N362 Exam #2
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
What is EMTALA?
It is a federal law that came into the 1980s that states that anyone who comes into the ER and wants a medical screening exam has to be given one regardless of financial or insurance status
What is the number one thing we want to avoid in the ER?
Sentinel events — patient safety event that results in death, permanent harm or severe temporary harm. This can lead to a delay in care and medication errors. It can also be affected by pt volume
What is the difference between disaster triage and ER triage?
ER triage - we’re looking to identify patients who are most critically ill, they receive the most resources regardless of potential outcome, while in disaster triage, we need to use the most resources to help the most people
What is the ABCDE of emergency nursing?
This is the primary survey
A: Airway
B: breathing
C: circulation
D: disability — assess neurologic functions
E: exposure — undress to assess for injury
What is the FGHI of emergency nursing?
Secondary survey
F: Full set of VS
G: Get labs & diagnostics
H: Head to toe assessment
I: inspect posterior surface (distracting injuries)
endotracheal tube
How fast can an anoxic brain injury occur in a patient with total airway occlusion?
3 minutes
How do you treat someone who is hemorrhaging and what should you be careful of?
Mass transfusions, hypovolemic shock
Arterial bleed vs venous bleed
Arterial bleed will shoot out, venous bleed will seep out
What is a cricothyroidotomy?
An emergency medical procedure that can open the airway below the upper airway and ventilation occurs through a bag valve mask
A 16 year old patient who was in a motor vehicle accident presented to the ER. Her breathing is rapid and irregular with a HR of 136/min, and +1 pulses. She is able to answer some questions, but appears to be confused, and is in and out of consciousness. What is the nurse concerned about and what is the next course of action? What is the goal of her interventions?
The patient is hemorrhaging. The patient needs to be put on fluid replacement to control the bleeding — the goal is to maintain adequate circulating volume in order to prevent HEMORRHAGIC SHOCK
What is the Belmont Level One?
it is a mass transfusion device that can put liters of fluid and blood into the body in a matter of seconds
Why might someone delay a primary closure of a wound coming from an animal bite?
There is a risk of infection, so it needs to be cleaned thoroughly and treated prophylactically first thru rabies shots
What is the goal in wound care?
Cleaning and doing a primary closure
How do you assess for trauma?
Start with circulation — trauma can cause uncontrolled hemorrhage, need to treat this first then go back to the ABCs
What are some ways you can stop trauma?
Tourniquets, pressure points, “stop the bleed” — packing the wound. You might also need to put a C-Collar on these patients if they fall, we have to protect the C-spine in case there’s injury to it
Why do we put forensic evidence in a paper bag and not a plastic bag?
A paper bag will allow to dry the evidence without compromising the materials
What are automatic protections?
Something that exists in daily life that we don’t have to rely on people to change their behavior about, i.e. airbags
What are the treatment goals for a patient who ingested poison?
You can remove or inactivate poison before it’s absorbed, but it’s not always possible
Treatment is very specific to the substance you’re dealing with
A 20 year old man presents to the ED, claiming that he ingested poison. What should the nurse do?
Ask what, when and how much of the substance was ingested, can also ask family or EMS
Need to monitor ABCs, VS, LOC, and ECG
Monitor UO (urine output) to make sure kidneys are working
Look for S/S of poisoning and tissue damage
Need a medical hx, particularly weight since meds are administered based on weight
Why do you want an EKG on a patient who might have ingested poison?
Certain meds can cause changes in the EKG
What is the primary way to remove toxins or decrease its absorption in the body?
Activated charcoal
What is gastric lavage and why is it not used anymore?
Gastric lavage is the medical term for pumping one’s stomach when you suspect they’ve ingested poison — you instill the solution and suction it back out. It is not used anymore since this method can result in a perforated esophagus
Why aren’t emetics used anymore in treating poisoning?
Emetics were used with the idea of vomiting up toxins, but this leads to a risk of aspiration where gastric contents can get into the lungs. This could result in significant risks of pneumonia or sepsis
What is the first step in any poisoning?
Contacting poison control
What is the most common substance to abuse?
Alcohol, it is a multisystem neurotoxin
What do you have to look out for as a nurse caring for a patient who abuses alcohol?
People who drink regularly have a higher propensity for falling
Observe for CNS depression + hypotension
Be alert for symptoms of withdrawal, delirium and occult injuries, and nutritional deficiency
They are at a higher risk for an intracranial bleed
Do frequent and consistent neuro checks
Why are alcoholics at a higher risk for an intracranial bleed?
A long term alcohol user tends to have a smaller brain and more friable vasculature in the head; the brain can move in the skull which can lead to vessels tearing more easily
What is the key to treating alcohol poisoning/withdrawal?
Maintaining airway
What are occult injuries?
