Lecture 6: Diseases of Infancy & Childhood
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Neonatal period
1st month
Infancy
1st year
Childhood
2 - 12 years
Adolescents
12 - 18 years
Leading cause of death under 1 year
Congenital anomalies
Prematurity & low birth weight & complications of prematurity
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)
Malformations
intrinsic error in fetal development
Deformations
Extrinsic disturbance (outside force) causing abnormal shape or position of a normally developed fetal structure
e.g. small uterus causing compression of parts of the fetus
Disruptions
extrinsic event causing secondary destruction of a normally developing fetal structure
Sequence
Cascade of anomalies explained by a single localized initiating event with secondary defects in other organs
can be due to malformation, disruption, or deformation
Malformation Syndrome
group of developmental abnormalities occurring simultaneously believed to be pathologically related however, can not be explained by a single, localized initiating defect
Most often is caused by single etiologic agent
Potter sequence
Oligohydramnios causing Potter sequence
Results in fetal Compression with classic phenotype in the infant:
Flattened facies; prominent infraorbital folds; retrognathia (abnormal posterior placement of mandible)
Positional abnormalities of hand & feet
Hip dislocation
Growth of chest wall & lungs compromised → pulmonary hypoplasia → fetal demise occasionally
Nodules in the amnion (amnion nodosum - fetal squamous cells aggregates on amnion)
What are the three main causes of congenital malformations?
Genetic, environmental, Teratogens
First trimester fetal loss is likely due to genetic causes whereas congenital infections will cause fetal loss later in pregnancy
What are the two major routes for perinatal infections?
In utero
During birth
Transplacental infections (TORCH)
Fever
Encephalitis, chorioretinitis, pneumonitis, myocarditis
Hepatosplenomegaly
Hemolytic anemia
Hydrops of fetus
Vesicular or hemorrhagic skin rashes
Toxoplasma gondii
protozoa
Chorioretinitis → vision loss
CNS involvement - microcephaly
Focal cerebral calcifications
Syphilis
(Treponema pallidum)
acquired in 3rd trimester; Gummas in fetal organs
Zika virus
Microcephaly & brain damage
Rubella virus
Rubella embryopathy/Congenital Rubella Syndrome (CRS): developing baby contracts rubella from mother in first trimester (3- 9 weeks of gestation) when organogenesis is occurring)
Triad of birth defects:
Occular: congenital cataracts
Congenital Cardiac defects:
patent ductus arteriosus/PDA
Heart murmur
CNS: Microcephaly
Also deafness, skin rash at birth, hepatosplenomegaly
Cytomegalo virus (CMV)
CNS involvement
Microcephaly, intellectual disability
Deafness
Chorioretinitis → vision loss
Hepatosplenomegaly
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)
acquired via passage through birth canal
Vitamin A (retinol/retinoic acid) used for treatment of acne
causes deregulation of TGF-beta signaling pathways & expression of homeobox (HOX) gene leading to Retinoic acid embryopathy
CNS, cardiac & craniofacial defects (cleft lip & cleft palate)
FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME
1st trimester
physical features tend to become less apparent with age
Prenatal & postnatal growth retardation (symmetric)
Microcephaly
Characteristic facial anomalies/features:
short palpebral fissures, maxillary hypoplasia, thin upper lip, low-bridge nose, frontal bossing
Psychomotor disturbances – emotional instability, impulsiveness
Intellectual disability
Hepatomegaly (fatty liver) with elevated serum transaminases
cigarette smoke-derived nicotine
Smoking is the most common cause of Low birth weight due to intrauterine growth retardation
May be prone to SIDS (sudden infant death syndrome)
maternal Diabetes
Fetal Macrosomia (↑ body fat + muscle mass with organomegaly):
