15 & 16 - Organic Compounds & Organic Chemical Reactions
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
To be accompanied with past exam questions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Delocalised electron
Electron shared between more than two atoms
Primary Alcohol
Carbon atom attached to hydroxyl group is attached to only on other carbon atom
Secondary Alcohol
Carbon atom attached to hydroxyl group is attached to two other carbon atoms
Tertiary Alcohol
Carbon atom joined to hydroxyl group is attached to three other carbons
Emulsion
Oil droplets in water
Volatile
Easily vaporised
Immiscible Liquids
Liquids that do not mix / do not dissolve in each other
Free Radicals
An atom or group of atoms with an unpaired e-
What is an elimination reaction?
Small molecule is removed from larger molecule to leave a double bond in the larger molecule
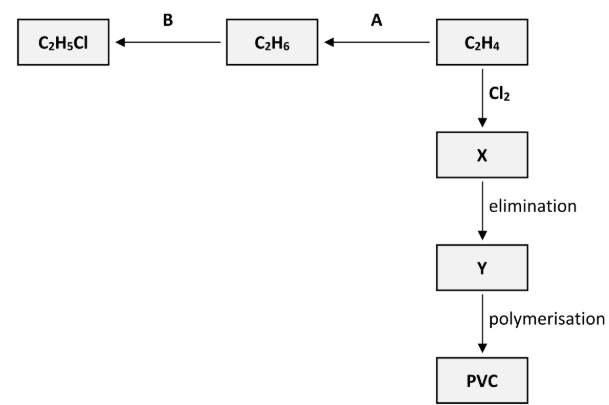
How does the geometry around the carbon atoms change during reaction A?
Planar
to tetrahedral
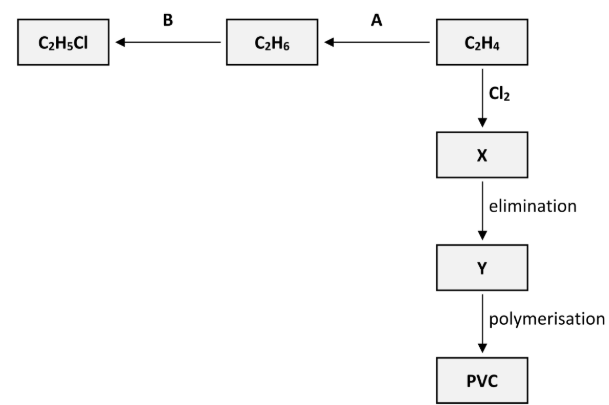
Reaction B takes place in the presence of chlorine (Cl2) gas and ultraviolet light.
Should reaction B be classified as an addition reaction, a substitution reaction or an elimination reaction?
Substitution
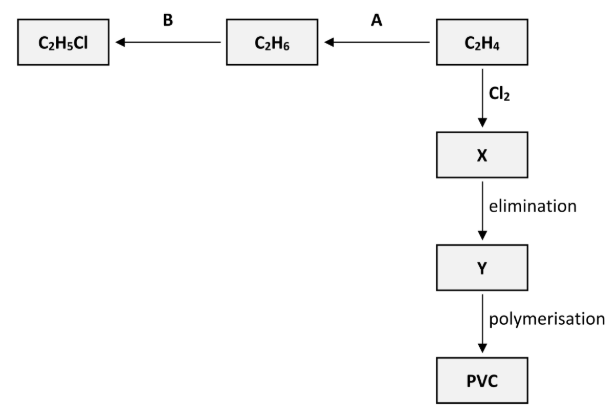
Reaction B takes place in the presence of chlorine (Cl2) gas and ultraviolet light.
Describe the mechanism for reaction B
Free Radical Substitution ( * is a free radical )
Initiation: Cl2 → 2Cl* in the presence of UV light
Propagation: C2H6 + Cl* → *C2H5 + HCl
Propagation: C2H5 + Cl → C2H5Cl + Cl*
Termination: e.g. *C2H5 + Cl* → C2H5Cl
