Microbial Symbiosis, Pathogen Reservoirs, and Disease Transmission in Infectious Diseases
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
164 Terms
Symbiosis
Means 'to live together'.
Mutualism
A type of symbiosis where both organisms benefit.
Commensalism
A type of symbiosis where one organism benefits and the other is neither helped nor harmed.
Amensalism
A type of symbiosis where one organism is harmed and the other is neither helped nor harmed.
Parasitism
A type of symbiosis where one organism benefits at the expense of the other.
Normal microbiota
Organisms that colonize the body's surfaces without normally causing disease.
Resident Microbiota
Microbiota that are a part of the normal microbiota and remain in the body throughout life.

Transient Microbiota
Microbiota that remain in the body for a short period and cannot persist due to competition, elimination, or changes in the body.
Opportunistic pathogens
Normal microbiota that cause disease under certain circumstances.
Reservoirs of infection
Sites where pathogens are maintained as a source of infection.
Animal reservoir
A type of reservoir where pathogens are maintained through direct contact with animals or their waste.
Human carriers
Asymptomatic infected individuals who can transmit pathogens.
Nonliving reservoir
Reservoirs such as soil, water, and food that can harbor pathogens.
Zoonoses
Diseases that are transmitted from animals to humans.
Tapeworm infestation
Caused by Dipylidium caninum, transmitted through ingestion of larvae in dog saliva.
Fasciola infestation
Caused by Fasciola hepatica, transmitted through ingestion of contaminated vegetation.
Malaria
Caused by Plasmodium spp., transmitted by the bite of Anopheles mosquito.
Toxoplasmosis
Caused by Toxoplasma gondii, transmitted through ingestion of contaminated meat, inhalation of pathogen, or direct contact with infected tissues.
Ringworm
