Midterm
1/299
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
300 Terms
sensory system
part of the NS that reports info about the state of the organism and environment
motor system
part of the NS that organizes and generates movement
associational system
part of the NS that provides higher order brain functions, such as perception, attention, memory, emotions, language, and thinking
central nervous system
part of NS subdivided into brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
part of NS subdivided into sensory, somatic, and autonomic divisions
reticular theory
idea that all neurons form a continuously connected network
neuron doctrine
neurons communicate at synapses rather than through physical activity
neuron
NS cell which processes info, senses environmental changes, communicates changes via electrical signaling, and controls body responses
dendrite
branchy target for synaptic input from axon terminals of other neurons whose complexity increases with the number of inputs
axon
shaft responsible for signal transduction from cell body; reads out info
action potential
all or nothing changes in electrical potential made by Nodes of Ranvier, requiring Na to allow neuron to reach threshold and K to bring it back down
Node of Ranvier
gap between myelin that propagates action potentials
saltatory conduction
action potentials jumping between Nodes of Ranvier, enhancing velocity
presynaptic terminal
where molecules are secreted into synaptic cleft, immediately adjacent to dendrite of next cell
postsynaptic specialization
areas of dendrites w/ receptors for molecules to bind, immediately adjacent to axon terminal of previous cell
synaptic cleft
gap between pre- and post- synaptic terminals
glia
NS cell which supports the signaling function of, insulates, nourishes, and supports neurons; includes astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, Schwann cells, microglia, and stem cells
astrocyte
CNS glial cell maintaining appropriate chemical environment for neuronal signaling, including blood-brain barrier formation
oligodendrocyte
CNS myelin generator
Schwann cell
PNS myelin generator
microglia
scavenger cells that remove cellular debris from injury sites and cell turnover, secrete cytokines
glial stem cell
precursor to glia
afferent
carries info to CNS
efferent
carries info away from CNS
interneuron
CNS cell that participates in local aspects of circuit function, such as DRG
agonist
muscle that performs target movement (extensor in knee jerk reflex)
antagonist
muscle that opposes target movement (flexor in knee jerk reflex)
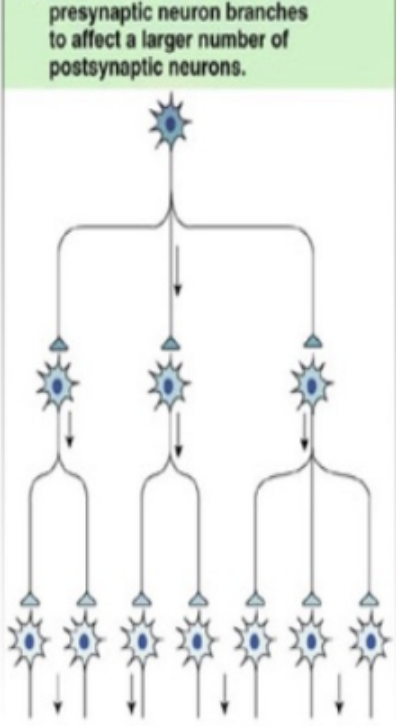
divergent circuit
neural circuit that spreads info
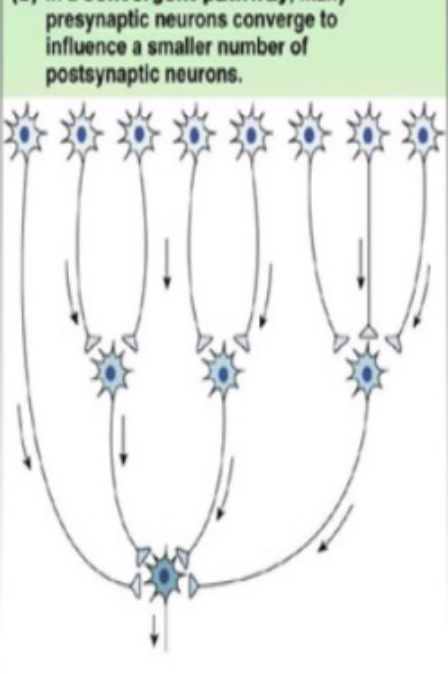
convergent circuit
neural circuit that integrates info
electrophysiological recording
technique to probe neural circuit function, subdivided into intracellular and extracellular recording
extracellular recording
an electrode is placed outside a neuron to detect temporal patterns of AP activity
intracellular recording
an electrode is placed inside a neuron to detect small. graded changes in electrical potential that can trigger APs and assesss communication among neurons w/in a circuit
calcium imaging
recording transient changes in [Ca] ion associated w/ AP firing to infer neural activity changes, where neurons are labeled w/ a Ca sensitive dye and then imaged
optogenetic
method introducing opsins into the NS so a neuron can artificially fire from light to assess neural circuit activity
opsin
bacterial channels transducing light energy into chemical signal activating channel proteins
basal ganglia
group of nuclei that control normal voluntary movement, w/ no direct spinal cord connections, made up of striatum (caudate & putamen), pallidum (globus pallidus & SNPR), SNPC, and subthalamic nucleus; uses center surround decision making