Maternal hyperglycemia causes ↑ insulin secretion by fetal pancreas due to hyperplasia of fetal pancreatic islets & growth promoting effects of insulin causes fetal macrosomia
Diabetic Embryopathy: Cardiac anomalies; neural tube defects & other CNS abnormalities; kidney, gut & skeletal system anomalies
Diabetes can also cause health problems in baby after birth:
RDS (respiratory distress syndrome)
Obesity later in life
Diabetes later in life
Timing of intrauterine injury
Early embryonic period (first 9 weeks): organs are crafted from germ cell layers
3 to 9 weeks embryo susceptible to teratogens → malformations
Peak sensitivity between 4th and 5th week – period of organogenesis
Fetal period (terminating at birth): Period of growth & maturation of organs
Greatly reduced susceptibility to teratogenic agents
Fetus susceptible to growth restriction & injury to already formed organs → CNS injury, gonadal injury
Full term
37 to 42 weeks
Post-Term
delivered after 42 weeks
Appropriate for gestational age (AGA)
infants with birth weight between 10th and 90th percentile for gestational age
Small for gestational age (SGA)
infants with birth weight <10 TH percentile for gestational age
at risk for CNS dysfunction, learning disabilities, sensory (visual/hearing) impairment
Large for gestational age (LGA)
infants with birth weight >90th percentile for gestational age
Prematurity
< 37 weeks
Risk factors for prematurity
Preterm Premature Rupture Of fetal Membranes (PPROM)
Intrauterine infections
Uterine, cervical & placental structural abnormalities
Multiple gestations
Fetal Growth Restriction (FGR)
FGR may result from three groups of abnormalities:
Fetal: proportional FGR (head & trunk proportionally involved)
Placental: disproportional FGR (relative sparing of the brain)
Maternal: disproportional FGR
Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome or Hyaline Membrane Disease (HMD)
Preterm
deposition of a layer of hyaline proteinaceous material in peripheral airspaces (alveoli) of infants
deficiency of pulmonary surfactant
Surfactant is synthesized & secreted by type II alveolar lining cells & stored in lamellar bodies
Fetuses begin to produce surfactant around 24-week gestation. By 34-35 weeks have enough surfactant to keep the alveoli from collapsing
replacement surfactant therapy
Surfactant ↓ the surface tension of fluid in alveoli of lungs → keeps alveoli from collapsing when an individual exhales
Synthesis of surfactant is regulated by:
Cortisol, Insulin, Prolactin, Thyroxin & TGF-beta
Corticosteroids induce the formation of surfactant in fetal lung & insulin suppress surfactant synthesis
Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome Risk Factors
Preterm
Maternal Diabetes mellitus: Insulin suppresses surfactant synthesis
Male
C-section delivery
Untreated Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Few minutes after birth infant breathing well
Within 30 minutes breathing becomes difficult
retraction of lower ribs & sternum on inspiration; expiratory grunt
Next few hours respiratory distress worsens
cyanosis develops & fine rales can be heard on both lung fields
Chest X-ray of infant:
uniform minute reticulogranular densities (‘ground glass picture’)
diffuse opacification of lung fields
What is the characteristic microscopic lung findings in RDS?
Atelectasis & alveoli poorly developed or collapsed
Hyaline membranes composed of fibrin & cell debris line alveoli
Minimal inflammation
After 48 hours reparative changes appear in lungs
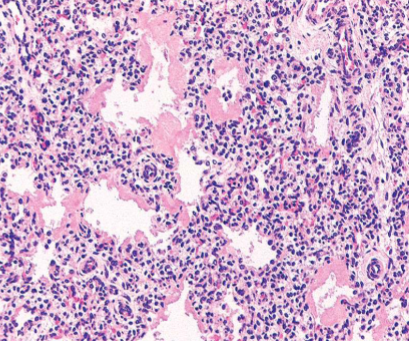
Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Eosinophilic thick hyaline membranes line alveoli
Complications of oxygen therapy in NRDS
Sustained high dose oxygen therapy delivered with positive pressure ventilation can cause injury to immature lungs due to oxygen derived free radicals
Retrolental fibroplasia (retinopathy of prematurity)
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: chronic lung disease
What are three major complications an infant who recovers from RDS at risk for?