Caused by Trichophyton spp. and Microsporum spp., transmitted through direct contact.
Anthrax
Bacterial disease caused by Bacillus anthracis, transmitted through direct contact with infected animals or inhalation.
Bubonic plague
Bacterial disease caused by Yersinia pestis, transmitted through flea bites from infected rodents.
Lyme disease
Bacterial disease caused by Borrelia burgdorferi, transmitted through tick bites from infected deer.
Salmonellosis
Bacterial disease caused by Salmonella spp., transmitted through ingestion of fecally contaminated water or food.
Rabies
Viral disease caused by Lyssavirus sp., transmitted through the bite of infected animals such as bats, skunks, foxes, and dogs.
Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome
Viral disease caused by Hantavirus sp., transmitted through inhalation of viruses in dried feces and urine from deer mice.
Yellow fever
Viral disease caused by Flavivirus sp., transmitted through the bite of Aedes mosquitoes.
Contamination
The mere presence of microbes in or on the body.
Infection
When organism evades body's external defenses, multiplies, and becomes established in the body.
Portals of Entry
Sites through which pathogens enter the body.
Parenteral route
Entry via the parenteral route circumvents the usual portals; pathogens deposited directly into tissues beneath the skin or mucous membranes.
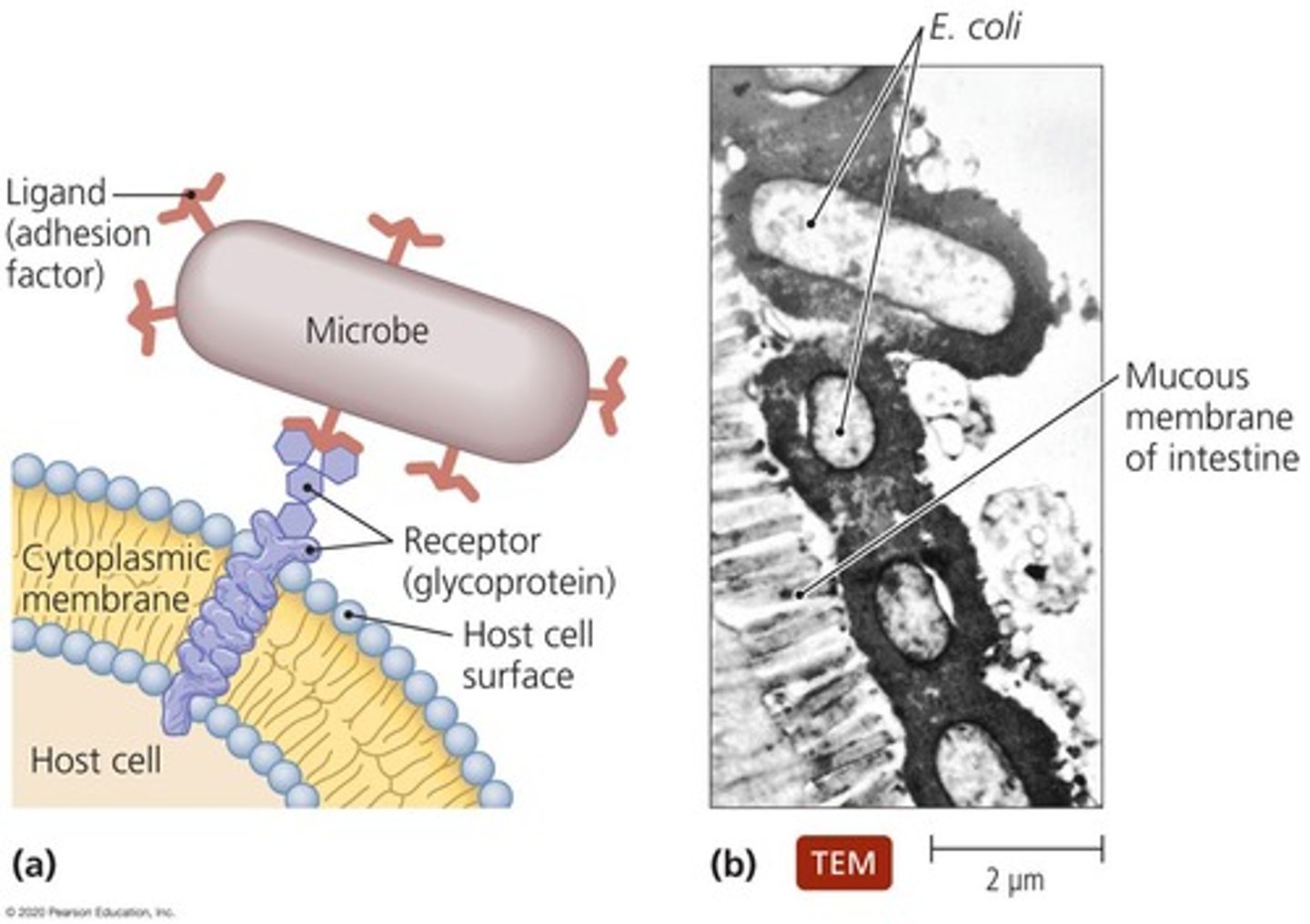
Adhesion
Process by which microorganisms attach themselves to cells; required to establish colonies successfully within the host.
Virulence Factors
Factors that contribute to the ability of a microorganism to cause disease.
Pathogenicity
Ability of a microorganism to cause disease.
Virulence
Degree of pathogenicity.
Adhesion factors
Specialized structures or attachment molecules that aid in the adhesion of microorganisms.
Biofilms
Complex communities of microorganisms that adhere to surfaces.