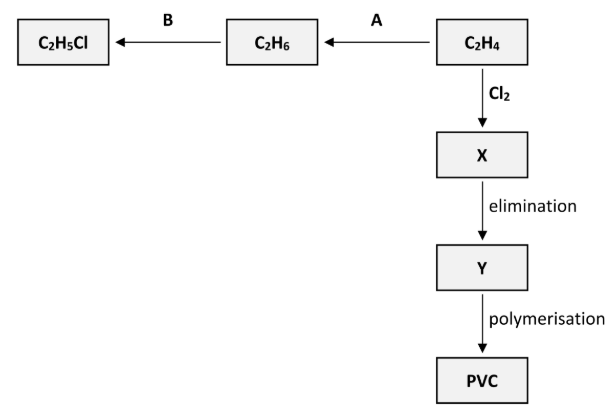
A trace quantity of C4H10 is formed during reaction B. Explain how the formation of C4H10 is evidence for the mechanism described
Shows existence of ethyl free radical / 2*C2H5 → C4H10
[note: C4H10 is butane]
Apart from the formation of C4H10, state one other piece of evidence for this mechanism
Reaction needs UV light to start
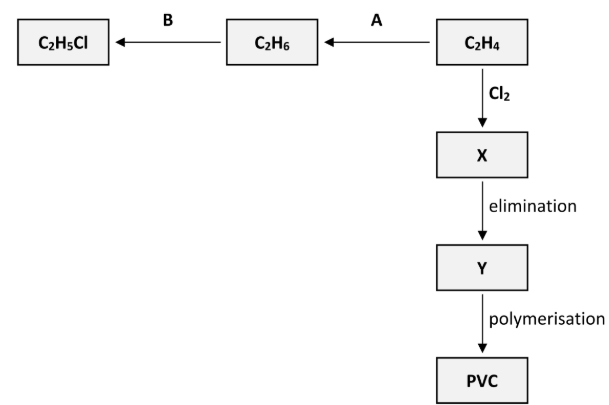
Polyvinylchloride (PVC) is synthesised in three steps from C2H4. These steps are an addition reaction to form compound X, then an elimination reaction to form compound Y and finally the polymerisation of Y to form PVC, as outlined in the reaction scheme diagram.
State the systematic IUPAC name for compound X
1,2-dichloroethane
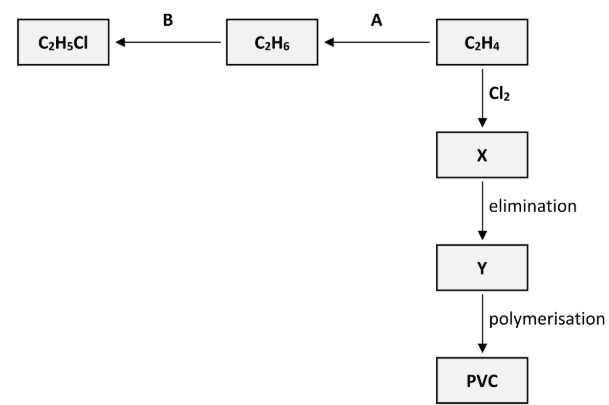
Polyvinylchloride (PVC) is synthesised in three steps from C2H4. These steps are an addition reaction to form compound X, then an elimination reaction to form compound Y and finally the polymerisation of Y to form PVC, as outlined in the reaction scheme diagram.
Name the inorganic compound that is eliminated when X is converted to Y
Hydrogen chloride
[ NOT HCl ]
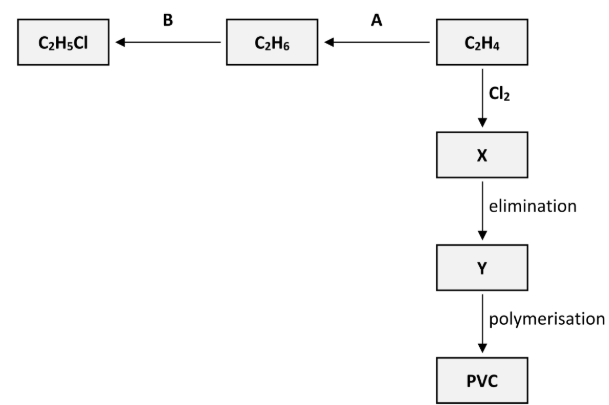
Polyvinylchloride (PVC) is synthesised in three steps from C2H4. These steps are an addition reaction to form compound X, then an elimination reaction to form compound Y and finally the polymerisation of Y to form PVC, as outlined in the reaction scheme diagram.
Draw the structure of a molecule of X showing all of its atoms and all of its bonds and indicate clearly which of its bonds are broken during the elimination reaction


