The cranium
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/117
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lab 5
Last updated 7:04 PM on 9/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
1
New cards
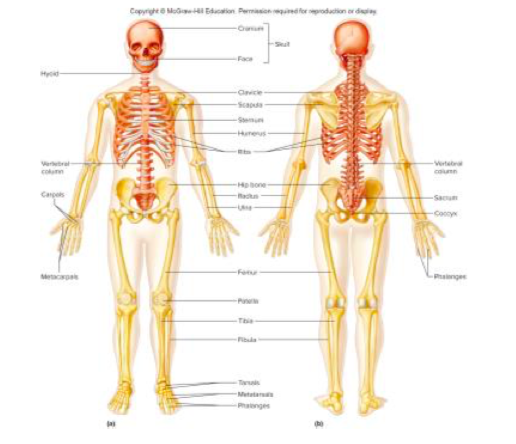
How many portions can the skeleton be organized and what are they?
Two major portions the axil skeleton and appendicular Skeleton
2
New cards
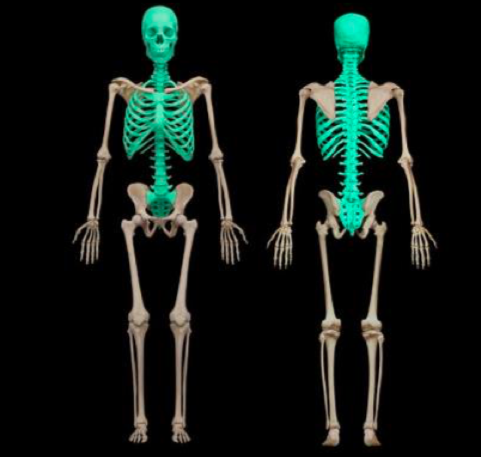
The axial skeleton
It consists of the bony and Cartilaginous parts that support the and protect the head, neck, and trunk
* Skull: cranium and facial bones
* Hyoid Bone: Supports the tongue and aids in swallowing
* Vertebral Column
* Thoracic cage : Ribs and sternum
\
* Skull: cranium and facial bones
* Hyoid Bone: Supports the tongue and aids in swallowing
* Vertebral Column
* Thoracic cage : Ribs and sternum
\
3
New cards
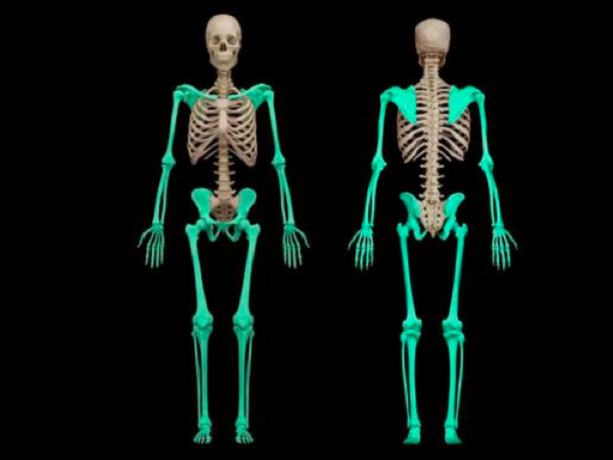
The Appendicular Skelton
This consists of the bones of the upper and Lower libs and the bones that anchor the limbs to the axil skeleton
* Pectoral gridle: Clavicle and scapula
* Upper limbs: Humerus , ulna, radius, carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges
* Pelvic girdle: 2 hip bones
* Lower limbs: femur, patella, tibia, fibula, tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges
* Pectoral gridle: Clavicle and scapula
* Upper limbs: Humerus , ulna, radius, carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges
* Pelvic girdle: 2 hip bones
* Lower limbs: femur, patella, tibia, fibula, tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges
4
New cards
Major Bones of the skeleton
5
New cards
Axial Skeleton
6
New cards
Appendicular skeleton
7
New cards
Condyle
Rounded process that usually articulates with another bone
Ex: Occipital condyle of the occipital bone
Ex: Occipital condyle of the occipital bone
8
New cards
Crest
Narrow, Ridgelike projection
Ex: LiliacE Crest of the lilum
Ex: LiliacE Crest of the lilum
9
New cards
Epicondyle
Projection situated above a condyle
Ex: Medial Epicondyle of the humerus
Ex: Medial Epicondyle of the humerus
10
New cards
Facet
Small, Nearly flat surface
Ex: Costal facet of the thoracic vertebra
Ex: Costal facet of the thoracic vertebra
11
New cards
Fontanel
