Lecture 10
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What are some of the functions that are perfomred by systems by interacting with neurons?
Visual System, Auditory System, Pain Sensing System, Memory System, Motor System
What are the problems in understanding system?
Unknown are greater
Complexity is vastly greater
Operation of many systems is highly counterintuitive
What is Retina?
Retina has a several layers of cells distributed across the inside of the eyes
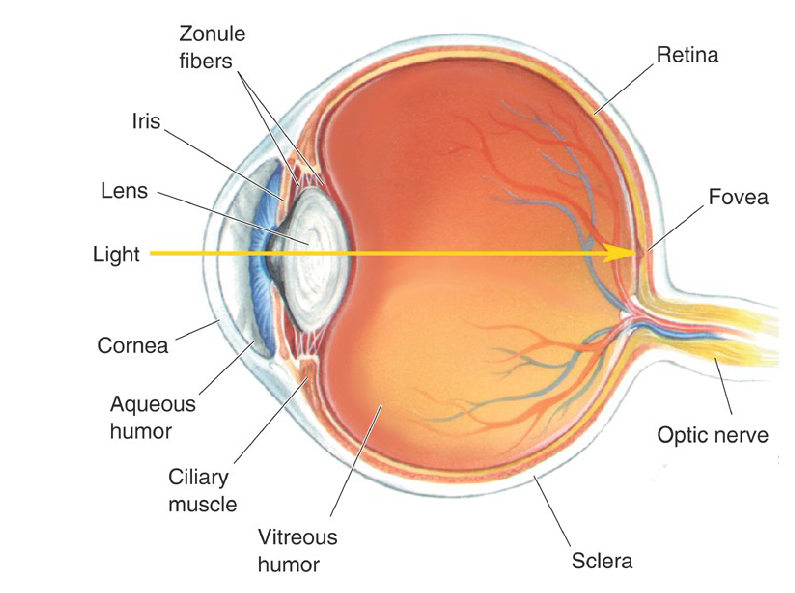
What is Fovea?
It is the portion of the Retina where light falls from an object that you are looking directly at.
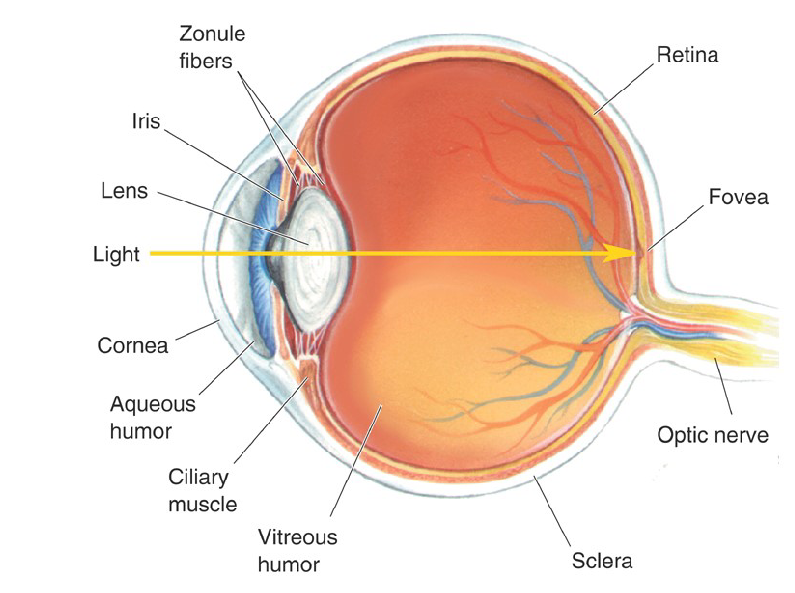
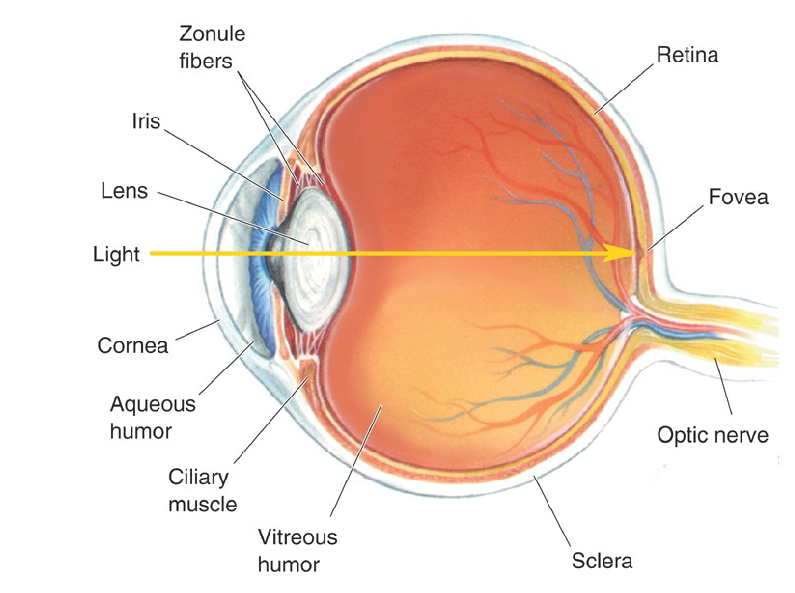
Characteristics of Fovea
Has Highest Acuity
Has the ability to resolve fine details and patterns of light
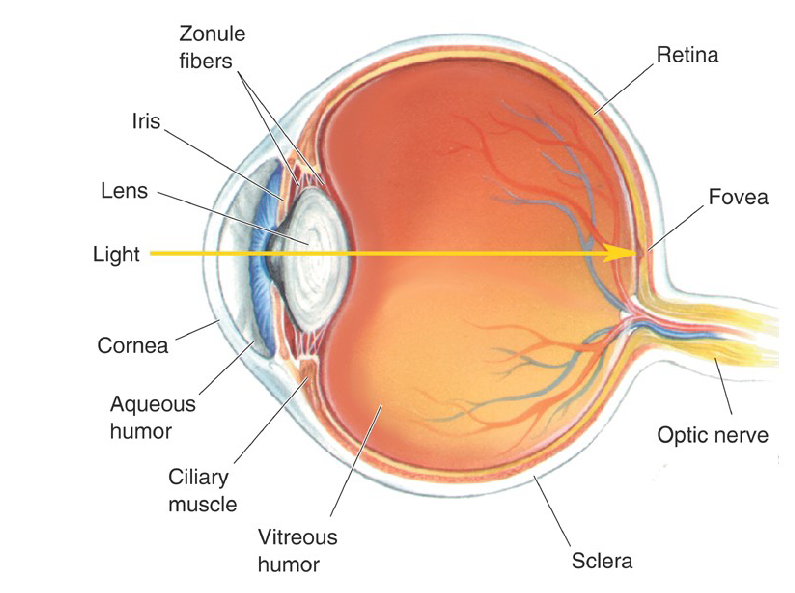
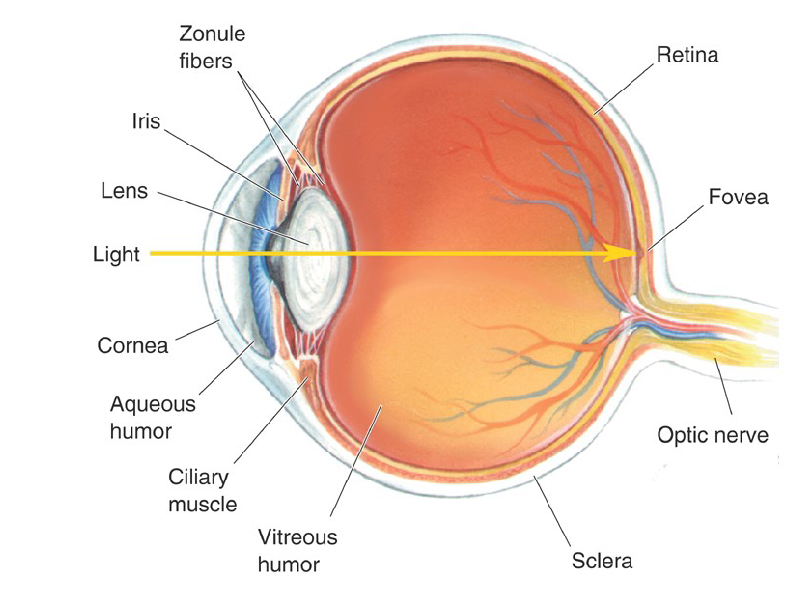
What is Optic Disk?