striatum
input nuclei of the basal ganglia made up of caudate and putamen, shrinks in Huntington’s
caudate
cortical inputs from multimodal association cortices and frontal lobe motor areas that control eye movement
putamen
cortical inputs from primary and secondary somatosensory cortices in parietal lobe, extrastriate visual, premotor, motor, and auditory association cortices
pallidum
output nuclei of the basal ganglia
globus pallidus
pallidum region responsible for MSN activity; internal relays to inhibit VA/VL thalamic nuclei, external degenerates in Huntington’s
substantia nigra pars reticula
pallidum region in midbrain that serves as inhibitory output, where axons from medium spiny neurons (MSNs) converge, sends axons to superior colliculus
substantia nigra pars compacta
basal ganglia region responsible for inhibitory output that degenerates in Parkinson’s causing dopamine output to decrease; releases dopamine to the striatum leading to direct pathway activation and indirect pathway inhibition; synapses on MSNs
medium spiny neuron
in striatum, give rise to inhibitory GABAergic projections that terminate in output basal ganglia, receive few inputs from each cortical axon
direct pathway
circuit that releases upper MNs from tonic inhibition and facilitates movement; inhibits internal globus pallidus to release inhibition on VA/VL thalamus to activate cortex, mediate focised activation; damage = trouble tying shoes
indirect pathway
circuit that increases tonic level of inhibition, inhibits movement by inhibiting VA/VL thalamus, and thus output to cortex, suppresses function units
focused selection
theory that direct and indirect pathways are organized in center surround manner
Huntington’s disease
neurodegenerative genetic trinucleotide repeat disease where external globus pallidus neurons degenerate, causing hyperkinetic movement
hemiballismus
damage to the subthalamic nucleus causing violent movements
subthalamic nucleus
region of basal ganglia; damage causes violent involuntary movements; receives input from cerebral cortex; provides inhibitory output to VA/VL complex of the thalamus; release glutamate to internal globus pallidus
Parkinson’s
major degeneration of NS w/ tremor at rest, rigidity, and bradykinesia; can be treated by Levodopa and deep brain stimulation
dyskinesia
difficulty moving
deep brain stimulation
Parkinson’s treatment where electrodes trigger blood flow and neurotransmitter release; parameters determined by trial and error
levodopa
primary pharmacological treatment to get brain to produce dopamine for Parkinson’s
Plato
early scientist (400 BCE) that believed that the eye sent out rays, which seized objects (extramission)
Theophrastus
300 BCE scientist who thought eye has internal fire from which the rays emanate (extramission)
Galen
200 CE scientist who thought optical pneuma was emitted from the eye, considered lens to be origin of vision, since cataracts obstruct vision (extramission)
extramission theory
our eyes shooting out energy causes us to see; 50% of Americans believe it & Plato, Theophrastus, and Galen
intromission theory
our eyes absorbing energy causes us to see, supported by al-Razi, Ibn al-Haytham, and Ibn Sina
al-Razi
900 CE scientist that noticed light levels controlled pupils, supported intromission theory
cornea
clear tissue at front of eye, provides 2/3 of eye’s optical power due to refraction
pupil
opening in the iris which expands (for more light in dim situations) and contracts to control the amount of light entering
lens
tissue that focuses incoming light on retina whose refractive power is affected by ciliary muscles; issues cause most vision issues (eg. myopia, hyperopia); thin for distant objects, thick for near
