Ultrasound
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Ultrasound is sound with a frequenzy gre
Human ear can hear sound in this frequency range
16-20,000 Hz
Generation of US occurs by applying a high frequency AC to a __________
piezoelectric crystal
Ultrasound enters the body and is attenuated in the tissue by ____, _____, and _____
absorption, reflection and refraction
Critical angle of US
15*
True/False: US intensity increases as the wave travels through tissue
False; decreases
US attenuation is greatest in tissues with ____________
with high collagen content
Fresnel Zone vs Fraunhofer Zone
Fresnel Zone | Fraunhofer Zone |
Near Field | Far field |
Maxima and minima area close to each other | Ideal: near part of the far field |
Length of near field depends on:
| Practical Application: Underwater Technique |
True/False: US generally heats smaller, deeper areas compared to superficial heating agents
True
High absorption coefficient = __________
more heating received; tissue with high collagen content
Low absorption coefficients are usually found in tissue with ________
high water content
US is well suited to heating these types of tissue
tendons, ligaments, joint capsules, and fascia
True/False: US is well suited to heating tendons, ligaments, joint capsules and fascia without heating overlying fat
True
True/False: US is not ideal for muscle heating
True
US is effective for heating small areas of ________ in muscle
Scar tissue (due to increased collagen)
True/False: The speed with which the ultrasound transducer is moved affects the increase in tissue temperature
False; does not affect the increase in tissue temperature
True/False: Changing the absorption coefficient alters the total amount of energy and the heat distribution
False; alters heat distribution but NOT the total amount of energy
Causes of nonuniformity of intensity and temperature increase of US
Variety of tissue types
Different absorption coefficients
Reflection at tissue boundaries
If the ultrasound intensity is too high, the patient will complain of a deep ache from overheating the ________
perioosteum
3MHz vs 1MHz US
3 MHz | 1MHz |
Lower depth of tissue penetration (1-2cm deep) | Deeper tissue penetration (up to 5cm deep) |
For superficial structures | For deep structures |
Higher max temperature | Lower max temp |
Mechanical Applications of US
Cavitation
Microstreaming
Acoustic streaming
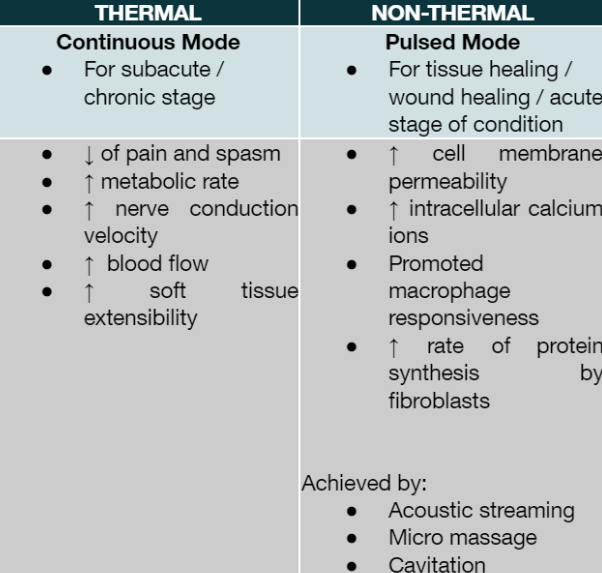
Non thermal effects can be delivered in ____ mode or _____ duty cycle
pulsed mode and 20% duty cycle
Effects of Low Average Intensity US
Increase intracellular calcium levels
Increase cell membrane permeability
Mast cell degranulation
Release of chemotactic factor and histamine
Promotes macrophage responsiveness
Increase rate of protein synthesis by fibroblasts and tendon cells
Stimulates proteoglycan synthesis by chondrocytes
Acoustic Streaming
