AP Human Geography Vocab
1/329
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
330 Terms
Human geography
Can be broadly defined as the study of human activities on Earth's surface
Fertile Crescent
Name given to land between Tigris and Euphrates rivers in Iraq where agriculture and civilization first began around 8000 BC
Geographic information system (GIS)
Family of software programs that allows geographers to map, analyze, and model spatial data
Cultural landscape
The human-modified natural landscape specifically containing the imprint of a particular culture or society
Natural landscape
Landscapes unaltered by human activities
Cultural ecology
The study of the interactions between societies and the natural environments which they live; also called environmental geography
Sense of place
People's attachment to and feelings about a particular region or location; characteristics that make a location seem unique
Carl Sauer
Defined the concept of cultural landscape as the fundamental unit of geographic analysis; argued that virtually no landscape has escaped human imprints
anthropogenic
referring to human-induced changes
Remote sensing
Process of capturing images of Earth's surface from airborne platforms such as satellites or airplane
Cartography
Theory and practice of making visual representations of Earth's surface in the form of maps
Global positioning system (GPS)
Integrated networks of satellites that orbit Earth, broadcasting location information to handheld receivers on Earth's surface
W.D. Pattison
Geographer who described four distinct traditions of geography: earth-science, culture-environment, location, and area-analysis
Thematic layers
Individual maps of specific features that are overlaid on one another in a Geographical Information System to understand and analyze a spatial relationship
Physical geography
Concerned with the spatial characteristics of earth's physical and biological systems
Sustainability
Approach to the environment that emphasizes restraint in the use of natural resources for future generations
Spatial perspective
Intellectual framework that allows geographers to look at Earth in terms of the relationship among various places
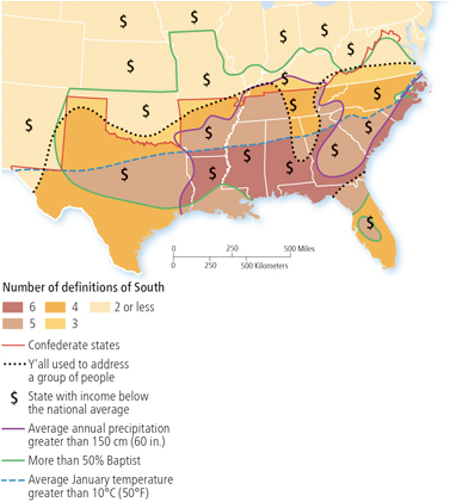
Region
Area larger than a single city that contains unifying social or physical characteristic
Geographic scale
Level at which a geographer analyzes a particular phenomenon, such as global, national, local, regional, neighborhood, etc.
Functional region
Region based on common interaction around a central focal point or node
Qualitative data/approach
Often associated with cultural or regional geography because they tend to be more unique to and descriptive of particular places and processes
Formal region
Region based on common themes such as similarities in language, climate, land use, etc.
Perceptual region
Region that exists in the minds of people but lacks clear, widely-accepted definition
Quantitative data/approach
Rigorous mathematical techniques and are particularly important in economic, political, and population geography where hard, numerical data abounds
Ptolemy
Roman geographer, author of Guide to Geography, which used a grid system of latitude and longitude
Contagious diffusion
The spread of a disease, an innovation, or cultural traits through direct contact with another person or another place
Latitude
Distance north or south of the Equator, measured in degrees
Prime Meridian
Meridian at zero degrees longitude passing through Greenwich, England
International Date Line
Arc that for the most part follows 180° longitude, although it deviates in several places to avoid dividing land areas. When you cross it heading east (toward America), the clock moves back 24 hours, or one entire day. When you go west (toward Asia), the calendar moves ahead one day
Site
Description of a place by local topography and other cultural or physical characteristics
Situation
Describes a place's relationship to other places around it; also called relative location
Relative distance
Measure of distance that includes the costs and time of overcoming the friction of absolute distance separating two places; used to describe amount of connectivity between two places
Connectivity
