LAM: Exam 2
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms

Soft Tissue Trauma of the oral cavity
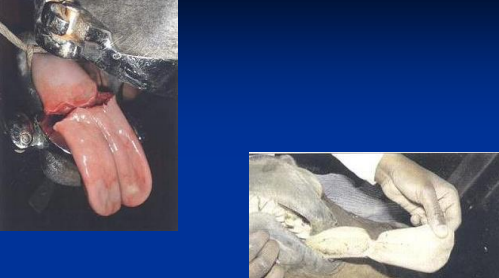
Lips, muzzle, cheek & tongue lacerations
Superficial: second intention healing → lips/cheek/muzzle
Deep mucosal: breaches oral mucosa → req closure
2-layer, absorbable mucosa-internal layer
Tongue lacerations: suture; partial amp(frenulum)
Fractures of the oral cavity
Et: kicks, collisions, cribbing, bit injuries
incisive bone, mandible, maxilla, teeth
Cs: drooling, lack of feed intake, malalignment, instability, crepitus, swelling, odor
Tx: soft feed, oral rinses, intraoral wiring, bone plates, screws, external fixation
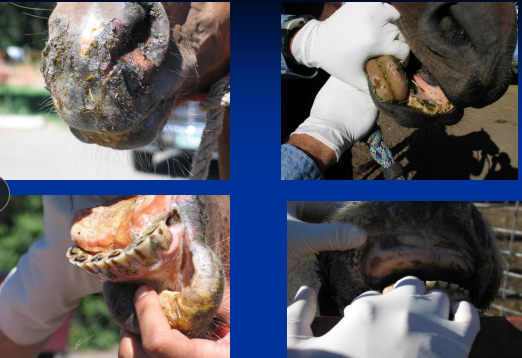
Oropharyngeal Foreign Bodies
Et: grass awns, splinters, wires
lingual/sublingual tissues, buccal recesses, palate, pharynx
Cs: stomatitis, glossitis, cellulitis, quidding, abscess, salivation, halitosis, dysphagia
Dt: speculum exam, palpation, rads, endoscopy
Tx: removal + antibiotics/NSAIDs + oral lavage
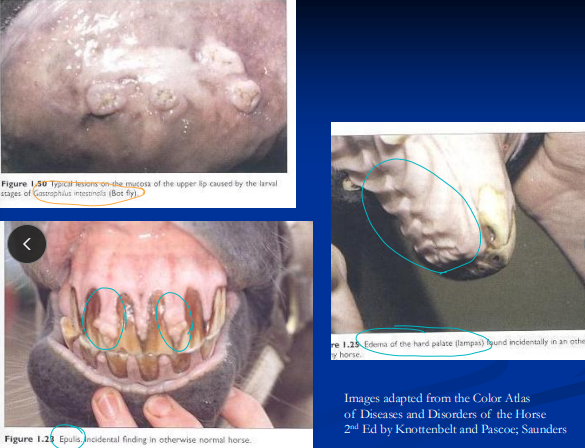
Stomatitis & Glossitis
Et:
Dental points: cheek/tongue lacerations
Parasites: Habronema, Gasterophilus(stomatitis), Helicocephalobus
Oral ulcers: blister beetles, VSV (report), NSAIDs, caustics, uremia : causes excessive drooling
Epulis: gingival hyperplasia, erupting teeth
Lampus: benign hard palate swelling with erupting incisors
Tx: lavage, NSAIDs, antibiotics
Salivary Gland Diseases
Sialoliths: obx, rupture, fistula
Trauma: salivary fistula/trauma/laceration
Obstruction: mucoceles; marsupialize
Slaframine toxicity: herd outbreaks of ptyalism; remove source
red clover with Rhizoctonia fungus
Congenital Oropharyngeal Defects
Cleft palate: nasal milk discharge, cough, FTT; Sx
Wry nose: lateral deviation of maxilla; malocclusion, nasal obx
Dental anomalies:
Parrot mouth: overbite, maxillary prognathism
Sow mouth: underbite, mandibular prognathism
Shear mouth, oligodontia, supernumerary teeth(delayed eruption)
Dentigerous cysts: draining tracts @ ear base
Gastrointestinal Neoplasia
Oropharyngeal
Melanoma: lip commissures; histopath
SCC: oral/pharyngeal tissues; histopath
Bone tumors: ossifying fibroma, osteoma, osteosarcoma; histopath
Dental tumors: odontoma, ameloblastoma; histopath
Esophageal
Et: SCC
Cs: recurrent choke
Px: Poor
Gastric
Et: SCC
Sig: Old
Cs: weight loss, chronic colic, poor appetite, choke
Dt: gastroscopy, biopsy, peritoneal cytology
Px: grave
Intestinal
Et: Lymphosarcoma (#1), adenocarcinoma, leiomyosarcoma, GIST
Cs: weight loss, chronic diarrhea, colic
Mimics IBD
Dt: biopsy, US, cytology
Px: poor
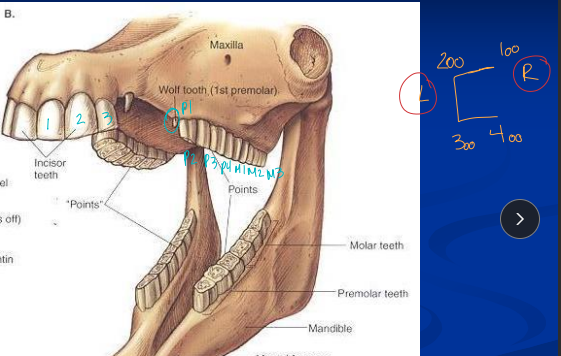
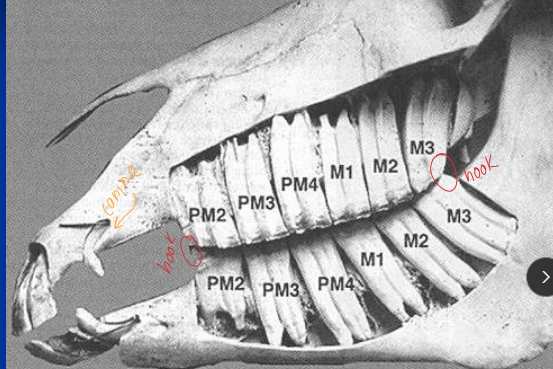
Dental Anatomy & Physiology
Hypsodont teeth: long crowns, short roots, enamel below gum line
Young: 24 teeth
@ 6m → 3 deciduous incisors & 3 premolars in each arcade
total 6 cheek teeth on each side
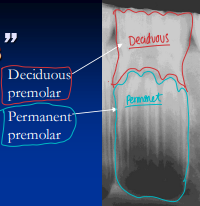
White: milk teeth
