CS Lec 3 Linked Lists
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
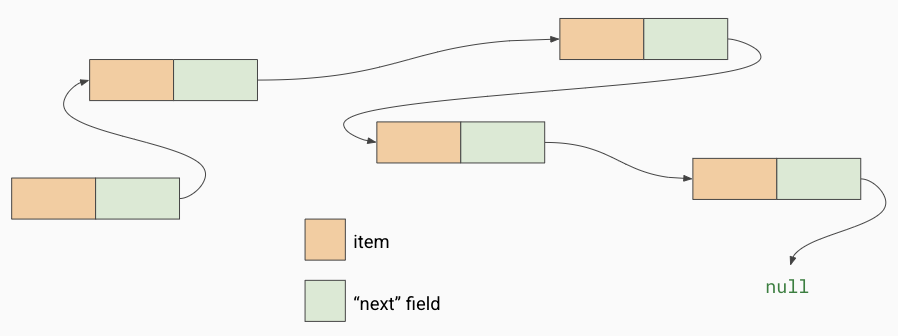
Linked Chain implementation
allows us to store each item individualy in memory. because the items aren’t stored next to each other(like they are in an array bag) we say they are not stored contiguously in memory
How can we keep track of all the items if we don’t have indexes like we do with arrays.
Using a linked chain allows each item to also store a reference to the next item in the chain. This way we can always go through the whole chain and access each items as if we were looping through an array.
What does each item in the linked have except for the last one
the data itself (T) and a reference that points to the next item in the chain. the last item has no such reference so it points to null.
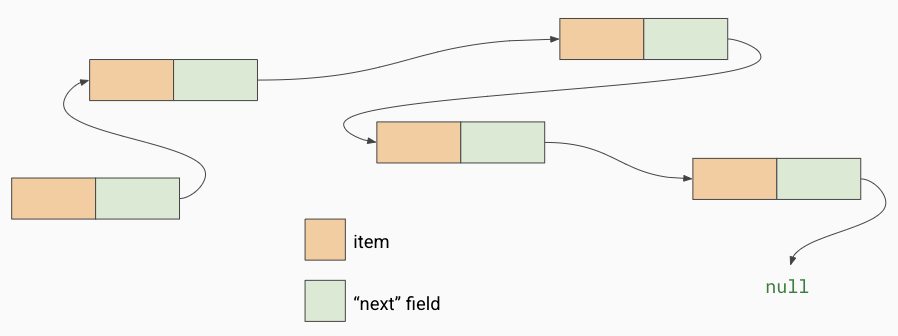
what does the last item have
no reference so it points to null, we can iterate through this by checking if ‘next’ is null, it it isn’t the set the current node to be ‘current.next’
Pros of using linked chains
bag can grow and shrink is size as needed
remove and ‘recycle’ nodes that are no longer needed
Java Garbage Collector use in bags
clean up any nodes that don’t have any references to them

The Node class
private inner class. exists only inside of the linkedbag class. The node class, and any node objects, are only accessed from inside the linkedbag class.

Linked bag implementation
same bag interface
uses a linked chain implementation
only one node
What are the steps of calling .add()
first node starts out as null
then we create a new node with the new data (newNode.next is null)
then we assign newNode.next to be firstNode (firstNode still null, so new Node.next is still null
last we assign firstNode to be newNode. now we have access to the first node in the chain from the LinkedBag class.
what is the first node?
the most recently added item
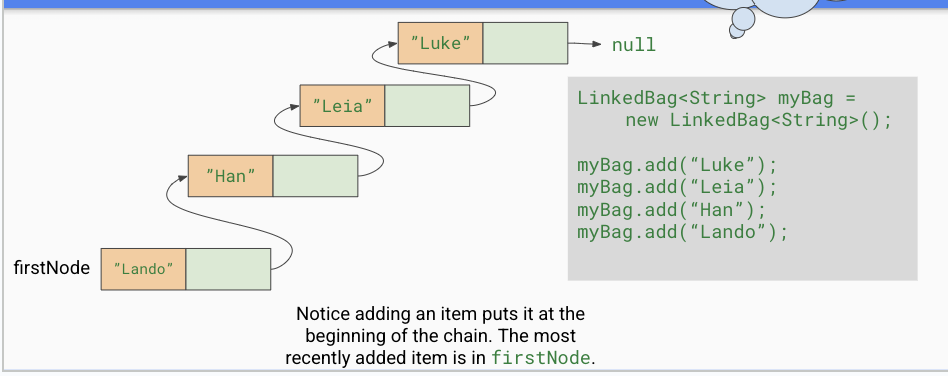
Why do we add new items to the beginning of the chain instead of end
if we add to the end, every call to add() would require us to navigate to the end of the list. adding to the beginning each time avoids this. imagine traversing to the end of a linkedlist with 1,000,000 items in it for every call to add()
What are the steps for .remove()
the node being removed is replaced with the first node
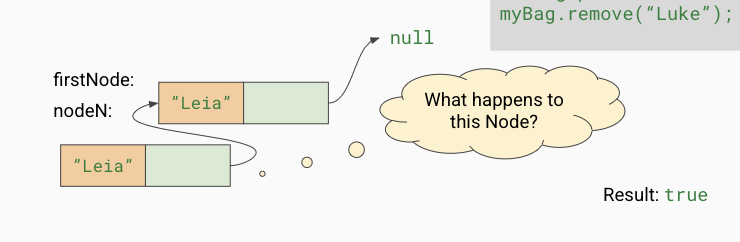
the original firstNode (“Leia”) is no longer referenced by anything else. it cannot be accessed by the java program anymore. java will mark this memory as “free” so another variable or object can use it. the java process that does this is called the garbage collector
What happens to a Node that is no longer referenced
It gets garbage collected
We have to call .remove() on it
It sits in memory forever
It gets reassigned to null