Anatomy test 2 Ledogar ETSU
1/60
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What are the primary functions of the lung
To oxidate blood, expel CO2, maintain pH
What are the components of the upper and lower respiratory tracts (airways)
Upper: Nasal cavity, oral cavity, pharynx, larynx
Lower: Trachea, lungs → bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli.
What are the comments of the conducting portion and respiratory portion of the lungs?
Conducting: bronchi, bronchioles, terminal bronchioles.
Respiratory: respiratory bronchioles, alveoli
How many primary, secondary, and tertiary brooch are there in the right lung.
The right lung has 3 primary bronchi, 2 secondary bronchi, and 10 tertiary bronchi.
How many primary, secondary, and tertiary brooch are there in the left lung.
The left lung has 2 primary bronchi, 1 secondary bronchus, and 10 tertiary bronchi.
How many bronchopulmonary segments are there per lung?
There are 10 bronchopulmonary segments
Which components of the bronchial tree contain hyaline cartilage
Primary, secondary, and tertiary.
Starting at the ventricle, what is the path of blood flow through the pulmonary circuit?
Right ventricle → pulmonary artery → lungs → left atrium → left ventricle → aorta → head and arms → vena cava → right atrium → right ventricle
With respect to gas exchange, what occurs at the lung alveoli
Oxygen is absorbed into the blood while CO2 is released from the blood.
How is the pressure within the pleural cavity involved in respiration/ventilation?
The pressure within the pleural cavity creates a negative pressure that helps keep the lungs expanded and facilitates inhalation by drawing air into the lungs.
Which skeletal muscles are involved in inspiration?
The diaphragm.
External intercostal.
Which skeletal muscles are involved in expiration?
(breathing out)
Internal intercoastal
Intermost intercostal
Transversus thoracis
How is the abdominal diaphragm innervated and what are the spinal levels?
Phrenic nerve
C3, C4, C5
How are changed in intrapulmonary pressure involved in respiration/ventilation?
Creates a pressure gradient for air to move in and out of.
breathing in the air pressure in the lungs is below atmospheric pressure
breathing out the air pressure in the lungs is higher then the pressure outside of lungs.
get it together pookie.
Which ribs articulate with the sternum directly by their own costal cartilages? What do we call these ribs?
1-7
True ribs
Which ribs articulate with the sternum indirecly by connecting with the seventh costal cartilage?
8-10
Which do not reach the sternum at all?
11-12
What do you call the ribs that connect to the sternum by costal cartilage?
false ribs
The ribs that do not touch the sternum at all are called what??
floating ribs
Look at the articulations between ribs and vertebrae on the mounted skeletons. For a typical articulation, how do the rib head and neck articulate with the vertebra?
The head connects to the superior Demi facets
the neck connects to 2 costal facets of the vertebra. (unless its rib 1 or rib 12!!!)
How do ribs 1&12 differ from typical ribs?
They only connect to 1 vertebra.
What are the 4 superior back muscles that attach to the thoracic vertebra and/or ribs
Trapezius
Latissimus dorsi
Rhomboideus major and minor
Quadratus Lumborum
There are thee intrinsic back muscles that attach to thoracic vertebrae. What are they?
Erector spinae
Semispinalis
Multifidus
ALL get spinal nerves
What is the upper limb muscle that attaches to the sternum?
Pectoralis Major
What does the Serratus posterior superior do?
raises the ribs
Intercostal nerves
What does Serratus posterior inferior do?
Depresses the ribs.
Intercostal nerves
How does the transverses thoracic muscle function?
Where is it?
How is it innervated?
Its a rib depressor (forced experation)
its inside of the thoracic cage
Intercostal nerves
How do the intercostal muscles function during respiration?
How are they innervated
They pull down on the ribs.
Intercostal nerves
How does the abdominal diaphragm function durning respiration?
How is it intervated?
Diaphragm domes when exhaling (pressure inside of lungs increase)
Diaphragm flattens when inhaling (pressure inside of lungs decrease)
Innervated by the phrenic nerve.
What is the structure and function of the pericardium?
Its a sac.
It protects the heart, holds it in place, and its a sac the heart “grows” into
What are all three layers of the heart wall
Epicardium (outside layer)
Myocardium (middle of the layers)
Endocardium (inside layer)
What is the path of blood through the systemic circulation, beginning at the left ventricle?
you should be able to draw this
How does the fetal circulation bypass the pulmonary circuit?
The baby doesn’t need blood in its lungs.
Foreman Ovale
Ductus Arterious
What is the superior boundary of the abdominal cavity?
the diaphragm
What is the inferior boundary of the abdominal cavity?
Pelvic area (forgot the name. sorry pookies)
What is the posterior boundary of the abdominal cavity?
Posterior abdominal wall
(spinal cord/vertebra)
What is the anterolateral boundary of the abdominal cavity?
Your side.
“the muscular structure that forms the front and sides of the abdominal cavity:
says google
The free edge of which abdominal muscles aponeurosis forms the inguinal ligament?
external oblique
Describe the actions and innervations of the diaphragm
Contracting and flattning to expand the lunging while you breathe.
Phrenic nerve
Describe the actions and innervations of the quadrates lumborum
Latteral flexion
helps to kinda stabilize the 12th rib
innervated by spinal nerves
Describe the actions and innervations of the rectus abdominis
Flexes the trunk (bending forward)
helps stabilize the abdomen
compresses abdomen
Intercostal nerves
Describe the actions and innervations of the external oblique
Laterally flexes trunk, rotates trunk
Thoracic and subcostal nerves.
