unit 2 - gradational processes
5.0(1)Studied by 4 people
Card Sorting
1/44
Last updated 6:24 AM on 1/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
1
New cards
weathering
* the __forces__ that essentially break down the surfaces on our earth
* the breaking down of rock into smaller particles
* 2 types: physical (mechanical) or chemical
* the breaking down of rock into smaller particles
* 2 types: physical (mechanical) or chemical
2
New cards
frost shattering
* physical weathering
* water enters pores or joints in a rock and as it freezes, expands, and cracks it
* water enters pores or joints in a rock and as it freezes, expands, and cracks it
3
New cards
thermal expansion
* physical weathering
* common in desert regions where temps. fluctuate
* during the day, the rocks get very hot and expand, but a night they become cool which causes them to contract (shrink) and cracks them
* common in desert regions where temps. fluctuate
* during the day, the rocks get very hot and expand, but a night they become cool which causes them to contract (shrink) and cracks them
4
New cards
erosion
* the __movement__ of original sediments
* the process by which soil and rock particles are worn away and moved elsewhere by gravity, wind, water or ice
* the process by which soil and rock particles are worn away and moved elsewhere by gravity, wind, water or ice
5
New cards
deposition
* the __depositing__ or laying down of sediments
* geological process where sediments, soil and rocks are deposited
* geological process where sediments, soil and rocks are deposited
6
New cards
mass wastage
* gravity exerting a downward pull on weathered particles
7
New cards
landslide
* rapid sliding of large rock masses as they “separate” from the slope
8
New cards
one method for stabilizing mass wastage
* long bolts (fastened into bedrock) = stabilizes soil and slope above
9
New cards
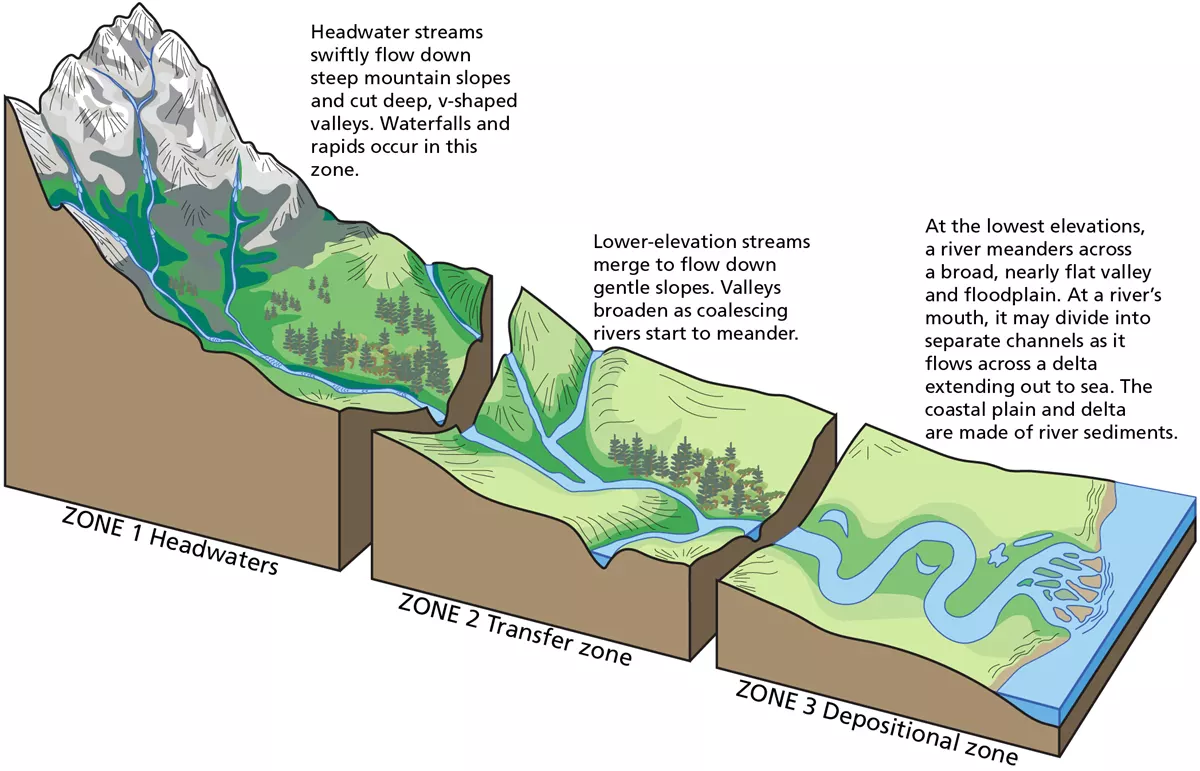
river stages/lifecycle
* young stream (steep slope), mature stream (moderate slope), old stream (gentle slope)
10
New cards
youthful stage
* deep cutting, v-shaped valleys
* fast flowing
* high erosion BUT low deposition (too fast!)
