Physical Science Vocabulary 🪶📜🌕ִֶָ☾♡
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The digital flashcard set for the Apologia Physical Science course! Happy studying!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Observation
the gathering of information using senses or with the aid of instruments
Hypothesis
a possible, testable explanation for one or more observations or a suggested, testable answer to a question
Controlled Experiment
an investigation in which the factors that influence the outcome are the same except for one — the factor being studied
Variable
a factor that can change in an experiment
Scientific Theory
a well-tested explanation of a phenomenon in the natural world
Scientific Law
a well-tested description of one phenomenon in the natural world that often includes mathematical terms
Inference
a logical conclusion drawn from observations, previous knowledge, and available information
Matter
anything that has mass and takes up space (has volume)
Atom
the smallest chemical unit of an element
Element
a pure substance that cannot be broken down into a simpler substance and contains only one type of atom
Compound
a pure substance that contains two or more elements chemically joined in a fixed proportion
Molecule
the smallest unit of a chemical compound, composed of two or more atoms bonded together
Solution
an evenly distributed mixture made by dissolving one substance in another
Solute
the substance in a solution that gets dissolved
Solvent
the substance in a solution in which the solute dissolves
Solid
the state of matter in which a substance has a definite shape and a definite volume
Liquid
the state of mater in which a substance has definite volume
Gas
the state of matter in which a substance has neither a definite shape nor definite volume
Density
the ratio of a substance’s mass to its volume (density = mass/volume)
Kinetic Energy
the energy an object has due to its motion
Valence Electrons
electrons that are in the highest energy level (the energy level farthest from the nucleus)
Reactants
substances that undergo a chemical change
Products
new substances formed as a result of a chemical change
Chemical Bond
a force of attraction between atoms or a group of atoms due to the sharing or transferring of electrons
Ion
an atom or group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge
Polar Molecule