Adult: 36-44 teeth, canines present in males
P1 = wolf teeth
total 6 cheek teeth on each side
Hooks on P2, 3rd molar
Growth: crowns until 6-9y; wear 2-3 mm/yr
Continuous eruption to match wear; reserve crown ↓ with age
Eruption times for permanent teeth
Incisors: (I1-3) erupt at 2.5, 3.5, 4.5 years
Canine (C1) at 4 to 5 years
Premolars: 2.5, 3 & 4 years for P2-4
Wolf teeth (P1) at 5-6 months
Molars (M1-3) at 1, 2, & 3.5 to 4 years
Dental Disease
Et:
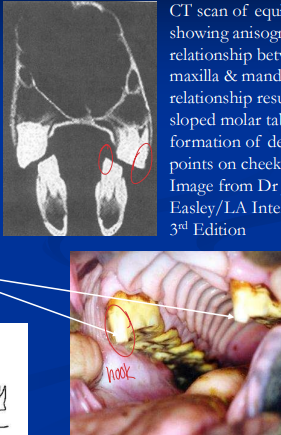
Points & hooks: sharp enamel lacerations; float regularly
Incisor abnormalities: retained, fractured, misaligned; extraction or stabilization
Canine teeth: unerupted (irritation), elongated (bit issues); file, extract
Wolf teeth: vestigial premolars; remove
Retained Premolar caps: impaction/infection (apical osteitis); remove + antibiotics
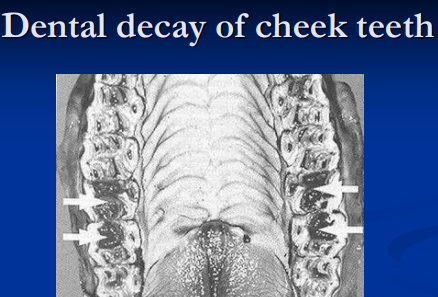
Dental caries/decay: infundibular defects, pulp exposure, fractures
Apical osteitis: infection, sinus, draining tracts; extraction, curettage, antibiotics
Malocclusions: Wave mouth (older horses), step mouth (missing opposing tooth), shear mouth (angled occlusion, narrow mandible), smooth mouth (aged, worn down); diastema, spaces between teeth that trap feed
Periodontal dz: malocclusion/diastema, gingivitis, bone loss, tooth loss
Cs: Weight loss, quidding, reluctance to eat, bitting problems, tilting head, drooling, bloody saliva, halitosis, unilateral malodorous nasal discharge
Tx: sinus trephination, buccotomy, repulsion, intraoral tooth extraction
Routine Dental Care
Exams: at birth, then 1-2x/year
Observation: body condition, drooling, swelling, quids
Feed test: observe mastication
Oral exam: requires sedation, irrigation, manual & visual exam
Full exam: full mouth speculum + good light
Ancillary diagnostics: radiography, CT/MRI, endoscopy
Floating: remove points/hooks
Wolf teeth: removal at 1-2y
Retained caps: extract if causing problems
Canine teeth: file sharp edges
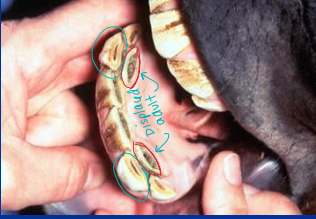
Extraction of cheek teeth
infection, fracture, loose tooth, malposition, dental tumors
Standing intraoral extraction preferred
lateral buccotomy → more challenging
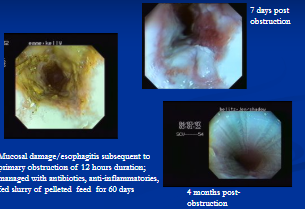
Esophageal Obstruction (Choke)
Et: intraluminal feed impaction at cervical, thoracic inlet, heart base, cardia
Poor dentition, coarse feed, feeding after exercise, pharyngeal dysfunction, neuro dx, previous choke, stricture, diverticulum, scaring, mass, megaesophagus
Cs: Saliva/ feed from nostrils, anxious, extended neck, gagging, retching, coughing, perforation, esophagitis
Dt: NG tube, endoscopy, US, rads
Tx: Remove feed/water 48h (aspiration), xylazine, acepromazine, lavage stomach w/ warm h2o, esophagotomy (refract)
Mild choke may resolve w/ sedation
Can cause Esophagitis
Chronic: complications are stricture, diverticulum, megaesophagus, recurrent obstruction
Esophageal Lavage
Why: choke
How:
NG tube, head lowered.
Never force tube past obx.
Warm water flush, drain repeatedly.
Massage bolus (if cervical)
Esophagotomy
Why: refractory choke, FB retrieval
How:
Longitudinal incision, primary closure if healthy tissue
Place NG prior esophagostomy tube for feeding
Longitudinal esophagotomy over or below obstruction
Rx: antibiotics
Esophageal Perforation
Et: prolonged choke, FB, NG tube, trauma.
Tx: Feeding via esophagostomy tube below perforation
Cervical: drainage/closure
Thoracic: usually fatal
Esophageal Strictures
Et: sequela of choke, trauma, reflux esophagitis, congenital
Cs: recurrent choke
Dt: endoscopy, contrast rads
Tx: balloon dilation, bougienage, esophagomyotomy, resection, grafts, soft diet
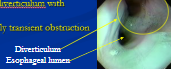
Esophageal Diverticulum
Pulsion: defect in the muscular wall
mucosa/submucosa herniates through muscle defect
Sig: post-choke, narrow neck
Tx: Sx
Traction: scar pulls wall out
Sig: wide neck, shallow
Tx: minimal clinical impact
Megaesophagus
Usually aquired
Et: obx, stricture, diverticulum, idiopathic, neuro dz, dysautonomia/grass sickness
Sig: Friesians(idiopathic)
Cs: dilated, hypomotile esophagus
Dt: endoscopy
Tx: feed slurry with horse’s head elevated
Esophagitis
Et: Choke, reflux esophagitis, NSAIDs, cantharidin
gastro-duodenal ulceration in foals (mostly)
Cs: progress to stricture/megaesophagus
Mechanisms of Intestinal Injury and Colic
Distension/stretching and Mesenteric tension
Simple: intraluminal blockage, non-strangulating displacement → distention, mesenteric tension
Ischemia
Strangulating: lumen + bld supply occlusion → ischemia, necrosis, perforation
Non-strangulating: Verminous arteritis (S. vulgaris) → arterial spasm, stenosis, embolism.
mesenteric artery
Acute inflam
SI (enteritis): ileus, distention, reflux, endotoxemia, hypovolemia
LI (colitis): ileus, diarrhea, fluid loss, PLE, endotoxemia.

Colic
Et: Distension, stretching, tension, ischemia, inflam
Cs: fever, pain, tachycardia, weak pulse, hemoconcentration, left shift, thrombocytopenia, prolonged clotting times, dogsitting, restless, no gastric sounds
Dt:
Nasogastric intubation: reflux suggests SI obx or gastritis
Rectal exam: distention, displacement, impaction, mesenteric bands, masses
Abd. US: distention, thick walls, displacement, sand, intussusception, hernia, colitis, peritonitis
Paracentesis: peritonitis, bowel compromise
Tx: xylazine, butorphanol, flunixin, detomidine, laparotomy, NG tube, cecal trocharization, fluids, plasma, polymyxin B, cathartics, laxities
Restore fxn, decompress, pain relief, stabilize
Predispositions for Colic in Horses
Foals: meconium impaction, enterocolitis, uroperitoneum
Weanlings/yearlings: gastric ulcers, ascarid impaction, intussusception, FBs
Adults: spasmodic, flatulent, gastric ulcers, LI impactions/displacements/volvulus, SI strangulations, typhlocolitis, verminous arteritis
Broodmares: uterine torsion, colon displacement/torsion
Stallions: inguinal hernia, testicular torsion
Older/obese horses: strangulating pedunculated lipomas
Miniatures/young: sand/hair/FB impactions

Peritoneal fluid analysis
Normal: clear, yellow, WBC <5,000/µL, protein <2.5 g/dL
Early obstruction: normal
Vascular compromise: serosanguinous, ↑ protein/WBC, toxic neutrophils
Necrosis: dark, degen neutrophils
Rupture: brown/green, bacteria, plant matter
Colic Surgery
What: Laparotomy
Why: Progressive/unrelenting pain, surgical lesions, progressive peritoneal fluid changes, CV deterioration, unresponsive to Rx
Pre-op: stabilize CV, penicillin + gentamicin, anti-inflam, NG tube, xylazine-ketamine-GG/diazepam, gas anesthesia
How:
Ventral midline incision
Inspect and palpate cecum, colon, peritoneal fluid
Correct displacements/volvulus, decompress, resect
Closure with absorbable suture, belly bandage
Px:
LI simple obx: good
SI obx: gaurded
LI torsion/volvulus: variable
Equine Gastric Ulcer Syndrome
Et: fasting, high concentrates, stress, exercise, NSAIDs
Squamous ulcers: near margo plicatus, lesser curvature; acid exposure : Omeprazole
Glandular ulcers: pyloric antrum, proximal duodenum; mucus barrier fail : Omeprazole, sucralfate
Cs: poor performance, girthy, cranky, inappatance, colic, bruxism, ptyalism, recumbency, diarrhea
foals have more CS than adults
Dt: endoscopy, Hyperkeratosis
Cs: ↓ stress, turnout, free-choice hay, stop grain/NSAIDs, rest, omeprazole, H2 antagonists, sucralfate, misoprostol, gastroenterostomy
Ranitidine: great inj in foals; H 2 blocker
Px: Squamous > glandular
Gastric Dilatation
Et:
Primary: grain overload, excessive fermentation, gas, fluid. : increased grains(Carbs)
Secondary: SI obstruction, reflux.
