Chemistry
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/22
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
1
New cards
Atom
the smallest thing to exist and the building blocks for everything
2
New cards
Nucleus
Center of an atom, positively charged
3
New cards
Orbitals/Shells
Surronds the nucleus, has electrons
4
New cards
Electron
Sub atomic particle, negatively charged,found in the orbitals
5
New cards
Proton
Sub atomic particle,positively charged,found in the nucleus
6
New cards
Neutrons
Sub atomic particle, no charge/neutral,found in the nucleus
7
New cards
Metals
solid,high density/melting point,malleable/ductile,good conductors, mixes to make alloys
8
New cards
Non-metal
exists in all 3 states,low density/melting point,brittle,insulators
9
New cards
Metalloids
properties of both metals and non-metals, semi-conduction,mostly solids,lusterous
10
New cards
Trend of the periods
The atoms get larger because they have more orbitals
11
New cards
Trend of the groups
The elements become less reactive from left to right because their outer shells are almost full or full
12
New cards
Chemical Properties
a characteristic of a particular substance that can be observed in a chemical reaction
13
New cards
Physical Properties
a characteristic of matter that is not associated with a change in its chemical composition (lusterous,solid,melting point)
14
New cards
Ancient Philosophers
Everything in the universe is made up of elements like fire,water,earth and wind - Before 400CE
15
New cards
Ancient Atomists
Atomas means “not to be cut” and parmanu means invisible grain, both refer to the smallest piece of matter. Atoms are uncuttable -400CE
16
New cards
John Dalton
Atoms are made up of a single material that is formed into different sizes and shapes. Atoms of different elements are different- 1803

17
New cards
J.J Thompson
There are small, negatively charged particles inside and atom called electrons. This theory led to the “plum pudding” model, in which negatively charged particles are stuck in a positively charged substance - 1897
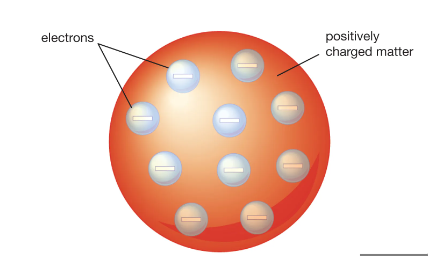
18
New cards
Ernest Rutherford
Atoms contain mostly empty space. Most of an atom’s mass is the nucleus. The nucleus is positively charged. - 1908
19
New cards
Niels Bohr
Electrons are scattered around the nucleus at a distance. Electrons location depends on how much energy they have. - 1913
20
New cards
Alkali metals
Chemical Properties - very reactive with water and air
Physical Properties - Lusterous,malleable,ductile,conducts heat/electricity
Physical Properties - Lusterous,malleable,ductile,conducts heat/electricity
21
New cards
Alkali earth metals
Chemical Properties- reacts with water and air, highly reactive
Physical Properties- good conductors,lustre when cut,low melting and boiling point,malleable,ductile
Physical Properties- good conductors,lustre when cut,low melting and boiling point,malleable,ductile
22
New cards
Halogens
Chemical Properties- Highly reactive, all oxidize
Physical Properties - Non-metals, noticeable colour,disenfectants
Physical Properties - Non-metals, noticeable colour,disenfectants
23
New cards
Nobel Gases
Chemical Properties - not reactive,don’t form compunds
Physical Properties - colourless,odorless,tasteless,glows brightly when electric currents pass through them
Physical Properties - colourless,odorless,tasteless,glows brightly when electric currents pass through them