a molecule that has slight positive and negative charges due to an imbalance in the way electrons are shared
Binary Compounds
compounds made of only two elements (bi)
Synthesis Reaction
a chemical reaction in which two or more substances react to form a single compound
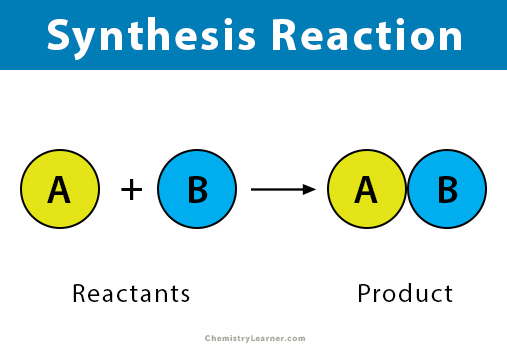
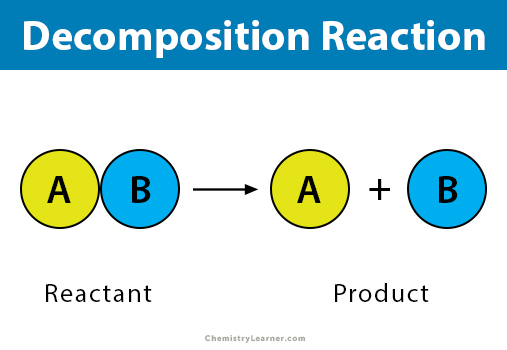
Decomposition Reaction
a chemical reaction in which a compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances (opposite of synthesis reaction)
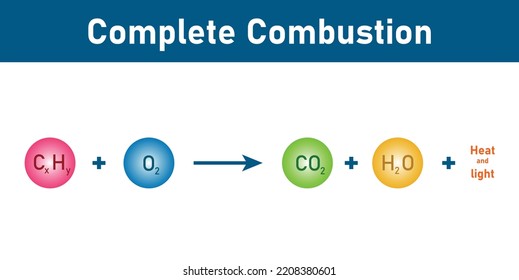
Combustion Reaction
a chemical reaction in which a substance reacts rapidly with oxygen, often producing heat and light
Chemical Energy
the energy stored in chemical bonds
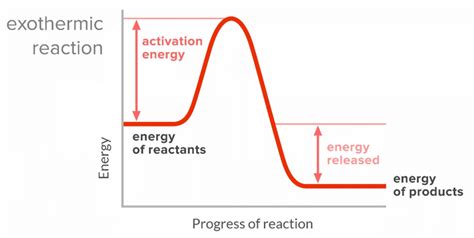
Exothermic Reaction
a chemical reaction that releases energy to its surroundings
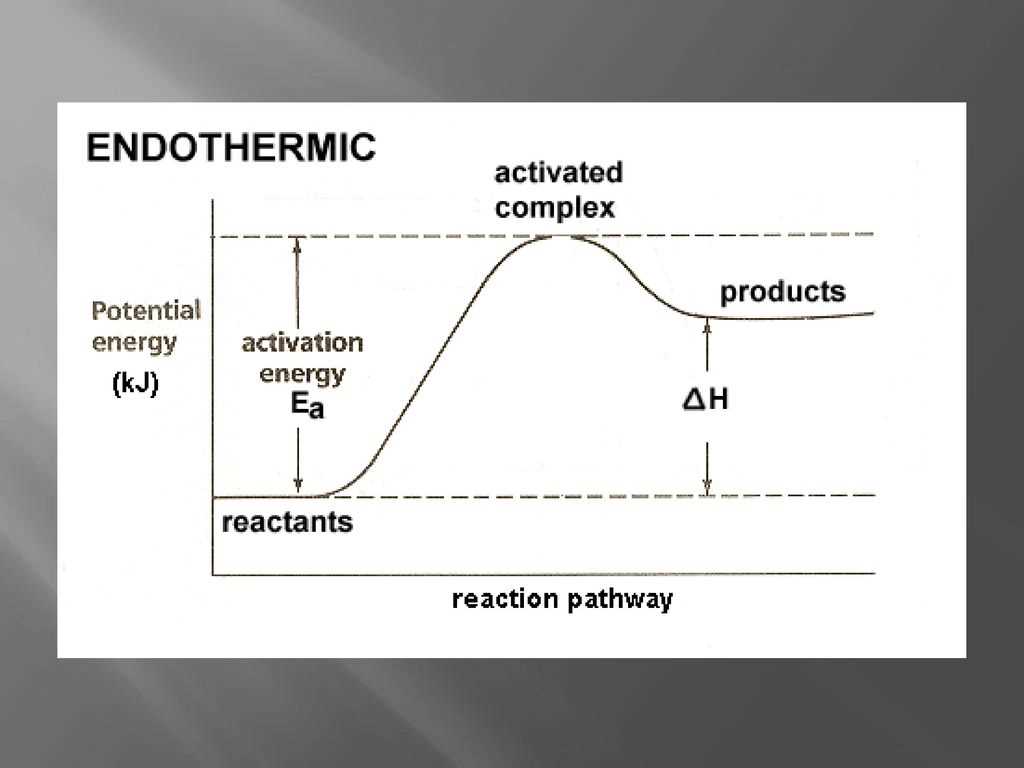
Endothermic Reaction
a chemical reaction that absorbs energy from its surroundings
Reference Point
a point against which motion is measured
Displacement
the distance an object travels plus the direction from the starting point
Vector Quantity
a physical measurement that contains both magnitude (number) and directional information
Scalar Quantity
a physical measurement that contains magnitude (number) and does not contain directional information
Average Speed
the ratio of the total distance traveled to the total time of the trip
Instantaneous Speed
the rate at which an object is moving at a given moment in time
Acceleration
the change in an object’s velocity over time
Force
a push or pull that acts on an object
Friction
a force that opposes motion, resulting when two objects rub against one another
Static Friction
friction that opposes the initiation of motion
Kinetic Friction
friction that opposes motion once the motion has already started
Free Fall
the motion of an object when it is falling solely under the influence of gravity
Inertia
the tendency of an object to resist changes in velocity
Newton’s First Law
an object in motion/at rest will stay in motion/at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force
Newton’s Second Law
when an object is acted on by one or more unbalanced forces, the net force is equal to the mass of the object times the resulting acceleration (f = ma)
Newton’s Third Law
for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction