9th Grade Biology - Evolution and Natural Selection (copy)
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Evolution
the process of change in a population over time
Adaptation
a characteristic that improves an organism's chance of survival
Fitness
ability to survive and improving their chance to pass on their genes to the next generation
Evidence for evolution
fossils, homologous structures, vestigial structures
Homologous structures
Similar structure resulting from common ancestry but different function
Vestigial structures
useless structures (snake and whale leg bones, human appendix) that were used by ancestors
Lamarks Theory of Evolution
organisms have an internal drive to become more perfect, and can selectively use and disuse parts of their body throughout their life. These acquired characteristics can then be passed onto offspring.
Directional Selection
when conditions favor individuals exhibiting one extreme of a phenotype
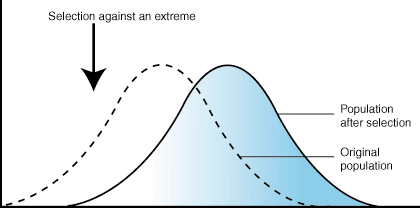
Stabilizing Selection
when conditions favor the most common phenotype
Disruptive selection
when conditions slop to favor the different extreams
Genetic drift
a random change of population
Founder effect
when a small number of individuals leave a large population to colonize a new area and bring with them only a small amount of genetic variation
Bottleneck effect
genetic drift occurs because of a natural disaster that wipes out the most individuals by chance, affects smaller populations
reproductive barriers
When species can not reproduce because of their genes
behavioral barriers
2 populations that are capable of interbreeding develop differences in courtship rituals or other behaviors
geographic barriers
2 populations are separated by geographic barriers
time barriers
Species reproduce at different times
Anatomy barriers
When species' bodies cannot reproduce based on anatomy
Cladograms
models that show possible evolutionary relationships between species
Common ancestor
The shared ancestor of species
natural selection
A process resulting in the evolution of organisms best fitted to the environment that can survive and pass on genes in a population
Analogous structures
Body parts in a species that share a common function, but not structure meaning they do not share a common ancestor
Speciation
the formation of new species in the course of evolution.