolutions create conditions for European Dominance?
Concert of Europe with balance of power for a century, enables European penetration of rest of Eurasia & outer world, creates a population "safety valve" by opening Americas to waves of emigration
Industrial Revolution
the complex of technological inventions in which substituting machines for human skill and inanimate power for human/animal force brings a shift to manufacture.
British Conditions for Industrial Revolution
needed a market to make large-scale production profitable, which they got in India and needed a product to send to market, which was cotton
British destruction of Indian cotton industry
British coerced Indian weavers into fixed contracts which gave British monopolistic control over Indian weaving. Weavers who did not sign contracts were subjected to considerable violence.
How did US emerge as a main cotton supplier?
had the 3 necessary ingredients: land (from Native Americans), cheap labor (slaves), and credit (provided by emerging Northern state markets and England)
Why invest in railroads?
there was excess capital from textiles to invest in railroads and foreign markets were risky, therefore the return of investment on railroads was better than nothing
What contributed to the fall of profits in the textile industry?
textiles were not self-governing market, as they relied on colonialism, producers were faced with option to either cut costs or increase production, but you couldn't cut costs as you were employing slaves, and you couldn't increase production as you had a limited energy supply.
Short Term impact of Industrial Revolution
harmed the proletariat as there work became much more demanding and dangerous, but created more opportunities for the bourgeoisie to grow their wealth
Long Term impact of Industrial Revolution
rises in wages and no meaningful increase in social mobility, workers stayed workers, while owners remained owners
Political Impact of Industrial Revolution
set terms for many of major fights of the 19th and 20th centuries (liberalism vs socialism vs monarchism)
Homo Economicus
bourgeoisie economic view of seeing workers as rational, self-interested, and only interested in accumulating wealth
Urbanization during Industrialization
migration from country to city, creation of urban proletariat with those working in factories, poor quality of life due to cramped living
Liberalism vs Democracy
both presume existence of a state, but liberalism focuses on purpose of the state and its limits while democracy focused in the source of state power and the selection of state agents
Construction of Empires
vertical integration, heterogeneous, segmented hierarchy, territorial discontinuity, territorial expansionists
Construction of Nation-States
horizontal integration, homogeneous, legal equality, territorial integrity, territory more likely to be fixed
Vertical Integration in Empires
Emperor, then Church/Nobles, then peasant groups
Sultan
Military and political leader with absolute authority over the Ottoman empire
Social Structure in Ottoman Empire
muslims vs non-muslims, framework for full vs second-class citizenship
Imperial Overreach
the idea that because empires are heterogenous, vertically segmented, and authoritarian, there is no natural stopping point for expansion and ultimately expand as far as their power allows.
Nationalism
idea that groups of people share some essential identity and should have a homeland or bounded territory. presents the idea that humanity is naturally divided into nations
What is the product of nationalism?
Nation-States
Problem with Nation-States
what happens when people do not correspond with a set territory or are trapped in a foreign territory
Colony
subordinate geographic component of an empire that is nor directly incorporated into the metropole. Indigenous population is subordinate but left more or less intact
Settler Colony
large scale migration from metropole into the settler colony with substantial disruption of the indigenous population.
3 Phases of European Imperialism
Old Imperialism, Free Trade Period, New Imperialism
Old Imperialism
direct settler colonialism in Americas and commercial colonies in Asia
Free Trade Period
Economic globalization which does not include much European incursion outside of France in Algeria and Britain in India
Monroe Doctrine
an American foreign policy opposing interference in the Western hemisphere from outside powers
Opium Wars
Wars between Britain and the Qing Empire caused by the Qing government's refusal to let Britain import Opium. China lost and Britain and most other European powers were able to develop a strong trade presence throughout China against their wishes.
The New Imperialism
the late 19th century drive by European countries to create vast political empires abroad
Indian Mutiny
discontent with British administration in India led to numerous mutinies in 1857 and 1858
Meiji Restoration
a Japanese state-sposored industrialization and westernization effort in late 19th century which involved the elimination of the Shogunate and power being handed over to the Japanese Emperor, who had previously existed as mere spiritual/symbolic figure. Idea that the only way to fight imperialists is to become imperialist
Reasons for Euro-American Global Dominance
Economic expansion, development of colonies, scientific racism & social darwinism, control of sea lanes.
Little Big Horn
A particularly violent example of the warfare between whites and Native Americans in the late nineteenth century. The battle came as the U.S. government tried to compel Native Americans to remain on the reservations and Native Americans tried to defend territory from white gold-seekers. This Indian advantage did not last long, however, as the union of these Indian fighters proved tenuous and the United States Army soon exacted retribution.
Why did Euro-Americans Succeed?
massive technological edge, economic advantage (steamship & railroad), communication edge (telegram), indigenous groups were divided, no one to supply indigenous resistance
Neo-Traditionalism
practice of mobilizing traditional resources to combat European influence and power
Swaraj
Gandhi's goal of 'self-rule'
Non-Cooperation
legal refusal to obey a law or policy as a way to protest
Civil Disobedience
an illegal, nonviolent, public refusal to obey allegedly unjust laws.
Gharbzadegi
"Weststruckness," "Westoxification," or "Occidentosis" of Iran
Tanzimet Reforms
Nineteenth century reforms by Ottoman rulers designed to make government and military more efficient.