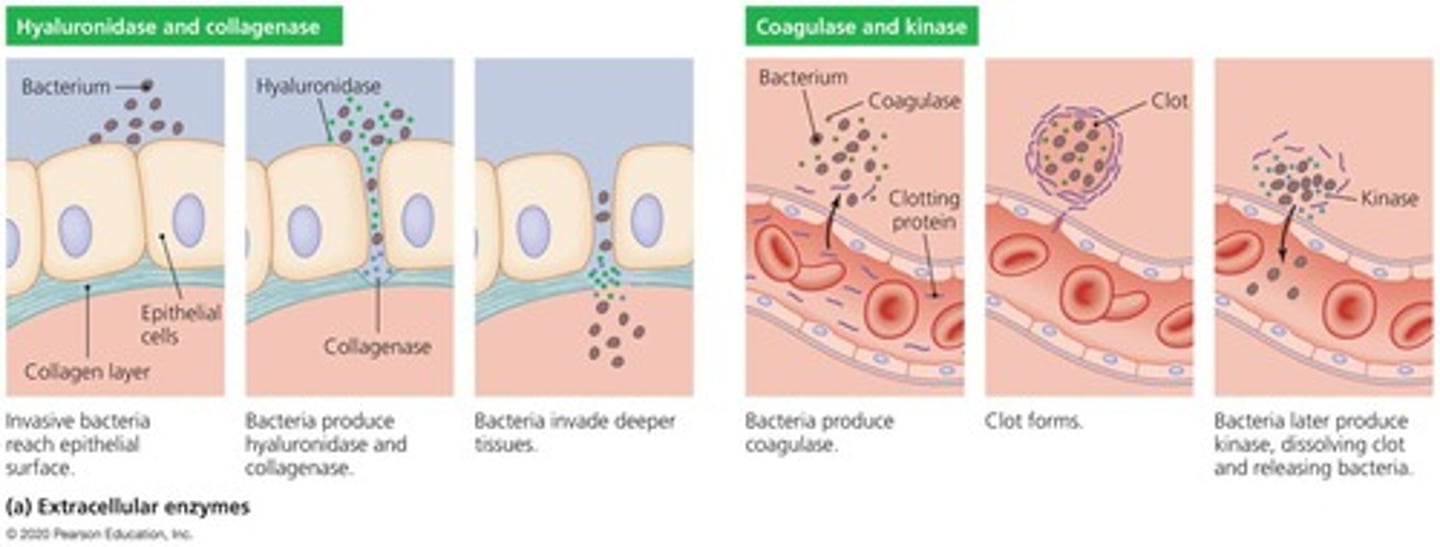
Extracellular enzymes
Secreted by the pathogen; dissolve structural chemicals in the body and help maintain infection, invade, and avoid body defenses.
Toxins
Chemicals that harm tissues or trigger host immune responses that cause damage.
Toxemia
Refers to the presence of toxins in the bloodstream.
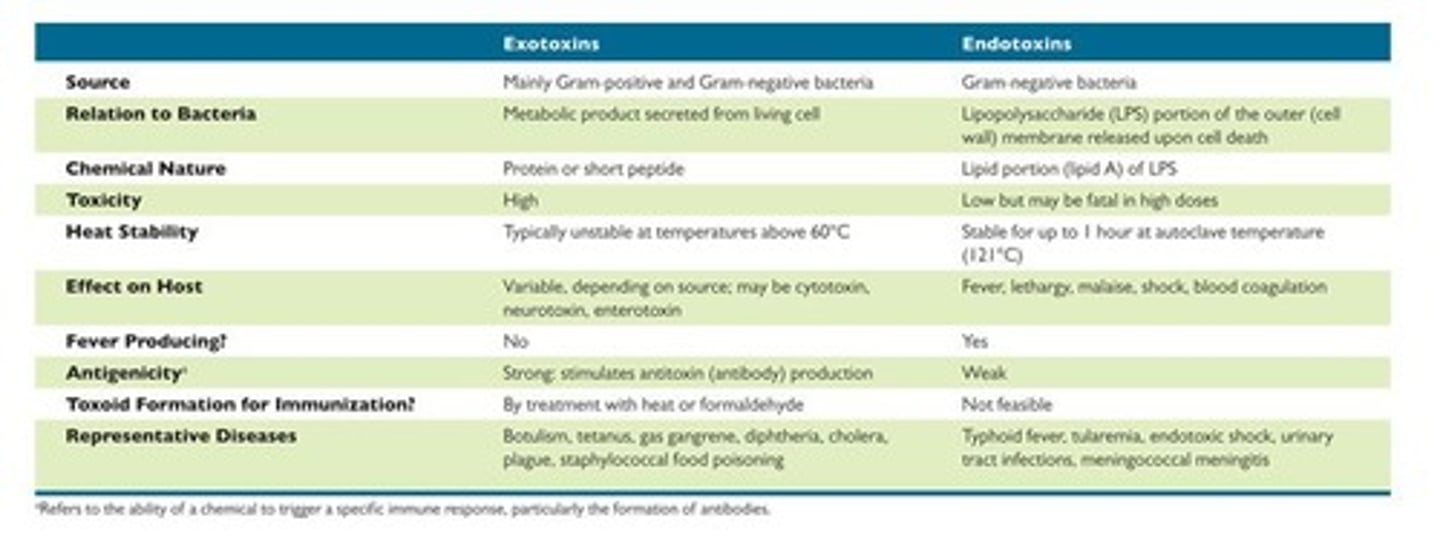
Exotoxins
Type of toxins that are secreted by bacteria and can cause damage to the host.
