8/25 - Specialized Bones and Bone Components
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Bone Components, Specialized Bones
Last updated 9:08 PM on 9/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
1
New cards
Cancellous
What type of bone is found in the interiors of long and short bones? It is spongy, porous, and contains red bone marrow, osteoclasts, and osteoblasts.
2
New cards
Red bone marrow
What substance found in cancellous bone is the producer of red blood cells?
3
New cards
Osteoblasts
What cells found in cancellous bone are the producers of bone?
4
New cards
Osteoclasts
What cells found in cancellous bone break down old bone?
5
New cards
5-10
What percentage range of cardiac output is directed towards the bones?
6
New cards
Nutrient
Which artery is the one which supplies blood/nutrients to the diaphysis or shaft of long bones?
7
New cards
Epiphyseal
Which arteries in long bones supply blood/nutrients to the epiphyses?
8
New cards
Metaphyseal
Which artery in long bones has an anastomoses with the nutrient artery and supplies blood/nutrients to the metaphysis?
9
New cards
Anastomosis
What is the term for the connection between arteries such as the metaphyseal and nutrient arteries in long bones?
10
New cards
Periosteum
What is the term for the dense connective tissue around bones that contain venules which collect blood from bone veins?
11
New cards
Cortical
What type of circulation occurs in bones which allows blood to flow from inside the bone to outside in veins? Also called centrifugal circulation.
12
New cards
Short
Which type of bones has the same width/length, can be found grouped together, has cancellous and compact bone? Examples are carpals.
13
New cards
Flat
Which type of bones have two major surfaces with two sheets of compact bone and a thin layer of cancellous bone in between? Examples are cranium, pelvic girdle, scapula.
14
New cards
sesamoid, splanchnic, pneumatic
What are the three types of specialized bones found throughout the body?
15
New cards
Sesamoid
What is the type of bone found in tendons where sudden changes of direction and significant friction occur, over the prominences of bones, and at synovial joints and against major bones? Example is the patella.
16
New cards
Splanchnic
What is the type of bone found in soft tissues away from the skeleton? Examples are the os penis and ossa cardis.
17
New cards
Pneumatic
What is the type of bone such as the skull bones that are invaded by nasal mucosa and linked to the nasal cavity? Examples are paranasal sinuses and post-cranial bones in birds.
18
New cards
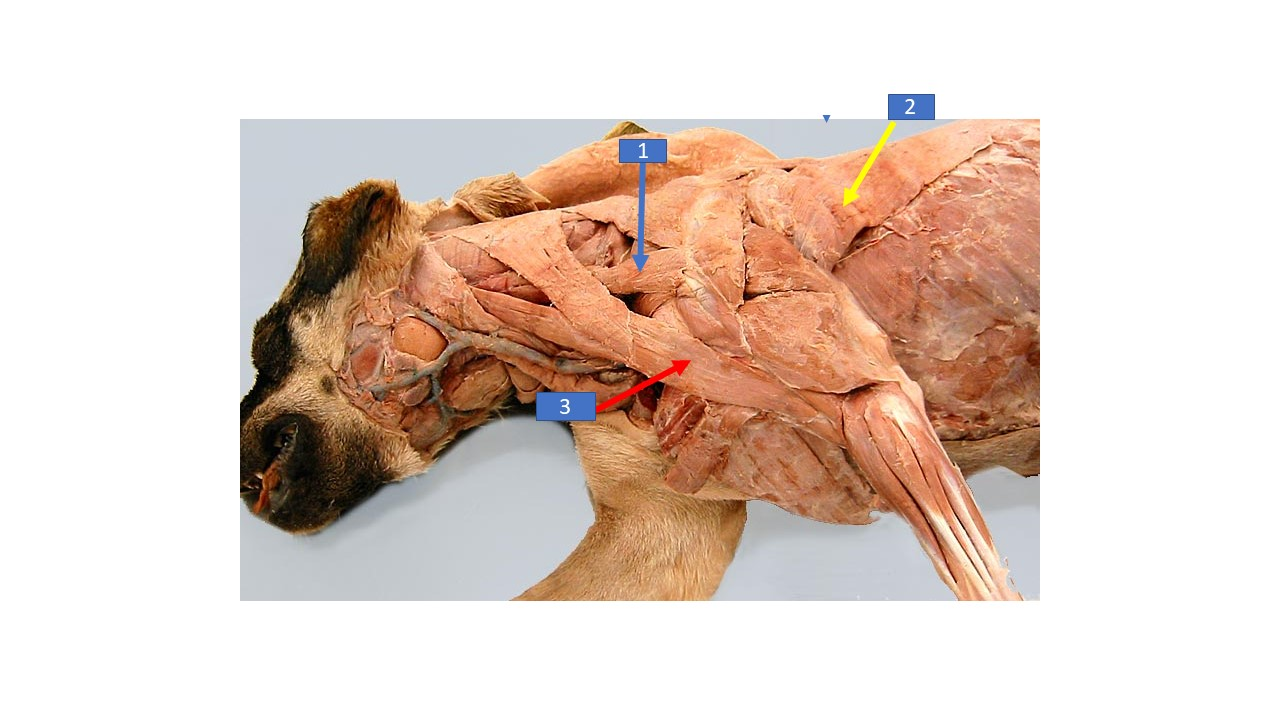
Omotransversarius
What is the extrinsic muscle labeled 1 in the diagram?