It is the retinal location where axons from a type of retinal cell collect, exit the eye and form the optic nerve.
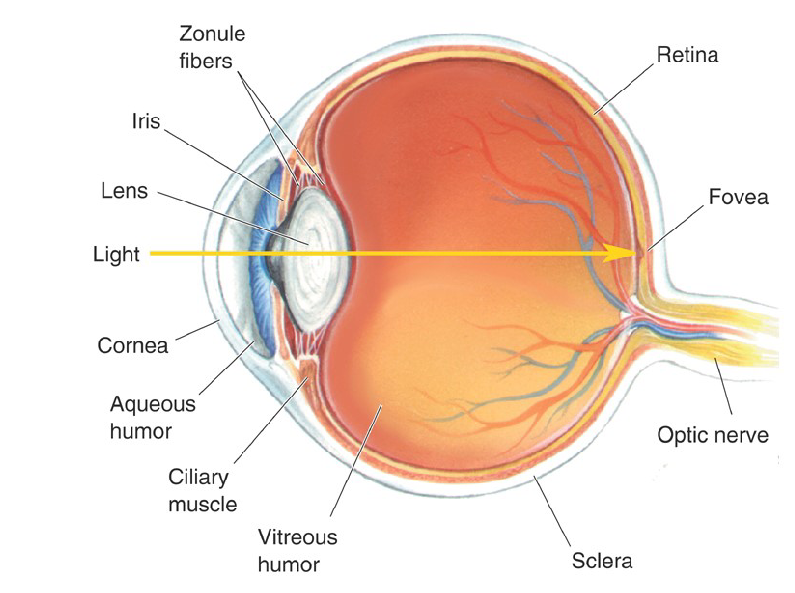
The Optic Never is the blind spot because there are no photoreceptors in the optic disk
The Optic Never is the blind spot because there are no photoreceptors in the optic disk
Receptive Fields
The location in the environment from whcih the appropriate stimulus will change that cell’s activity
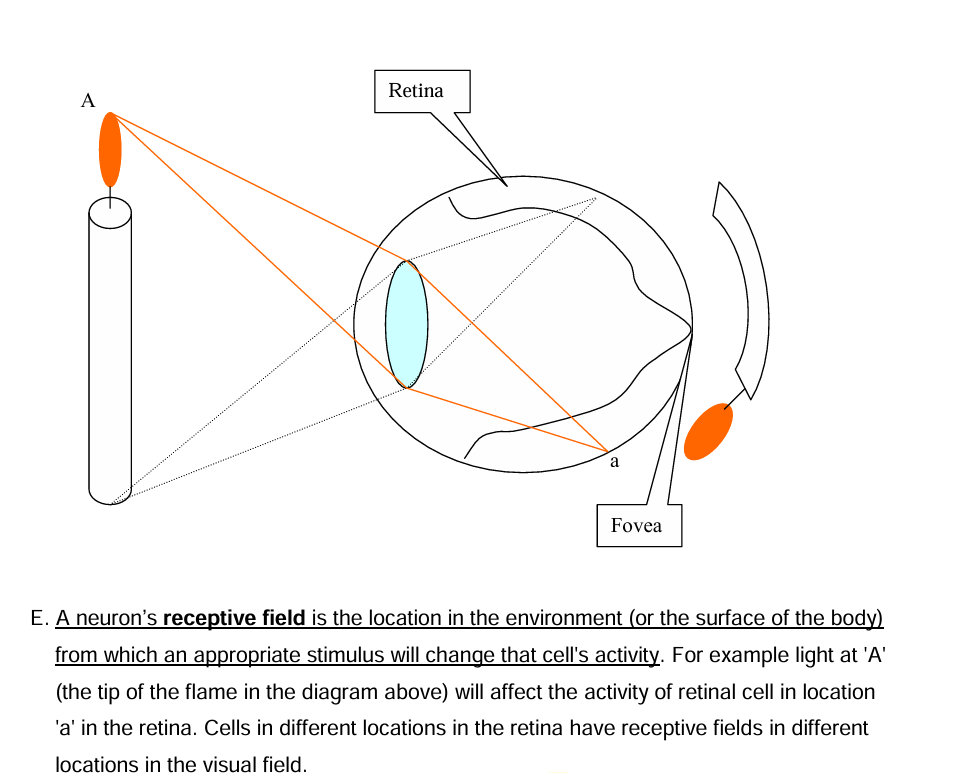
What’s happenign in the picture?
What is directly sensitive to light?
Photoreceptors
How many photoreceptors are there?
Rods & Cones
Charcateristics of Rods
around 120 million rods in the human retina
only exist outside of the fovea
Are Achromatic (Insensitive to colors)
Highly sensitive to LIGHT & are responsible for vision in very dim light.
Are bleached in bright light and hence unresponsive in bright light
Are NOT responsible for High Acuity vision (Not good for fine details)
Characteristics of Cons
6 millions cons in the human retina.
Less sensitive to Light Intensity & are inoperative in dim light.
Fovea has a lot of cons than Rods.
Are sensitive to color. IT have 3 subtypes and selectively sensitive to RED, BLUE & GREEN wavelengths of light.
Photoreceptors project to which cells?
Bipolar cells
What are the 5 types of cells in the Retina?
Photoreceptors
Bipolar cells (BPs)
Retinal Ganglion cells (RGCs)
Horizontal cells (HCs)
Amacrine cells (ACs)
Which one is the only OUTPUT cell in the Retina?
Retinal Ganglion cells
How are information passed from eye to the rest of the place?
By RGCs since it’s the only way info gets passed from EYE to the rest of the cisual systems and then their Axon form the Optic Tract