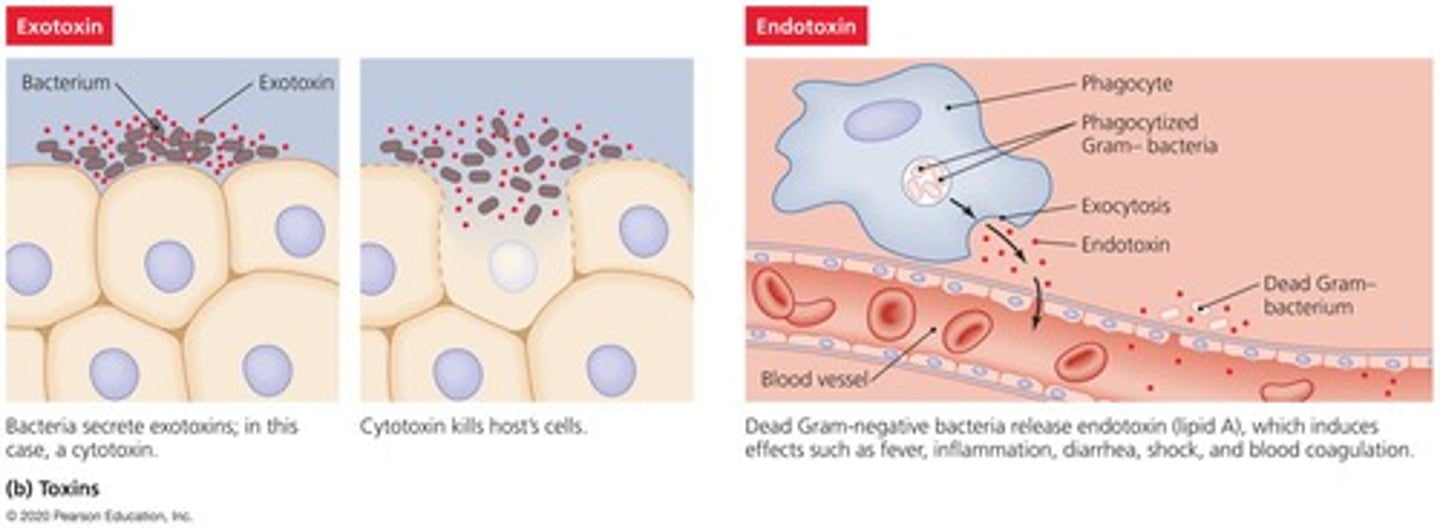
Endotoxins
Type of toxins that are part of the bacterial cell wall and can trigger immune responses.
Antiphagocytic factors
Factors that prevent phagocytosis by the host's phagocytic cells.
Bacterial capsule
Composed of chemicals not recognized as foreign; slippery and difficult for phagocytes to engulf.
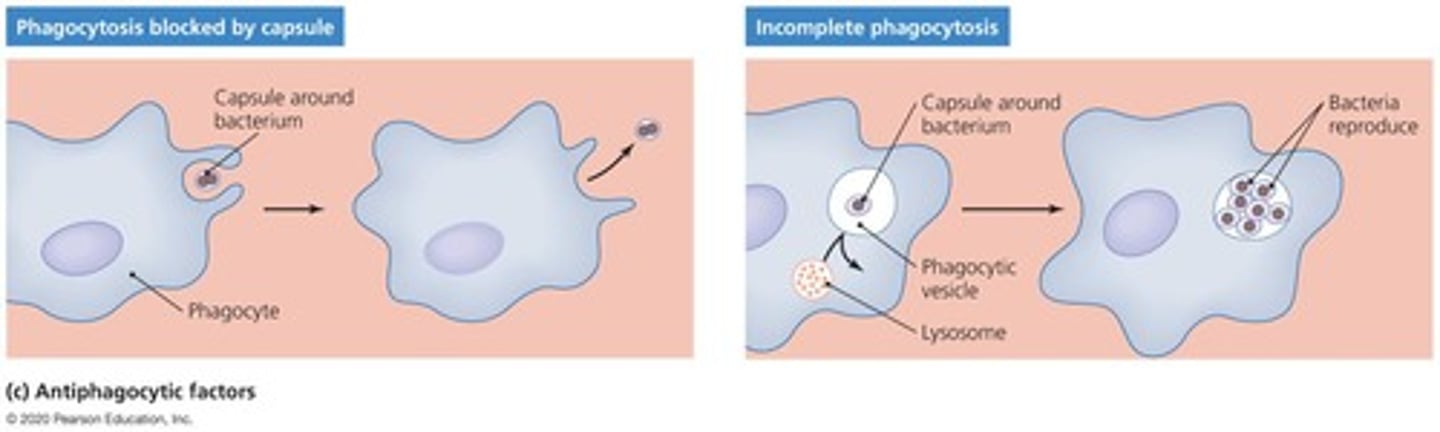
Antiphagocytic chemicals
Prevent fusion of lysosome and phagocytic vesicles; leukocidins directly destroy phagocytic white blood cells.