19
New cards
latissimus dorsi
What is the extrinsic muscle labeled 2 in the diagram?
20
New cards
Cleidobrachialis
What is the extrinsic muscle labeled 3 in the diagram?
21
New cards
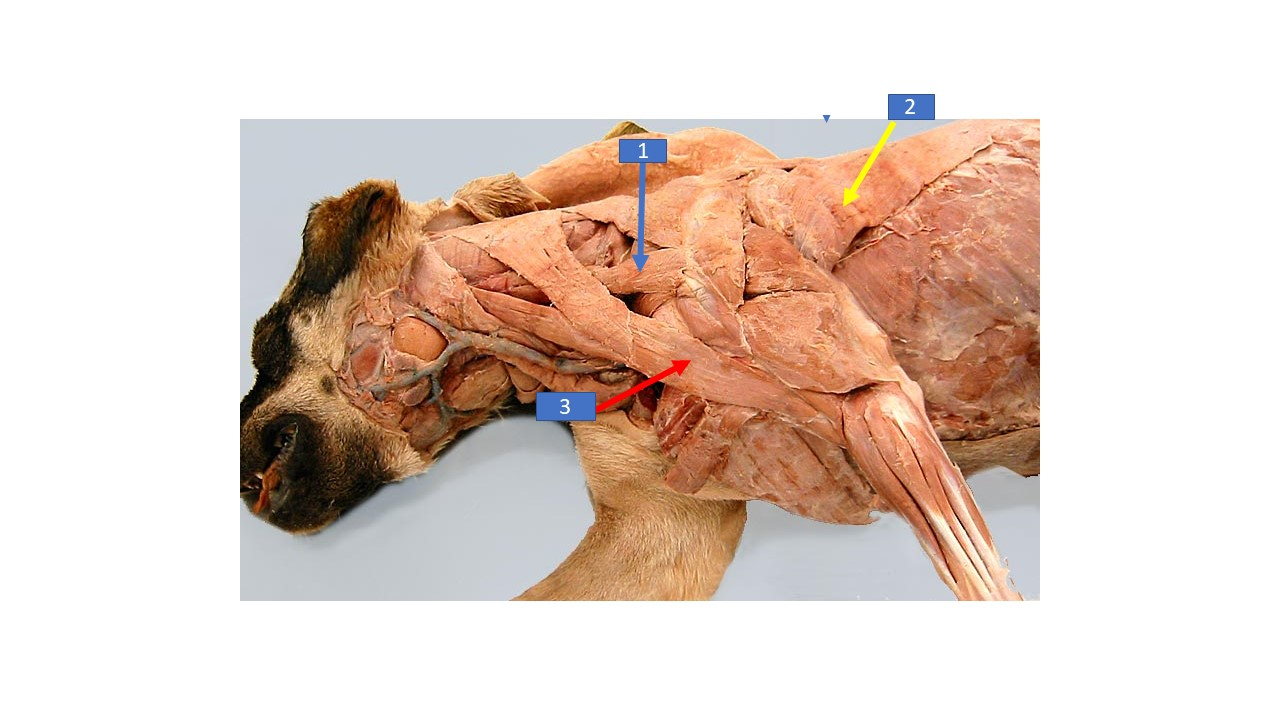
Rhomboideus
What is the extrinsic muscle labeled 2 in the diagram?
22
New cards
Serratus ventralis
What is the extrinsic muscle labeled 1 in the diagram?