Polyvinylchloride (PVC) is synthesised in three steps from C2H4. These steps are an addition reaction to form compound X, then an elimination reaction to form compound Y and finally the polymerisation of Y to form PVC, as outlined in the reaction scheme diagram.
Draw the structure of a molecule of Y showing all of its atoms and all of its bonds and indicate clearly which of its bonds are formed during the elimination reaction

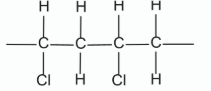
Draw two repeating units of the polymer PVC
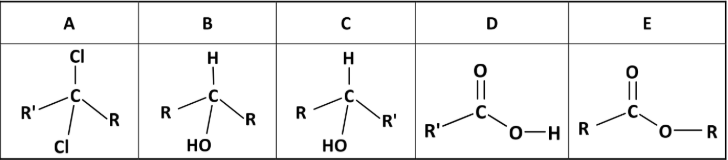
State the systematic IUPAC names for compounds A, B, C, D and E
A: 2,2-dichlorobutane
B: propoan-2-ol
C: butan-2-ol
D: propanoic acid
E: methyl ethanoate
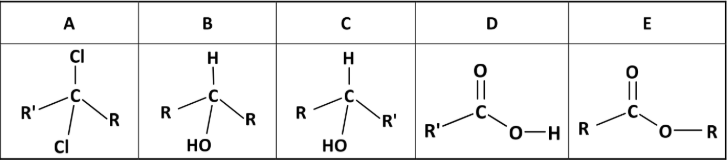
Classify compound B as a primary or a secondary alcohol. Justify your answer
Secondary
OH is bonded to a carbon which is bonded to two other carbons
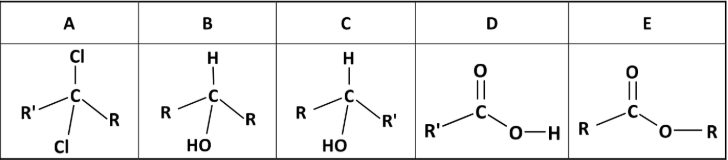
Are compounds D and E structural isomers? Justify your answer
Yes
Same number of atoms of each type / same molecular formula
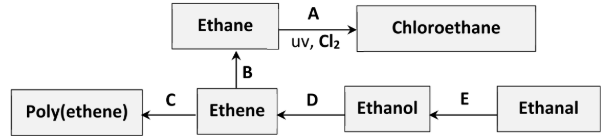
Identify the elimination reaction in the scheme
D (ethanol to ethene)
[preparation of ethene experiment is an elimination rxn]
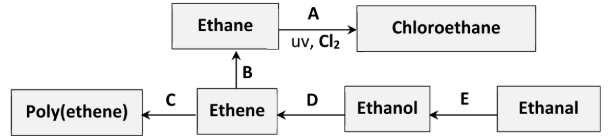
The same reactant and metal catalyst can be used in conversions B and E.
Identify (i) the reactant, (ii) a suitable metal catalyst, for these conversions
i) H2 (hydrogen gas)
ii) Nickel / platinum / palladium / copper
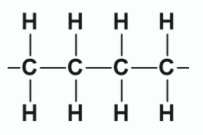
Draw two repeating units of the polymer poly(ethene)
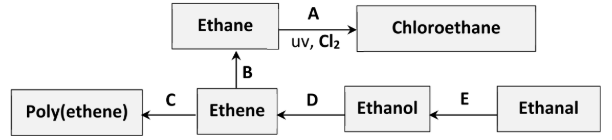
How does the geometry around the carbon atoms change during conversion C?
planar //
tetrahedral
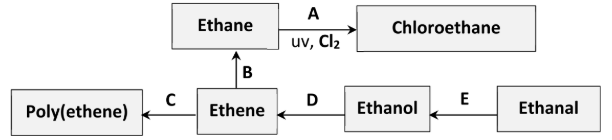
Identify the inorganic product of conversion A
Hydrogen chloride
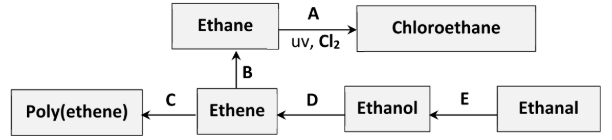
Traces of butane are formed during conversion A. What is the significance of this result?
Evidence for free radical substitution reaction (mechanism) /
evidence for termination
Account for the significant difference in the boiling points of ethanal compared to propane (both have Mr = 44)
Ethanal has stronger intermolecular forces / C=O is polar in ethanal / propane has weaker intermolecular forces / propane is non-polar / ethanal is polar
Account for the significant difference in the boiling points of ethanoic acid compared to propanol (both have Mr = 60)
Ethanoic acid has stronger hydrogen bonding /
ethanoic acid forms dimers /
propanol has weaker hydrogen bonding
Suggest a reason why the volume of benzene in petrol is limited to about 1% despite the fact that it improves petrol’s octane number
Toxic / harmful / carcinogenic / causes cancer / mutagenic / damages DNA
Name the oil refining process in which hexane is converted into benzene
Dehydrocyclisation (reforming)
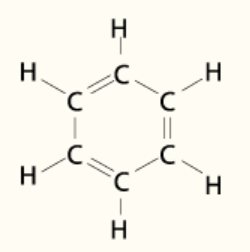
A single benzene molecule has 42 electrons. How many of these electrons
i) are involved in carbon to hydrogen bonding,
ii) are involved in carbon to carbon sigma bonding,
iii) are involved in delocalised pi bonding,
iv) are involved in carbon to carbon bonding,
v) are not involved in bonding?
i) 12
ii) 12
iii) 6
iv) 18
v) 12

