Chapter 10- Gases
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chemistry: The Central Science AP Edition, 14th ed. published by Pearson
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Boyle’s Law
the volume of a fixed quantity of gas is inversely proportional to its pressure; V = constant x 1/P or PV = constant
Charles Law
the volume of a fixed quantity of gas at constant pressure increases as the temperature increases; V = constant x T or V/T = constant
Gay-Lussac’s Law of combining volumes
at a given temperature and pressure, the volumes of gases which react are ratios of small whole numbers; the pressure and Kelvin temperature of a gas are directly proportional, provided the volume remains constant; P1/T1 = P2/T2
Combined Gas Law
relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature of a fixed amount of gas; combination of Boyle’s, Charles's, and Gay-Lussac’s laws; (P1V1)/T1 = (P2V2)/T2
Avogadro’s Hypothesis
equal volumes of gas at the same temperature and pressure will contain the same number of molecules
Avogadro’s Law
the volume of gas at a given temperature and pressure is directly proportional to the number of moles of gas; 22.4 L of any gas at 0 degrees C contain 6.02 × 1023 gas molecules; V = constant x n
Gases
composed of nonmetallic elements, simple moleculars formulas, and low molar masses; made up of molecules or atoms that are arranged without structure; no fixed shape or volume
Vapor
substances that are liquids of solids under ordinary conditions that also exist in the gaseous state; H2O exists as liquid water, solid ice, or water vapor
Iiquid
has a definite volume but no definite shape; made up of atoms or molecules that are connected by bonds and their particles can flow freely; less rigid than solids but more rigid than gases
Solid
a substance that has definite shape and volume; particles are arranged in a specific arrangement; firm or hard
Properties of Gas
expand spontaneously (to fill a container); highly compressible; form homogeneous mixtures; nonmetallic elements; different chemical properties
Absolute Zero
0 K or -273.15 degrees C; William Thomson proposed an absolute-temperature scale known as Kelvin scale
Density as it relates to gases
d = (nM)/V = (PM)/(RT); depends on its pressure, molar mass, and temperature; the higher the molar mass and pressure, denser the gas; higher temperature, less dense the gas; less dense gas will lie above a denser gas without mixing (hotter gas is less dense so it rises); molar mass of a gas = M = (dRT)/P
Kinetic Molecular Theory
the theory of moving molecules; pressure of a gas caused by collisions with container but its magnitude is determined by how often and how forcefully the collisions happend; proportional to temperature so at any temperature, same average kinetic energy; if absolute temperature is doubled, average kinetic energy of its molecules doubles; KE = ½ mu²
5 Parts of Kinetic Molecular Theory
random motion (gases consists of molecules in continuous random motion); negligible molecular volume (combined volume of all of the gas’ molecules is relative to its total volume); negligible forces (attractive and repulsive forces between gas molecules are insignificant); constant average kinetic energy(as temperature stays constant, the average kinetic energy of molecules does not change; energy can be transfered during collisions though); average kinetic energy proportional to temperature (proportional to absolute temperature; at any temperature, all gas molecules have same average kinetic energy)
Diffusion
spread of one substance throughout a space for a second substance; faster for light gas molecules; significantly slower than RMS speed; slowed by gas molecules colliding with each other
Effusion
escape of gas molecules through a tiny hole; Graham’s Law
Graham’s Law of Effusion
r1/r2 = sqrt(M2/M1); r1 and r2 - effusion of two gases; M1 and M2 - molar masses; a lighter gas has the higher effusion rate; rate of effusion is proportional to the rms speed (root mean square speed- speed of molecule having the same kinetic energy and average kinetic energy)
Maxwell Boltzmann
the distribution of speeds for a gas at a certain temperature; higher temperatures increase average particle speed; high molar mass, average particle speed decreases; average kinetic energy increases as temperature increases because temperature increase increases particle speed that is directly proportional to kinetic energy; molar mass does not affect average kinetic energy because increasing molar mass decreases particle speed which cancel out so kinetic energy stays the same
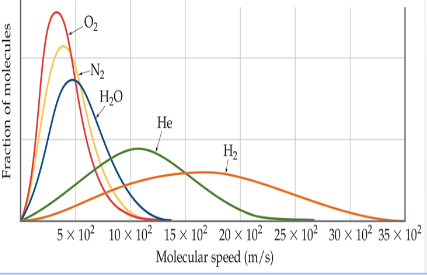
What causes deviations from the ideal gas law?
higher pressure = greater deviation → gas molecules get closer, intermolecular distance decreases so attractive forces take over; temperature increase = more ideal gas → because gas molecules move faster and apart so more energy is available to break intermolecular forces; increase with increasing molecular complexity (volume + attractive forces) and increasing mass (volume); volumes of real gases are larger and have smaller pressures of ideal gases
Ideal Gas
V = (nRT)/P; molecules do not interact with each other; molecules’ combined volume is much smaller than the volume the gas occupies
Standard Temperature and Pressure
0 C and 1 atm
Pressure (P)
force per unit; SI is pascals (Pa); bars (bar = 105 Pa); atmosphere (atm) and torr (torr or mmHg); barometer measures atmospheric pressure; manometer measures pressure of enclosed gases
Volume (V)
liters
Temperature
kelvins
Dalton’s Law of partial pressure
each gas exerts if present alone under same conditions; add all of the partial pressures up to make total pressure; partial pressure = mole fractions times total pressure
Mole Fraction
ratio of moles of one component of a mixture to the total moles of all components
root-mean-square (RMS) speed, urms
varies in proportion to the square root for the absolute temperature and inversely with the square root of the molar mass; = sqrt((3RT)/M) but most probably speed of a gas molecules is ump = sqrt((2RT)/M)
Mean free path
mean distance traveled between collisions; moving molecules has short path; collisions between molecules limit diffusion rate
as pressure increases, volume
decreases
as volume increase, pressure
decreases
as temperature increases, volume
increases
as pressure increases, n
increases