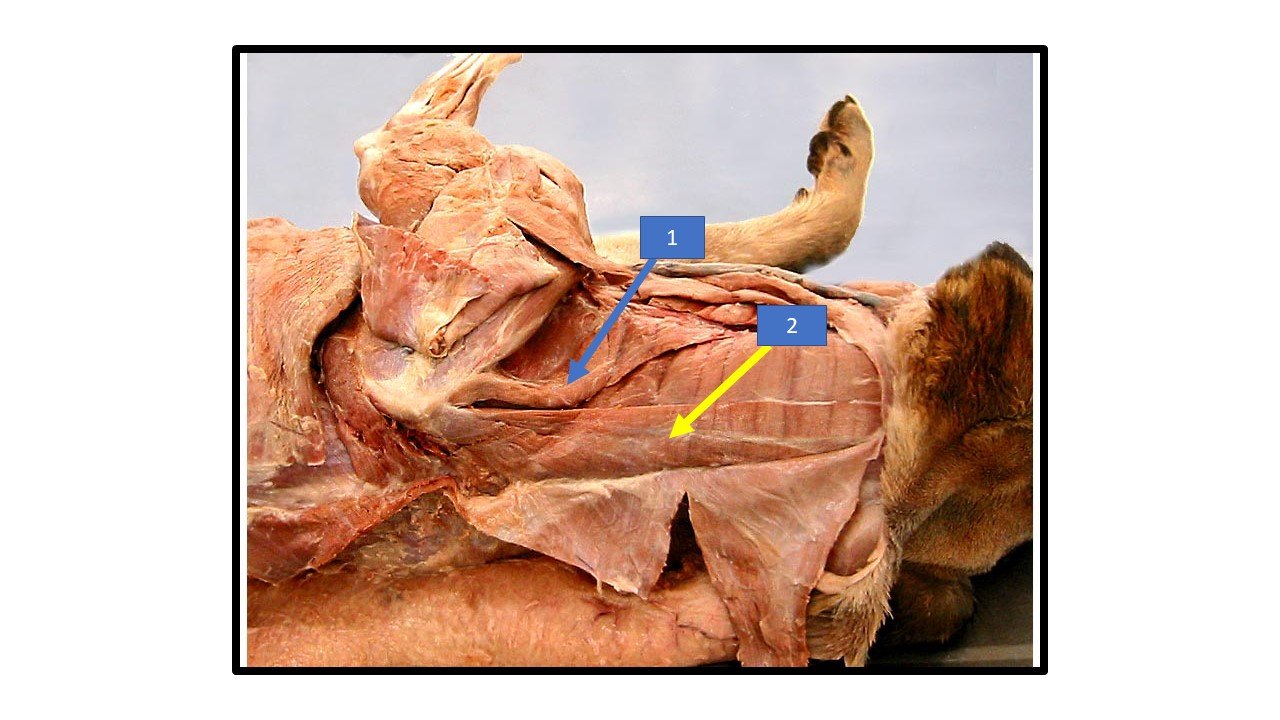
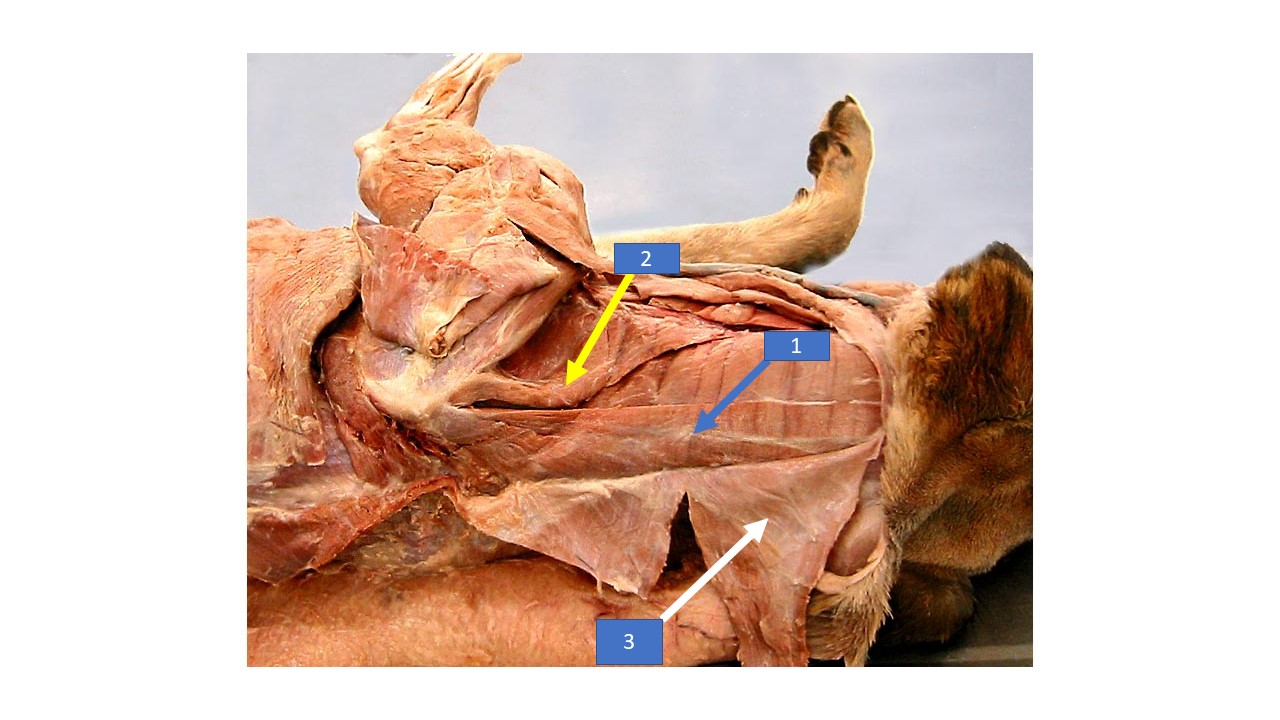
23
New cards
