World History Sem 1 Final
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
139 Terms
power
ability to influence actions / behaviors or others; usually form of coersion
identity
qualities, beliefs, traits, and / or personalities; makes up individuals / groups (changes)
production
process of making goods / services for consumption / trade
examples of goods
bread, steel
examples of services
haircuts, construction
1450 - 1750
timespan of the Early Modern Era
what the Early Modern Era was defined by
“Age of Exploration”
“encounter” between people across the globe
conquest & empire building
globalization in trade
sustained contact between “Old World” & “New World”
Old World
Europe, Asia, Africa
New World
N. & S. America, Australasia
state
organized political community with a single system of government
bureaucracy
type of administration based on specialization, fixed rules, and a hierarchy
autocracy
type of gov’t where one person (usually monarch) possessed the power to rule and govern
absolutist monarch
monarch with no checks on their power and could do what they wanted
constitutional monarch
monarch had limits placed on their power by the elites / nobility
ethnocentrism
attitude that one’s own group, ethnicity, or nationality is superior to others; defined most societies of the early modern Era
Pre-Reformation Europe religion
Christendom
Post-Reformation Europe religion
Protestant, Catholic, Orthodox, + other
Islamicate
consisted of N. Africa, Mid. East, W. Asia; Sunni majority, Shi’a minority
“Middle Kingdom”
Chinese concept that China was below heaven but above the rest of the world
World Systems Theory
argues:
1) world can be divided into three economic regions: core, semi-peripheral, peripheral
2) relationship between regions determined by technological, military, and economic advantages
3) relationship between regions is unequal and will remain so until massive economic shift
Asia and Middle East
economic “core” for most of history; very large and the middle of trade respectively
European “Dark Ages”
occured after fall of Roman Empire in 476 C.E. and where Europe & N. Africa shifted between semi-peri and peri status
Islamic Conquests of the Midle East and the Crusades
_______ encouraged European states and merchants to find a way around the Muslim World and get to Asia.
provincial goods
goods made by local artisans for local consumption
luxury goods
spices, procelain/chin, silks
serfs
peassanted tithed to lord’s land
tithe
labor / produced ta that peasants paid to lords
chattel slavery
people used as property; relatively rare globally at beginning of EME
core countries
exploitative and usually use other countries for own benefit
semi-peripheral
hover between core and peripheral; usually on brink of industrialization or attempting to
peripheral
on the edge and usually exploited
mid 16th century
time period where:
Spain has large empire in N.S. America
Portugal has large trade post empire in Asia plus holdings in S. America & Africa
France, England, and Dutch are encouraged to break into global trade as well
Columbian Exchange
widespread transfer of plants, animals, culture, people, tech, diseases, and ideas between new World and Old World
Columbian Exchange time frame
15th and 16th centuries
Europe —> Americas
wheat, sugar, bananas, rice, grapes, dandelions, horses, pigs, cattle, sheep, goats, chickens, smallpox, measles, typhus
immediate population collapse
What happened to the native population in the Americas after the Europeans arrived?
Americas —> Europe
potatoes, corn, cassava, tomatoes, pumpkins, squash, peanuts, cacao, tobacco
silver
popular hard currency for exotic goods
1500 -1700
time period where Spain controlled 85% of the world’s silver production
Potosi mine
popular silver mine; labor fueled by Atlantic Slave Trade
additional demand for cows due to demand for candles and leather working in the mines
most silver shipped to Acapulco
inflation
________ occurred after silver supply increased drastically and its value went down
examples of joint stock companies
Dutch East India Company, British East India Company
joint stock company
when people share profit in order to reduce risk in business
god, gold, glory
factors motivating European exploration
cash crops
agricultural crops grown for profit; generally labor intensive to grow and process
Ex. sugar, tobacco, cotton, etc.
sugar
produced from sugar cane; reed like grasp native to New Guinea, later introduced to China, India, Muslim World, and eventually Europe & Americas
1096 - 1291
time range when Europeans most likely got the first taste of sugar
Azores (1440s)
chain of extinct volcano islands; Portuguese establish sugar plantations in these areas due to tropical climate ; fueled by Muslim and African slaves
Caribbean people were wiped out
African slaves were used and replaced native Caribbean people because ___________.
