Extensions to Mendel's Principles
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
”sex-linked” characteristics
the inheritance of characteristics coded on sex chromosomes
Pattern of inheritance of sex-linked characteristics is _________ from autosomes
different
Most sex-linked characteristics are __-linked
X
Pattern of sex-linked inheritance was first described in __________ (2 forms of X determine whether white- or red-eyed)
Drosophila
If X+ is dominant over XW, a cross between a white-eyed female (XWXW) and a red-eyed male (X+Y) will produce…
0% white-eyed females and 100% white-eyed males
If X+ is dominant over XW, a cross between a red-eyed female (X+XW) and a white-eyed male (XWY) will produce…
50% white-eyed offspring
Sex-linkage (XX-XY): eye color alleles only on X chromosome (X-linked)
Females = homozygous or heterozygous, males = hemizygous
• Females inherit an X from father, males inherit a Y from father
• Males and females inherit one of two Xs from mother
X and Y have different _____
genes
X and Y pair as “_________” during meiosis
homologs
ZZ-ZW Sex-linkage
similar to XX-XY but reversed (females hemizygous, males homo/hetero)
each ____ cell expresses an opsin protein involved in detecting red, green, or blue light (can sense color); mutations in opsin genes effect ability to see colors
cone
Red and green opsin genes are on X chromosome, making color-blindness __-_____
X-linked
human X-linked traits
eye color
color blindness
hemophilia (blood clotting factors)
muscular dystrophy
is the X or Y chromosome shorter (64 genes)?
Y
Y chromosome genes are associated with…
male development and fertility (most not well understood)
Y and X evolved from ________
autosomes
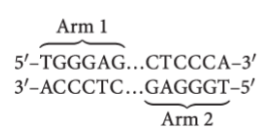
Palindromic sequences
Extensive repetitive & palindromic DNA sequences
important for internal recombination (maintain chromosome)
Phenotype is often associated with amount of ______ produced
protein
Two copies of chromosome will typically ‘______’ the amount of protein
double
Autosomes and XX females have two copies of each chromosome, whereas males have only one X. Thus, for genes on X, females would have twice the amount of ‘____ ______’
gene dosage
To compensate for the doubled amount of gene dosage in females, one X chromosome is randomly __________ early in development (except some X genes escape, and not all diploid organisms compensate)
inactivated
Dominance
allelic interaction
Dominance does not relate to patterns of inheritance; it is an interaction between…
the products of genes
_________ can occur at different levels because phenotype can be observed at different levels
Dominance
genetic __________ often have a molecular phenotype, a cellular phenotype and a physiological phenotype
diseases
alleles may be dominant at one level and ____________ at another level
co-dominant
Phenotype of __________ determines the type of dominance
heterozygote
Barr body
inactivated, highly condensed X chromosome

Calico cat coat
example of X chromosome inactivation (indicates which was inactivated)
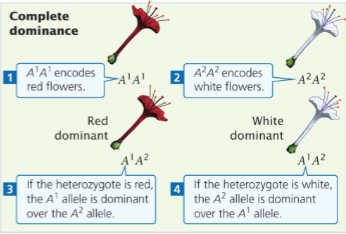
Complete dominance
Heterozygote has same phenotype as one of homozygotes
Incomplete dominance
Heterozygote has a phenotype intermediate between homozygotes
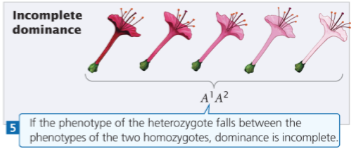
Incomplete dominance results in a _______ phenotypic ratio from a heterozygous cross
1:2:1
Genotypic and phenotypic ratios are the same in incomplete dominance because each genotype has its own __________
phenotype
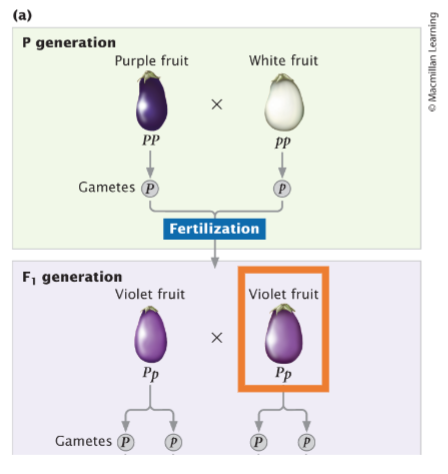
If an F1 eggplant is used in a test cross with a homozygous recessive plant, what proportion of the progeny from this cross will be white?