Stages of Infectious Disease
The disease process occurs following infection and typically includes five stages: Incubation period, Prodromal period, Illness, Decline, Convalescence.
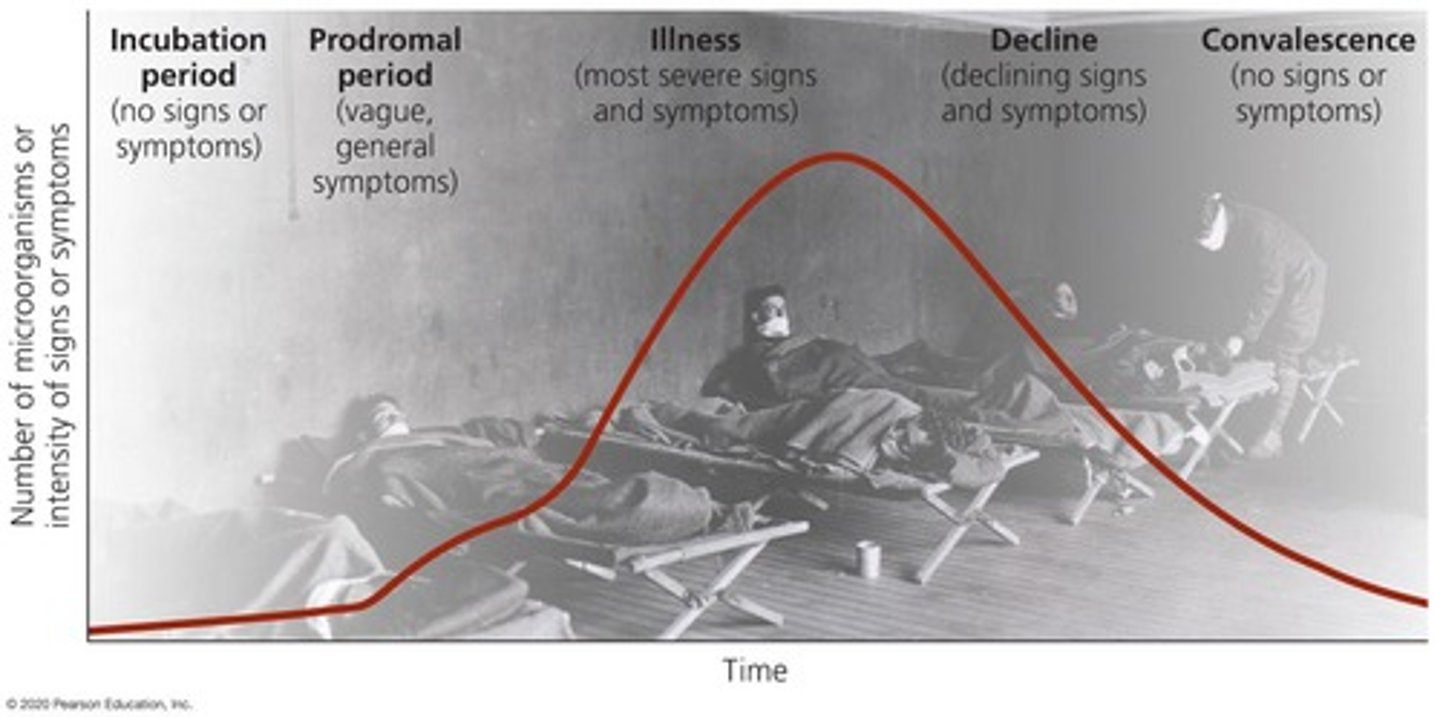
Incubation period
The time between exposure to the pathogen and the onset of symptoms.