Soft spot in the skull where membrane cover the space between bones
Ex: Anterior Fontanel between the frontal and partial bones
Ex: Anterior Fontanel between the frontal and partial bones
12
New cards
Foramen
Opening through a bone that usually is a passageway for blood vessels, nerves, or ligaments
Ex: Foramen magnum of the occipital bone
\
Ex: Foramen magnum of the occipital bone
\
13
New cards
Fossa
Relatively deep pit or depression
Ex: Olecranon fossa of the humerus
Ex: Olecranon fossa of the humerus
14
New cards
Fovea
Tiny pit or depression
Ex: Fovea capitis of the femur
Ex: Fovea capitis of the femur
15
New cards
Head
Enlargement of the end of a bone
Ex: Head of the humerus M
Ex: Head of the humerus M
16
New cards
Meatus
Tublike passageway within a bone
Ex: External Acoustic meatus of the temporal bone
Ex: External Acoustic meatus of the temporal bone
17
New cards
Process
Prominent Projection on a bone
Ex:Mastoid process of the temporal boneS
Ex:Mastoid process of the temporal boneS
18
New cards
Sinus
Cavity within a bone
Ex: Frontal sinus of the frontal bone
Ex: Frontal sinus of the frontal bone
19
New cards
Spine
Thorline porjection
Ex: Spine of the scapula
Ex: Spine of the scapula
20
New cards
Sulcus
Furrow or groove
Ex: Intertubercular sulcus of the humerus
Ex: Intertubercular sulcus of the humerus
21
New cards
Trochanter
Relatively large process
Ex: Greater trochanter of the fumer
\
Ex: Greater trochanter of the fumer
\
22
New cards
Tubercle
Small, knoblike process
Ex: Greater tubercle of the humerus
Ex: Greater tubercle of the humerus
23
New cards
Tuberosity
Knoblike process usually larger than a tubercle
Ex: Radial Tuberosity of the radius
Ex: Radial Tuberosity of the radius
24
New cards
The skull
* It is made up 22 bones: 8 Cranial bones and 14 facial bones; there are also 3 bones in each middle ear
* Expect for Lower jaw, skull bones are connected by immovable joints called sutures
* Expect for Lower jaw, skull bones are connected by immovable joints called sutures
25
New cards
Bones of the cranium
This encloses and protects the brain, provides attachment for muscles, and contains air-filled paranasal sinuses that reduce its weight and increase vocal resonance
26
New cards
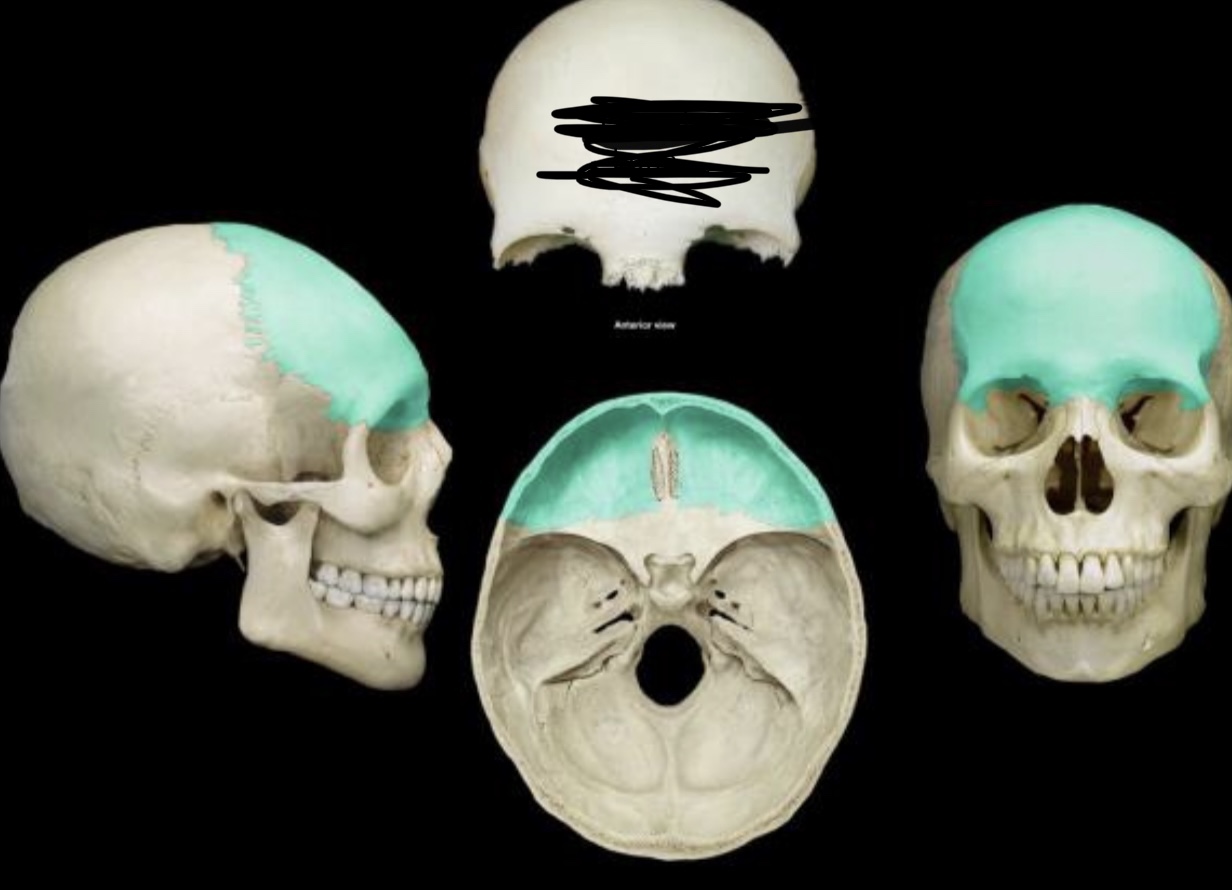
Frontal bone (Bones of the cranium)