Cs: colic, reflux, splenic displacement, distended SI(2ndary), rupture
Dt: NG intubation, rectal exam, US
Tx: decompression w/NG tube
leave in place if secondary
Grain Overload..
Et: access to grain bin, rich alfalfa, lush pasture
Corn, barley, oats, sweet feed, commercial pellets
Cs: acute gastric dilation, rupture, colitis, acidosis, endotoxemia, laminitis
Tx: gastric lavage, mineral oil, fluxin, decompress (once CS)
Gastric Impaction
uncommon
Et: poor dentition, coarse forage, beet pulp, persimmon seeds (phytobezoars), grain overload
Frisians
Dt: US, gastroscopy, laparotomy
Tx: crystalloid fluids, cola lavage (persimmon), massage, sx
Px: fair to poor
Gastric Rupture
Et: dilation, impaction
Cs: Rapid septic peritonitis, endotoxemia, death
Dt: US, paracentesis (feed material), necropsy
Tx: euthanasia
Small Intestinal Adynamic Ileus
Et: poor propulsive motility
Dt: Enterogastric reflux (NG tube), imaging w/ distended loopsCs: Abdominal pain, post-op ileus, enteritis, peritonitis, neonatal weakness
Tx: NG decompression, prokinetics, Sx
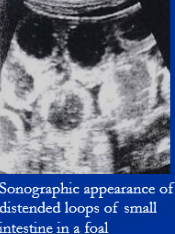
Small Intestinal Obstructions
Abd. pain, Nasogastric reflux, SI distention
Simple Intraluminal
Ascarid: foals (post-deworming heavy burden)
Ilea: Bermuda hay & tapeworms
FB: baling twine, plastic
Strangulating
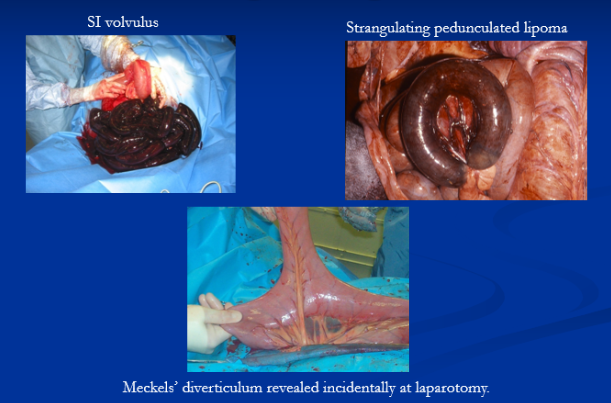
Pedunculated lipoma: old, overweight horses
SI volvulus: all ages
Meckel’s diverticulum complications
Cs: Abdominal pain
Dt: Enterogastric reflux (NG tube), imaging w/ distended loops
Tx: Sx emerg
Adynamic Ileus
Inhibition of propulsive bowel → functional obstruction
Sx complication, Enteritis
Tx: underlying dz, supportive care: NG tube decompression, ± motility drugs
Small Intestinal Incarcerations (Entrapments)
Et: Epiploic foramen entrapment
Mesenteric rents / gastrosplenic lig tears
Umbilical/body wall/diaphragmatic/ inguinal hernia
Sig: cribbing
Cs: Abdominal pain
Dt: Enterogastric reflux (NG tube), imaging w/ distended loops
Tx: Sx
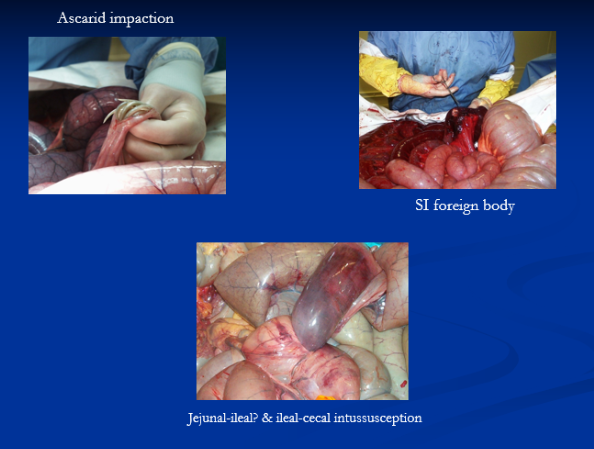
Intussusceptions & Intestinal Adhesions
Small Intestinal: Jejunum, jejunal-ileal, ileo-ileal, ileo-cecal
Ileal-cecal: tapeworms.