Necrotizing enterocolitis
Perinatal infection & sepsis
Intraventricular hemorrhage
Necrotizing enterocolitis
Multifactorial - Associated with prematurity
Apoptosis of enterocytes induced by platelet-activating-factor (PAF)
Strong association with enteral feeding/introduction of formula feeds → introduction of bacteria in gut → bacterial overgrowth → inflammation → tissue injury → mucosal necrosis of gut → gangrene/necrosis of small/large bowel → perforation → sepsis and shock
symptoms usually do not appear until after first oral feeding
Bloody stools, Abdominal distension, Hypotension, Circulatory collapse
Elevated PAF
Abdominal X-ray: Gas within the intestinal wall (pneumatosis intestinalis); free abdominal air
Terminal ileum, cecum and right colon shows distension, congestion & may get gangrenous with perforation & peritonitis leading to sepsis and shock
Mucosal or transmural necrosis, ulceration, bacterial colonization & submucosal gas bubbles
What are the two major ways to control RDS in an at-risk fetus?
Corticosteroids given to mothers in premature labor
Surfactant administered to infants
Ventilator support
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)
Sudden death of an infant under 1 year of age in which cause remains unexplained after a thorough case investigation
most die at home while asleep in the crib mostly in prone or side position
90% of deaths occur ≤ 6 months age, mostly between 2 & 4 months
Sudden Unexpected Infant Death (SUID)
all sudden deaths in infants due to known or unknown causes
What is the most common nonspecific finding at autopsy in SIDS?
Non-specific subtle autopsy findings
Multiple petechiae of thymus, pleura & pericardium
Pulmonary congestion ± pulmonary edema
Subtle changes in brain stem: hypoplasia of arcuate nucleus or ↓ in brain stem neuron population
What are the three factors of the triple risk hypothesis?
Vulnerable infant: Infant + Parent factors
Critical development period: First 6 months of life
One or more exogenous stressors: Environmental
Parental Risk Factors
Young maternal age (age <20 years)
Maternal smoking during pregnancy
Drug abuse in either parent, specifically paternal marijuana and maternal opiate, cocaine use
Short inter-gestational intervals
Late or no prenatal care
Low socioeconomic group
African American and American Indian ethnicity
Infant: vulnerable infant Risk Factors
Brain stem abnormalities (medulla oblongata) associated with defective arousal, and cardiorespiratory control
Prematurity and/or low birth weight
Male sex
Product of a multiple birth
SIDS in a prior sibling – genetic predisposition
Antecedent respiratory infections
Environment Risk Factors
Prone or side sleep position → hypoxia, hypercarbia
Sleeping on a soft surface
Sleeping with parents in first 3 months
Hyperthermia
Postnatal passive smoking
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Autosomal recessive (AR)
Disorder is due to severe deficiency of enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) → Hyperphenylalaninemia → brain damage & intellectual disability
Inability to convert phenylalanine to tyrosine
without this enzyme, intermediate products phenylacetic acid are excreted in urine & sweat & imparts strong mousy or musty odor to infants
phenylalanine & its metabolites contribute to brain damage
By 6 months severe intellectual disability
Seizures
pigmentation of hair & skin & eczema
restricting phenylalanine intake early in life
Maternal PKU
marked phenylalanemia
intellectually disabled & microcephalic
congenital heart disease
It is imperative that maternal dietary restriction of phenylalanine be initiated before conception & be continued throughout the pregnancy
Galactosemia Deficiency
Autosomal Recessive (AR) disorder of galactose metabolism resulting in accumulation of galactose-1-phosphate in blood & tissues
Lactose is converted to glucose + galactose in the intestinal microvilli by lactase
Galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase (GALT) is involved in the first step in the transformation of galactose to glucose
GALT enzyme deficiency/absence → galactosemia
Galactosemia Presentation