Forms anterior part of the skull, above eyes; features include the supraorbital foramen and the frontal sinuses
27
New cards
Parietal Bones (Bones of the cranium)
Form the rood and sides of the skull, just behind the frontal bone; they join along the midline at the sagittal suture and meet the frontal bone along the coronal suture
28
New cards
Anterior View of the skull
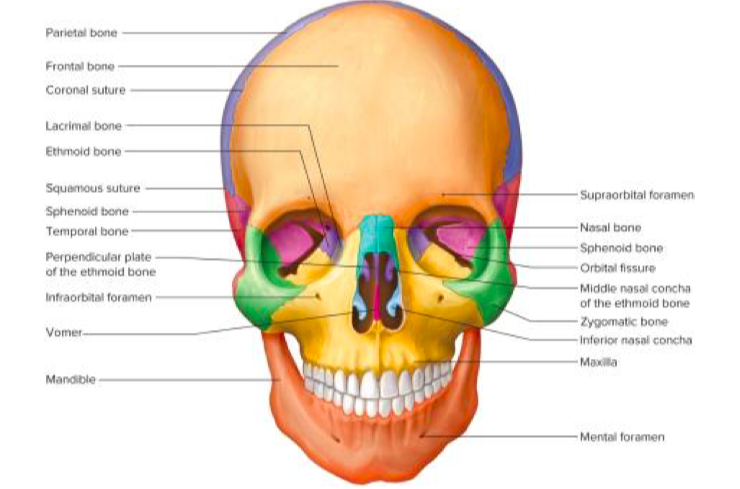
29
New cards
The paranasal sinuses
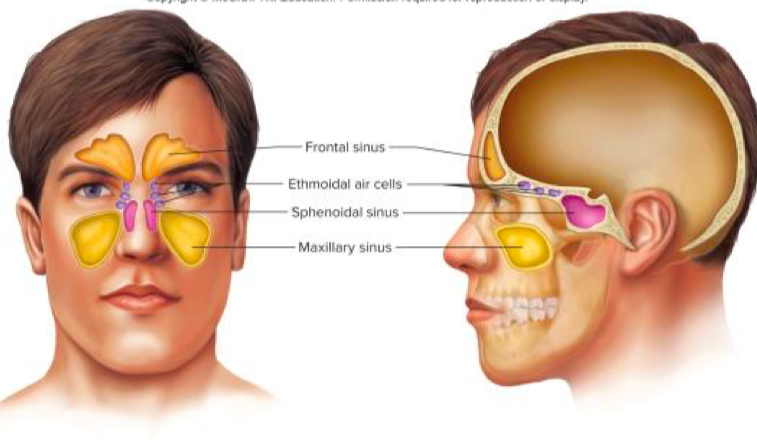
30
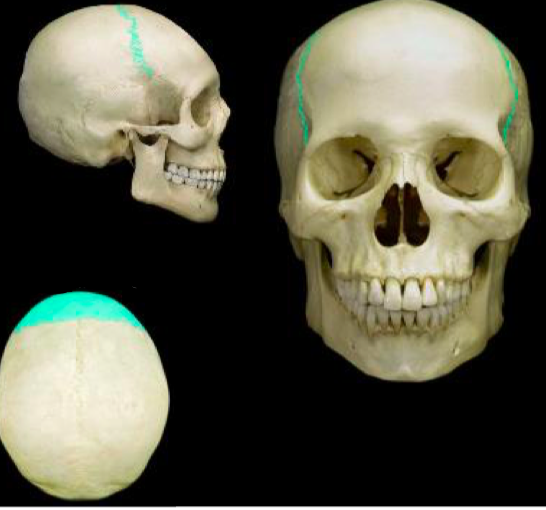
New cards
Coronal Suture Frontal bone
31
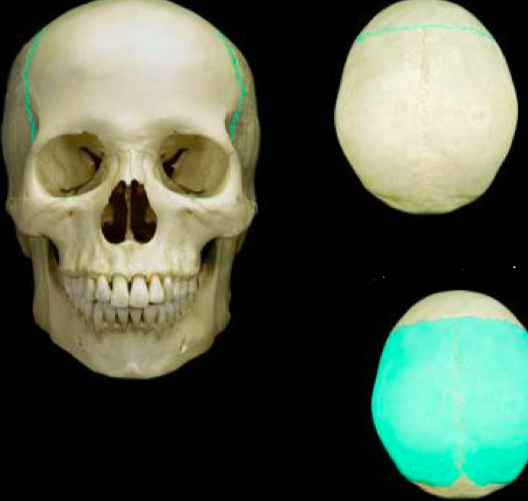
New cards
Coronal Suture Parietal bones
32
New cards
Lambdoid suture Occipital bone
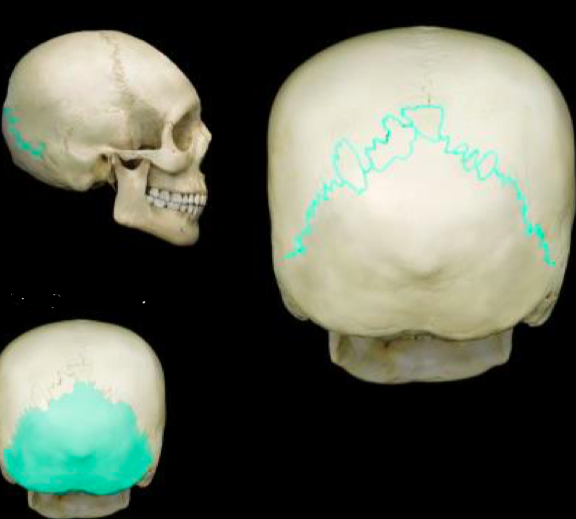
33
New cards
Lambdoid Suture Parietal Bones
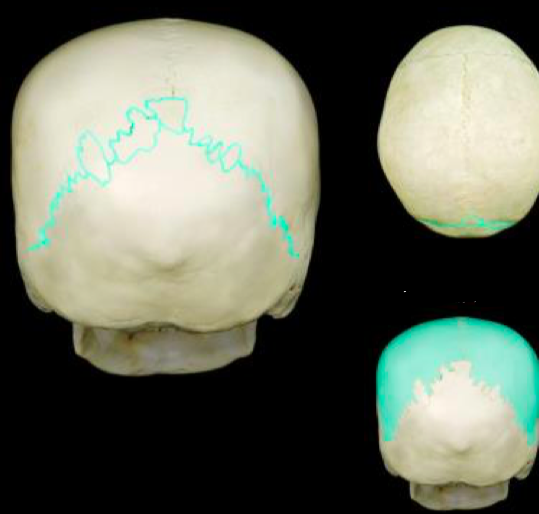
34
New cards
Labled
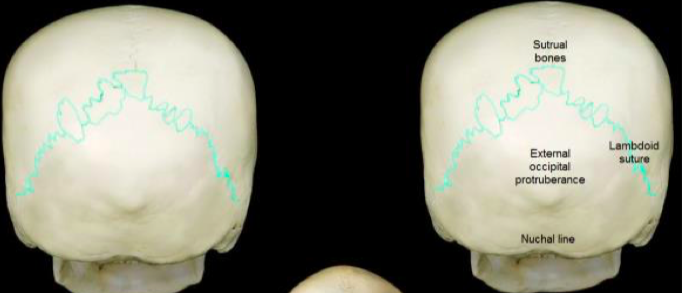
35
New cards
Ligamentum
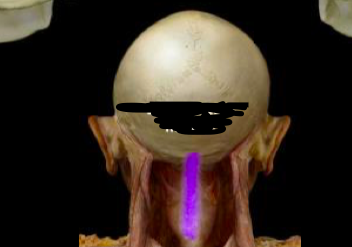
36
New cards
Sagittal suture partial bones
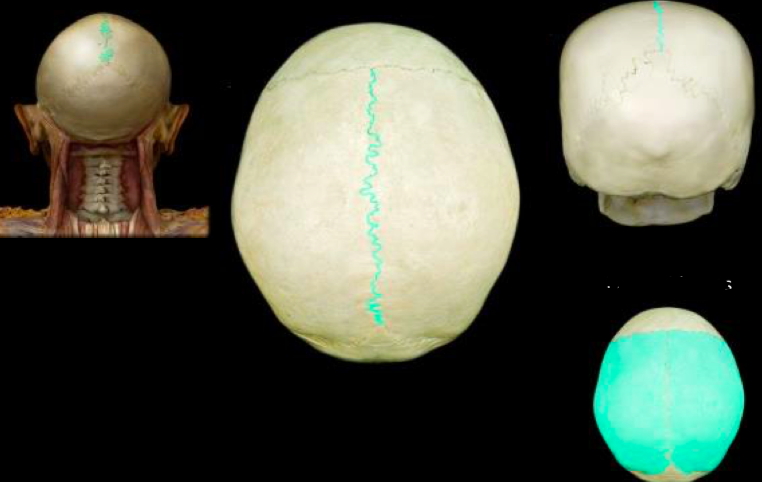
37
New cards
Squamous suture parietal bone
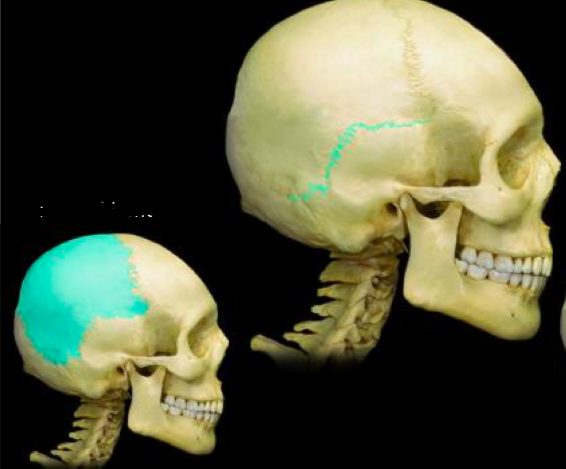
38
New cards
Squamous Suture temporal bone
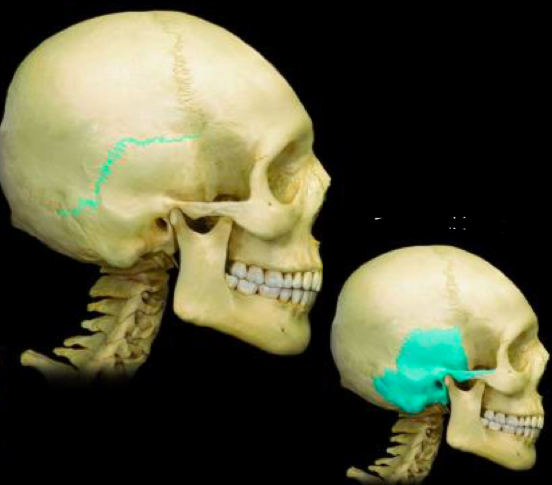
39
New cards
Frontal Bone
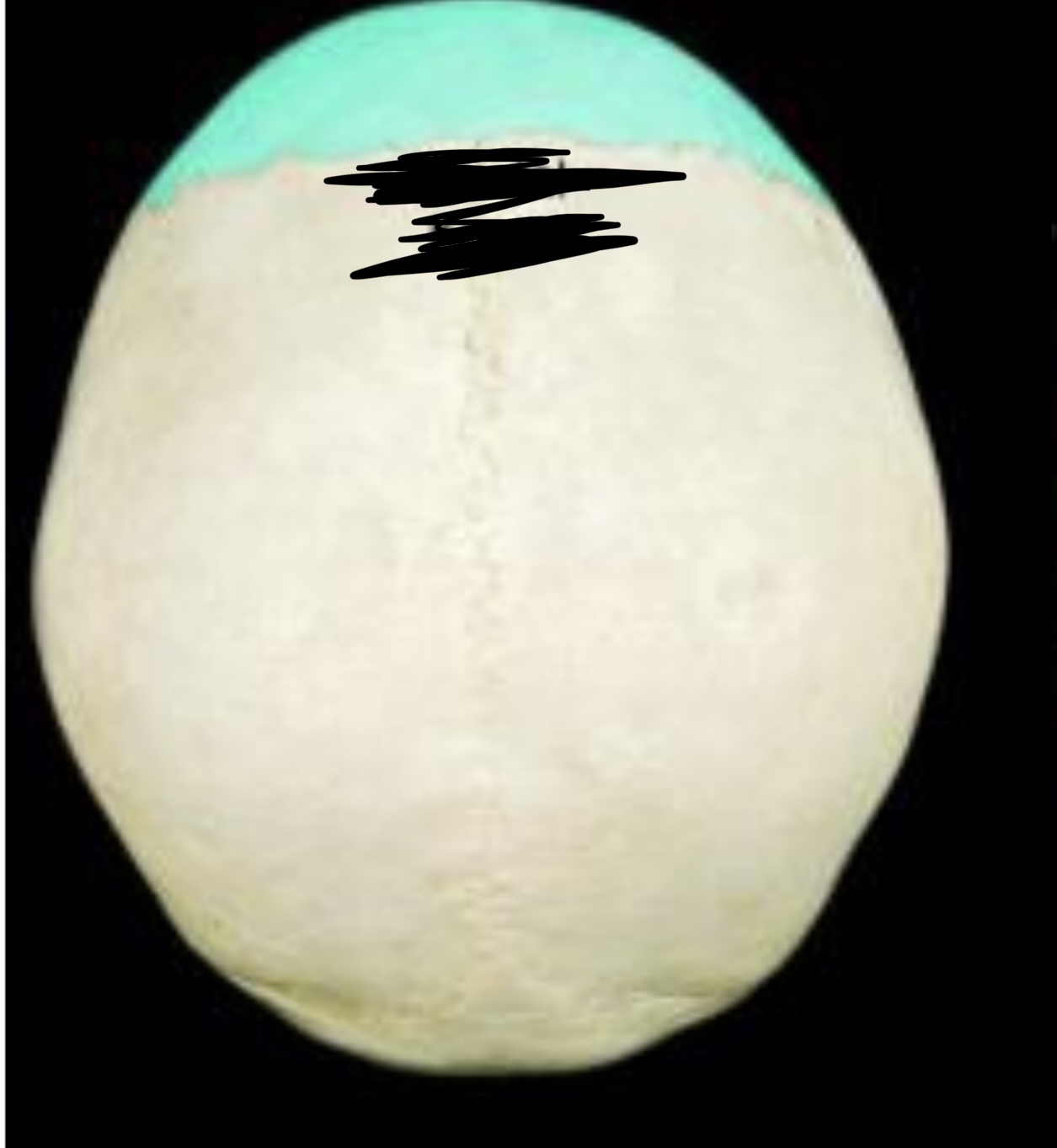
40
New cards
Partial bones
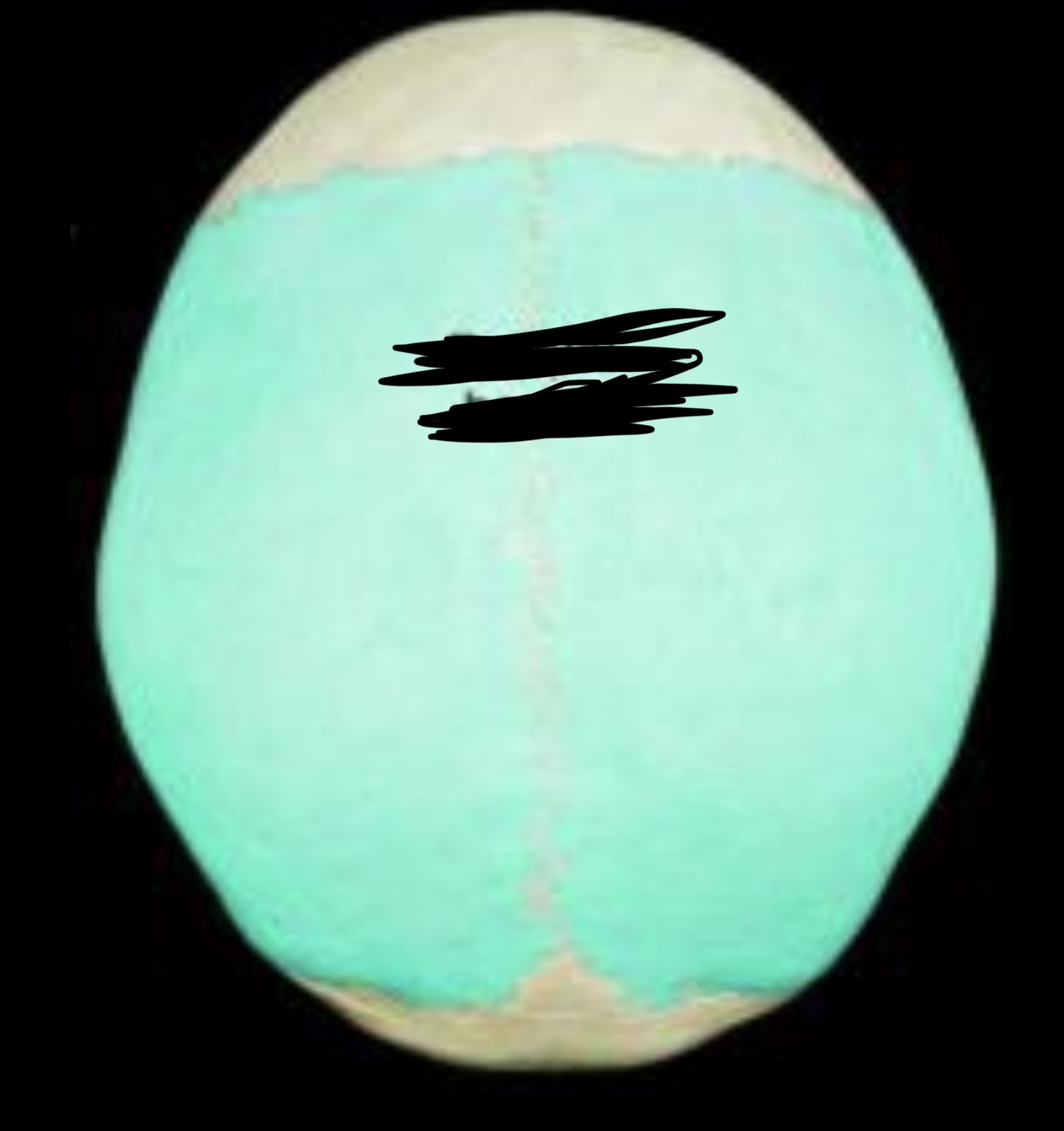
41
New cards
Optical bone
42
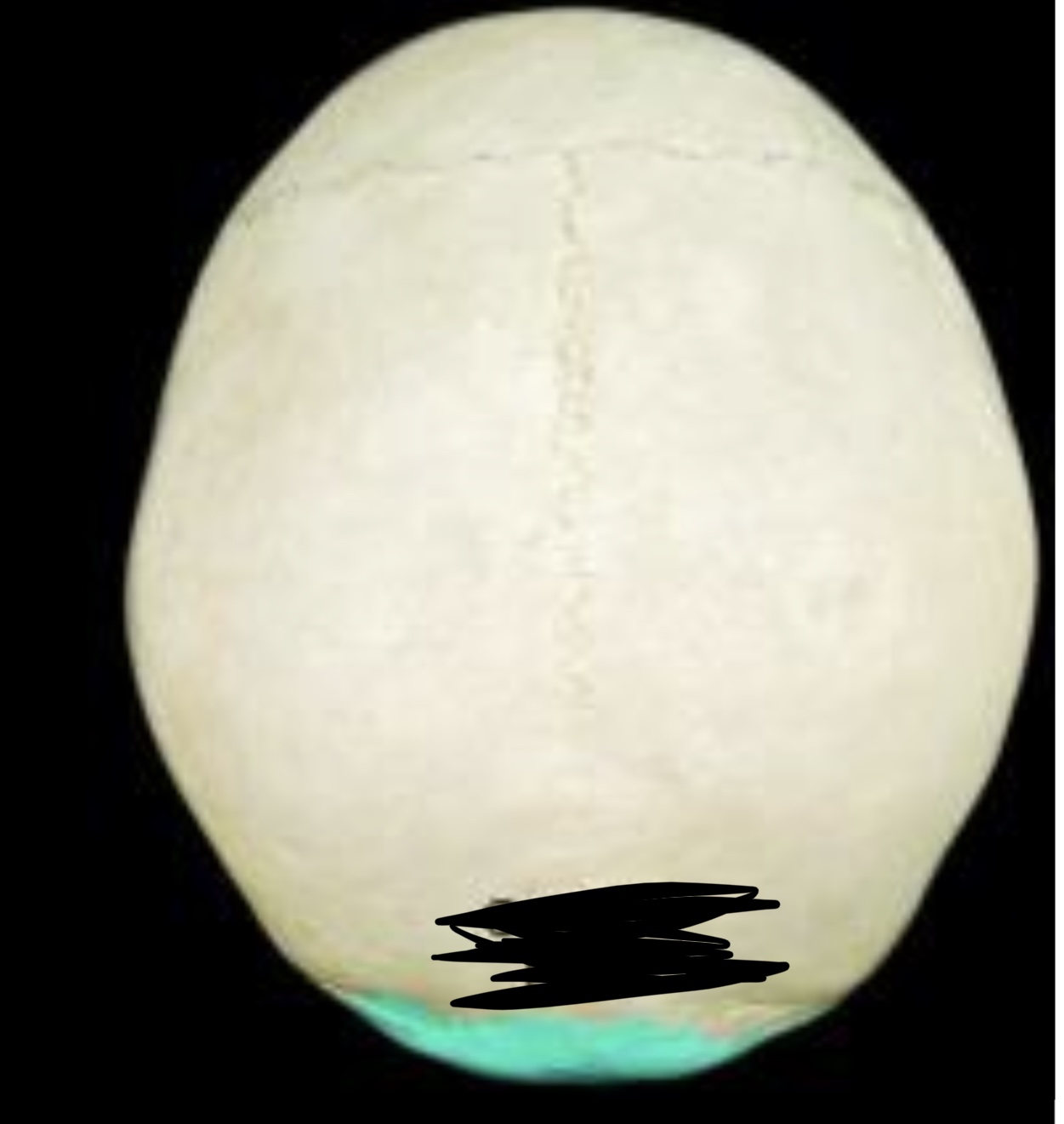
New cards
Lambdoid suture
43
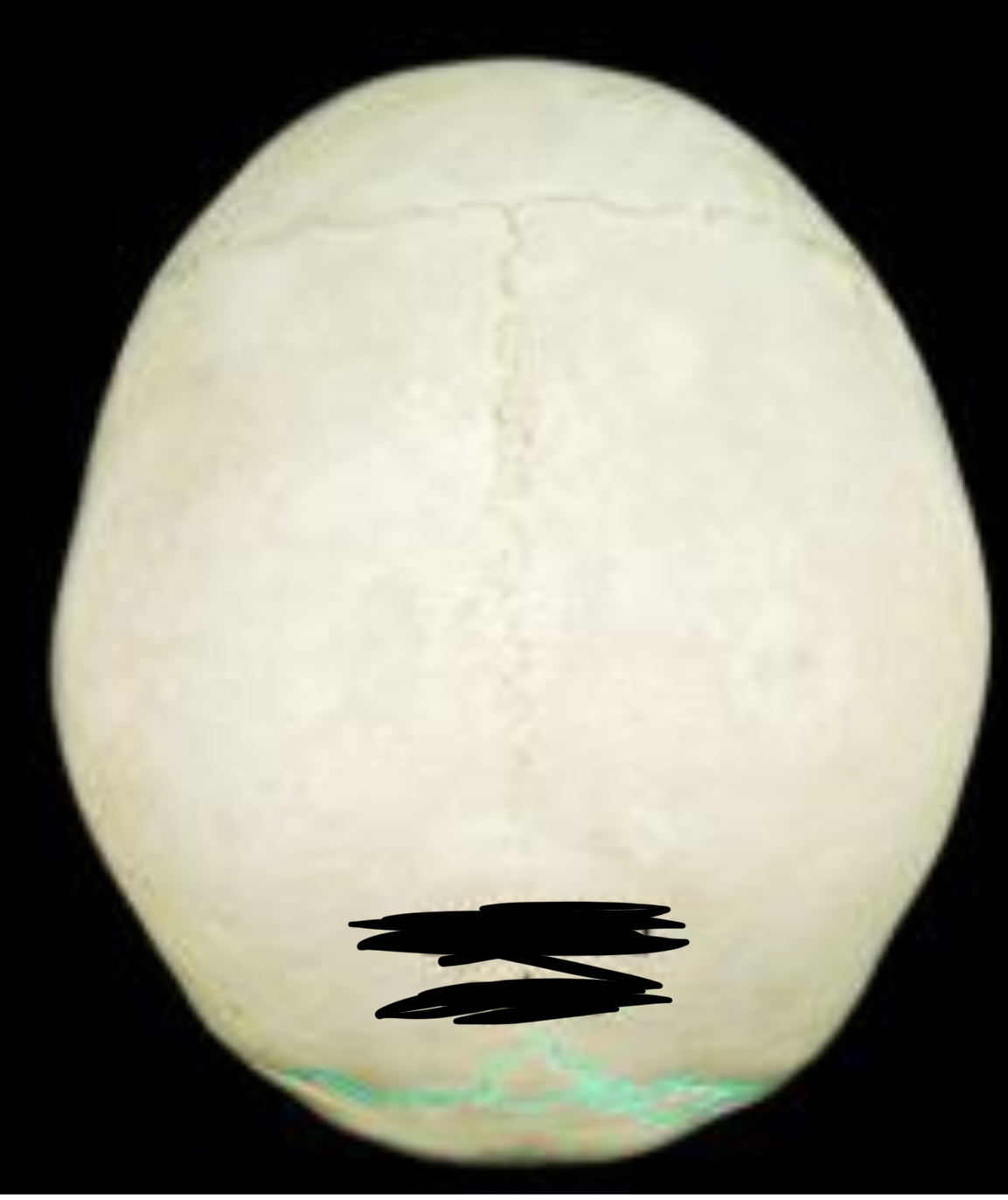
New cards
Sagital suture
44
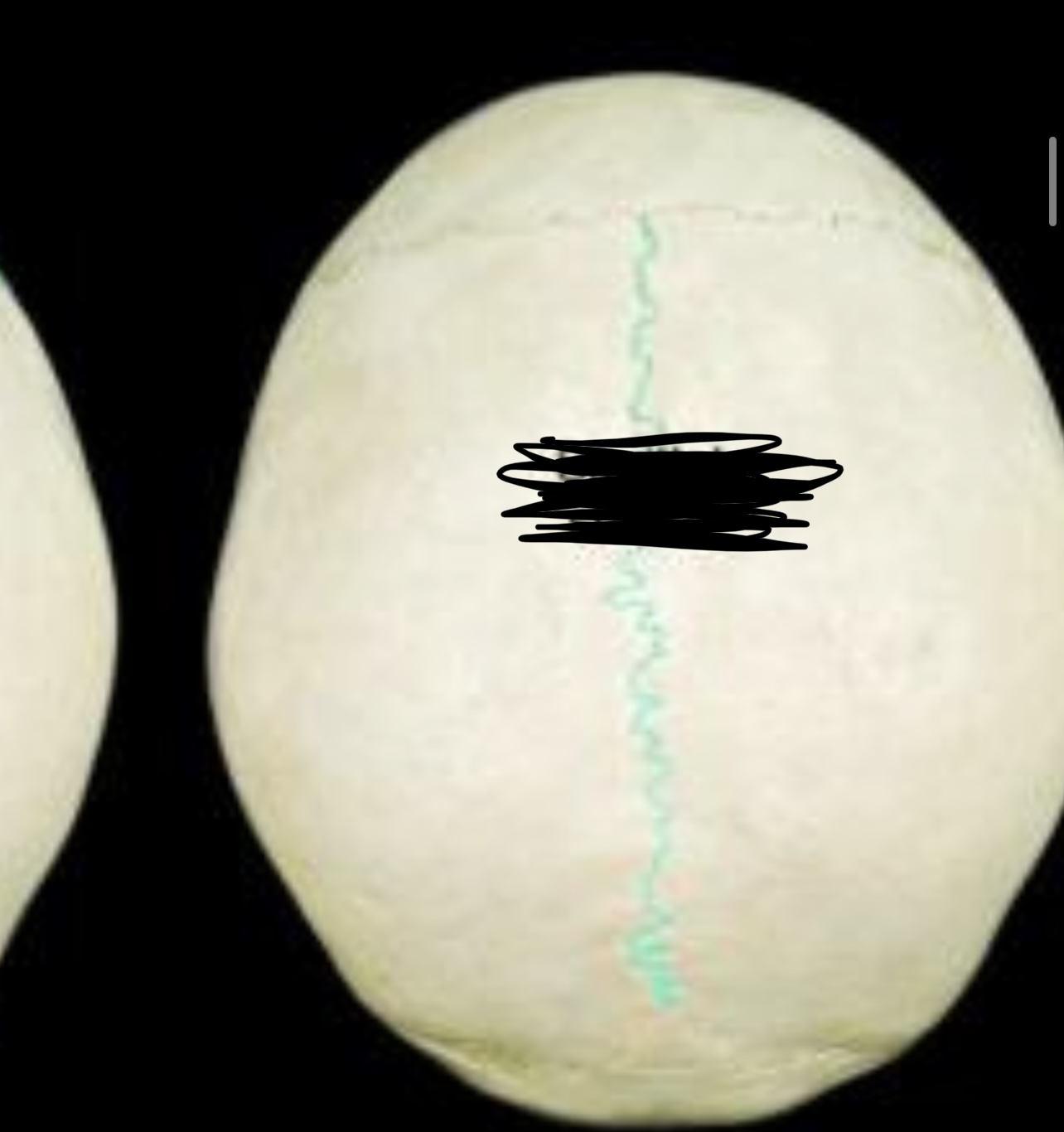
New cards
Coronal suture
45
New cards
Where does the occipital bone form?
it forms the back of the skull and the base of the cranium; features include foramen magnum, and occipital condyles; joins parietal bones at lambdoid suture
46
New cards
Where does the temporal bone form?
form parts of the sides and base of the cranium; features include the external acoustic meatus, mandibular fossae, mastoid process, styloid process, and zygomatic process; connects to parietal bones at squamous suture
47
New cards
Where does the sphenoid bone form?
It forms the base of the cranium sides of the skull and protions of the orbits; features include the sella turcica and sphenoidal sinuses
48
New cards
Where is the ethmoid bone located?