Adhesions: post-surgery or peritonitis
Sig: young, hypermotility or enteritis
Dt: Enterogastric reflux (NG tube), imaging w/ distended loops
Cs: Abdominal pain
Tx: Sx resection/anastomosis
Large Intestinal
Et: Cecal-cecal or ceco-colic.
Sig: young
Cs: severe pain, weight loss, diarrhea, mass
Tx: surgery
Px: fair-poor
Large Intestinal Impaction
Most common: pelvic flexure or transverse colon
Colon
Et: dehydration, poor teeth, coarse hay, sand, NSAIDs
Cs: intermittent mild colic, palpable mass(left side involved)
Tx: fluids, hypotonic saline, fluxin, laxatives, cathartics, psyllium, MgSO4, Sx
Cecal: abd. rectal palpation
Et: ortho Sx, stall rest, NSAIDs, motility dz
Cs: rupture
Tx: aggressive fluids and laxatives!!, typhlotomy, bypass (ileocolostomy)
Sand Accumulation
Et: sandy soil, feeding on ground
right dorsal colon
Cs: colic, diarrhea, impaction, abd. pain
Dt: sand in feces, US, rads
Tx: psyllium, fluids, analgesics, Sx, avoid ground feeding

Enterolithiasis
Et: Struvite (Mg-ammonium phosphate) stones in large colon
Sig: CA, AZ, FL, IN, alfalfa diet, high mineral
Cs: chronic colic, acute obx
Dt: rads
Tx: Sx removal
Dorsal Displacement of Large Intestine
Left → can move freely “floating colon”
Et: Colon trapped between spleen & left kidney, nephrosplenic lig.
Non-strangulating
Cs: mild pain
Dt: rectal exam, US
Tx: rolling, phenylephrine, controlled exercise, Sx
Right
Et: Colon wrapped around cecum, displaced to right body wall
Non-strangulating
Cs: Progressive pain, distention, cardiovascular compermise
Dt: rectal exam, US
Tx: Sx
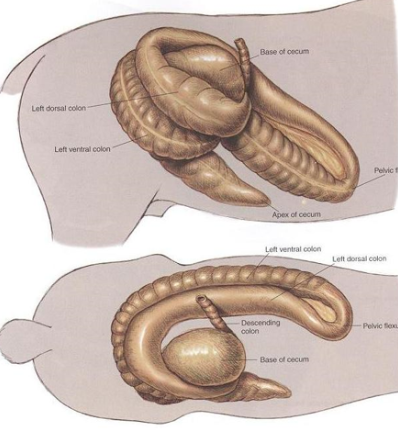
Large Colon Volvulus/Torsion
Et: 360° twist, ischemia
Twist LC at mesenteric attachment near base of the cecum
Twist LC at mesenteric attachment at sternal and diaphragmatic flexures
Cs: Severe pain, rapid CV compromise
Tx: Sx emerg
Px: poor

Simple Obstructions of Small Colon & Rectum
Et: impaction, Fecaliths, FB
Sig: foals, minis
Cs: Meconium retention
Dt: rectal “snake”, rads
Tx: fluids, laxatives, cathartics, pain med, decompression, Sx
Congenital Disorders affecting the Colon and Rectum
Atresia coli: rare, fatal
Intestinal aganglionosis
Aka: Lethal White Syndrome
Et: foals homozygous overo Paint mutation
Cs: fail to pass meconium, severe colic, fatal
Rectal Conditions in Horses
Prolapse
Mild (I/II): submucosa, conservative tx, osmotics, kneading
Severe (III/IV): insusseption of rectal wall, Sx
Tears
Et: Iatrogenic
Id: Grades I–IV depth-based
I/II: mucosal, Laxatives, feed restriction, low residue feed
III: muscoa and serosa into mesorectum, Sx
IV: muscoa and serosa into peritoneum, Sx
Strangulating/Trauma: Pedunculated lipoma, mesocolic tears, cervical tear prolapse, intramural hematoma
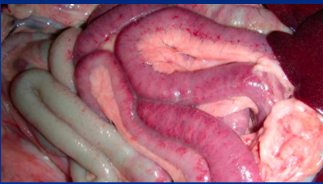
Proximal Enteritis
Et: acute inflam of duodenum/proximal jejunum
C. difficile toxins in adults → Infection suspected
Cs: edema, hemorrhage, trans-mural inflam, ileus, depression, fever, colic, distended SI, large gastric reflux, toxemia, hypovolemia
laminitis
DDx: SI obstruction/strangulation = explore lap
Tx: NG decompression, fluids, flunixin, plasma, antibiotics, lidocaine CRI
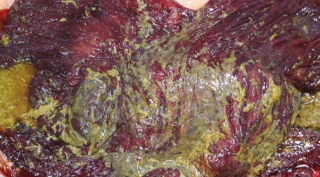
Acute Colitis / Typhlocolitis
Common
Et: bacti, viral, grain overload, antibiotics
LPS translocation (100%), bacti translocation (30%)
Cs: fever, tachycardia, injected MM, diarrhea (cowpie → watery → hemorrhagic), hypovolemia, shock, PLE, endotoxemia, acute fibrinous necrotizing colitis
laminitis, renal failure, bowel infarction, peritonitis, thrombophlebitis
Dt: hemoconcentration, left shift w/ toxic chnage, thrombocytopenia, azotemia, acidosis, ↓ protein
Tx: Fluids, Flunixin, Antibiotics, polymyxin B, plasma, smectite, metronidazole, bismuth, digital hypothermia, frog support, sand bedding, transfaunation, hay
Salmonellosis
Salmonella enterica enterica → sporatic
Et: G-, many serovars, zoonotic
nosocomial major concern
Invades L1 mucosa
Cs: inapparent, fever, neutropenia, acute colitis, neonatal septicemia
Dt: fecal PCR, culture
major DDx for acute typhlocolitis
Tx: fluids, NSAIDs, antibiotics (septicemia), biosecurity!