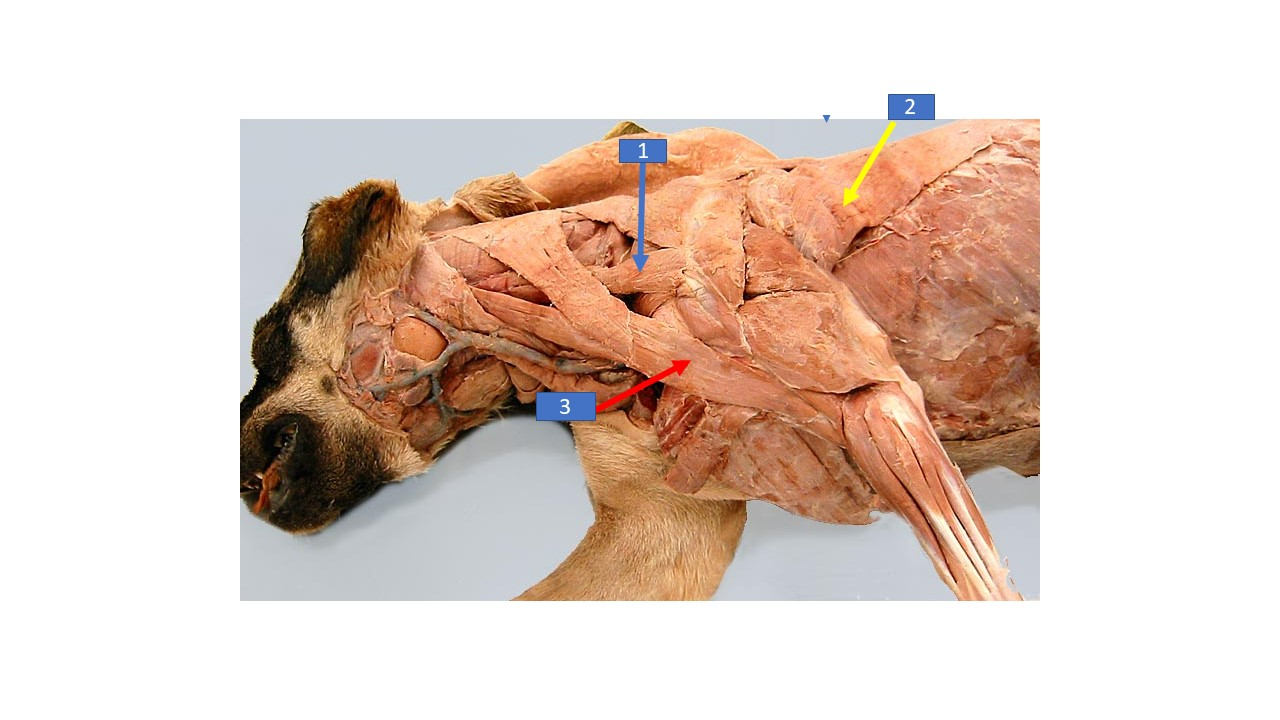
Trapezius
What is the extrinsic muscle labeled 1 in the diagram?