1/2
Codominance
when both alleles are expressed, retaining their own identity; ie., a heterozygote simultaneously expresses phenotypes of both homozygotes
AB blood alleles
ABO type depends on carbohydrate chains added to cell surface proteins and lipids
Antigen and thus blood type are determined by polymorphic glycosyltransferases (codominance)
Penetrance and expressivity dominance
Dominant allele may not always show expected phenotype due to effects of other genes and environment
Penetrance
% of individuals with a particular genotype that express expected phenotype (100% = dominant phenotype is seen in every indiciudal with that allele; 50% = only half of those with dominant allele show that trait)
Expressivity
the degree to which a trait is expressed
penetrance vs expressivity
penetrance: is trait present or not?
expressivity: to what degree is trait expressed?
Example of penetrance and expressivity
polydactyly in humans: caused by dominant allele, but some individuals with dominant allele do not have the phenotype (penetrance), and number of extra digits varies (expressivity)
lethality dominance
Some alleles are lethal in the homozygous state —> death during development
Because some of the progeny die due to lethality dominance, the expected _____ is altered
ratio
mouse coat color example of lethality dominance
Y is recessive lethal but color dominant
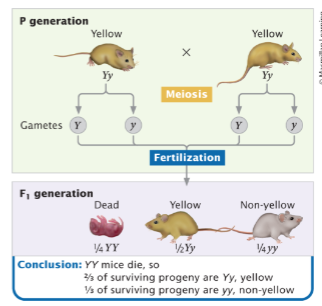
A cross between two green corn plants yields 2/3 green progeny and 1/3 yellow progeny. What is the genotype of the green progeny if the dominant allele is recessive lethal and color dominant?
Ww (WW individuals died)
A cross between two green corn plants yields 2/3 green progeny and 1/3 yellow progeny. What is the genotype is lethal?
WW
multiple alleles
when there are more than two alleles in population (still only two alleles in diploids)
Human ABO blood type shows ________ ________ (and co-dominance)
multiple alleles
in Mendel’s dihybrid crosses, the genes at each locus:
a) independently assorted during meiosis (to produce 9:3:3:1 phenotype)
b) were independent in their influence on phenotype (seed shape, seed color)
Frequently, genes at two loci do not act __________ on phenotype
independently
the effect of genes at one locus often depends on presence of gene(s) at different locus
Products of genes at different loci interact to produce new, unpredicted phenotype
Example of a gene interaction that produces novel phenotypes
genes at two loci interact to produce fruit color in peppers
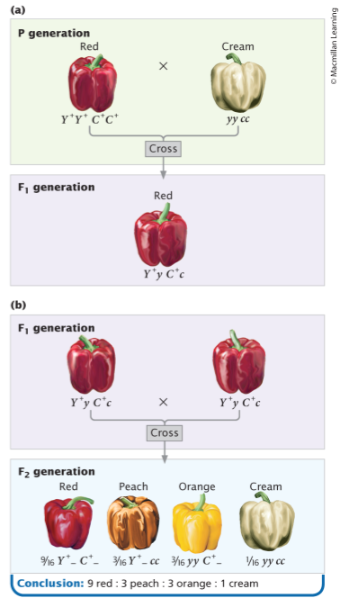
gene interaction with epistasis