Located in front of the sphenoid bone; features include the cribriform plates, croata galia a perpendicular plate superior and middle nasal conchae and ethomoidal sinus
49
New cards
The facial structure
* It contains 13 immovable bones and a movable lower jawbone
* These bones form the basic shape of the face and provide attachments for muscles that move the jaw and control facial expressions
* These bones form the basic shape of the face and provide attachments for muscles that move the jaw and control facial expressions
50
New cards
Maxillae bone of facial structure
Form the upper jaw, hard palete floor of the eye orbits sides of the nasal cavity house the upper teeth and contain large maxillary sinuses features include the maxillary sinus palatine and alveolar processes and alveolar arch
51
New cards
Palatine bones
Are L shaped bones located behind the maxillae that from the floor & lateral walls of the nasal cavity and the portion of the hard palate
52
New cards
Zygomatic bones
Form the cheekbones and lateral walls of the orbits; features include the temporal process, which joins the zygomatic process to form zygomatic arch
53
New cards
Lacrimal bones
Form part of the medial walls of the orbits
54
New cards
Nasal bones
Form the bridge of the nose
55
New cards
Vomer bone
Makes up a portion of the nasal septum to
56
New cards
Inferior nasal conchae
Are fragile scroll shaped bones that support mucous membranes in the nasal cavity
57
New cards
Mandible
Or lower jawbone supports the lower teeth and includes the body mandibular condyle coronoid process and alveolar arch
58
New cards
Frontal bone
59
New cards
Supraorbital notch
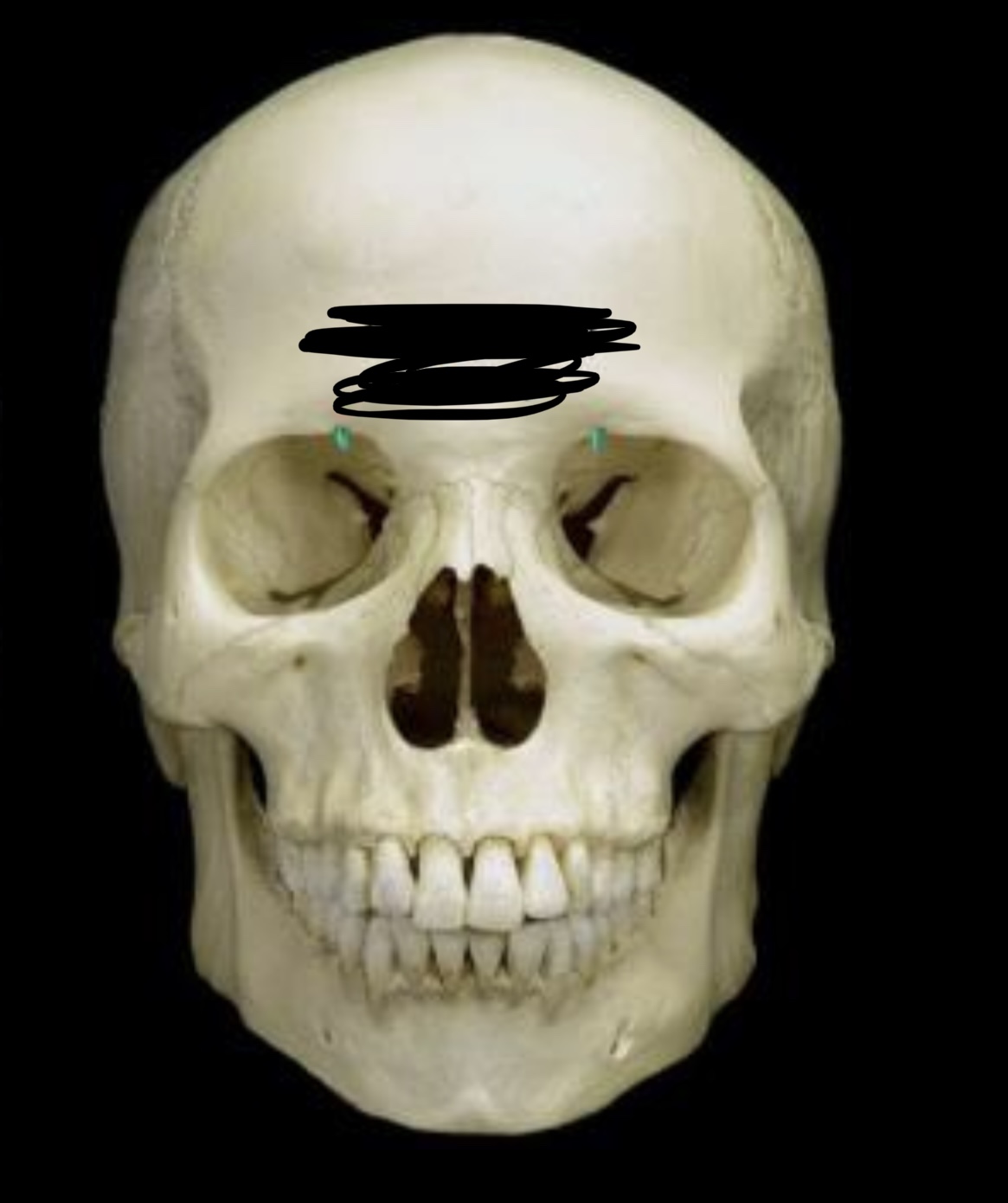
60
New cards
Lateral view of skull
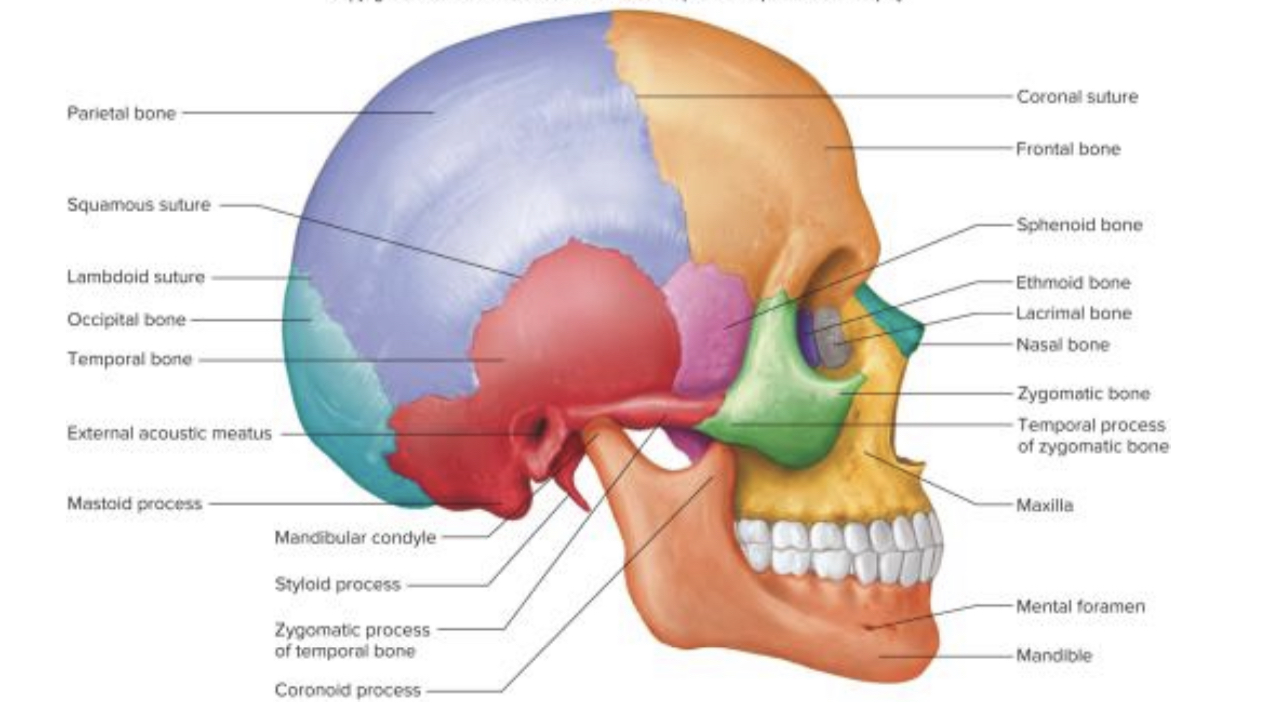
61
New cards
Parietal bone
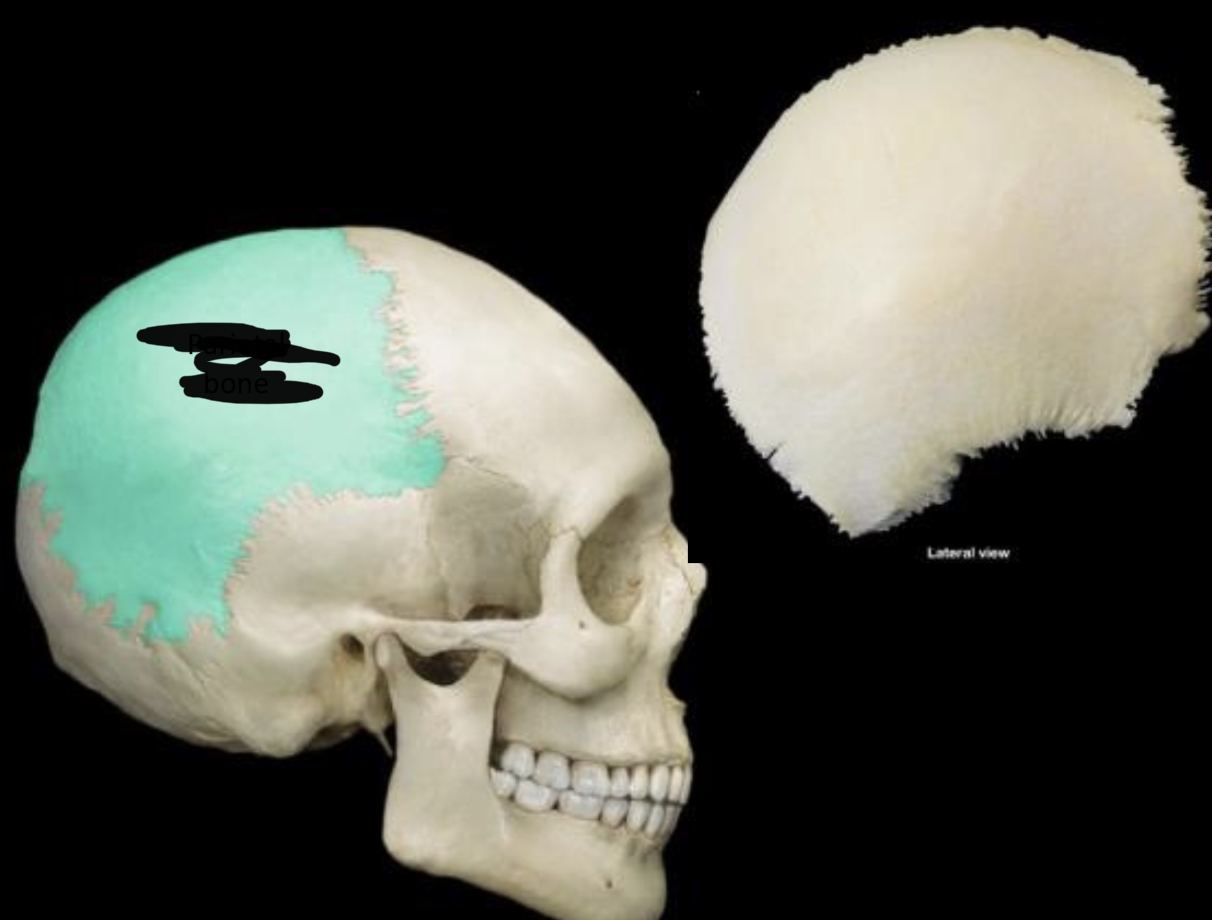
62
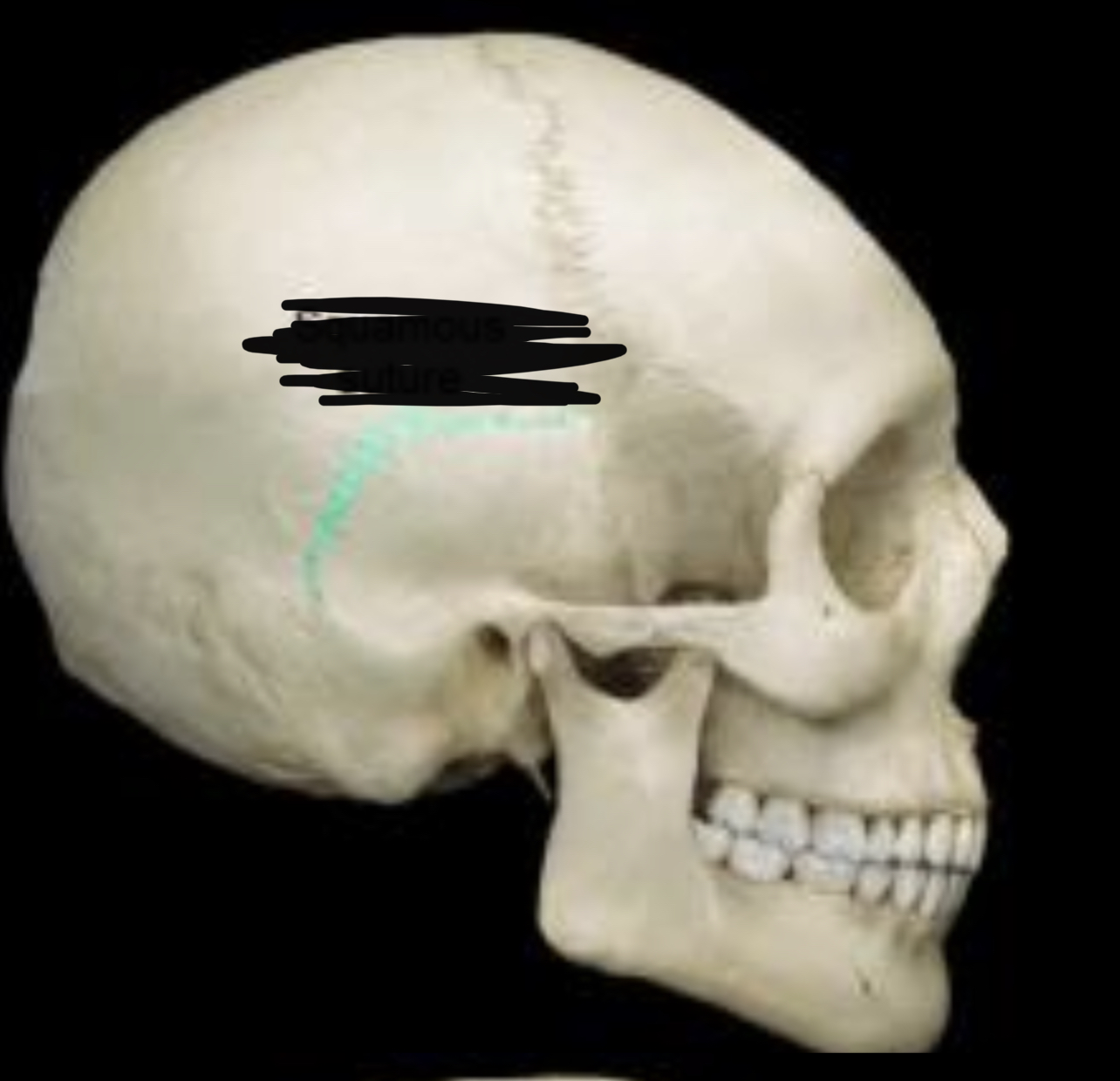
New cards
Squamous suture
63
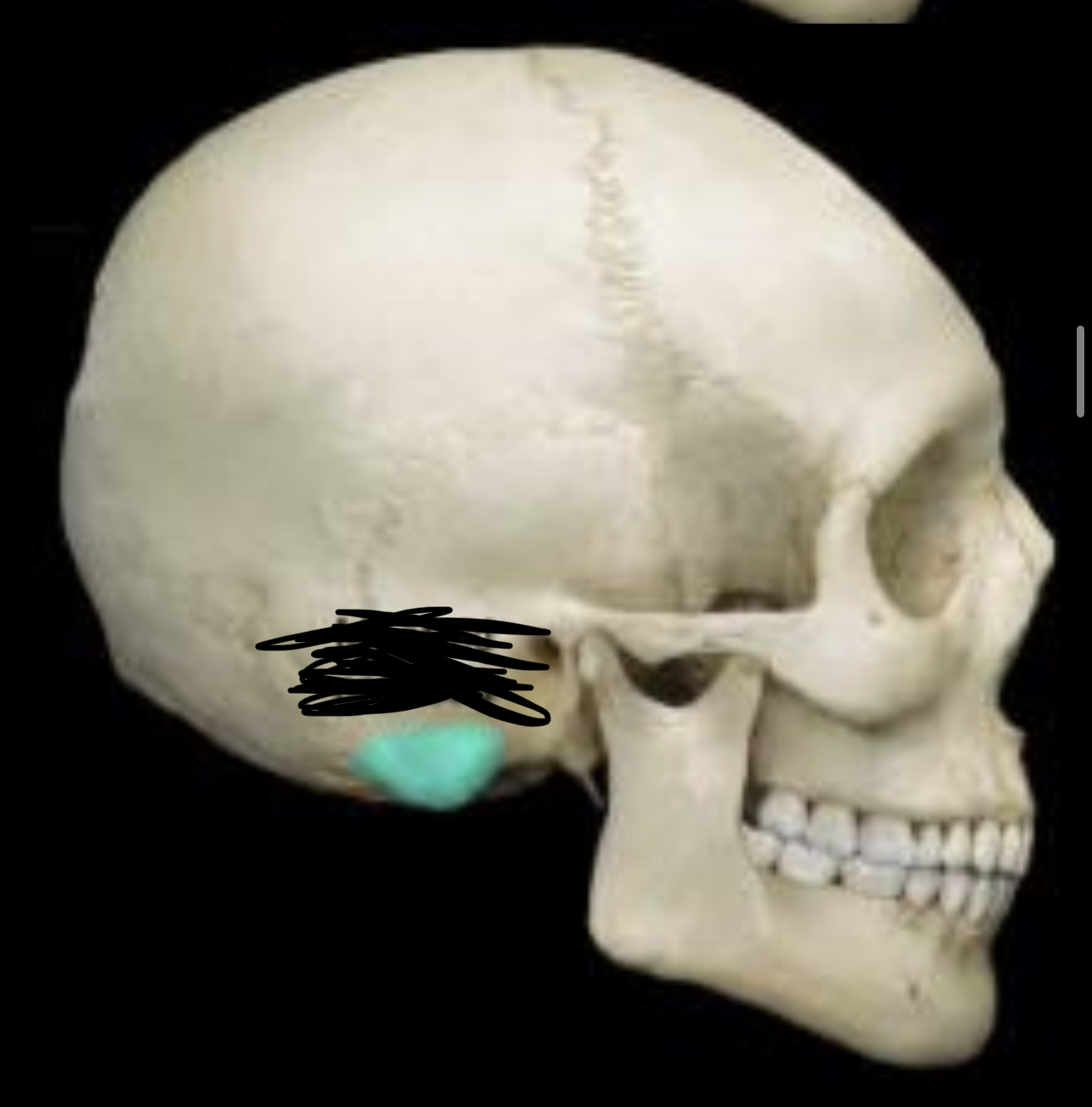
New cards
Mastoid process
64
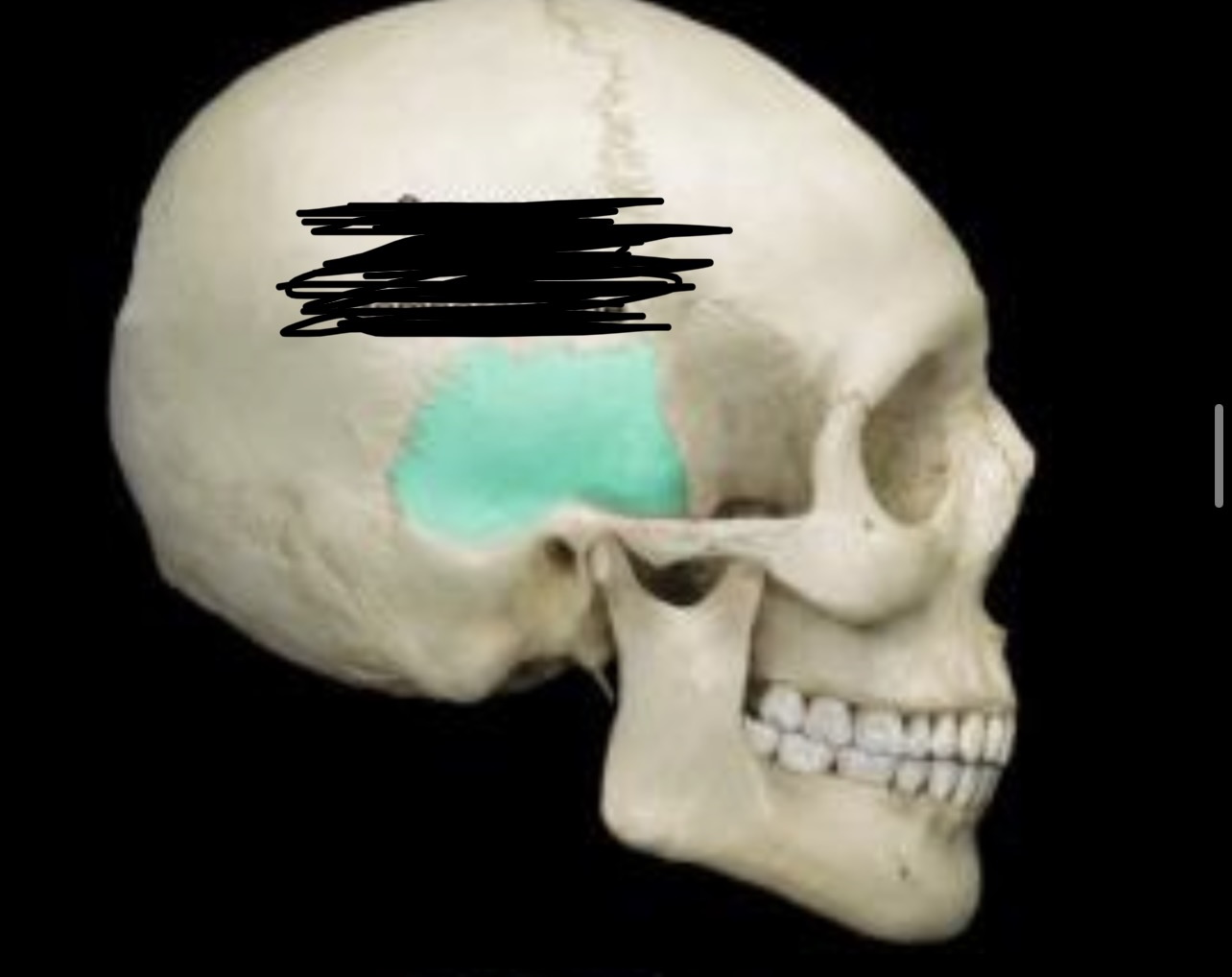
New cards