Injuries that might not be visible on the outside
A 17 year old girl presents to the ED looking frightened and agitated. She is accompanied by her boyfriend, who states that she has been complaining of abdominal pain, and bouts of headaches and dizziness. She has a history of running away, self-harm and homelessness. The nurse suspects that she is a victim of human trafficking. How should the nurse deal with this?
Use targeted, appropriate questions like “do you know who he is,” “do you have control over your situation” etc etc
You can ask to speak to the patient alone!!!! This is something you are allowed to do as a nurse
What is the NYS Mental Health Law?
It governs our care of people who are intoxicated or inebriated who may need psychiatric care, these are laws that provide for transportation to an ED by order of different community members
Someone calls 911 stating that their family member has been exhibiting plans of taking their own life. What is the appropriate NYS mental health hygiene that corresponds to this?
9.41, police officers take in someone who is at risk for suicide to be evaluated by a psychiatrist
You are sitting in a zoom call with a patient receiving therapy. All of a sudden, they disclose that they had plans to kill themselves and had already popped pills in their mouth beforehand. What is the appropriate NYS mental health law that corresponds to this call?
9.45, initiated by psychiatrists, psychologists, or social worker
What is the NYS mental health law that is initiated by a physician?
9.57
During Santacon, you receive calls about intoxicated college students who are so drunk they can barely walk. What is the appropriate NYS mental health hygiene law that corresponds to this?
22.09
Who is at high risk for burn injuries?
Young children, older adults, disabled patients and males
Most burns occur in the home. True or false.
True
Which is not a function of skin?
Gives a protective barrier from outside elements
Helps with Vitamin D synthesis
It gives us our good looks and recognition
Helps with Vit K synthesis
Helps with thermoregulation
Helps with Vit K synthesis
Rationale:
Vit K is synthesized in the intestines, vit D is synthesized in the skin and is good for absorbing Calcium
What are some things you can educate your patient on to prevent burns?
Sun exposure
Make sure they supervise their children
Avoid smoking in bed
Avoid running cords under rugs
First degree burns
superficial injuries that involve the outermost layer of skin, i.e. sunburn
Second degree burns
involve entire epidermis and portions of the dermis; painful w/ blisters
Third degree burns
full thickness, it burns past the underlying tissue, there is a lack of sensation
Fourth degree burn
deep burn necrosis, extends into deep tissue, muscle, or bone
What is the rule of nines?
this is the most common method used to estimate TBA burned, it’s based on anatomic regions where body parts are divided into 9s
What type of burns can you use the rule of nines on?
Only 2nd and 3rd degree burns
What happens when 30% of your body is burnt?
Hypoperfusion and organ hypofunction occurs when fluid shifts d/t the systemic response that releases cytokines and mediators into the body
What are the phases of burn injury?
Emergent or resuscitative phase: onset of injury to completion of fluid resuscitation
Acute or intermediate phase: from beginning of diuresis to wound closure
Rehab phase: from wound closure to looking at more physical and psychosocial adjustment i.e. skin grafting
When do you insert NG tubes in a burn patient?
NG tubes are inserted in pts who exceed 20-25% burns on their body
When do you insert an ECG in a burn patient?
Those who have electrical burns
What are we most worried about in burn patients?
Fluid loss, there is a rapid shifting of electrolytes and fluids from intravascular to interstitial spaces d/t the body’s inflammatory response, which can lead to dehydration as the body tries to compensate for fluid loss
Why do we use lactated ringer’s/isotonic solutions for burn patients?
It buffers metabolic acidosis since it contains lactate, and its composition and osmolality closely resemble normal bodily physiological fluids
Following a burn accident, a patient is tachycardic, has a HR of 150, BP of 90/51, RR of 8 with deep, long breaths intermittently. After further inspection, the patient also appears to have edema at the site of their burn injury. What is the nurse worried about and what should her next action be?
The patient is going into shock, need to watch out for metabolic acidosis and administer lactated ringer’s/isotonic solutions
Is the following statement true or false?
Breathing must be assessed and a patent airway established immediately during the initial minutes of emergency burn care.
True
We need to replace ____ of the fluid loss within __ hours
50%, 8 hours
Fluid and elyte shifting can cause
Metabolic acidosis, hyponatremia and hyperkalemia
Radiation therapy
uses high energy ionizing rays or particles to treat cancer, which destroys the ability of the cancer cells to grow and multiply
IMRT — intensity modulated radiation therapy
form of high precision RT that can deliver extremely controlled doses of radiation to malignant tumors
brachytherapy
a form of radiation therapy where they put radioactive substances such as seeds, needles or capsules near the tumor inside your body and it stays there. helpful because it delivers large amounts of RT to tumor for a short period of time
What is brachytherapy commonly used for
Breast, prostate, cervix, vagina cancers
How often should a nurse monitor an implant placement from a brachytherapy?