The degree of economic, social, cultural, or political connection between two places; also called topological space
Coordinate system
A standard grid, composed of lines of latitude and longitude, used to determine the absolute location of any object, place, or feature on Earth's surface
Time-space convergence
Idea that relative distance between some places is actually shrinking as technology enables more rapid communication and increased interaction between those places
Complementarity
The actual or potential relationship between two places, usually referring to economic interactions; for example, how one place may be able to provide goods via trade to another place that needs them but does not have means to obtain them directly
Expansion diffusion
The general spread of ideas, innovations, fashion, or other phenomena to surrounding areas through contact and/or exchange
Intervening opportunities
Idea that one place has a demand for some good or service and two places have a supply of equal price and quality, the buyer will use the closer of the two suppliers, thereby blocking the third from being able to share its supply of goods or services; frequently utilized because transportation costs usually decrease with proximity
Accessibility
The relative ease with which a destination may be reached from some other place
Friction of distance
Measure of how much absolute distance affects the interaction between two places; also called Tobler’s First Law of Geography
Absolute distance
Distance that can be measured with a standard unit of length, such as a mile or kilometer
Distance decay effect
The decrease in the interaction between two phenomena, places, or people as the distance between them increases
Law of retail gravitation
Law that states that people will be drawn to large cities to conduct their business because large cities have a wide influence on the area that surround them
Breaking point
Outer edge of a city's sphere of influence, used in the law of retail gravitation to describe the area of a city's hinterlands that depend on that city for its retail supplies
Parallels
Lines of latitude
Hierarchical diffusion
Transmission of a phenomena first between large cities with high inter-connectivity and then to smaller cities and towns
Transferability
Refers to the costs involved in moving goods from one place to another
Relocation diffusion
Occurs when people migrate from one place to another, bringing with them cultural traditions from their previous homelands
Longitude
Distance east or west on the earth's surface, measured in degrees from the prime meridian
Gravity model
Mathematical formula that describes the level of interaction between two places, based on the size of their populations and their distances from each other
Cognitive map
An image of a portion of Earth's surface that an individual creates in his or her mind; may include knowledge of actual locations and relationships among locations as well as personal perceptions and preferences of particular places.
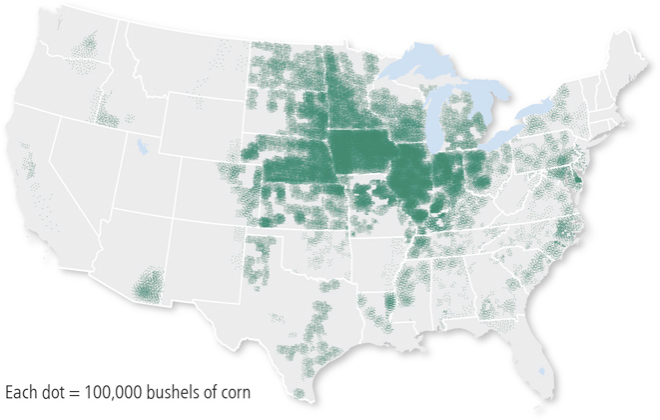
Dot map
Thematic maps that use points to show the precise locations of specific observations or occurrences, such as crimes, car accidents, or births.
Geoid
The actual shape of the Earth, which is rough and oblate, or slightly squashed. Earth's diameter is longer along the equator than along the north-south meridians.
Isoline
A map line that connects points of equal or very similar values, such as a contour line connecting similar elevations
Location chart
On a map, a chart or graph that gives specific statistical information about a particular political unit or jurisdiction.
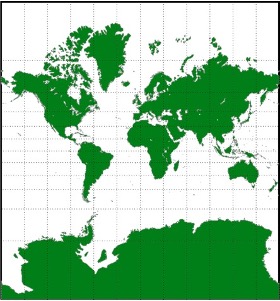
Mercator projection
A true conformal cylindrical map projection, this projection is particularly useful for navigation because it maintains accurate direction. These projections are famous for their distortion in area that makes landmasses at the poles appear oversized.
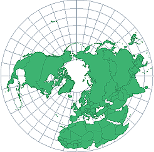
Azimuthal projection
A planar projection formed by placing a flat piece of paper on the globe; usually centered on the North or South Pole
Proportional symbols map
A thematic map in which the size of a chosen symbol--such as a circle or triangle--indicates the relative magnitude of some statistical value for a given geographic region.