ciliary muscles
eye muscles that adjust the thickness of the lens
retina
light sensing neural tissue at the back of the eye, which signals via graded potentials, regulated by cGMP gated channels
fovea
centre of retina responsible for HD vision, w/ high [cones] and visual acuity
optic nerve
bundle from retinal ganglion cell axons; pathway where retinal signals get sent to rest of the brain
optic disk
blind spot in retina where it meets the optic nerve, no photoreceptors
myopia
images are focused in front of the retina, far images are blurry, affecting ~50% of people, treated w/ concave lenses
hyperopia
images are focused behind retina, close images are blurry, treated w/ convex lenses, includes presbyopia
presbyopia
age related hyperopia
astigmatism
condition arising from spherical aberrations of the eye, leading to different focal points for different parts of the visual field
retinal
molecule in photopigments which converts between cis and trans to active transducin and begin vision pathwat
transducin
g protein activated by conversion of 11-cis to 11-trans retinal, which activates PDE
phosphoesterdiase
compound activated by transducin, which hydrolyzes cGMP into GMP, which closes gGMP gated ion channels
achromatopsia
true color blindness due to a lack of cones affecting 1/30k people
off bipolar cell
ionotropic cell active in the dark, which is activated by photoreceptors and activates ganglion cells; stratify in deeper layers of IPL and connect to ON ganglion cells
on bipolar cell
cell w/ metabotropic glutamate receptors on dendrites, depolarized by photoreceptors in light, hyperpolarized in dark, activates ganglion cells indirectly through A2 amacrine cells
inner nuclear layer
location of bipolar cell soma
inner plexiform layer
location of bipolar cell axons
amacrine cell
retinal cell that connects on bipolar cells to retinal ganglion cells; can provide lateral inhibition to bipolar and ganglion cells
on center ganglion cell
retinal cell activated by off bipolar cells which are excited by light in the center, inhibited by light in the surround
off center ganglion cell
retinal cell inhibited by light in the center, excited by light in the surround
horizontal cell
retinal cell that provides negative feedback to photoreceptors through lateral inhibition
luminance
physical measurement of light intensity
brightness
sensation elicited by light intensity
color oppency
creating ganglia that prefer different colors, includes parasol (magnocellular), midget (parvocellular) and bistratified (koniocellular)
parasol
center surround retinal ganglion cells responsible for detecting luminance & motion w/ its large receptive field
midget
red/green retinal ganglion cell, w/ small receptive field and high acuity due to small receptive field
bistratified
blue/yellow retinal ganglion cell
optic chiasm
where ~60% of retinal ganglion cell axons cross brain hemisphere
nasal
portion of visual field closest to nose that crosses at the optic chiasm
temporal
portion of visual field closest to ear whose retinal ganglion axons stay ipsilateral
melanopsin
photopigment crucial for circadian rhythms, why circadian rhythm is sensitive to blue light
superior colliculus
brain region that coordinates head and eye movements to visual target; also axial musculature in the neck
pupillary light reflex
both pupils respond to monocular visual stimulation; retinal ganglion cells → pretectum → EWN (midbrain) → oculomotor nerve → ciliary ganglion → constrictor muscles of the iris
saccadic eye movement
ballistic eye movement occuring when focusing
smooth pursuit eye movement
following stimuli w/ eye
optokinetic reflex
gaze stabilization reflex combining both saccadic and smooth pursuit eye movements
primary visual pathway
retinal ganglion → LGN (of thalamus) → V1