Every 4-6 hours
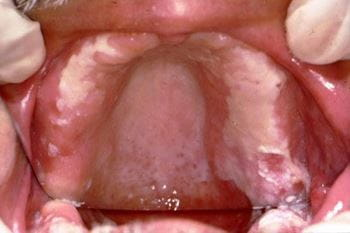
stomatitis/mucositis — an effect of RT where there is an inflammation and redness of the oral mucosa
xerostomia — dryness of tongue
osteoradionecrosis — an iatrogenic disease caused by RT of oral and oropharyngeal cancers, there is severe bone/tissue damage in the mouth
Tooth decay & caries — there is a change in saliva, may feel thick and sticky or the mouth may feel dry
Chemotherapy
Antineoplastic agents are used to kill tumor cells by interfering with the cell cycle, most often used to treat cancer, much less likely to damage cells that are at rest such as most normal cells
immunotherapy
uses substances made by the body or in a lab to boost the immune system and help it find and destroy cancer cells; can be used alone or in combo with chemo or other cancer treatments
examples: cytokines, monoclonal antibodies
Targeted therapy
uses drugs to target specific genes and proteins that help cancer cells survive and grow
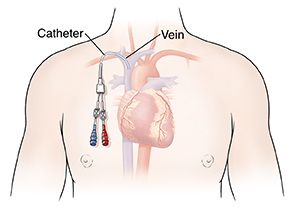
CVAD
Extravasation; this occurs when IV chemo drug leaks out of the vein
A patient with leukemia started receiving chemotherapy around 2 weeks ago. Among the nurse’s responsibilities when caring for a cancer patient includes caring for skin integrity. What should the nurse do to prevent skin breakdown?
Assess skin integrity
Minimize trauma and protect the skin
If skin has dry breakdown — apply lotion
If skin weeps — apply non-adhesive absorbent dressing
Tell patient to protect skin, use sunblock after treatment
Can refer to consult with a wound-ostomy-continence nurse (CWOCN)
A client has been receiving chemotherapy to treat cancer. Which of the following assessment findings suggests that the client has developed mucositis?
A. White cottage cheese-like patches on the tongue
B. Yellow tooth discoloration
C. Red, open sores on the oral mucosa
D. Rust-colored sputum
C. Red, open sores on the oral mucosa
Rationale: Mucositis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa. White cottage cheese-like patches on the tongue is indicative of thrush. Yellow tooth discoloration is a side effect of radiotherapy. Rust colored sputum suggests pneumonia
You have reported your assessment findings to the doctor who diagnoses the patient with mucositis. With chemo, mucositis typically heals by itself when there is no infection, and healing can take up to 4 weeks. What are some nursing interventions you can implement while caring for this patient?
Inspecting mouth daily to check for yeast; if found, antifungals is needed i.e. nystatin
Putting the patient on a soft, bland diet & maintaining hydration
Saliva substitute
Applying topical anesthetics & oral care
Xerostomia is a side effect more specific to radiotherapy, especially if the procedure was done near the salivary glands. The radiation causes the saliva to change from a thin fluid to thick, sticky and acidic substance unable to cleanse the mouth. This makes swallowing difficult and can lead to other dental problems. Some nursing interventions include:
Mouth care, use soft bristle brushes
Sugarless sour candies
Saliva substances
Sauces, gravies, liquids on foods to make them moist
Another side effect of chemotherapy is myelosuppression, which causes a decrease in all types of WBCs. This puts a chemo patient at significant risk for infection, as they are now immunosuppressed. What are some nursing interventions to minimize infection risks?
Monitor CBC and granulocyte count
Monitor ANC level (infection risk)
Watch for NADIR - the lowest white cell count during that treatment cycle, happens in every chemo pt
Handwashing
Restricting visitors
Why can’t we give chemo patients a rectal temperature?
It can cause spontaneous bleeding
Patients undergoing chemotherapy are also at an increased risk of thrombocytopenia, which could lead to spontaneous bruising and bleeding. What are some nursing interventions a nurse could take to minimize injury?
Assess for bruising, check CVAD site if they have one, or gross blood from other sites
Assess for petechiae
Do not give IM injections or rectal temp d/t possibility of causing spontaenous bleeding
Monitor PLT levels & transfuse if ordered
Nausea and vomiting is a common side effect of RT and chemo. List some nursing interventions to help alleviate these symptoms in a patient.
Assess strategies that have worked for the pt — important!
Make sure anti-emetics are administered prior to any meal times — you don’t want to just give them anything
Monitor lab values r/t nutrition
Cold, salty, dry crackers and toast may be tolerated
What is the most common meds given to chemo patients for anticipatory N/V?