24
New cards
Superficial pectoral
What is the extrinsic muscle labeled 2 in the diagram?
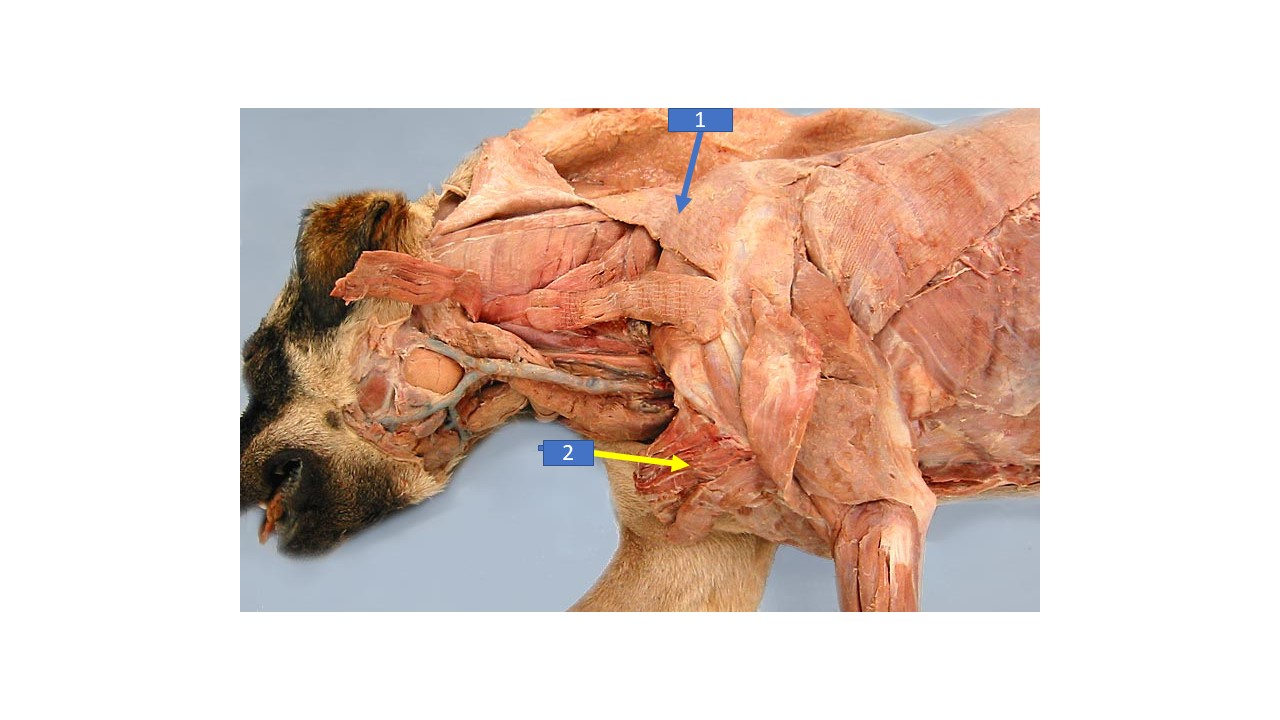