Describe the actions and innervations of the internal oblique
Flex the trunk (bend forward)
Laterally flex torso (bend to the side)
Rotate the trunk
Intercostal nerves
Describe the actions and innervations of the transverses absominis
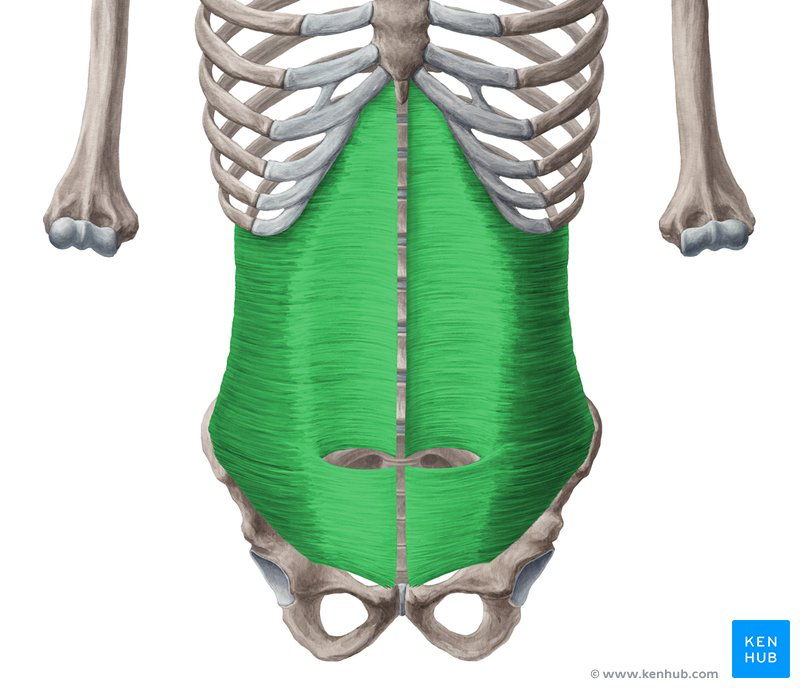
Compress abdominal contents
Internal costal nerves
Describe the structure of the rectus sheath above and below the arcuate line.
Above the arcuate line the rectus sheath has both an anterior and posterior layer.
Below the arcuate line the rectus sheath only has a anterior layer
Describe the primary functions of the digestive system organs in the abdomen.
Breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, eliminate waste products.
Which components are involved in propulsion
small intestines
Which comments are are involved in absorption
large intestine
Describe the four concentric layers of the GI tract
Mucosa
Sub Mucosa
Muscularis Externa
Serosa
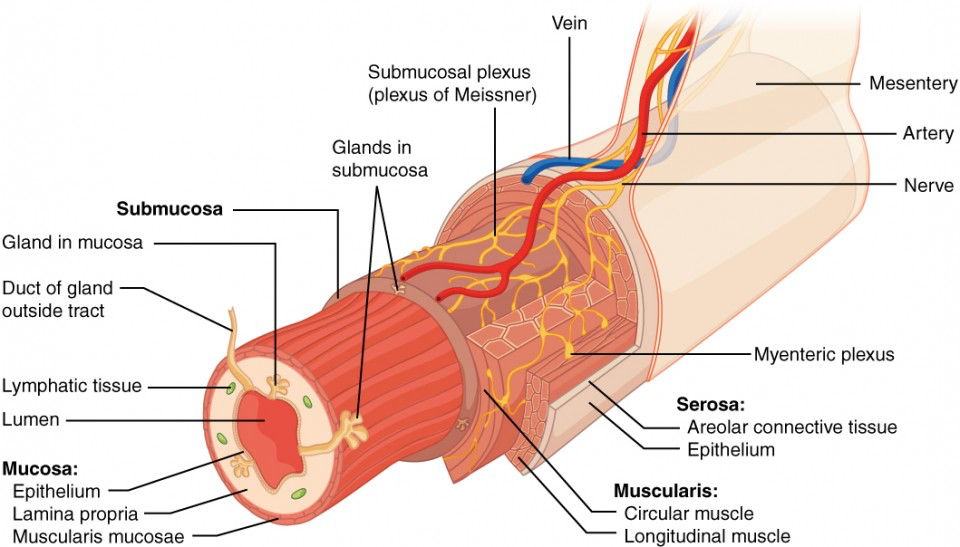
Which organ has three layers of muscular external rather than two
The stomach
what function does the mucosa serve
protection, lubrication, and sensing
what functions does the submucosa serve
providing a network of blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves.
what functions does the muscularis externa serve
Facilitate the movement of food through the GI tract
This is through contractions called peristalsis
What function does the serosa serve
A protective outer layer on internal organs
Which abdominal organs are intraperitoneal
stomach, spleen, uterus, ovaries, liver,
transfer colon. sigmoid colon
Which abdominal organs are retroperitoneal
Kidneys, aorta, vena cava
asending and descending colon.
What are the supposed functions of the appendix
Safe house for microflora
immune function
Describe the function of peristalsis
wave movement, only helps with movement
What muscle works with peristalsis
Longetidual
Describe the function of segmentation
mixing, it can move but its mostly for mixing.
What muscle helps segmentation
Circular