Squamous portion of temporal bone
65
New cards
External auditory meatus
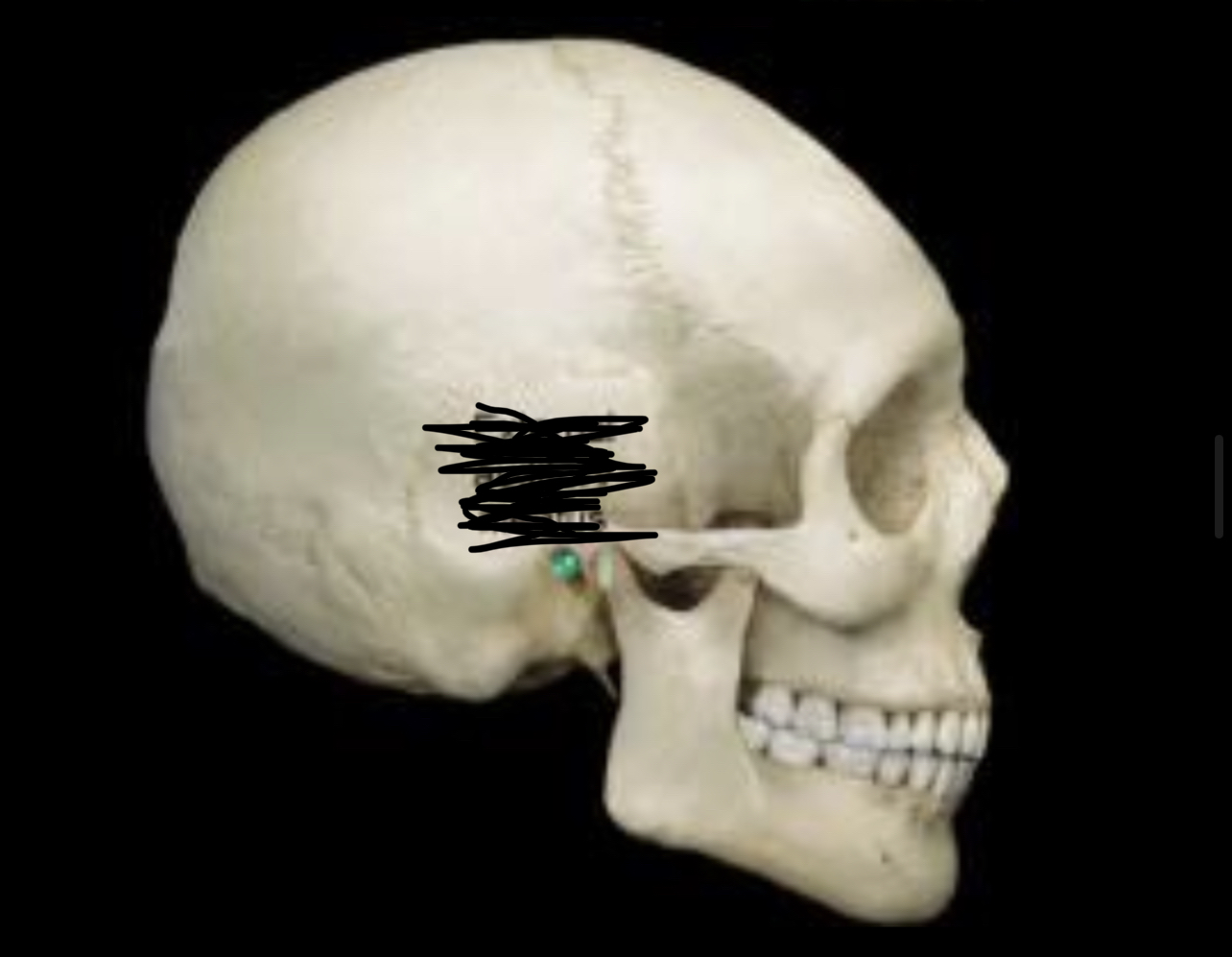
66
New cards
Zygomatic process of temporal bone
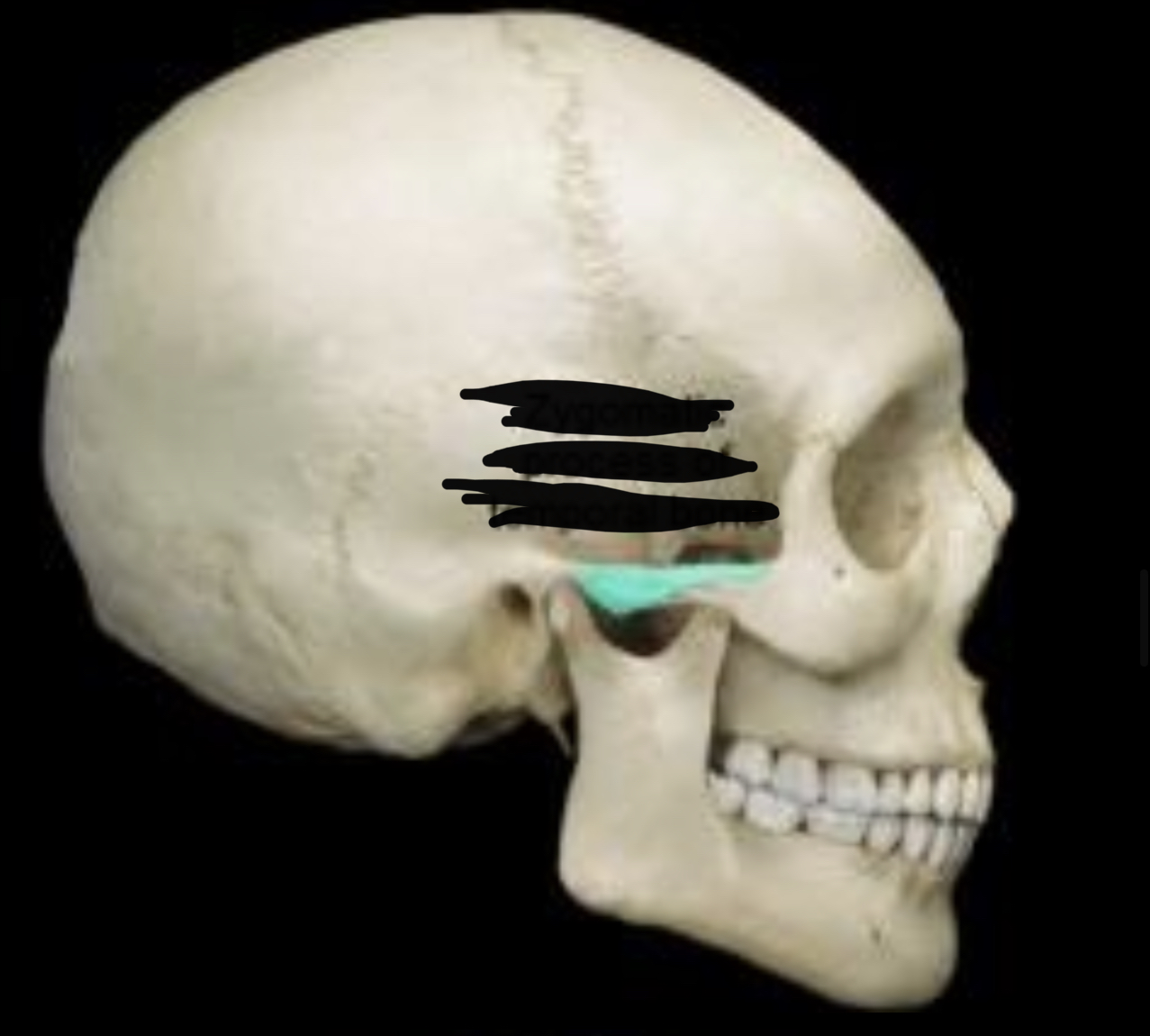
67
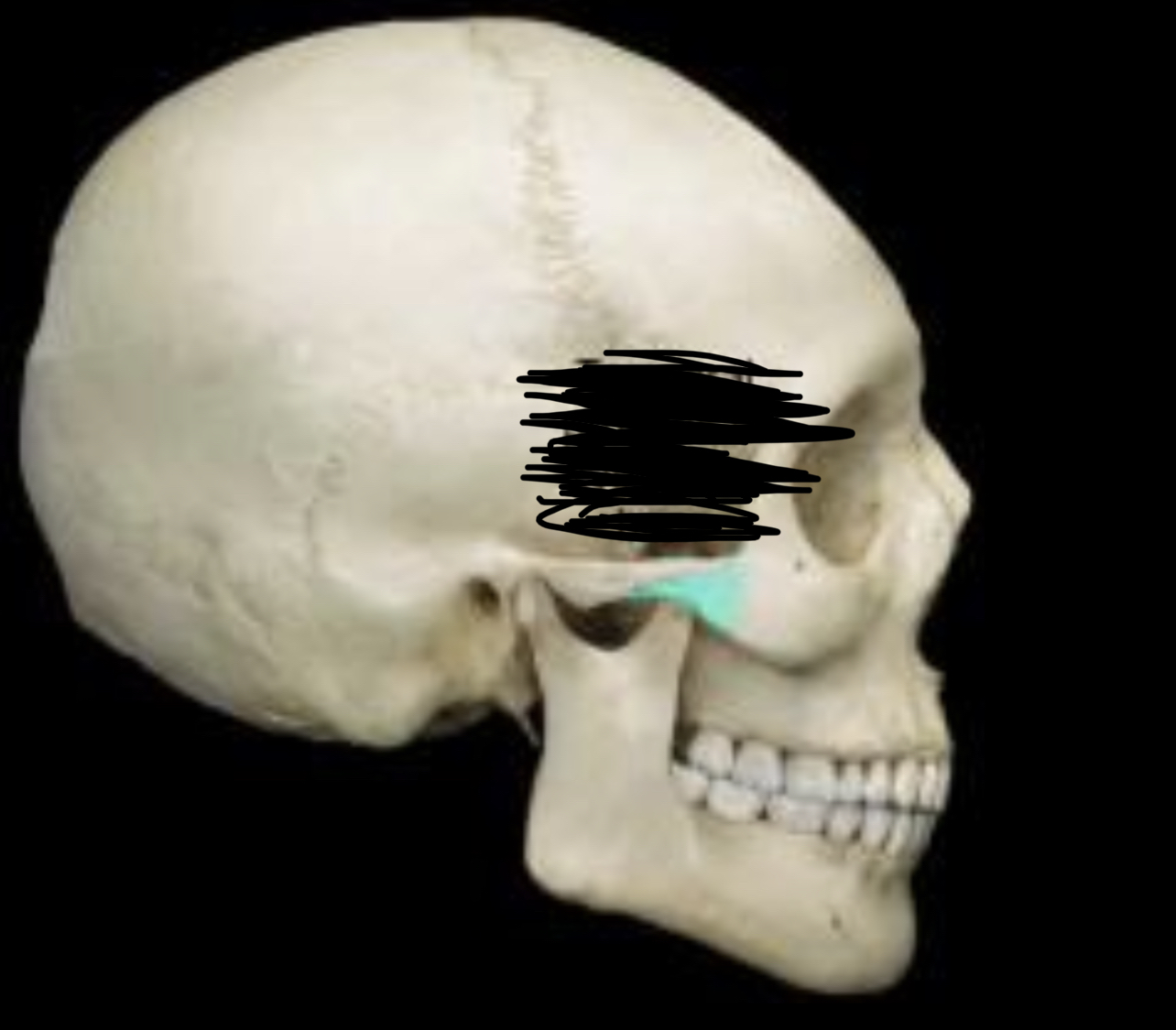
New cards
Temporal process of zygomatic bone
68
New cards
Zygomatic bone
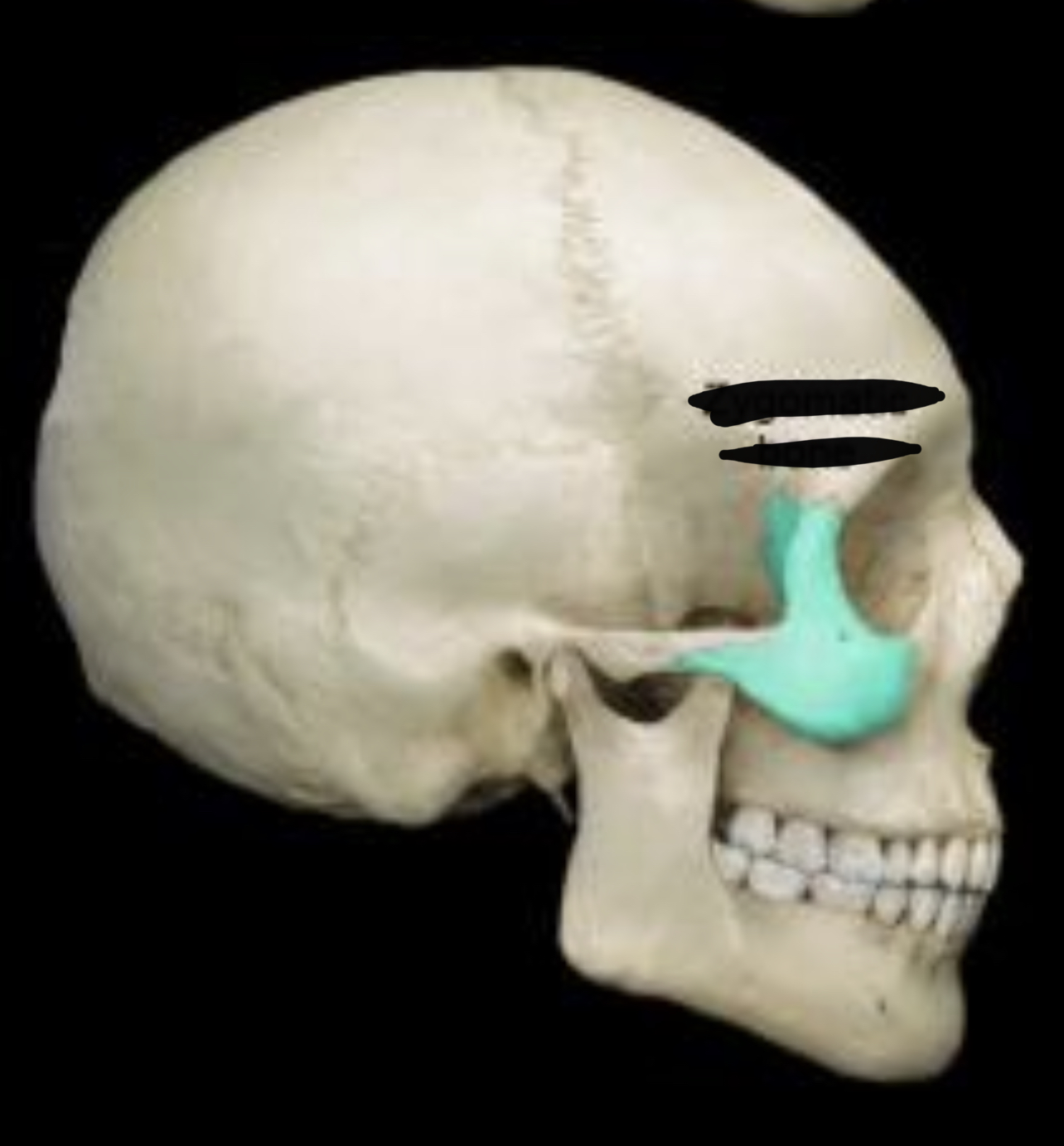
69
New cards
Greater wing of sphenoid bone
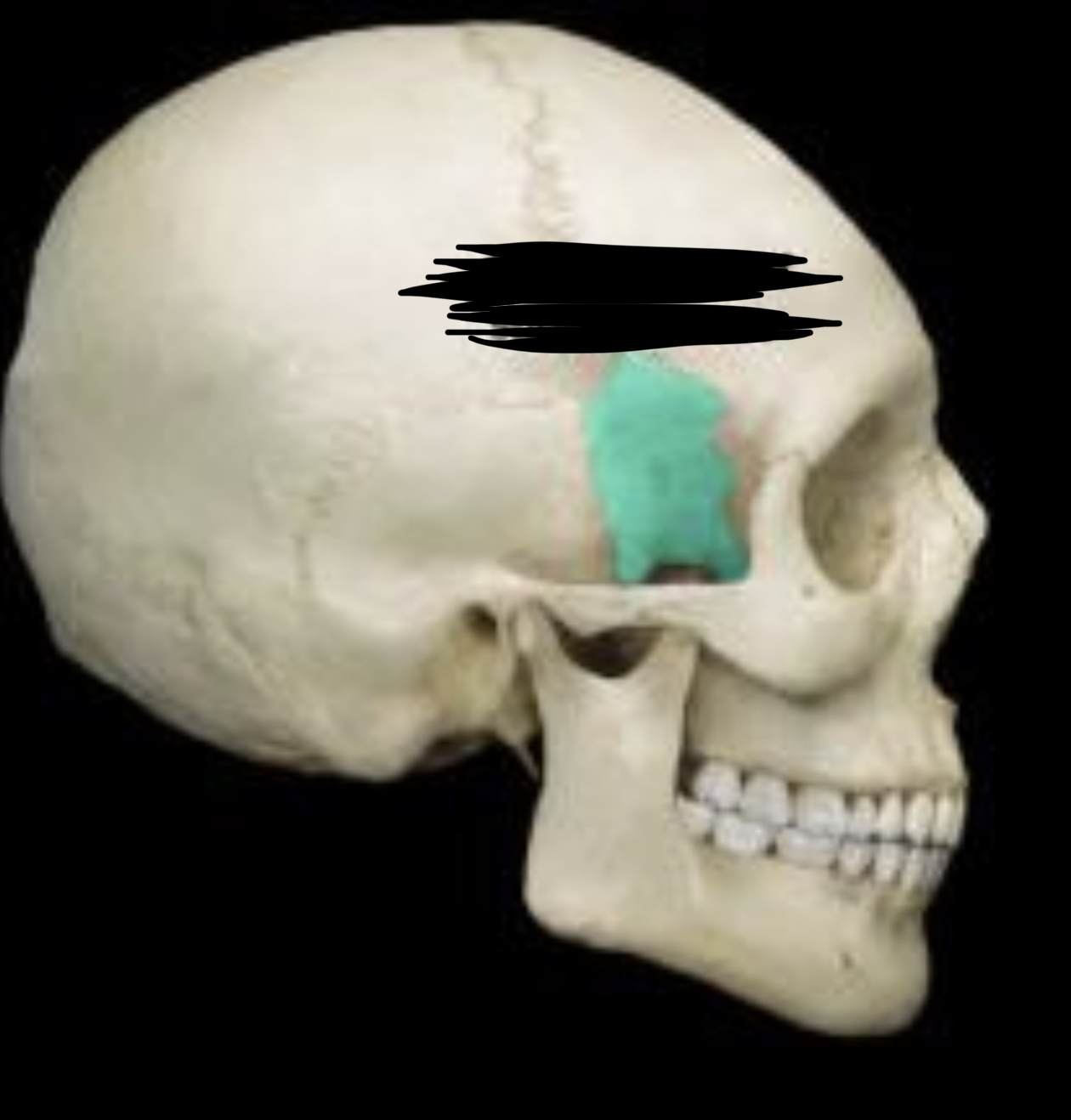
70
New cards
Temporal bone lateral view
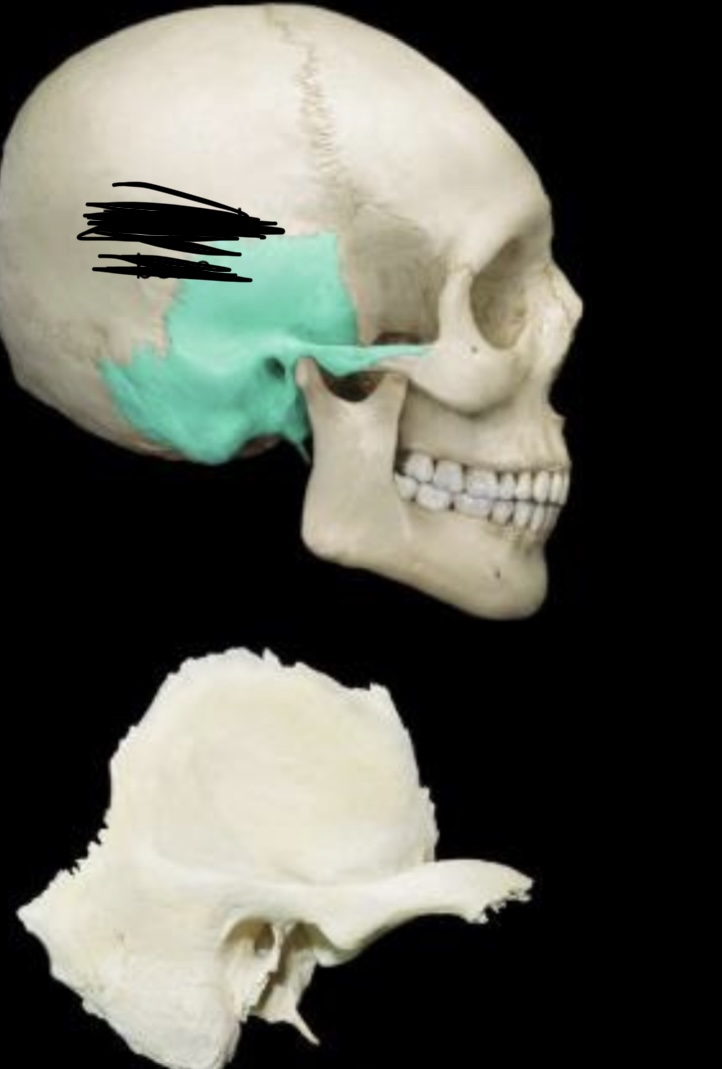
71
New cards
Temporal bone medial view
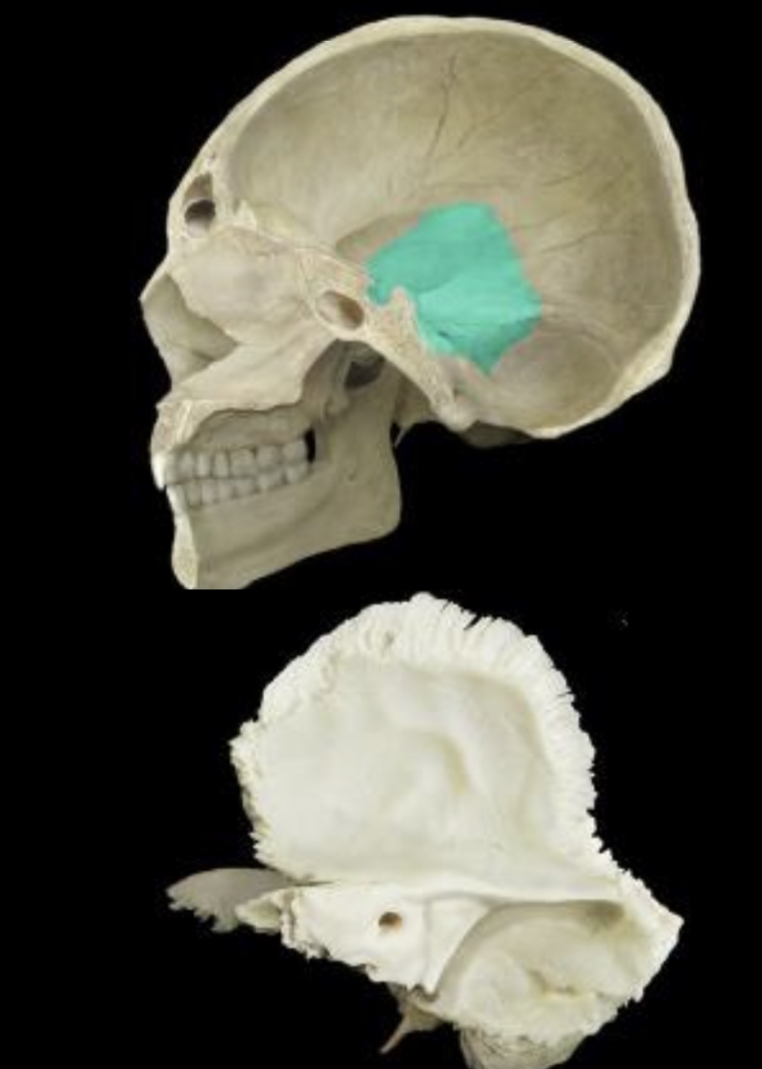
72
New cards
Inferior view of skull
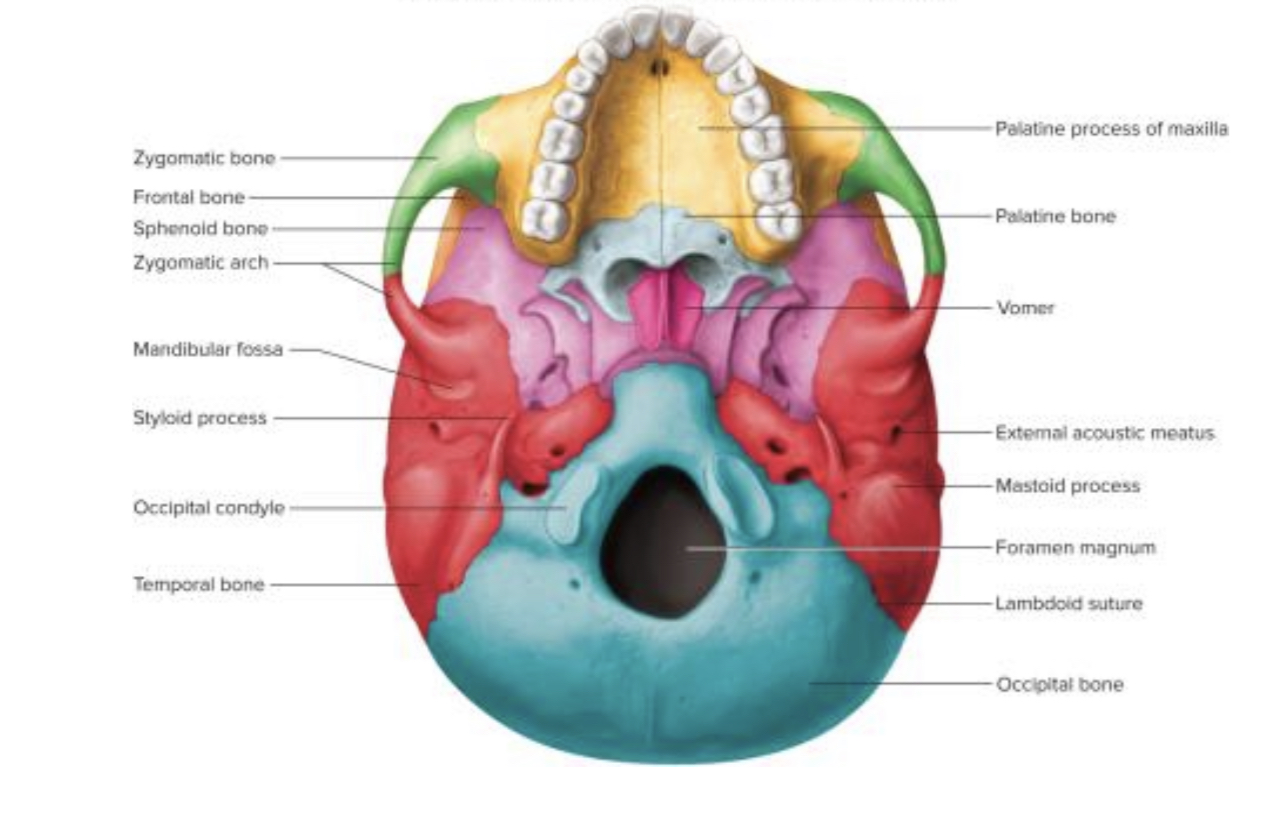
73