The steady, circular flow of cellular fluids induced by US
Reason why US is being used in phonophoresis
Cavitation
The formation, growth, and pulsation of gas-filled bubbles by US
Micromassage
microscopic movement or oscillations of body fluids and tissues induced by US
Thermal vs Non-Thermal Effects
the use of ultrasound to increase the percutaneous absorption of a drug, usually an anti-inflammatory or anesthetic agent
Phonophoresis
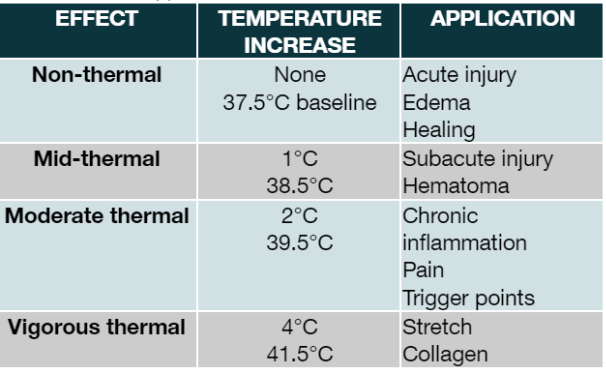
Indications for Thermal US
Before stretching shortened soft tissues
Reduction of pain
Non-thermal / Pulsed Indications for US
To accelerate tissue healing
Dermal ulcers
Surgical skin incisions
Tendon injuries
Bone fractures
Phonophoresis / Sonophoresis
Transdermal drug delivery
More localized
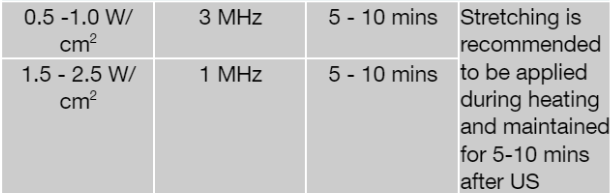
US intensity for Soft tissue lengthening
1 MHz for 5-10 minutes
US intensity for pain control
1.5 W/cm² for 3 weeks
US intensity for Skin incision healing
PULSED US x 0.75 or 3 MHZ x 0.5w/cm2 x 20% cycle for 5 minutes daily
US intensity for acute phase of tendon inflammation
pulsed mode at low intensity (0.5 - 1W / cm²)
US intensity for non union fractures
1.5 MHz frequency, 0.15 W/cm2 intensity, 20% duty cycle for 20 minutes
Clinical Application Guidelines
Depth of penetration of 3Mhz
1-2 cm
Depth of penetration of 1MHz
up to 5 cm
The ratio of spatial peak intensity to the spatial average intensity
Beam non-uniformity ration
Application guidelines for shortened soft tissues
Application guidelines for painful areas
0.5 - 3.0 W/cm² x 1 or 3 MHz x 3-10 minutes
Application guidelines for wound healing
0.5 - 1.0 W/cm² x 3MHz x 3-10 mins x 20% duty cycle
Application guidelines for carpal tunnel syndrome
0.15-1.0 W/cm² x 1 MHz x 5-15 mins
Application guidelines for phonophoresis
0.15 - 1.0 W/cm² x 3 MHz x 5-10 mins x 20% duty cycle
US duration is usually _____ for each treatment that is 2x the Effective Radiating Area
5-10 mins; 20 cm² area = ERA of 10cm² = 5-10 mins
Direct method of application
Moving the US transducer head help keep hot spots from forming
The speed of moving the US head, between 2 & 8 cm/sec, does not alter the effects
Strokes overlapping half of ERA is recommended
Fastest rate of heating occurs with slightly warm conduction gel
Properties:
Non-staining
Not irritating to skin
Ease of application
Cost
Glove or balloon technique is AKA
Bladder technique
Underwater treatment ideally uses _________
degassed water
Contraindications of US
Malignant tumor
Pregnancy
CNS tissue
Joint cement or plastic components of arthroplasty
Pacemaker
Thrombophlebitis
Eyes
Reproductive Organs
Precautions
Acute inflammation (used pulsed mode)
Epiphyseal plates
Fractures
Breast implants
Documentation of US
Duty cycle
Frequency
Intensity
Duration
Area of the body to be treated
Patient position
Method of application
Goal or rationale of treatment