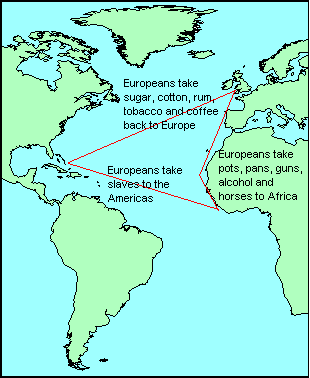
Triangle Trade
What is being depicted?
race
social construct based on physical characteristics
static / fixed
biological difference (Ex. being “black” or “white”)
ethnicity
membership of a group based on characteristics
fluid; can and does change over time
about identity / membership (Ex. can be “Jewish” / “American”)
othering
identifying as an “other”; bad when creating caste for people
racism
acting on ethnocentrism + discrimination of group based on physical characteristics
Catholic view on Africans / Indians
decided Africans and Indians had souls after much contemplation
Protestant view on Africans / Indians
mainly ignored Indians / Africans
purpose for slavery in Early Modern Era
labor, political power and prestige; tapped into preexisting slave trade routes
Great Divergence
when the “west” overtook the “rest”
agrarian / agricultural society
any community whose economy is primarily based on producing crops / maintaining farmland
industrial / industrialized society
society drive by use of technology to enable mass production of goods, organized along division of labor
industrialization
period of social or economic change that transforms a human group from agrarian society into industrialized society
extensive reorganization of economy for purpose of manufacturing
land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship
four factors of production
economic base
combined factors of production, either agricultural or industriral
superstructure
anything not directly involved in factors of production; “house” on top of base
Ex. military, philosophy, art, culture
cottage production / industry
production in rural areas; small, rural shops using hand / simple machines
First Industrial Revolution
advances in science, new tech, change in consumer taste, and steady increasing levels in connection around the world
consumerism
idea that purchasing, using, and / or consuming goods is a positive thing
wants and needs are infinitely stretchable
Merchants and producers realized _________.
imperialism
policty of extending a country’s power and influence through diplomacy or military force; usually control by a more powerful state over less powerful state
agricultural revolution
revolution in 17th - 18th centuries; farming techniques evolved and new tech introduced
tenant farmers
paid rent for land from landowner with labor, part of harvest, or money
enclosure movement
turned tenants and sharecroppers into landless farm laborers, many of whom moved to cities to seek work
time when Columbian Exchange is mostly complete
1700
Enlightenment / Age of Reason
wave of social, political ,and philosophical changes in Europe, primarily during the 18th century; used reason to understand how the world worked
3 origins of Enlightenment
1) Wars of Religion in 16th - 17th centuries (Prot. Vs. Cath.)
2) Pre-Enlightenment thinkers (Renaissance) + Rene Descartes
3) scientific revolution —> “Scientific method” —> logic
philosophes
included major thinkers like Plato, Aristotle, and Maquielli
social characteristics of philosophes
disdain of messiness and chaos; preference for democracy, discussion, and imposition
desire to create social standards based on reason
utilitarianism
greatest good for greatest number
tolerance
the mentality that no opinion is worth burning your neighbor for
freedom
liberty to all men; anti-absolutism
legal reform
justic and freamwork of gov’t
constitutionalism
legal framework for gov’t
public education
introduced from Prussia and educated men better for the draft
Seven Years’ War (1756 - 1763)
a result of disputed boundaries and commerical competition
outcome of Seven Years’ War
France ejected from N.A., colonies ceded to britina; Britain’s foothold in India strengthens and in a position to dominate world trade
British raised taxes for colonies in order to recover from war
“Le Defecit”
socio-economic wasteful spending in France; extreme poverty and massive debt
feudalism
the estates’ system; clergy, aristocracy, and commoners
Jan 1789
the month where Louis calls assembly of Three Esates —> “Estates General
Third Estate
underrepresented peasants regardless of their size; developed slogan “Liberty, Equality, Fraternity”
Bastille
prision and armory; stormed on July 14, 1789 for weapons in peasant revolution
“The Declaration of the Rights of Man”
turned French subjects to citizens, and adopted from the Declaration of Independence; left and right politics came from French Rev.
political factions left to right
socialist / communist, leftist, liberal, centrist / moderate, conservate, right wing, fascist
First Coalition
invaded France in 1792; mass conscription of able bodied men to military service
national assembly replaced by national convention
Radical Phase
1793 - 1794; constitutional monarchy put in place, and Louis + royal family put on guillotine
1793
Maxmillian Robespierre and Committe of Public Safety gain power to protect revolution from threats; eventually ends up executing thousands of people for “treason”
Napoleon Bonaparte
Corsican; supported Jacobins and rose through ranks of Revolutionary Army; crowned himself emperor in 1804 and inevitably turned back to monarchy
Napoleon’s ambitions
________ included him wanting to turn Europe into one politicla entity and defeating virtually everyone except the British.
“Continental System”
Napoleon’s goal to isolate Britain and promote France’s mastery over Europe
nationalism
rose up in protest to Napoleon putting his brother in power; belief that tpoeple should be loyal to their nation
Penninsular War
Portugal refused to comply w/ Continental System; allied with English who viewed Spanish resistance as opportunity to weaken Napoleon
result: five years later —> French thrown out from Spain