What is Serial or Hierarchical?
A strictly organized sequence of synaptic connections that relays sensory information from the Periphery to Specific Areas of the brain in an order.
What is Divergence/Convergence?
Divergence: Sensory input can spread to Multiple Areas or Targets.
Convergence: Sensory input can integrate multiple signals.
What is Network?
More complex, interconnected circuits allowing for integration and modulation of sensory information.
Why does only RGCs have axons?
Because Axons are used for long-distanced transfer of information. In the retina, the cells are usually close tgt hence axons or AP are not needed.
What cells use AP?
RGCs and ACs
What does BPs, HCs & PRs use?
Graded depolarization to relesae neurotransmitter to the next cell.
What is caused by a depolarization?
depolarization increases neurotransmitter release. Small depolarization cause small release of neurotransmitter and vice versa.
What is Retina’s only output cell type?
Retina Gangilion Cell
What cell type is directly affected by light?
Photoreceptors cells
what are the 3 targets of RGC axons?
superior colliculus
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN)
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN)
What is the system of phot receptor advantageous?
More light detection by increasing surface area and concentrates photopigments, making rods so sensitive that they can detect a single photon
Amplification through G-proteins when Opsin activates many G-proteins which trigger multiple Enzymes to break down cGMP. IT heavily amplifies the signal, making sure that even weak light produces a strong response.