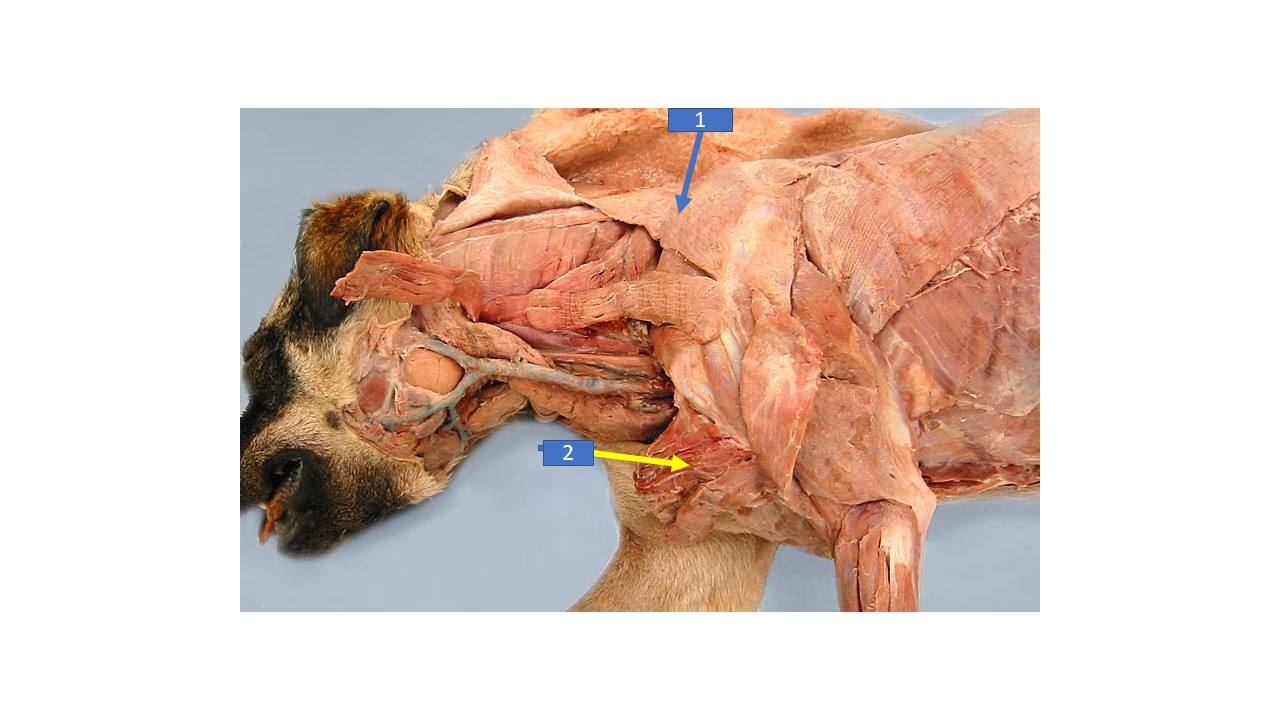
25
New cards
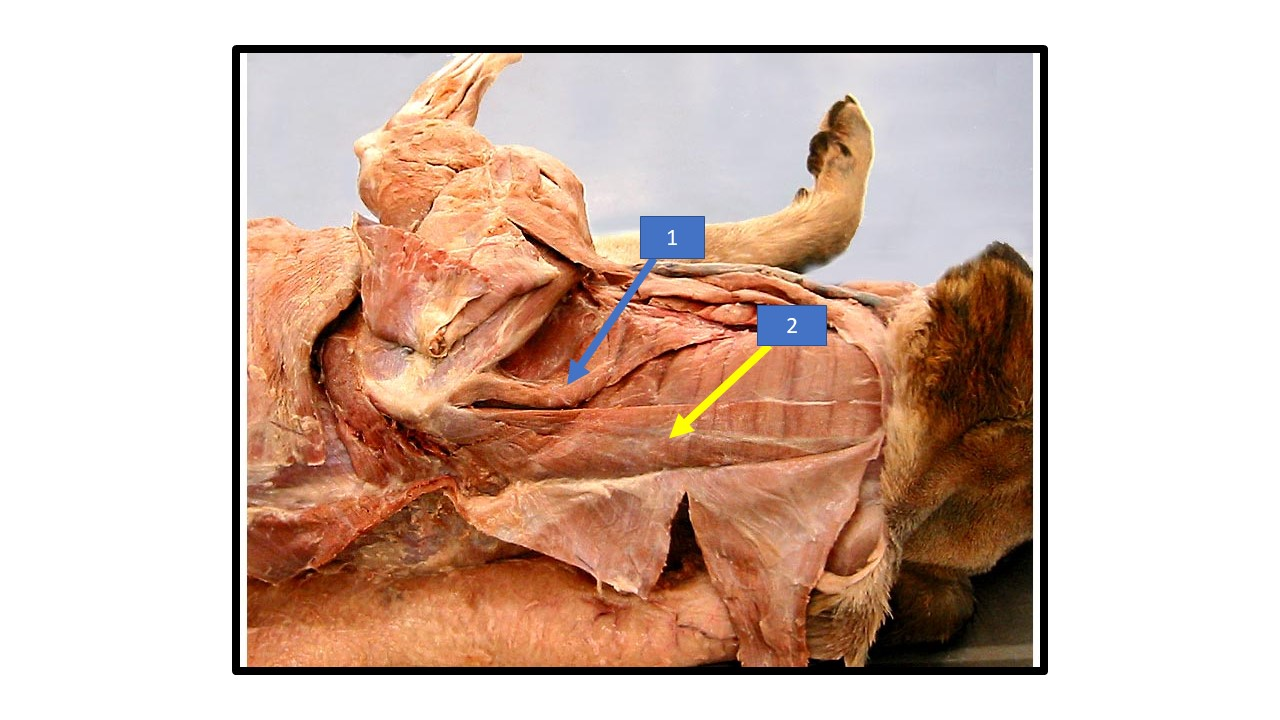
Rhomboideal
What is the extrinsic muscle labeled 1 in the diagram?