Liver (fatty change and fibrosis), lens of eye (cataracts), cerebral cortex, spleen, kidney (aminoaciduria & E. Coli sepsis), heart muscle & RBC
Symptoms usually manifest after birth as soon as infant starts on milk
Vomiting & diarrhea within few days of milk ingestion → failure to thrive
Jaundice & hepatomegaly in first week → liver failure
Cataracts in first few weeks
Intellectual disability in 6 to 12 months
Hemolysis & coagulopathy
suggested by finding reducing sugar other than glucose in urine & confirmed by GALT assay in leukocytes/erythrocytes
removal of galactose from diet for at least first two years of life can prevent some of the severe complications
Older patients inspite of dietary restrictions can have speech disorder & gonadal failure & rarely ataxia
Cystic Fibrosis (CF)/Mucoviscidosis
Autosomal Recessive
Inherited disorder of epithelial ion transport causing thick secretions in exocrine glands & in epithelial lining of respiratory, gastrointestinal & reproductive tracts causing blockage & severe damage to multiple organs to include: Lungs, Pancreas, Liver, GIT, Reproductive system
Due to mutation of CFTR (Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator) gene (located on chromosome 7q31.2) there is ↓ production or abnormal function of CFTR, an epithelial chloride & bicarbonate channel protein
Most common mutation is a deletion of 3 nucleotides coding for phenylalanine that causes misfolding of CFTR
Cystic Fibrosis Pathogenesis
Sweat gland: function of CFTR gene is to reabsorb Cl & augment reabsorption of Na
CFTR gene mutation → ↑ sodium & chloride (salt) in the sweat (hypertonic sweat)
Respiratory, intestinal epithelium & reproductive tracts:
CFTR mutation → ↓ chloride secretion in the lumen, ↑ sodium & water reabsorption leads to dehydrated mucus layer, defective mucocilliary action & mucus plugging with obstruction of organ passages
Airway surface fluid deficient in antibacterial activity
Cystic Fibrosis Clinical Manifestations
Sino-pulmonary:
chronic persistent cough with thick sputum
recurrent lung infections- Staph aureus, H. influenza, Pseudomonas aeruginosa
recurrent sinusitis, nasal polyps
Gastrointestinal: thick mucus can block tubes that carry digestive enzymes from pancreas to small bowel
Pancreatic insufficiency due to inflammation & fibrosis → ↓ pancreatic enzymes (lipase, insulin)
protein, fat malabsorption → Large foul-smelling greasy stools
hyperglycemia/diabetes due to loss of islets of Langerhans (not till adults)
Deficiency of fat-soluble vitamins D, E, A, K
poor weight gain & growth
Intestinal blockage at birth present with meconium ileus → distended abdomen
Distal intestinal obstruction → rectal prolapse
Liver – jaundice; fatty liver; Biliary cirrhosis
Male genital tract abnormalities → infertility due to obstructive azoospermia due to congenital bilateral absence of vas deferens due to bi-allelic CFTR mutations
Morphology in CF
Plugging of ducts with viscous mucus in various organs:
Pancreas:
ducts plugged with mucus
atrophy of exocrine pancreas with fibrosis
islets initially are not affected
Liver:
Hepatomegaly with steatosis
plugging of bile canaliculi with mucinous material & portal inflammation
biliary cirrhosis may develop
Genitalia:
azoospermia & infertility in males who go on to adulthood
congenital absence of bilateral vas deferens
Sweat gland- normal histology
Intestines: small intestine may have mucus plugs causing obstruction & meconium ileus
Lungs:
Pneumonia, bronchiectasis
Mucus creates hypoxia & production of alginate which forms a capsule around bacteria preventing antibiotics to act
What is the single most common cause of death in CF?
Cardiorespiratory complications
CF Diagnosis
New-born screening:
Measurement of immunoreactive trypsinogen (IRT) in blood of newborn babies: ↑ IRT
positive IRT test should be confirmed with sweat test because of high false positives
Sweat test:
Persistently elevated sweat chloride concentration
Infant sweat tastes salty & diagnosis is usually made by mother
Gene sequencing: Gold standard for diagnosis
What are the current treatment options for CF?
Clearing of pulmonary secretions & treatment of pulmonary infection
Transplantation
bilateral lung transplant, liver, pancreas
Gene therapy