Prodromal period
The stage of an infectious disease characterized by early symptoms.
Illness
The stage of an infectious disease where symptoms are most severe.
Decline
The stage of an infectious disease where symptoms begin to subside.
Convalescence
The stage of recovery following an illness.
Incubation Periods of Selected Infectious Diseases
Staphylococcus foodborne infection: <1 day; Influenza: About 1 day; Cholera: 2 to 3 days; Genital herpes: About 5 days; Tetanus: 5 to 15 days; Syphilis: 10 to 21 days; Hepatitis B: 70 to 100 days; AIDS: 1 to >8 years; Leprosy: 10 to >30 years.
Symptoms
Subjective characteristics of disease felt only by the patient.
Signs
Objective manifestations of disease observed or measured by others.
Syndrome
Symptoms and signs that characterize a disease or an abnormal condition.
Asymptomatic/subclinical
Infections lack symptoms but may still have signs of infection.
Pain
A symptom sensed by the patient, often associated with discomfort.
Nausea
A symptom sensed by the patient, characterized by a feeling of unease in the stomach.
Headache
A symptom sensed by the patient, often described as pain in the head.
Chills
A symptom sensed by the patient, often associated with fever.
Sore throat
A symptom sensed by the patient, characterized by pain in the throat.
Fatigue
A symptom sensed by the patient, described as tiredness or lethargy.
Malaise
A symptom sensed by the patient, characterized by a general feeling of discomfort.
Itching
A symptom sensed by the patient, often causing a desire to scratch.
Abdominal cramps
A symptom sensed by the patient, characterized by pain in the stomach area.
Swelling
A sign detected or measured by an observer, characterized by an increase in size of a body part.
Rash or redness
A sign detected or measured by an observer, often indicating irritation or infection.
Vomiting
A sign detected or measured by an observer, characterized by expulsion of stomach contents.
Diarrhea
A sign detected or measured by an observer, characterized by frequent loose or liquid bowel movements.
Fever
A sign detected or measured by an observer, characterized by an elevated body temperature.
Pus formation
A sign detected or measured by an observer, indicating infection or inflammation.
Anemia
A sign detected or measured by an observer, characterized by a decrease in red blood cells.
Leukocytosis/leukopenia
A sign detected or measured by an observer, indicating an increase/decrease in the number of circulating white blood cells.
Bubo
A sign detected or measured by an observer, characterized by a swollen lymph node.
Tachycardia/bradycardia
Signs detected or measured by an observer, indicating an increase/decrease in heart rate.
Etiology
Study of the cause of disease.
Hereditary diseases
Caused by errors in the genetic code received from parents.
Congenital diseases
Anatomical and physiological defects present at birth caused by various factors.
Degenerative diseases
Result from aging.
Nutritional diseases
Result from lack of some essential nutrients in diet.
Endocrine diseases
Due to excesses or deficiencies of hormones.
Mental diseases
Emotional or psychosomatic disorders.
Immunological diseases
Characterized by hyperactive or hypoactive immunity.
Neoplastic diseases
Characterized by abnormal cell growth.
Infectious diseases
Caused by an infectious agent.
Iatrogenic diseases
Caused by medical treatment or procedures.
Idiopathic diseases
Diseases with an unknown cause.
Healthcare-Associated diseases
Diseases acquired in a health care setting.