Benzodiazepine
A 73 year old patient with advanced cancer has been receiving intensive chemotherapy for a few months now. His family approached the nurse, raising some concerns about the patient’s nutrition and weight gain. They observe that he has been rapidly losing weight, accompanied with persistent weakness and fatigue. He is rapidly wasting and that no matter how much nutrients he eats, it doesn’t seem like he is gaining any weight. The nurse explains to the family that the patient has:
Cancer-Related Anorexia-Cachexia Syndrome (or CACS)
A 56 year old patient with lung cancer starts showing symptoms of cardiac tamponade. As a nurse, what assessments would you expect to see?
Hypotension, JVD (jugular venous distension) and muffled heart sounds
What are the early signs of increased ICP?
LOC, severe headaches, lethargy, weakness
A nurse assess a cancer patient during her hourly rounding. During her assessments, she finds that the patient has irregular respirations, a widening pulse pressure, and bradycardia. The nurse suspects that the patient has:
Increased ICP
A patient in late-stage lung cancer is presenting symptoms of SVC syndrome. What assessments would you expect to find?
Face/neck swelling, distended neck and chest veins, dyspnea, upper extremity swelling, orthopnea, cyanotic appearance of skin
A patient with lymphoma is beginning to exhibit signs of spinal cord compression. What assessments would you expect to find?
Early signs: back pain that worsens when supine, coughing, straining or flexion of neck and motor weakness and sensory loss
Late signs: Loss of sensation for deep pressure, urine or fecal incontinence/retention, impotence, muscle atrophy and paralysis
Following an MRI, the doctors found that the patient with breast cancer has spinal cord compression. What is the best nursing interventions to implement?
decrease severity of symptoms, pain control
Maintain muscle tone by assisting ROM exercises
Monitor B&B patterns and perform ongoing neuro assessments
Why are we worried about tumor lysis syndrome?
Tumor lysis syndrome can cause cardiac arrhythmias because it causes hypocalcemia, hyperkalemia, hyperuricemia, hyperphosphatemia
What is the definitive study of cardiac implications in infants and children?
Cardiac catheterization
What are some s/s to look out for in pediatric cardiac complications?
Cyanosis
Clubbing
Squatting
Central edema
Poor feeding
Crackles
Poor weight gain
What are some types of cyanotic heart diseases
tricuspid atresia and tetralogy of fallot
tetralogy of fallot:
a CHD composed of four heart defects: aortic stenosis, overriding of aorta, VSD, right ventricular hypertrophy
tricuspid atresia
CHD where the valve between the RA and RV was not properly developed so there’s no blood flow going between that and through the PA into the lungs
Acyanotic vs Cyanotic heart diseases
Acyanotic: blood has enough oxygen, but is pumped abnormally around the body; increased pulmonary blood flow
Cyanotic: heart defects that reduce the amount of O2 delivered to the rest of the body; decreased pulmonary blood flow
A mother recently gave birth to a baby at 36 weeks gestation, who is now 2 weeks old. The baby has been having on and off respiratory infections. During the NICU nurse’s assessment, she found that the baby is tachypneic, tachycardic with a widening pulse pressure. Pulmonary edema is also present, with murmurs and rhonchi present upon auscultation of the chest. What should the nurse be concerned about and what should her next course of action be?
The nurse should be worried about acyanotic heart diseases (remember, there is an increase in pulmonary blood flow). She should be working to keep O2 SATs up and put the neonate on fluid restriction and diuretics. Also take accurate I&Os and take frequent breaks with IV feeding
A baby who was born at 34 weeks gestation has a BP of 80/40 with rales and murmurs present upon auscultation. Labs were ordered, and the echo shows that the baby has a ventricular hypertrophy and CXR shows cardiomegaly. What is the nurse worried about and what treatments should the nurse consider to help?
Patent ductus arteriosis (PDA); Tx includes:
Surgical correction for term infants or those for whom indocin did not work that are symptomatic
Indocin for premature infants or those too ill for surgery; watch urine output —> can cause kidney damage
Patent ductus arteriosus
occurs when the ductus arteriosus fails to close within the first few weeks of life
what is the second most common CHD?
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
How is VSD best diagnosed?
MRI or echo
A nurse notices that a 3 day old infant becomes diaphoretic while feeding, which is never a good sign in neonates. Upon further inspection, she finds that the infant is cyanotic, tachycardic, dyspneic and has clubbing of the extremities. What should she be worried about?
Cyanotic heart diseases
A nurse finds that 6 day old baby is showing signs of hypercyanotic spells or tet spell. What should her assessment findings be?
Incr rate and depth of breath
Incr HR
Cyanosis
Pallor
Diaphoresis
Loss of consciousness happening after waking from sleeping