Clostridia-associated colitis in adults
Necrotizing, often hemorrhagic typhlocolitis; exotoxins
Clostridium perfringens
Type A: sporadic & antibiotic-associated
Clostridioides difficile (formerly Clostridium difficile)
Sporadic & antibiotic-associated forms
Nosocomial infections
Dx: fecal toxin assays
Maintenance: Treat endotoxemia, shock, hypoproteinemia
Oral metronidazole
Potomac Horse Fever
Seasonal
Et: Neorickettsia risticii
fluke larvae, bugs/aquatic snails, waterways
Sig: Mid-Atlantic, Midwest, CA, TX, Summer
Cs: Acute Colitis
Fibrinous, necrotizing typhlocolitis
Dt: PCR (bld, feces), paired sera
Tx: tetracyclines, killed vaccines
Equine Coronavirus
self-limiting
Cs: anorexia, fever, depression, leukopenia, diarrhea, acute colitis
Dt: fecal PCR
Tx: supportive
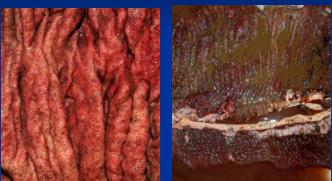
Larval Cyathostomiasis
Et: Encysted larvae in LI mucosa mass emergence
small strongyles (cyathostomins)
Sig: 2-3y, seasonal, deworming
Cs: acute colitis
mass emergence of L4
Tx: fluids, larvicidal deworming
moxidectin, high-dose fenbendazole
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea
Disruption of normal flora
Et: Dysbiosis, Salmonella, C. difficile/perfringens overgrowth
Cs: acute colitis
Tx: stop antibiotics → then test, transfaunation
Grain overload
Et: CHO fermentation
Cs: enteric acidosis, dysbiosis, endotoxemia, acute colitis
acute gastritis & gastric dilatation &/or enterocolitis; med. emergency
Laminitis = common sequelae
Tx: critical care + herd prophylaxis, oil, NSAIDs

Blister beetle toxicosis
Cantharidin is a vesicant toxin
Et: beetles or cantharidin in alfalfa hay
Cs: colic, diarrhea, shock, hematuria, hypocalcemia, lamanitis, myocarditis
Multisystemic toxicosis and acute colitis
Dt: ↓ Ca, urine cantharidin
Tx: fluids, mineral oil/charcoal, shock therapy
Px: guarded
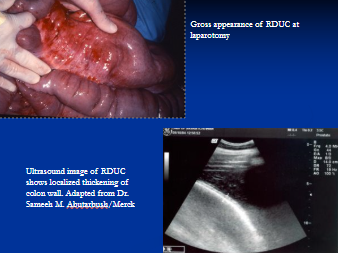
Right dorsal colitis
Et: NSAID, PBZ, localized ulcerative dz of right dorsal colon
Cs: chronic colic, diarrhea, ↓ protein, edema
Acute colitis
Dt: NSAID history, fecal occult blood, US thickening
Tx: ↓ residue/psyllium/oil diet, sucralfate, misoprostol, metronidazole
Infiltrative & Inflam Bowel Disease
Et: cellular infiltration of intestinal wall
Granulomatous enteritis, Lymphocytic–plasmacytic enteritis, Idiopathic focal eosinophilic enteritis, multisystemic eosinophilic dz
Cs: weight loss, thickened bowel wall, ↓ protein, chronic diarrhea, colic
malabsorption and maldigestion
Dt: Rectal palpation, US, glucose/D-xylose, biopsy
Tx: steroids, azathioprine, larvicidal deworming, Sx (IFEE)
Px: poor (GE, LPE, MEED), fair (IFEE)
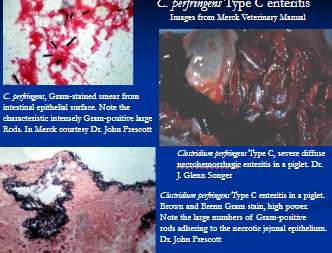
Clostridial enterocolitis
Et: C. perfringens A, C, C. difficile, antibiotic-associated
Sig: Foals <1 week
Cs: Hemorrhagic diarrhea, colic, rapid shock
Dt: toxins assay, culture, cytology
Tx: NPO, IV fluids, antibiotics, metronidazole, plasma, husbandry change
Px: poor
Foal heat diarrhea
Sig: Healthy foals, 9-14d
Cs: Mild diarrhea
Tx: self-limiting
Equine Rotavirus
The major viral diarrhea in foals
Et: Destroys villi
Sig: foals <2m
Cs: Profuse watery diarrhea, malabsorption, osmotic diarrhea
Dt: ELISA, EM
Tx: supportive; vax mares
Rhodococcus equi enterocolitis
Primarily causes respiratory disease
Sig: weanlings
Cs: pneumonia, SI/LI ulcerative enteritis, abscesses, peritonitis, diharrhea
Dt: US, culture/PCR
Tx: macrolide + rifampin (long-term)
Lawsonia intracellularis
Et: Proliferative enteropathy
Sig: Weanlings 6m
Cs: weight loss, edema, ↓ protein, diarrhea, thick ileum/jejunum (hose gut)
Dt: US, PCR, serology
Tx: tetracyclines, supportive care
Ascarids (Parascaris equorum/univalens)
Adult Round worm → jejunum
Et: Prepatent 10-12w
Sig: Foals, pasture
Cs: SI obx post-deworming, pot belly, liver/lung pathology, abd. pain!!