Give the systematic IUPAC names of B and C
B: ethane //
C: methylbenzene

Which one of the four compounds has molecules that contain only carbon atoms that are in planar geometry?
A (ethene)

Compound B undergoes free radical substitution to produce compound D
State the reagent and conditions required to bring about this conversion
Cl2 //
UV light

Compound B undergoes free radical substitution to produce compound D.
Describe the mechanism for this reaction
Free Radical Substitution ( * is a free radical )
Initiation: Cl2 → 2Cl* in the presence of UV light
Propagation: C2H6 + Cl* → *C2H5 + HCl
Propagation: C2H5 + Cl → C2H5Cl + Cl*
Termination: e.g. *C2H5 + Cl* → C2H5Cl
How can the addition of a little tetraethyl lead to the reaction mixture provide evidence for the free radical substitution mechanism?
Provides free radicals / increased rate

Compound D can also be synthesised directly from compound A.
i) State the reagent required to bring about this conversion
ii) What organic reaction type is involved in this conversion?
i) Hydrogen chloride
ii) Addition

Compound A can undergo addition polymerisation.
i) Name the polymer produced in this reaction
Poly(ethene)

Compound A can undergo addition polymerisation.
ii) Draw two repeating units of the polymer

Compound A can undergo addition polymerisation.
iii) How does the geometry around the carbon atoms change during the polymerisation reaction?
Planar // to tetrahedral
Explain with the aid of a diagram, the acidic nature of the carboxylic acid functional group.
-COOH loses proton (H+) forming -COO- and proton (H+) //
-COO- is stable / delocalised charge on -COO-
Give an example of a reaction that demonstrates the acidic nature of ethanol
Reaction with sodium
Would you expect to observe a reaction when a drop of pure ethanol is added to damp solid sodium carbonate on a clock glass? Explain
No
Ethanol is not strongly acidic / ethanol weakly acidic
Write a balanced chemical equation for the formation of the pure ester E from methanoic acid and ethanol
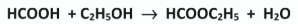
Give the systematic IUPAC name for the ester formed from methanoic acid and ethanol
Ethyl methanoate
How many carbon atoms in a molecule of ethyl methanoate are in planar geometry?
1
Classify this esterification reaction as a redox reaction, an acid-base reaction or a substitution reaction
Substitution
Identify a structural isomer of ethyl methanoate
Methyl ethanoate
Identify the products of the base hydrolysis reaction between the ester methyl methanoate and an NaOH solution
Methanol //
sodium methanoate
Explain why the boiling point of ethanoic acid is significantly higher than that of methyl methanoate although the two compounds have the same molecular formula
Hydrogen bonds in ethanoic acid /
no hydrogen bonds in methyl methanoate
Ethanoic acid dimerises (see diagram)
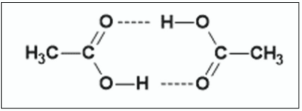
2022 q11 part b