a&p ch4 tissues mcq exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/56
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
1
New cards
merocrine glands
secrete products by exocytosis as secretions are produced (sweat, pancreas).
2
New cards
holocrine glands
accumulates products within, then ruptures (sebaceous oil glands).
3
New cards
apocrine glands
accumulate products within, but only apex ruputues; whether this types exists in humans is controversial (maybe mammary cells).
4
New cards
found in columnar epithelia
what type of epithelia are goblet cells found?
5
New cards
cardiac muscle
Where do you find the intercalated discs?
6
New cards
areolar and reticular connective tissue
What type of loose connective tissue would you find macrophages?
7
New cards
White fat
has nutrient storage and richly vascularized as it functions in shock absorption, and insulation
8
New cards
Hyaline
found at tips of long bones, nose, trachea, larynx, and cartilage of the ribs
9
New cards
Elastic
found in ears and epiglottis
10
New cards
Fibrocartilage
found in areas such as intervertebral discs and knee
11
New cards
epithelial, areolar, dense irreg., blood, bone
regenerate extremely well
12
New cards
smooth muscle, dense reg.
moderate regeneration:
13
New cards
cardiac muscle, nervous tissue
no functional regeneration
14
New cards
areolar, adipose, reticular
loose
15
New cards
dense regular, dense irregular, elastic
dense
16
New cards
osteoblasts, osteocyte, collagen, inorganic calcium salts, osteons, lacunae, hematopoietic stemcells
Know what you may find in bone
17
New cards
Fibroblasts
found in connective tissue proper
18
New cards
Chondroblasts
found in cartilage
19
New cards
Osteoblasts
found in bone
20
New cards
Microvilli
increase surface area
21
New cards
Cilia
aids in movement
22
New cards
ground substance and fibers
What connective tissue structural elements make up the extracellular matrix?
23
New cards
fat cells, macrophages, white blood cells, fibroblasts
What type of cells will you see in areolar connective tissue?
24
New cards
Main functions are to protect, absorb, filtrate, excrete, secrete, and sensory reception.
What is a big function of epithelial tissue? Be able to make a connection to body function.
25
New cards
Collagen fibers
touch; provides high tensile strength
26
New cards
Elastic fibers
networks of long, thin, elastin fibers that allow for stretch and recoil
27
New cards
Reticular
short, fine, highly branched collagenous fibers
28
New cards
Tissues
groups of cells similar in structure that perform common or related function
29
New cards
Histology
study of tissues
30
New cards
exocrine secrete substances into a ductal system to an epithelial surface, endocrine secrete products directly into the bloodstream
Know the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands.
31
New cards
Inflammation sets stage
Step 1:
step in tissue repair
release of inflammatory chemicals causes, clotting of blood to occurs
step in tissue repair
release of inflammatory chemicals causes, clotting of blood to occurs
32
New cards
Organization restores blood supply
Step 2:
epithelium begins to regenerate
epithelium begins to regenerate
33
New cards
Regeneration and fibrosis effect permanent repair
Step 3: epithelium thickens and begins to resemble adjacent tissue
34
New cards
ground substance, fibers, cells
Know the main components of CT
35
New cards
bind and support, protect, insulate, storing reserve fuel, and transporting substances (blood)
Know the main job of connective tissue.
36
New cards
cardiac-walls of the heart, skeletal-attached to bones, smooth-walls of hollow organs
Where would you find cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and skeletal muscle?
37
New cards
mesenchyme
a type of animal tissue comprised of loose cells embedded in a mesh of proteins and fluid, called the extracellular matrix
38
New cards
epidermis
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
39
New cards
The structure of glands. Categorize the multicellular exocrine glands. Be able to look at a picture and categorize it. Be able to categorize it from a description as well.
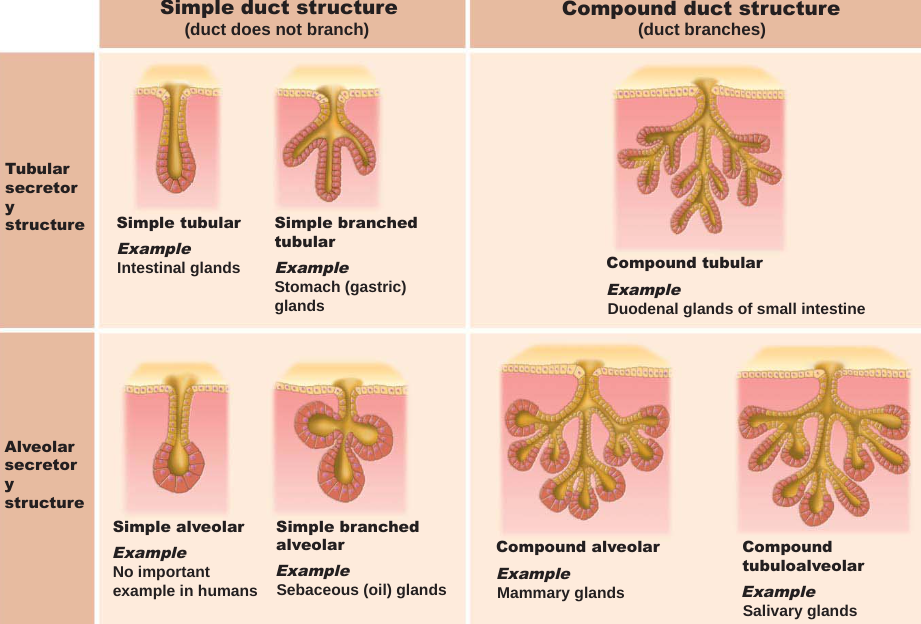
40
New cards
actin, myosin
What makes up myofilaments?
41
New cards
epithelial, ct proper
Membrane linings and coverings are composed of what two tissues?
42
New cards
apical- upper free side, basal-lower attached side
Define apical surface and basal surface.
43
New cards
smooth and cardiac muscle are involuntary while skeletal muscles are voluntary.
List the muscle tissues and categorize them as voluntary or involuntary.
44
New cards
mesothelium
is a protective membrane found in covering the lungs, abdomen, heart, and testes.
45
New cards
You name stratified epithelium by looking at the outermost layer
How do you name stratified epithelium?
46
New cards
simple squamous epithelium
-cells are FLATTENED LATERALLY, cytoplasm is SPARSE
-function where RAPID DIFFUSION is priority
-see weird/squiggly shape with lots of nuclei in between
-KIDNEYS, LUNGS, HEART LINING, BLOOD & LYMPHATIC VESSELS, VENTRAL BODY LINING
-function where RAPID DIFFUSION is priority
-see weird/squiggly shape with lots of nuclei in between
-KIDNEYS, LUNGS, HEART LINING, BLOOD & LYMPHATIC VESSELS, VENTRAL BODY LINING
47
New cards
simple cuboidal epithelium
-SINGLE layer of cells
-SECRETION & ABSORPTION
-see donuts
-forms WALLS of SMALLEST DUCTS of GLANDS, KIDNEY TUBULES, OVARY STRUCTURE
-SECRETION & ABSORPTION
-see donuts
-forms WALLS of SMALLEST DUCTS of GLANDS, KIDNEY TUBULES, OVARY STRUCTURE
48
New cards
simple columnar epithelium
-single layer of TALL, CLOSELY packed cells
-MUCUS secreting GOBLET CELLS
-ABSORPTION, secretion of MUCUS, ENZYMES, & other substances
-NONCILIATED: DIGESTIVE TRACT, GALLBLADDER, EXCRETORY DUCTS
-CILIATED: SMALL BRONCHI, UTERINE TUBES, UTERUS
-MUCUS secreting GOBLET CELLS
-ABSORPTION, secretion of MUCUS, ENZYMES, & other substances
-NONCILIATED: DIGESTIVE TRACT, GALLBLADDER, EXCRETORY DUCTS
-CILIATED: SMALL BRONCHI, UTERINE TUBES, UTERUS
49
New cards
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
-cells vary in height & appear stratified but is SINGLE layered
-many cells are ciliated
-SECRETION & MOVEMENT of MUCUS via CILIARY SWEEPING action
-NONCILIATED: SPERM-CARRYING DUCTS, DUCTS OF LARGE GLANDS
-CILIATED: UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT, TRACHEA
-many cells are ciliated
-SECRETION & MOVEMENT of MUCUS via CILIARY SWEEPING action
-NONCILIATED: SPERM-CARRYING DUCTS, DUCTS OF LARGE GLANDS
-CILIATED: UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT, TRACHEA
50
New cards
fixed
List the steps in preparing tissue to be viewed under a microscope.
1: tissue is preserved with solvent
1: tissue is preserved with solvent
51
New cards
sectioned
List the steps in preparing tissue to be viewed under a microscope.
2: cut into thin slices to transmit light/electrons
2: cut into thin slices to transmit light/electrons
52
New cards
stained
List the steps in preparing tissue to be viewed under a microscope.
3: to enhance contrast though artifacts detract from what the sample looks like in living tissues
-light microscopy uses colored dyes
-electron microscopy uses heavy metal coatings
3: to enhance contrast though artifacts detract from what the sample looks like in living tissues
-light microscopy uses colored dyes
-electron microscopy uses heavy metal coatings
53
New cards
cutaneous membrane
-Another name for skin
-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium (epidermis) attached to a thick layer of connective tissue (dermis)
-Unlike other membranes, skin is a dry membrane
-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium (epidermis) attached to a thick layer of connective tissue (dermis)
-Unlike other membranes, skin is a dry membrane
54
New cards
mucous membrane
-Mucosa indicates location, not cell composition, Also called mucosae
-Line body cavities that are open to the exterior (example: digestive, respiratory, urogenital tracts)
-moist membranes bathed by secretions (or urine)
-Epithelial sheet lies over layer of loose connective tissue called lamina propria
-May secrete mucus
-Line body cavities that are open to the exterior (example: digestive, respiratory, urogenital tracts)
-moist membranes bathed by secretions (or urine)
-Epithelial sheet lies over layer of loose connective tissue called lamina propria
-May secrete mucus
55
New cards
serous membrane
-Also called serosae
-Found in closed ventral body cavities
Constructed from simple squamous epithelium (called mesothelium) resting on thin areolar connective tissue
parietal serosae line internal body cavity walls
visceral serosae cover internal organs
Cavity between layers is filled with slippery serous fluid, so these are moist membranes
Special names given to show location: pleurae (lungs), pericardium (heart), peritoneum (abdomen)
-Found in closed ventral body cavities
Constructed from simple squamous epithelium (called mesothelium) resting on thin areolar connective tissue
parietal serosae line internal body cavity walls
visceral serosae cover internal organs
Cavity between layers is filled with slippery serous fluid, so these are moist membranes
Special names given to show location: pleurae (lungs), pericardium (heart), peritoneum (abdomen)
56
New cards
endothelium
can be found in most artieres, brain veins and capillaries, skin, lung, heart, and muscle.
57
New cards
Brown fat
uses lipid fuels to heat bloodstream rather than to produce ATP, as does white fat.