Dt: US
Tx: prevention: benzimidazoles q 60d until 12-18m
Macrocyclic lactone resistance
Large Strongyles
GI bug
Et: S. vulgaris, extra-intestinal migration
Rare but re-emerging
migrate via intestinal arterioles to the walls of mesenteric
Cs: arteritis, infarction, peritonitis, mesenteric artery thrombosis
Tx: Resection, routine ivermectin
Small Strongyles
Et: Encyst in LI mucosa, Cyathostomins
Sig: yearling horses
Cs: diarrhea, ill thrift
Tx: larvicidal deworming
moxidectin, high-dose fenbendazole
resistance common
Tapeworms
Et: At ileocecal valve, Anoplocephala perfoliata
oribatid mite : intermediate host
distal small intestine and cecum, at the ileocecal valve
Cs: impaction, intussusception
Tx: annual praziquantel, high-dose pyrantel in fall/winter

The Equine Peritoneum
Structure:
Parietal: lines abdominal wall & diaphragm
Visceral: covers abdominal organs
Fluid: Clear, slightly amber, low protein (<2.5 g/dL), low cellularity (<5,000/µL)
Contains fibrinolytic activity, phagocytic defense
Histo: single layer mesothelial cells + CT stroma, vessels, lymphatics, nerves
Fxn: produces peritoneal fluid for lubrication + defense
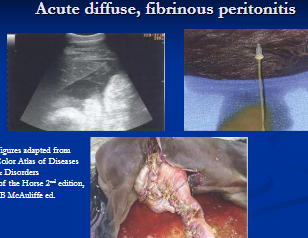
Peritonitis
Et: secondary dz (#1), Iatrogenic, mixed bacti (Hem/Lymph)
neutrophil recruitment + fibrin-rich exudate (seals defect)
Cs:
Local: min signs
Acute: Fever, depression, toxemia, dehydration, pain, stilted gait, septic
Chronic: abscesses/adhesions, recurrent colic, weight loss, fever
Dt: Abdominocentesis
neutrophils, degen changes, intracellular bacti, ↓ glucose, ↑ lactate
Tx: fluids, NSAIDs, antibiotics (sing bacti), laparotomy, lavage
Acute septic = emerg Tx
chronic/primary = Rx
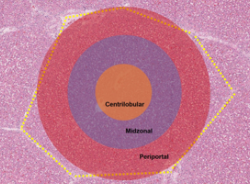
General Hepatic Injury
subclinical dz → common
No gallbladder, constant flow of bile into duodenum
Holds 10% of BV
Considerable regeneration potential
large reserve capacity → sig. liver dz w/out CS
Et: Disruption in protein, carb, lipid metabolism
poor detoxification, ↓ vit/mineral storage, ↑ ammonia & toxins, hepatic encephalopathy
Cs: Lethargy, anorexia, fever, depression, colic, endotoxemia, diarrhea, encephalopathy, jaundice, photosensitization, ventral edema, hemolysis, laryngeal paralysis, loss of BCS(chronic)
Ddx: biliary obx w/ R colon disp = no fever
Dt: ↑ SDH/AST (hepatocellular injury), ↑ GGT (biliary dz), ↑ billirubin(jaundice), ↑ bile acids, ↓ glucose, ↓ BUN, ↑ ammonia, ↓ albumin, ↑ globulins, prolonged clotting times, ↑ fibrinogen, ↑ PCV, imaging/US, biopsy
↑ AST alone = mm injury / rhabdomyolysis
Hemolysis & hemoglobinuria = end stage!
Tx: tx specific dz!, out of sunlight, Fluids (K+, dextrose), propofol, detomidine, ↓ protein + ↑ CHO diet, lactulose, neomycin, mineral oil, sedation as needed
Reactive hepatopathy = 2ndary hepatopathy
Bacterial Cholangiohepatitis & Cholelithiasis
Calcium bilirubinate concentrations in biliary tree
Et: Ascending G – bacteria, 2ndary SI obstruction
E. coli, Actinobacillus
Cs: Fever, colic, jaundice, depression, icterus, inflammatory leukogram, abd pain, dilated bile ducts
Ddx: biliary obx w/ R colon disp = no fever
Dt: Biopsy (neutrophilic periportal inflam), inflam leukogram, ↑ GGT > ↑ AST & SDH
Tx: medical support, Prolonged pentoxifylline, ursodiol, NSAID, Sx
Px: Good if early; recurrent if stones remain.