* generally flows in a fairly straight direction
* associated with rapids and waterfalls
* fast flowing
* high erosion BUT low deposition (too fast!)
* generally flows in a fairly straight direction
* associated with rapids and waterfalls
11
New cards
mature stage
* flood plains have begin to form on either side of the river
* riverbed tends to get wider and meandering begins (squiggling)
* flow slows to a moderate speed
* deposition is taking place
* riverbed tends to get wider and meandering begins (squiggling)
* flow slows to a moderate speed
* deposition is taking place
12
New cards
old stage
* a lot of meandering
* river widens and is much more shallow
* deltas are being formed
* deposition is everywhere!
* river widens and is much more shallow
* deltas are being formed
* deposition is everywhere!
13
New cards
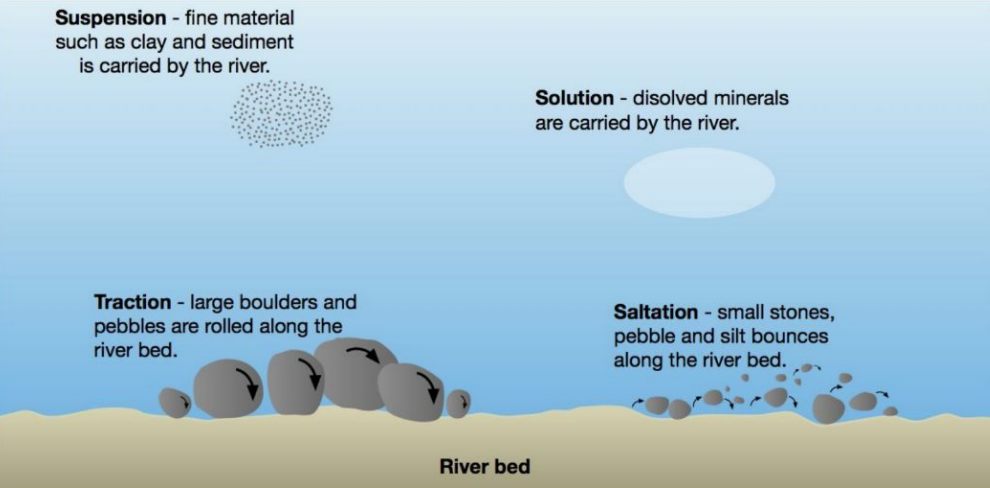
erosional action from rivers
14
New cards
hydraulic action
forces of water flowing in the river loosens sediment/rocks in the riverbed and carries them downstream and deposits when flow diminishes
15
New cards
abrasion (aka corrasion)
debris such as sand can act as powerful abrasion agent against river banks and beds (think polishing)
16
New cards
attrition
fast moving water (like a flood) picks up rocks, moves them along striking other rocks and breaking them apart
17
New cards
solution
minerals from rocks dissolve in water and create their own solution
18
New cards
suspension
very light material is carried along in the water and doesn’t touch the bottom (floating in air)
19
New cards
saltation
particles that are heavy bounce down the river bed
20
New cards
traction
heavy particles are dragged along the bottom of the river bed
21
New cards
features of rivers
22
New cards
oxbow lake
formed when a river “straightens” by cutting through a meander
23
New cards
cutbanks
the side of a meandering river where the water moves the fastest and greatest erosion occurs
24
New cards
point bar
depositional feature located on the inside curve of a meandering river where flow slows and increased deposition occurs
25
New cards
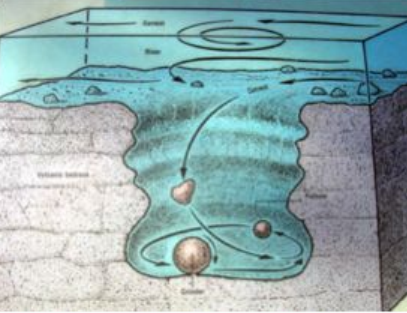
pothole
rivers can dig a pothole in the sediments at the bottom of the river (think “blender”)
26
New cards
river landforms
27
New cards
floodplains
created when rivers overflow (seasonally) leaving behind rich alluvial (clay, silt, sand, gravel) deposits
28
New cards
levees
natural banks created by the deposition of sediment (flooding), they can act as a natural protectant against floods
29
New cards
dike
person-made levee
30
New cards
delta
build up of sediments at the mouth of a river where it deposits more material than can be carried away
* arcuate (fan-shaped) delta
* bird’s foot delta
* estuarine delta
* arcuate (fan-shaped) delta
* bird’s foot delta
* estuarine delta
31
New cards
types of waves
32
New cards
spilling (constructive) waves
* flat, low in height and have a long wavelength
* their swash carries material up beach
* the wave energy gets weaker as it returns to the ocean (backwash)
* builds up the beach
* their swash carries material up beach
