Lecture 3 - Protein Structure
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is a protein?
Linear polymer of L-amino acids connected by peptide bonds
How many levels of structure do proteins have?
4 (1o, 2o, 3o, 4o)
Primary Protein Structure
Linear L-amino acid sequence held by covalent peptide bonds
Determines properties of protein
Secondary Protein Structure
Spatial arrangement stabilized by hydrogen bonding; alpha helices and beta sheets
Tertiary Structure
Folding of secondary structure for packing (minimal volume); H-bonds, salt bridges, hydrophobic effect
Quaternary Structure
Interaction of multiple polypeptides (ex. hemoglobin - dimer of dimers)
Which structure is most favorable?
Primary; it is more disordered (extended)
Expect coupling not to be required
Which structure is least favorable?
Tertiary/Quaternary; less disordered (more compact)
Would expect coupling
Peptide Bond
Carbonyl carbon bonded to nitrogen of another amino acid
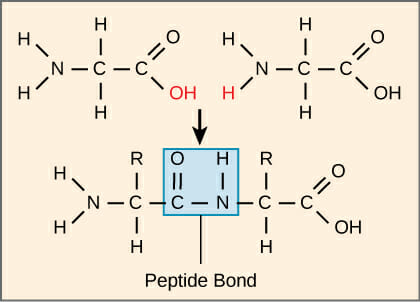
What reaction forms bond between two amino acids?
Dehydration reaction (water leaves)
What molecule leaves from peptide bond formation?
Water
Oxygen leaves from the hydroxyl group of one amino acid
2 hydrogens leave from nitrogen of the other
What 2 atoms is the peptide bond between?
Carbonyl carbon and amide nitrogen
Amino acid residue
Single amino acid on a polypeptide (different from free amino acid)
Partial double bond character results from…
Resonance between carbonyl oxygen and amide nitrogen (polypeptides are resonance-stabilized)
What orientation are peptide bonds in?
Planar; causes to be rigid, limits space for folding or rotation
Are polypeptides usually found cis or trans?
Trans, keeps R-groups further apart limiting steric hindrance
What is the problem in cis amino acids?
Steric repulsions will destabilize protein structure
Phi angle
Angle of rotation around the bond between alpha-carbon and nitrogen
Psi angle
Angle of rotation allowed between alpha-carbon and carbonyl carbon
Ramachandran Plot
Uses phi and psi angles on a graph to determine what structure is present in a protein (ex. alpha-helices have specific phi and psi values)
Secondary structure requires that R-groups are…
In trans arrangement
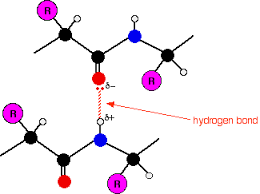
What bond stabilizes ALL secondary structures?
Hydrogen bonds between amide hydrogens and carbonyl oxygens
Alpha Helix Structure
Right-handed corkscrew; helical shape stabilized by H-bonds
Turn pattern/pitch of alpha helices
One turn every 4 residues, and each residue faces the same side of the helix
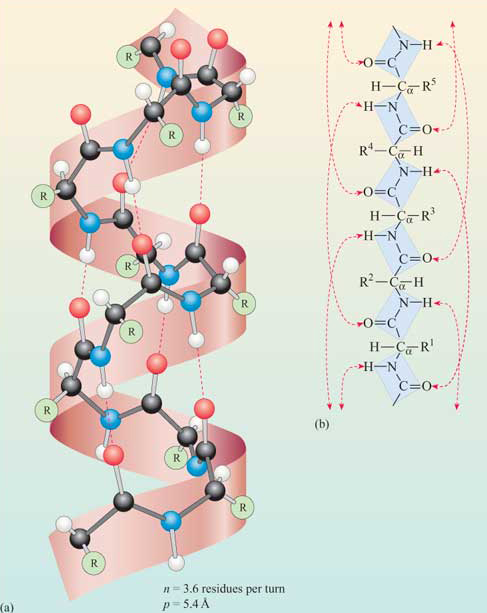
In alpha helices where are hydrogen bonds formed?
Within the structure, parallel to axis; carbonyl oxygen of residue n and amide hydrogen of n+4
In alpha-helices where do R-groups face?
All OUT
Proline’s Importance in secondary structure
Disrupts both alpha-helices and beta-sheets because of its rigidity and lack of hydrogen bonding ability
Why can’t proline hydrogen bond?
Its amide nitrogen has no hydrogen
A proline in amino acid sequence means…
There are two separate structure (either helix or sheet)
Amphipathic Helix
An alpha-helix has both non-polar and polar parts, allowing it to interact with water and hydrophobic environments.
Beta Sheet
Secondary structure with individual strands stabilized by hydrogen-bonding between
In beta sheets, where are the hydrogen bonds?
BETWEEN adjacent strands; not within
What way do B-sheet R-groups face?
Opposite each other (one left, one right)
Orientation of B-sheets can be…
Antiparallel or parallel
How are amino acid sequences written?