Tyzzer’s Disease
Et: Clostridium piliforme; Gram–, spore-forming
portal circulation / bacteremia
Spores: soil and adult feces
→ sporulation in GI→ liver
Sig: foals 1-6w
Cs: Peracute fever, depression, diarrhea, encephalopathy
SEVERE Necrotizing hepatitis, myocarditis, enteritis
Dt: Necropsy with silver stain, acidosis, low glucose, high AST
Tx: tetracyclines
Px: Grave, highly fatal
Theiler’s Disease / EqPV-H
Et: Equine Parvovirus-Hepatitis
4-12w: antitoxins, plasma, blood + horizontal transmission
Sig: adult - most asymptomatic
Cs: subclinical, fulminant necrosis, encephalopathy, jaundice, “dish rag” liver, small liver
Dt: PCR (serum = supportive, liver = diagnostic)
Tx: Supportive
Px: guarded, recover or die in 7d
highly fatal
Equine Hepacivirus (EqHV)
Similar to hepatitis C
Et: Mild transient hepatitis vs persistent infection
foals maintain high viremia
Cs: 1)chronic active hepatitis / 2)fibrosis/progressive inflammation
Dt: dont seroconvert, no ↑ liver enzymes

Pyrrolizidine Alkaloid Toxicosis
Et: ragwort, rattleweed, houndstongue → baled into hay
flower + seeds (most) > leaves> stems> roots
Path: alkaloid exposure→ pyrroles → DNA cross-linking → megalocytosis, biliary hyperplasia, bridging progressive fibrosis
Exposure over weeks to months
Cs: #1 cause of liver failure, neuro, photosensitivity, colic
Dt: Megalocytosis, biopisy, assess herd, biochem
Tx: no tx, eliminate source, ↑ protein diet, fluids, pentoxifylline
Hyperlipemia & Hepatic Lipidosis
Complication of hyperlipemia
Et: Triglyceride mobilization → fatty infiltration of liver → failure
Negative energy balance
Sig: Ponies, donkeys, obese pregnant mares
Dt: ↑ triglycerides + hepatic signs
Tx: manage ↑ lipids, pergolide, fluids, diet, reverse neg energy balance
Chronic Active Hepatitis / Cirrhosis
Chronic/sustained inflammation response
Et: Bacti (neutrophilic), immune/EqHV (lymphoplasmacytic), toxins
Cs: acute hepatic encephalopathy, gradual/progressive fibrosis
Dt: ↑ GGT, ↓ BUN, ↓ albumin, ↑ globulins, ↑ bile acids, polycythemia, liver biopsy
Tx: underlying dz, antibiotics, steroids, azathioprine, ursodiol, pentoxifylline, nutrition
Px: Poor if persistent encephalopathy, bile acids >20, severe fibrosis
Non-hepatic Hyperammonemia
Et: Acute colitis, bacti overgrowth, ammonia absorption
common in adult horses
Cs: Diarrhea, colic, feed refusal, encephalopathy, bindless, mania
no liver dz
Dt: ↑ ammonia, acidosis, ↑ lactate, ↑ glucose
metabolic acidosis, elevated l-lactate, hyperglycemia
Tx: Supportive, neomycin, lactulose, detomidine, propofol, crystalloid fluids (no bicarb, add KCL), sodium benzonate
Anatomical Biliary Obstructions
Et: R dorsal displacement of colon, duodenal strictures (foals)
DDX cholangitis/cholelithiasis
Cs: Colic, jaundice, ↑ GGT/bilirubin
No fever
Tx: Surgical correction
Duodenal strictures in foals w/ ulcerated duodenitis

Pituitary Pars Intermedia Dysfunction (“Equine Cushing’s”)
Et: ↓ dopamine, ↑ ACTH & POMC peptides
Middle aged - older ~ 19y over weight
unregulated release ACTH
hyperplasia Melanotropes of pituitary pars intermedia (PI) normally secrete of pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC)
controlled by dopaminergic neurons in the hypothalamus
Cs: hypertrichosis, muscle wasting, PU/PD, laminitis, infections, lethargic, hair coat change, delayed shedding, insulin dysregulation
Dt: resting ACTH, TRH stim test.
stress leukogram & possible steroid hepatopathy
Tx: Pergolide (Prascend®) → dopamine agonist, low carb/high fat diet, clipping, preventive care
no cure

Equine Metabolic Syndrome
Sig: “easy keepers,” ponies, Arabians, Morgans, Mustangs
Cs: obesity, insulin dysregulation, laminitis
Dt: ↑ resting insulin, dynamic insulin testing
Tx: ↓ CHO diet, restricted pasture, hay at 1.5% BW, exercise, thyroxine, metformin
type 2 DM


Hyperlipemia / Hyperlipidemia
Et: fat mobilization → TG >500 mg/dL → hepatic lipidosis
negative energy balance
Sig: ponies, minis, donkeys
Measure/monitor TGs in all sick minis
Cs: depression, anorexia, diarrhea, colic, lipemic plasma
Tx: dextrose, NG feeding, insulin
Px: guarded if advanced
Misc Endocrine Disorders
Thyroid disease: congenital goiter, iatrogenic hyperthyroidism, thyroid neoplasia.
Parathyroid: nutritional secondary hyperparathyroidism (“big head disease”), hypocalcemia (lactation tetany, blister beetle).
Adrenal: rare Addison’s, pheochromocytoma, anhidrosis.
Pancreas: Type I DM rare, Type II (EMS/PPID overlap), islet cell tumors rare.