* the wave energy gets weaker as it returns to the ocean (backwash)
* builds up the beach
33
New cards
plunging (destructive) waves
* large wave height but short wavelength
* high downward forces and strong backwash
* the high downward energy helps erode beach material
* occurs at cliffs as well as beaches
* high downward forces and strong backwash
* the high downward energy helps erode beach material
* occurs at cliffs as well as beaches
34
New cards
longshore drift
* waves normally approach the shore on an angle
* sand is driven up-beach by the power of incoming waves and is transported along the beach in a horizontal motion
* longshore drift = zig-zag movement of sand along the beach
* sand is driven up-beach by the power of incoming waves and is transported along the beach in a horizontal motion
* longshore drift = zig-zag movement of sand along the beach
35
New cards
erosional features of waves
* with cliffs, hydraulic action opens up a crack
* crack grows into a cave through abrasion and hydraulic action
* cave breaks through the headland and forms an arch
* arch is eroded and collapses, forming a stack
* crack grows into a cave through abrasion and hydraulic action
* cave breaks through the headland and forms an arch
* arch is eroded and collapses, forming a stack
36
New cards
spit
* sand, silt and clay from eroded coastlines are slowly carried by longshore drift and ocean currents
* forms a protruding feature off the coast
* forms a protruding feature off the coast
37
New cards
tombolo
* natural pathway that joins an island to the mainland
38
New cards
stack
* isolated pillar left behind when an arch collapses
39
New cards
glacier
* a long-lasting body of ice (decades or more) that is large enough to move under its own weight
* can advance, stay stationary, and retreat
* can advance, stay stationary, and retreat
40
New cards
glacier formation
* glaciers need 2 things to form:
* prolonged cold
* an accumulation of snow
* prolonged cold
* an accumulation of snow
41
New cards
types of glaciers
42
New cards
alpine (valley) glacier
* higher altitude
* follow the river valleys as they move from the mountains to the lowland areas
* often join with other alpine glaciers to create massive valley glaciers.
* follow the river valleys as they move from the mountains to the lowland areas
* often join with other alpine glaciers to create massive valley glaciers.
43
New cards
continental glacier
* higher latitude
* when valley glaciers are no longer confined to river valleys, they spread out to large ice sheets
* can be more than a kilometer thick
* move very slowly
* when they retreat, they leave behind rich deposits of soil, and many lakes across the prairies
* when valley glaciers are no longer confined to river valleys, they spread out to large ice sheets
* can be more than a kilometer thick
* move very slowly
* when they retreat, they leave behind rich deposits of soil, and many lakes across the prairies
44
New cards
snow layers
* new snow (snowflakes)
* old snow
* firn (crunchy ice crystals)
* glacial ice
* old snow
* firn (crunchy ice crystals)
* glacial ice
45
New cards
moraines
sediment left behind by glaciers