26
New cards
Serratus ventralis
What is the extrinsic muscle labeled 2 in the diagram?
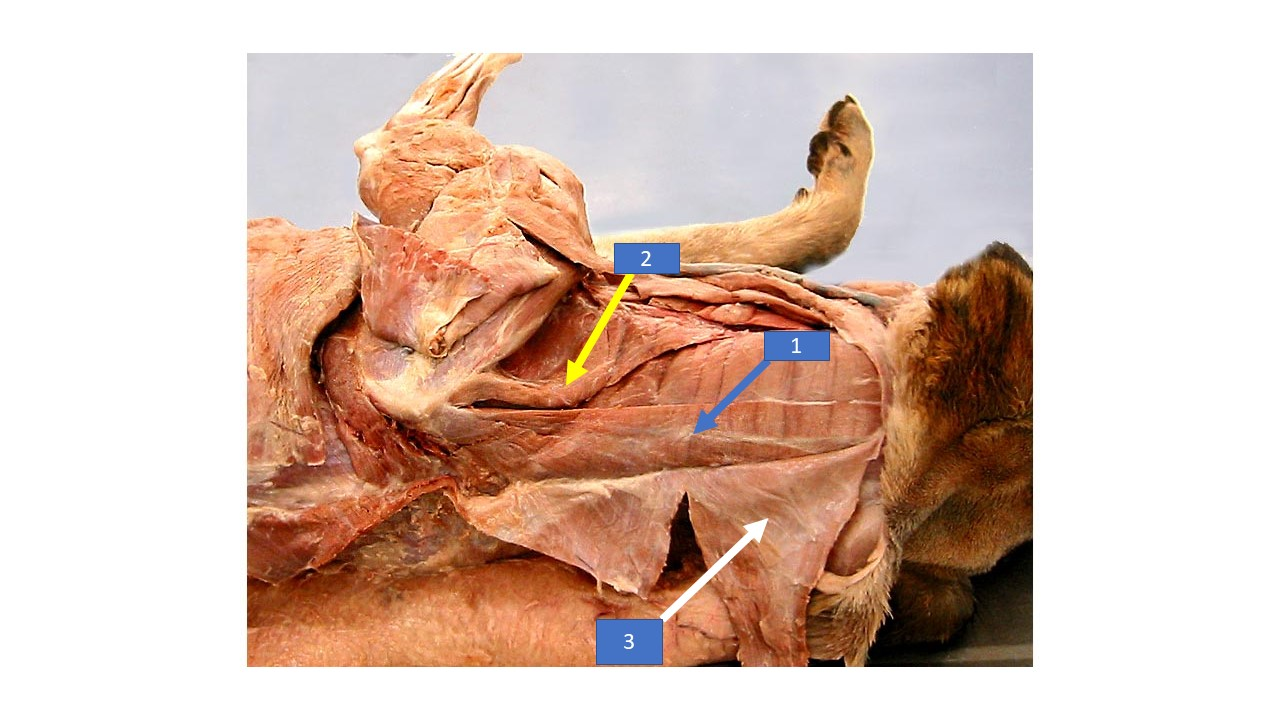
27
New cards
cleidocervicalis
What is the extrinsic muscle labeled 3 in the diagram?