Visualization
Use of sophisticated software to create dynamic computer maps, some of which are three-dimensional or interactive.
Reference map
A map type that shows reference information for a particular place, making it useful for finding landmarks and for navigation.
Resolution
A map's smallest discernable unit.
Robinson projection
A projection that attempts to balance several possible projection errors. It does not maintain area, shape, distance, or direction completely accurately, but it minimizes errors in each.
Small scale map
These maps usually depict large areas, reveal greater distortion, and are less detailed.
Choropleth map
A thematic map that uses tones or colors to represent spatial data as average values per unit area.
Thematic map
A type of map that displays one or more variables--such as population, or income level--within a specific area.
Cartogram
A type of thematic map that transforms space such that the political unit with the greatest value for some type of data, such as population, is represented by the largest relative area.
Projection
A mathematical method that involves transferring the earth's sphere onto a flat surface. The term can also be used for the type of map resulting from the transferal.
Map scale
The ratio between the size of an area on the map and the actual size of the same area on Earth's surface.
Large scale map
These maps usually have higher resolution, cover much smaller regions, and are more detailed.
Topographic map
Maps that use contour lines to represent constant elevations. If you took a one of these maps out into the field and walked exactly along the path of a contour on your map, you would always stay at the same elevation.
census tract
Small county subdivisions, usually containing between 2,500 and 8,000 persons, delineated by the US Census Bureau as areas of relatively uniform population characteristics, economic status, & living conditions.
forced migration
The migration event in which individuals are forced to leave a country against their will.
exponential growth
Growth that occurs when a fixed percentage of new people is added to a population each year.
demographic transition
A sequence of demographic changes in which a country moved form high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates through time.
age-sex distribution
A model used in population geography that describes the ages and number of males and females within a given population.
cohort
A population group unified by a specific common characteristic, such as age, and subsequently treated as a statistical unit.
chain migration
The migration event in which individuals follow the migratory path of preceding friends or family members to an existing community.
baby bust
Period of time during the 1960s and 1970s when fertility rates in the United States dropped as large numbers of women from the baby boom generation sought higher levels of education and more competitive jobs, causing them to marry later in life.
arithmetic density
The number of people living in a given unit area.
baby boom
A cohort of individuals born in the United States between 1946 and 1964, which was just after World War II in a time of relative peace and prosperity.
demography
The study of human populations, including their temporal and spatial dynamics.
carrying capacity
The largest number of people that the environment of a particular area can sustainably support.
Generation X
A term coined by artist and author Douglas Coupland to describe people born in the United States between the years of 1965 and 1980.
dependency ratio
The ratio of the number of people who are either too old or young to provide for themselves to the number of people who must support them.
immigration
The process of individuals moving into a new country with the intentions of remaining there.
emigration
The process of moving out of a particular country, usually the individual person’s country of origin.
crude birth rate
The number of live births per year per 1,000 people.
demographic accounting equation
An equation that summarizes the amount of growth or decline in a population within a country during a particular time period taking into account both natural increase and net migration
crude death rate
The number of deaths per year per 1,000 people.
doubling time
Time period required for a population experiencing exponential growth to double in size completely.
creole
A pidgin language that evolves to the point at which it becomes the primary language of the people who speak it; usually formed by the mixing of a colonizer language with an indigenous language.
Indo-European family
Language family including the Germanic & Romance languages; spoken by about 50% of the world.
literacy
The ability to read and write.
acculturation
The adoption of cultural traits, such as language, by one group under the influence of another.
syncretic
Traditions that borrow from both the past and present; refers to the blending of different customs to form a new, unique custom or culture.
cultural trait
The specific customs that are part of the everyday life of a particular culture, such as language, religion, ethnicity, social institutions, and aspects of popular culture.
Sino-Tibetan family
Language family that spreads through much of East & Southeast Asia; comprised of Chinese & Burmese.
culture
A total way of life held in common by a group of people, including learned features such as language, ideology, behavior, technology, and government.
pidgin
Language that may develop when two groups of people with different languages meet, combining simplified characteristics of each language.
artifact
Any item—such as clothing, tools, and artwork—that represents a material aspect of culture.