Germ theory of disease
Infections by pathogenic microorganisms cause disease
Koch's Postulates
A set of postulates one must satisfy to prove that a particular pathogen causes a particular disease
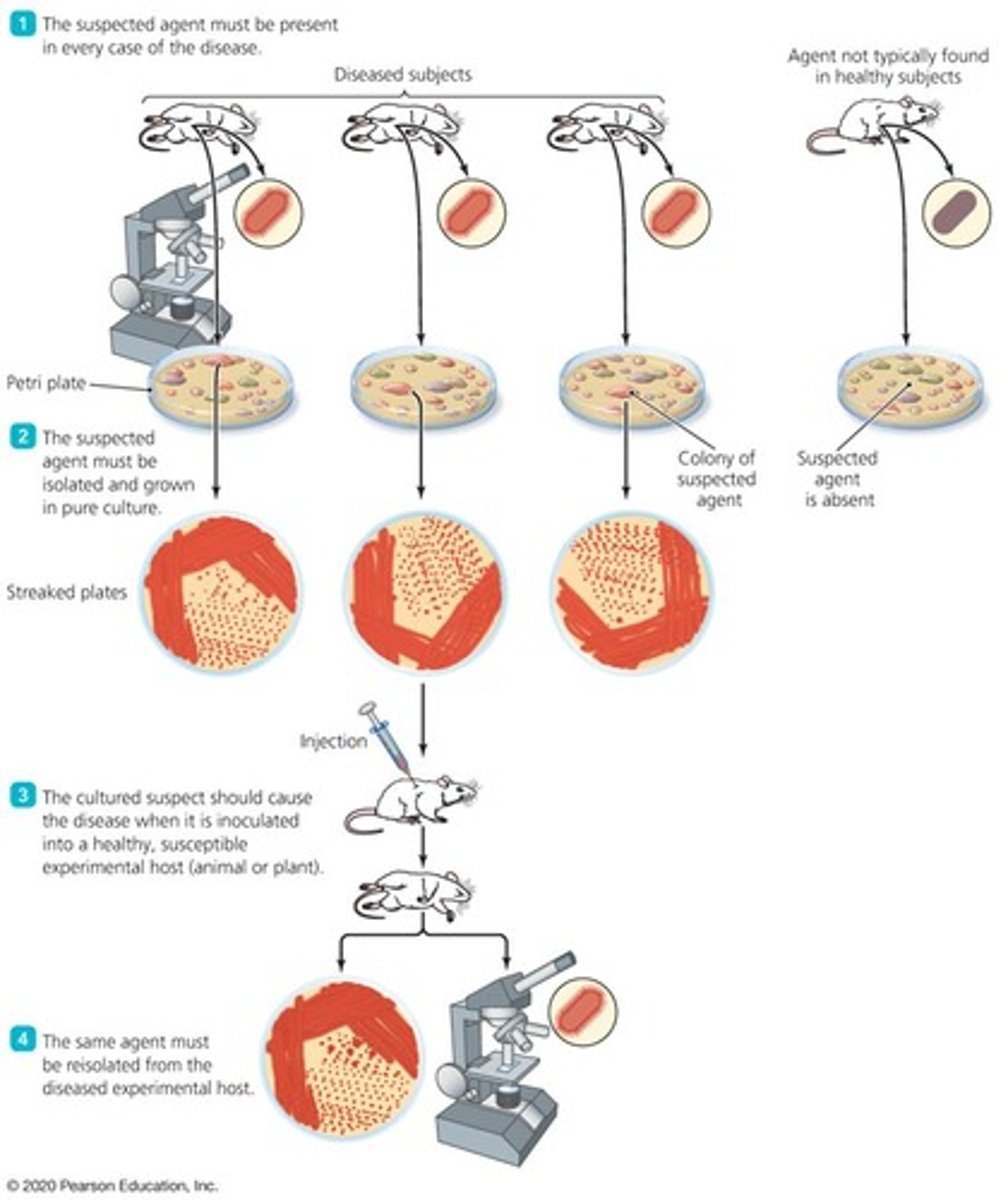
Exceptions to Koch's postulates
Some pathogens can't be cultured in the laboratory, diseases caused by a combination of pathogens and other cofactors, ethical considerations prevent applying Koch's postulates to pathogens that require a human host
Difficulties in satisfying Koch's postulates
Diseases can be caused by more than one pathogen, pathogens that are ignored as potential causes of disease
Transmission
Transmission is from a reservoir or a portal of exit to another host's portal of entry
Contact transmission
Transmission involving body contact between hosts
Direct contact transmission
Usually involves body contact between hosts; transmission within a single individual can also occur
Indirect contact transmission
Pathogens are spread from host to host by fomites
Droplet transmission
Spread of pathogens in droplets of mucus by exhaling, coughing, and sneezing
Vehicle Transmission
Transmission of pathogens through a medium such as air, water, or food
Airborne transmission
When pathogens travel more than 1 m via an aerosol
Waterborne transmission
Important in the spread of many gastrointestinal diseases; fecal-oral infection
Foodborne transmission
Spread of pathogens in and on foods; inadequately processed, cooked, or refrigerated foods