Genetics Chapter 1 Pt. 2
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
meiosis
special type of eukaryotic cell division cycle that occurs during the generation of gametes in animals(sperm and eggs), or spores in plants and single-cell eukaryotes
outcome of meiosis
4 haploid cells
do homologous chromosomes pair up in meiosis
homolgous chromosomes pair to form tetrads during prophase 1
in anaphase 1 the tetrads...
are disjoined and the homologouschromosomes are segregated to daughter cells
in anaphase 2 the chromosomes...
are disjoined and aresegregated to daughter cells
tetrads
the paired chromosomes consisting of four chromatids
reduction division
another name for meiosis I, the division where homologous pairs separate.
equational division
another name for meiosis II because cells in meiosis II have the same number of chromosomes at the beginning and at the end of the process.
in meiosis I, the number of chromosomes in daughter cells is
half the original
dyads
pairs of individuals
synaptonemal complex
an ordered protein structure that forms between homologous chromosomes during meiotic prophase I. It mediates the pairing of the chromosomes and facilitates crossing over; disappears late prophase I
crossing over
Process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis, occurs in prophase I
five substages of meiotic prophase I
leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, diakinesis
leptotene
DNA begins to partially condense
zyogotene
homologous chromosomes pair to form tetrads (or bivalents). The synaptonemal complex begins to form
pachytene
condensation continues and the individual chromatids become more visible. Crossing over occurs:the exchange of fragments of DNA between the paired homologous chromosomes
diplotene
the homologous chromosomes begin topartially separate. the chiasmata become visible: pointsat which crossing over already occurred
diakinesis
the homologous chromosomes pull further apart (but they remain together). Further condensation occurs in preparation for metaphase
what substages does crossing over occur in
zygotenem pachytene, diplotene
following pachytene, the sister chromatids...
are no longer identical DNA molecules because crossing over and recombination occurred between non-sister chromatids
middle prophase I
chromosomes begin to condense, the spindle forms
late prophase I
homologous chromosomes pair, crossing over takes place, and the nuclear membrane breaks down
metaphase I
homologous pairs of chromosomes line up along the metaphase plate
anaphase I
Homologous chromosomes separate and move toward opposite poles
telophase I
chromosomes arrive at the spindle poles and the cytoplasm divides
outcome of meiosis I
2 haploid cells
meiosis II
resembles mitosis, chromosomes are disjoined, chromatids are segregated to daughter cells
prophase II
the chromosomes recondense
metaphase II
individual chromosomes line up on the equatorial plate
anaphase II
sister chromatids separate and move toward opposite poles
telophase
chromosomes arrive at the spindle poles and the cytoplasm divides
outcome of meiosis II
4 haploid cells
meiosis gametogensesis
spermatogenesis and oogenesis
spermatogenesis
production of sperm, equal cytokinesis, outcome: 4 gametes (sperm:haploid)
oogenesis
unequal cytokinesis: one cell receives all the cytoplasm, the rest of the cells become polar bodies, outcome: only one gamete (the egg: haploid)
fertilization
produces a zygote (2n)
steps of spermatogenesis
1. Primary Spermatocyte - a diploid cell in testes undergoes Meiosis I to produce
2. Secondary Spermatocyte - a haploid cell with 2 sister chromatids undergoes Meiosis II to produce
3. Spermatids - haploid cell with 1 chromatid that will mature
4. Sperm - mature spermatids
5. sperm fuses with egg to form zygote - diploid cell
6. zygote undergoes mitosis and eventually produces specialized cells, gonads, to start cycle all over again.
steps of oogenesis
1. Primary Oocyte - diploid cells housed in the fetus; 1 undergoes Meiosis at a time.
2. Secondary Oocyte - haploid cell with sister chromatids per chromosome
a.) 1st cell - secondary oocyte
b.) 2nd cell - polar body that eventually disintegrates. (uneven division)
3. Sperm fuses with secondary oocyte
a.) meiosis II occurs
b.) egg develops
c.) 2nd polar body will form and disintegrates
4. Sperm and egg form zygote
5. zygote undergoes mitosis and eventually produces gonads to start cycle all over again.
S. cerevisiae can exist in two forms
diplophase (fuse to form one a/α cell) or haplophase (a or α)
if environmental condition deteriorate, the diplophase S. cerevisiae cells may undergo...
meiosis, (sporulation); to generate four spores inside an ascus that remain dormant
when environmental conditions improve for S. cerevisiae...
the ascus germinates to release four haplophase cells (sexual reproduction)
meiosis fails
organisms that do not contain a chromosome complement consisting of an even multiple of the haploid number.; produce unbalanced gametes
seedless watermelons
tetraploid plant paired with a diploid plant; sterile and no seeds
mules
female horse (2n=64) and male donkey (2n = 62), most are sterile with 63 chromosomes
what would happen if the chinese muntjac and indian muntjac interbred?