N to C terminus
Alpha helix vs. beta sheet
Compact vs. Extended
Hydrogen bonds within vs. between strands
Both H-bond
R-groups all facing out vs. opposite directions (in and out)
n+4 pitch vs. n+3 (X-P-G) pitch
Can be single chain vs. must have multiple strands
Keratin vs. Fibroin
More stable vs. Less stable
(Entropy increases as you extend the molecule)
Beta-turns
Compact, abrupt turns (allow for 180 degree reversal) following n+3 pitch
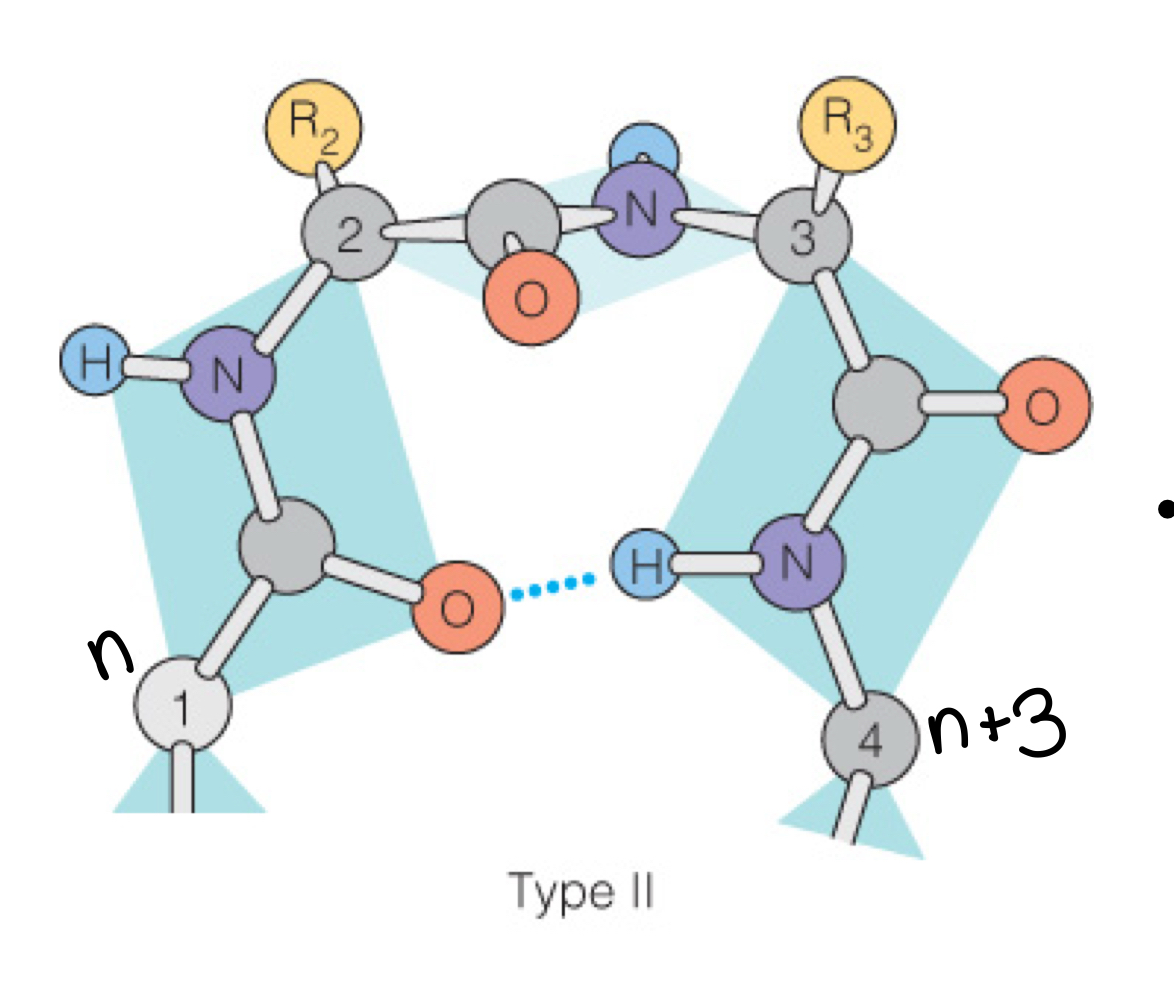
Amino acid motif for beta turns
X-P-G
Proline at position 2, glycine at 3
Where are beta turns usually found?
Globular proteins
Types of beta turns
Depends on what orientation the R-groups are in (cis or trans = type 1 or 2)
What determines whether beta-sheet or alpha helix forms?
Primarily backbone hydrogen bonding, but also charge-pairing
Intermolecule = beta, intramolecule = alpha
How does Glycine affect secondary structure?
Not able to interact with other amino acids to stabilize; in too high amount, can even destabilize and break structure
Why does glycine destabilize secondary structures?
It has a a very small side chain, interfering with its ability to interact
(Only hydrogen is its side chain)
Intrinsically Disordered Proteins (IDP)
Proteins that retain little structure and are very flexible; NO tertiary structure (1/3 of eukaryotic cells)
Example of an IDP
Protein tau (found in Alzheimers)