one gene masks (hides) the effect of a gene at another locus
example of gene interaction with epistasis
Lab coat color depends on pigment production (‘first’ locus), then pigment deposition (‘second’ locus)
Gene actions must happen in sequence: pigment must be produced before it can be deposited
Black is dominant to brown (BB bb) = hypostatic gene
Deposition is dominant to non-deposition (EE ee) = epistatic gene

recessive epistasis
2 recessive alleles are required at the second locus to mask the first locus
Sex-__________ characteristics are determined by autosomal genes, but expressed differently depending on sex of the individual
influenced
example of a sex-influenced characteristic
goat beard presence depends on allele (Bb) that is dominant in males and recessive in females
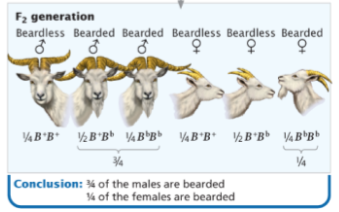
sex-limited trait
expressed in only one sex

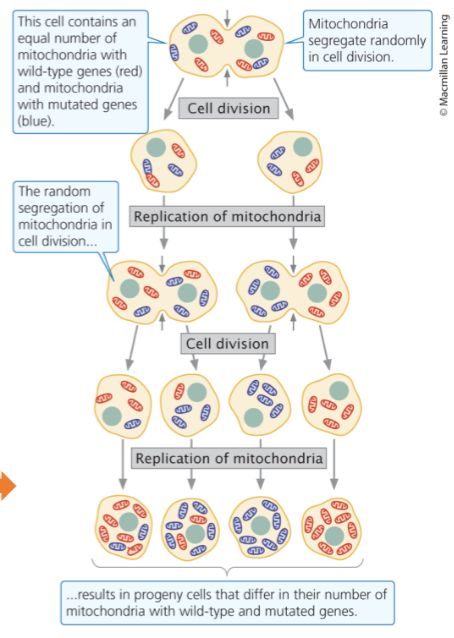
Cytoplasmic inherited traits are present in both males and female but inherited only from _______
mother
Cytoplasmic inheritance
Characteristics encoded by genes in cytoplasm (mitochondrial and chloroplast DNA)
Different cells and different individual offspring will have range of phenotypes due to random __________ of heteroplasmic organelles in cytoplasmic inheritance
inheritance
Genetic maternal effect
Genotype of mother determines phenotype of offspring (neither male parent nor offspring’s genotype affects offspring’s phenotype)
In cases of genetic maternal effect, the paternal genotype only becomes apparent in ___ because the father’s genes contribute to genotype of daughters
F2
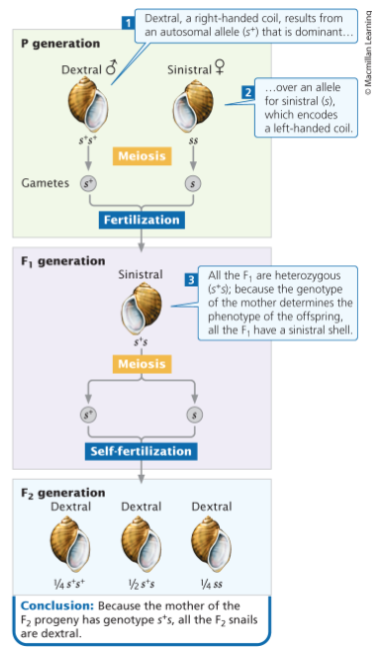
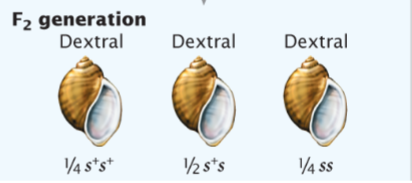
In a species that exhibits the genetic maternal effect, which females will produce sinistral offspring (s+ = dextral dominant)?
only ss
genomic imprinting
the expression of an allele is determined by the parent from which it was inherited
Maternal genomic imprinting
the allele inherited from the mother is silenced
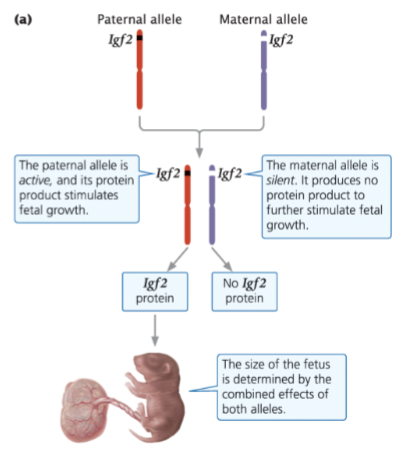
Paternal genomic imprinting
the allele inherited from the father is silenced
Genomic imprinting depends on ____ ___________ and is a form of epigenetics
DNA methylation
Example of environmental effects on phenotype
temperature-sensitive alleles in rabbits (rabbits raised in colder climates have more dark fur)
Continuous characteristics (quantitative characteristics)
show continuous variation (e.g., human height) and may also be influenced by environmental factors
continuous characteristics often involve genes at many loci (________ characteristics)
polygenic