embryonic mitotic divisions may generate a viable adult, but the hybrid will be sterile due to meiotic failures
nondisjunction
occurs if chromosomes or chromatids do not separate during anaphase I or anaphase II of meiosis; both chromosomes/chromatids migrate to the same gamete; after fusion with a normal gamete, trisomic and monosomicaneuploidies may occur
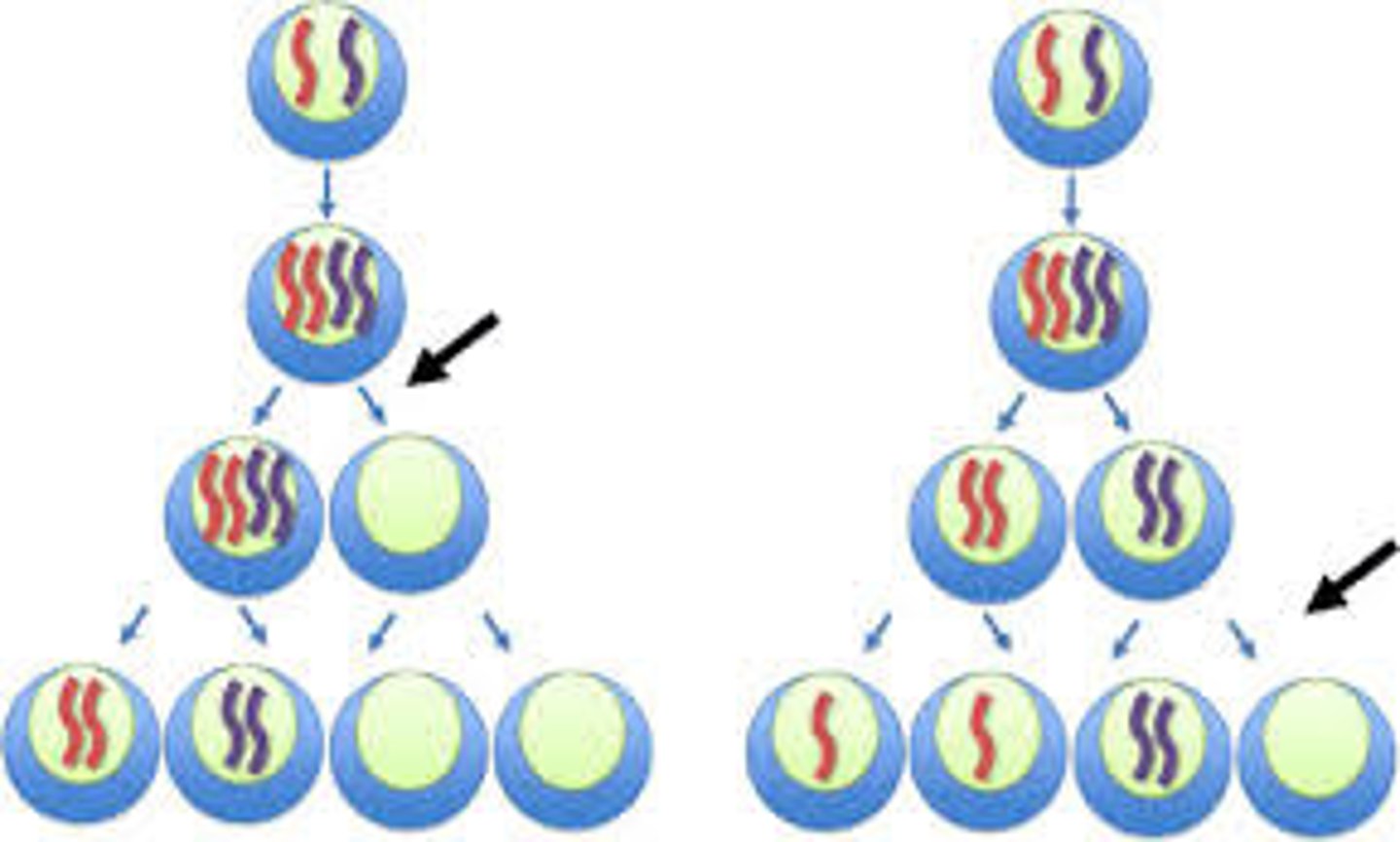
trisomy
3 copies of a chromosome
down syndrome
Non-disjunction of chromosome 21, viable, results in trisomy-21 aneuploidy
patau syndrome
trisomy-13, survival beyond neonatal period is uncommon
edward syndrome
trisomy-18, survival beyond neonatal period is uncommon
turner syndrome
Non-disjunction of X chromosome can also result in themonosomy-X aneuploidy
monosomy
only one copy of a chromosome is present
cri-du-chat syndrome
loss of a piece of one of the two copies of a chromosome, as opposed to the entire loss of one of the two copies; results in a partial monosomy