statistical tests - T-test (test 1)
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
t test
statistical test evaluating the means of 2 groups
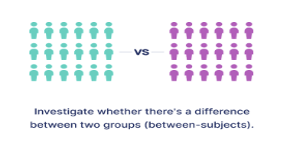
independent sample t test
when these two groups are independent (or unrelated to one another), we can use a procedure known as the unpaired (AKA, independent-groups or two-sample) t test.
unmodified use of “t test” implies this test.
this independent t test tests for differences in two group means or compares means for two independent groups of cases.
normality
variable where the 2 groups are being compared is normally distributed in each population
variance
variances of the variable in the 2 populations are equal (called homogeneity f variance)
independence
observations within each group and between each group are independent, meaning that knowing the value of any one observation tells us nothing about the value of another observation

paired t test
when we are comparing 2 means, this procedure is called the dependent groups
the basic procedure for hypothesis testing and confidence interval estimation, as well as their interpretations, are essentially the same
1 sample t test
used to determine whether an unknown population mean is different from a specific value.
use the test for continuous data.
your data should be a random sample from a normal population.
we need one variable
we also have an idea, or hypothesis, that the mean of the population has some value.