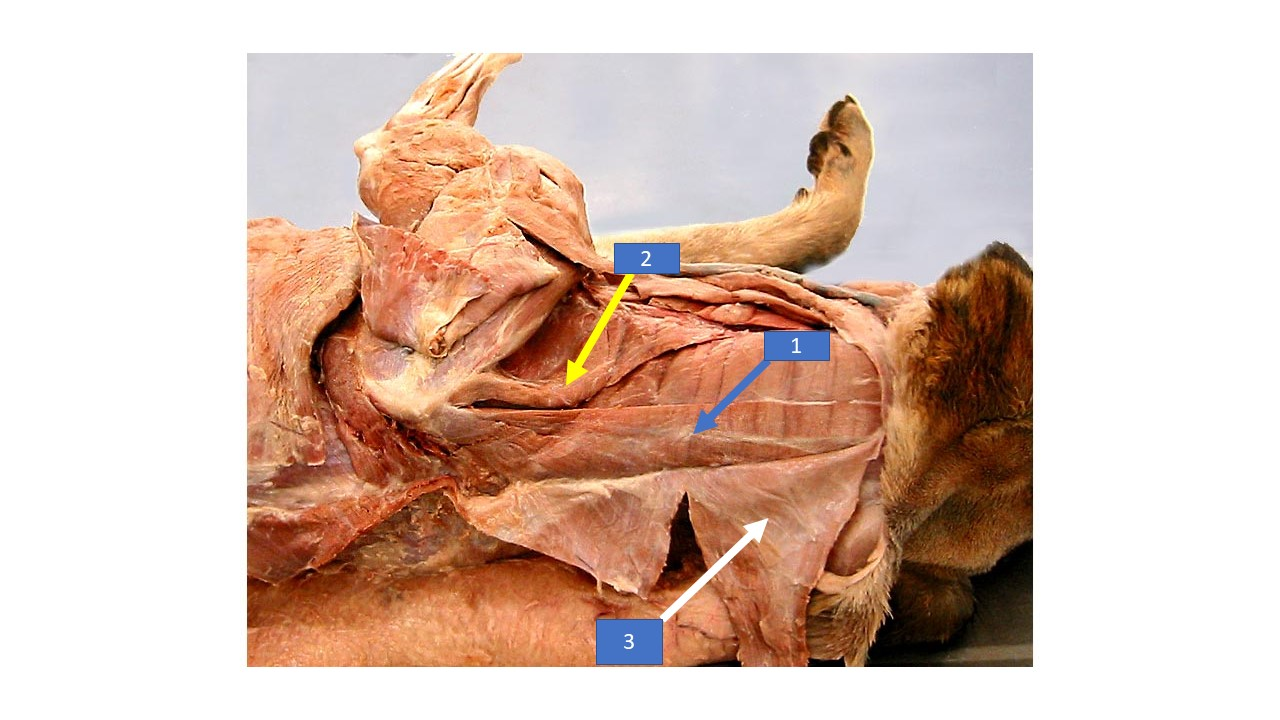
28
New cards
deep pectoral
What is the extrinsic muscle labeled with the right arrow in the diagram?
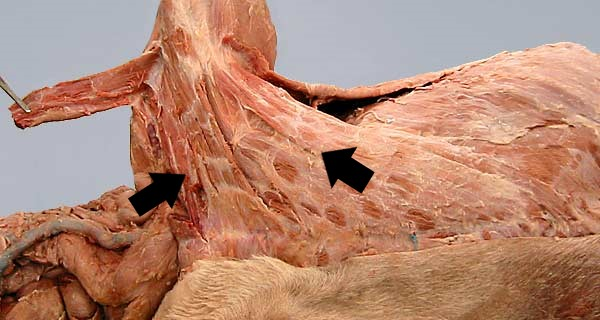
29
New cards
superficial pectoral
What is the extrinsic muscle labeled with the left arrow in the diagram?
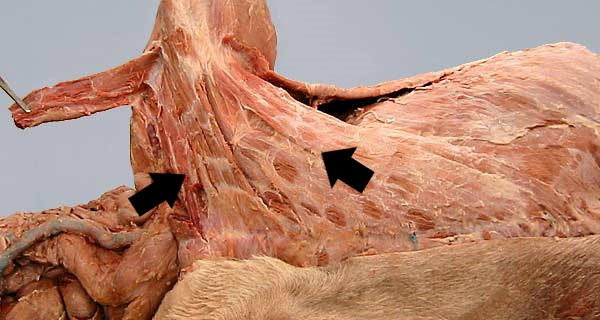
30
New cards
Clavicular intersection
What is the term used for the division point between the cleidobrachialis and the cleidocervicalis portions of the brachiocephalic muscle?
31
New cards
cleidocervicalis, cleidomastoid
What are the two upper portions of the brachiocephalicus muscle? They both go to different areas of the neck and are named accordingly.
32
New cards
deep pectoral
What is the extrinsic muscle that lies on the chest, below the superficial pectoral?
33
New cards
Extrinsic
Muscles that originate from the body and attach to the appendage are known as what?
34
New cards
Intrinsic
Muscles that are contained entirely on an appendage are known as what?