New cards
Occipital bone inferior view
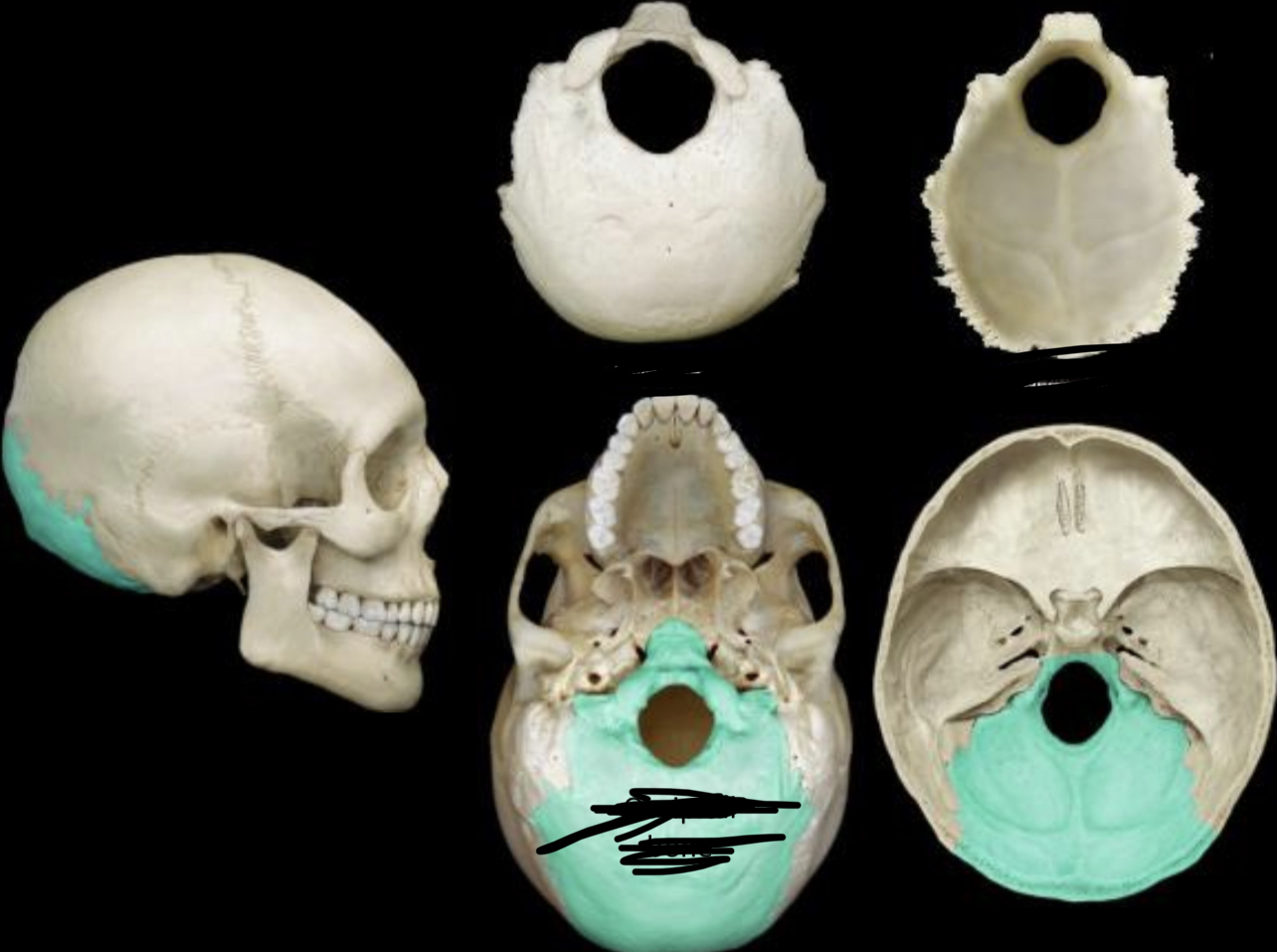
74
New cards
Hypoglossal canal
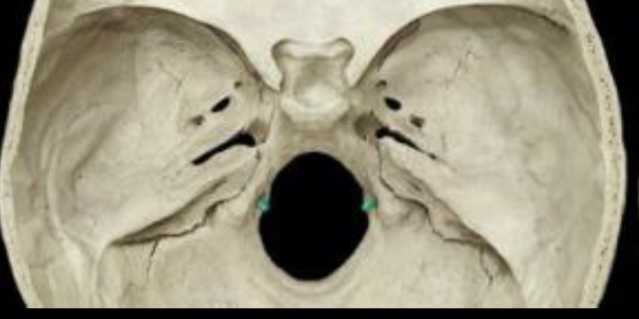
75
New cards
Foramen magnum
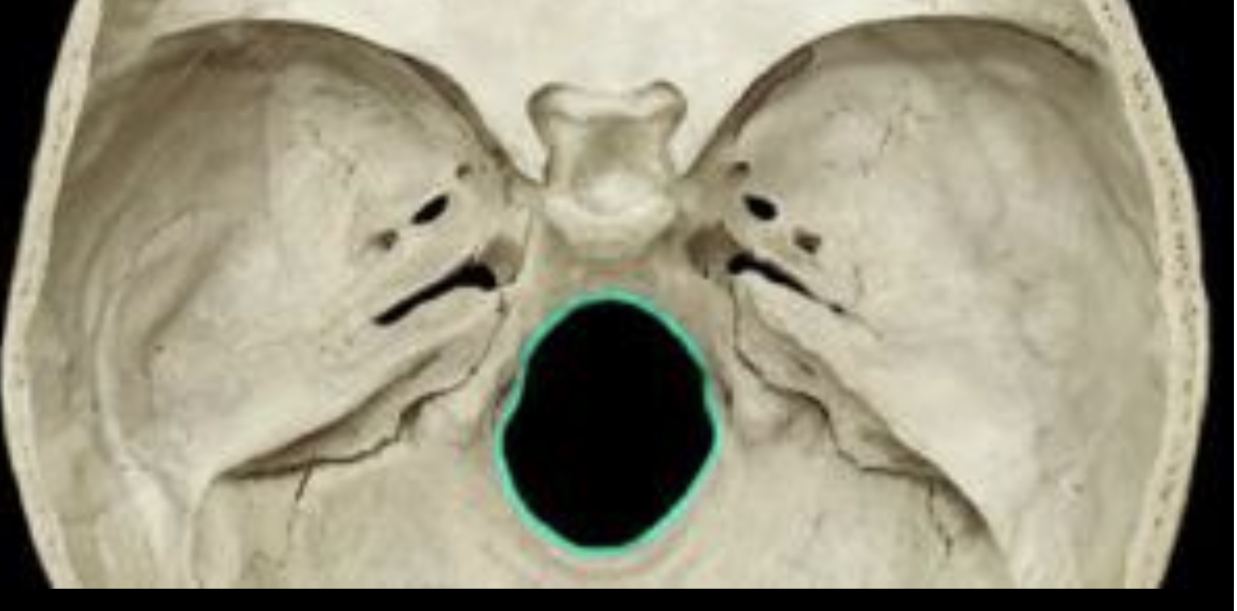
76
New cards
Jugular foramen
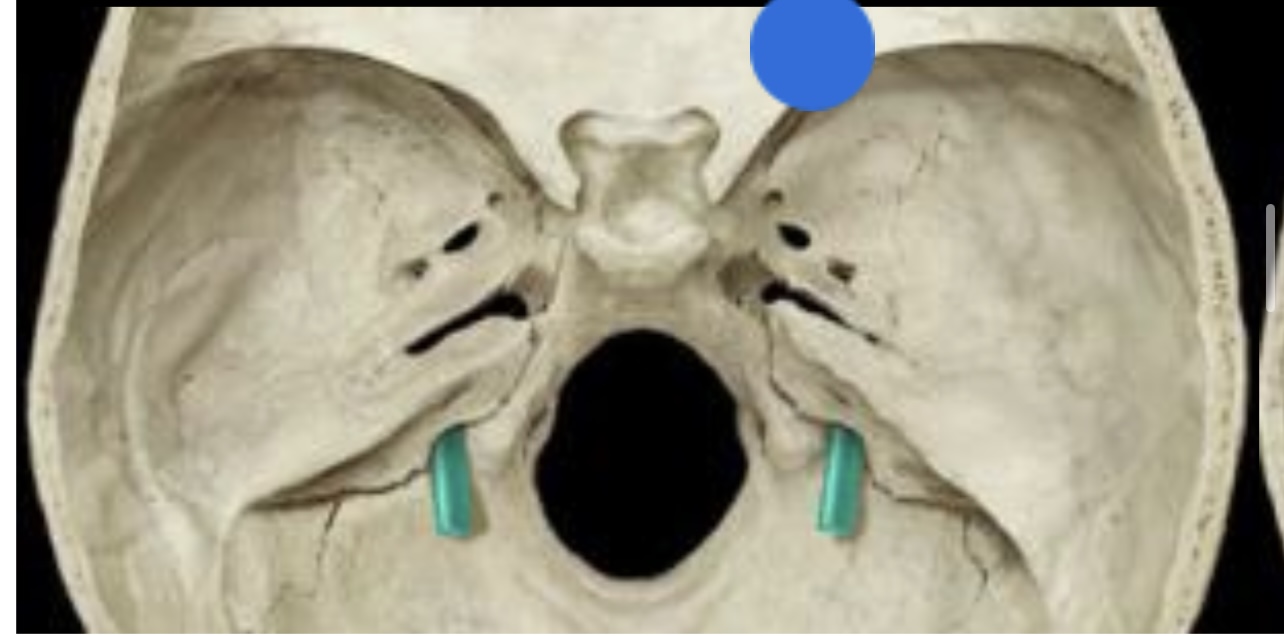
77
New cards
Internal acoustic meatus
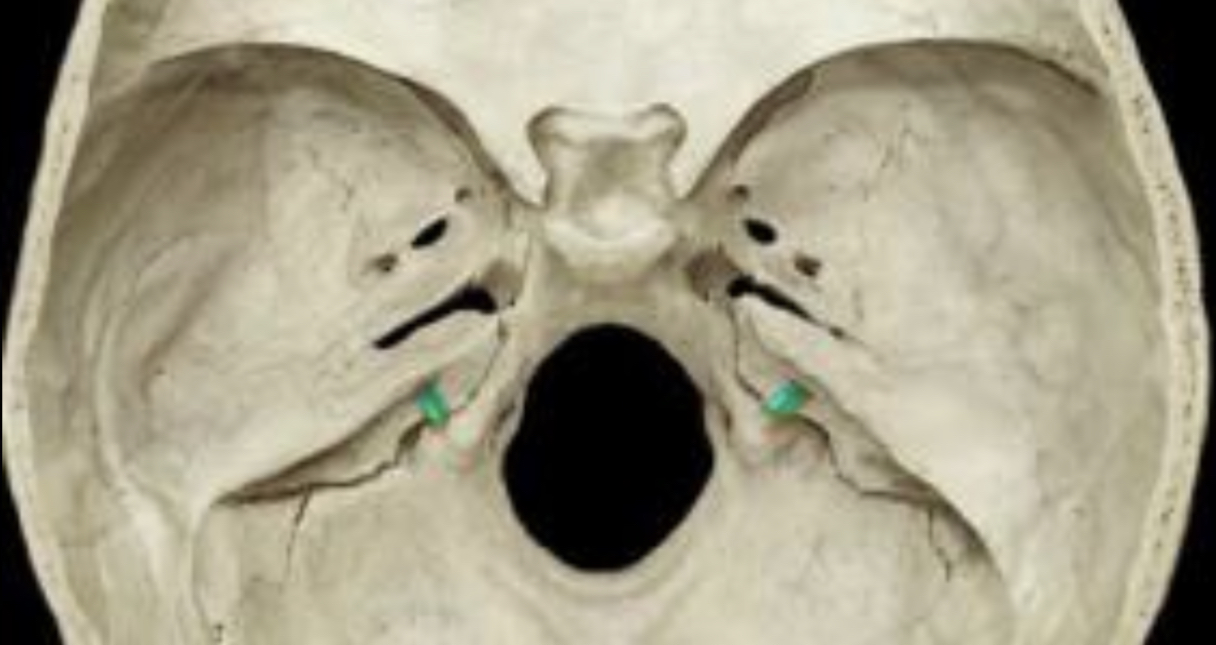
78
New cards
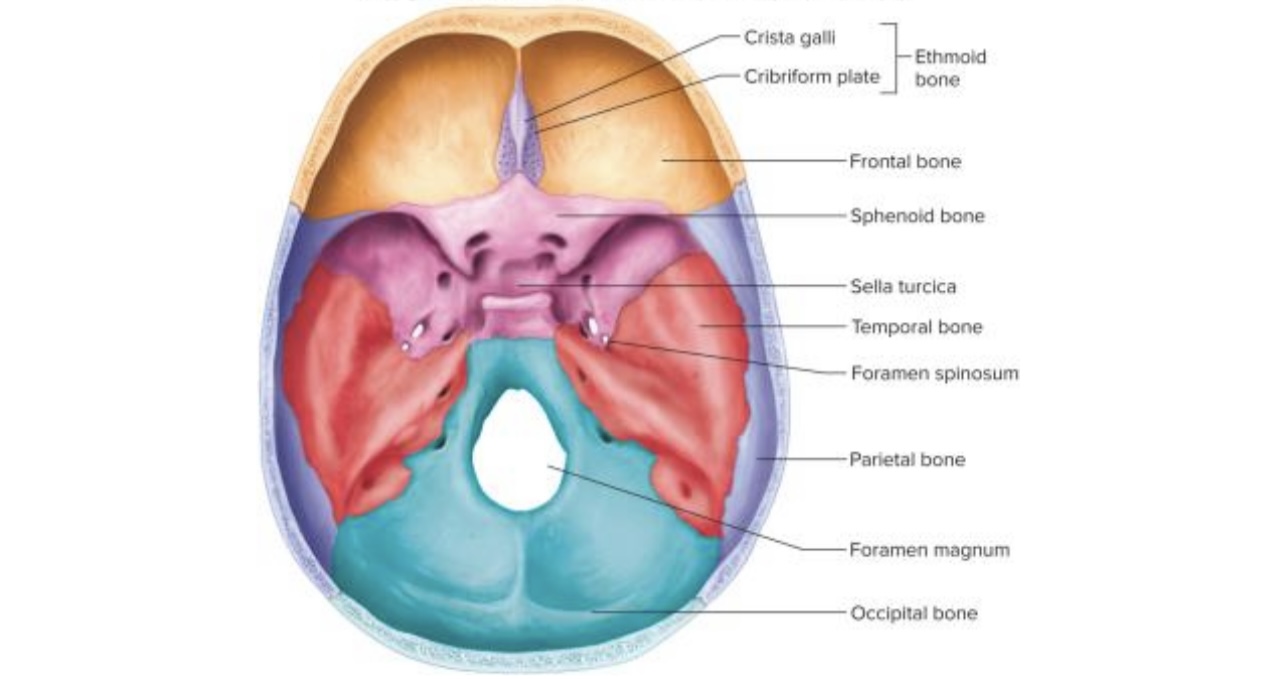
Floor of the Cranial Cavity, Viewed from Above
79
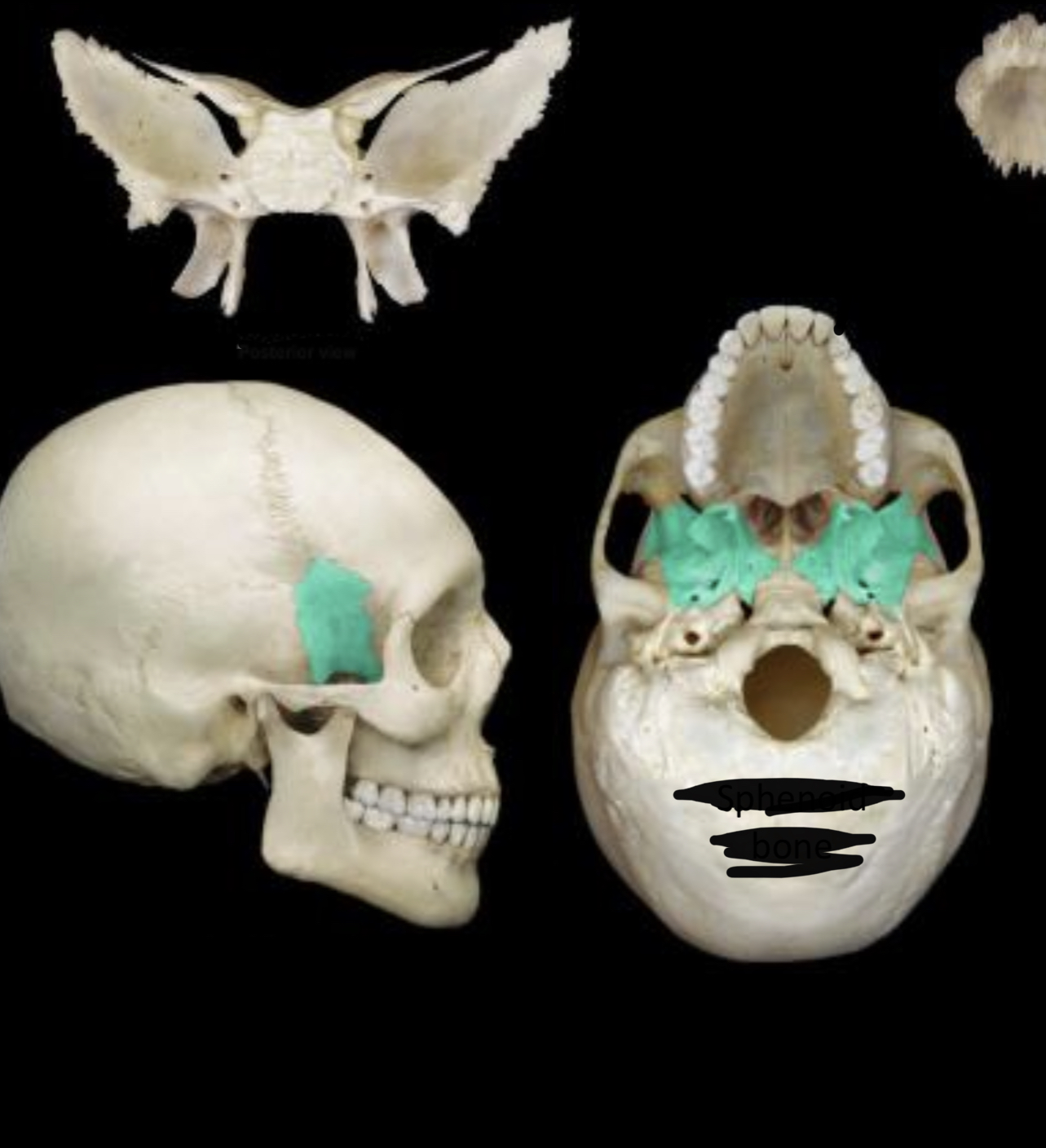
New cards
Sphenoid bone Posterior view
80
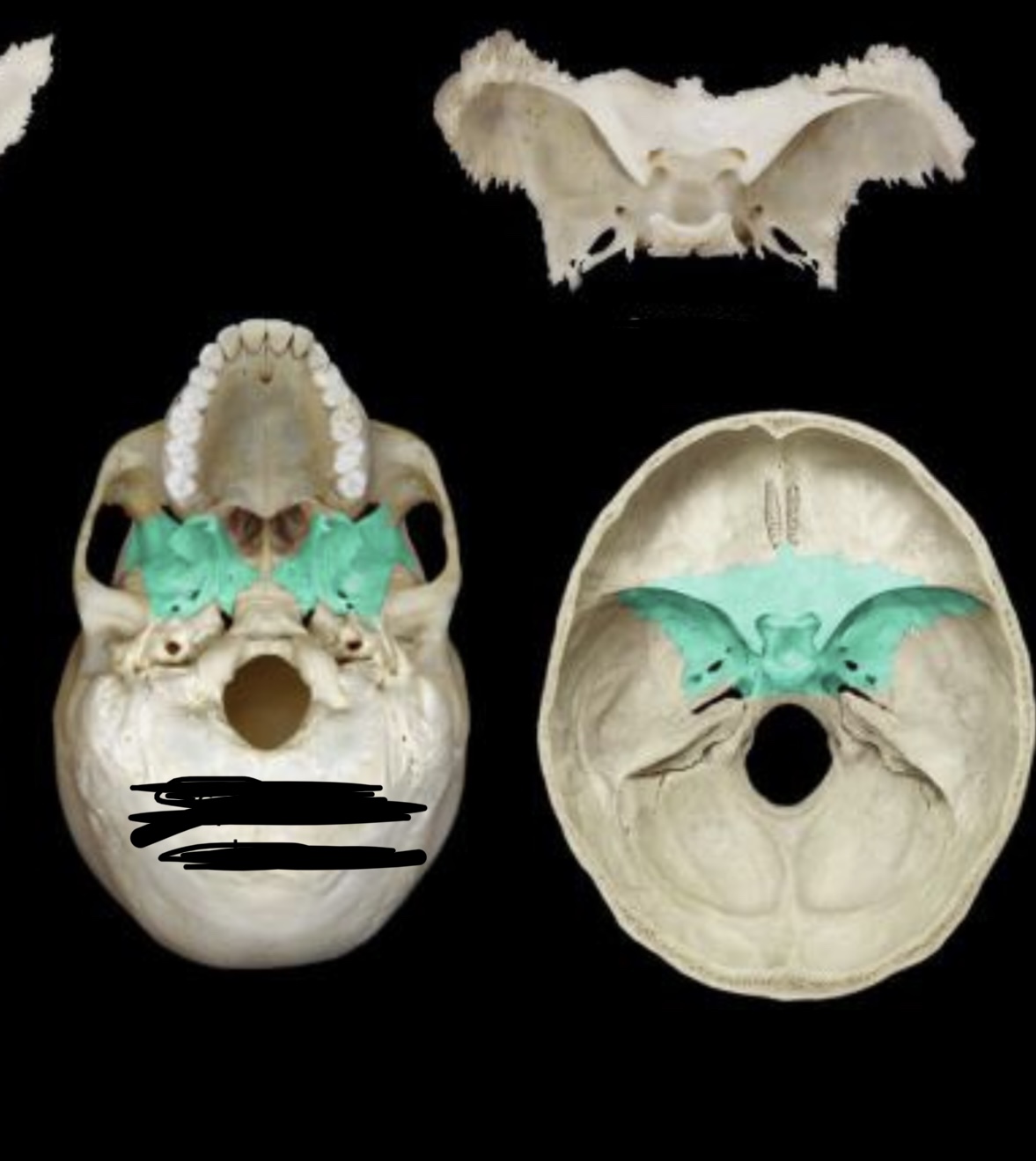
New cards
Sphenoid bone Superior view
81
New cards
Sphenoid foramina Foramen rotundum
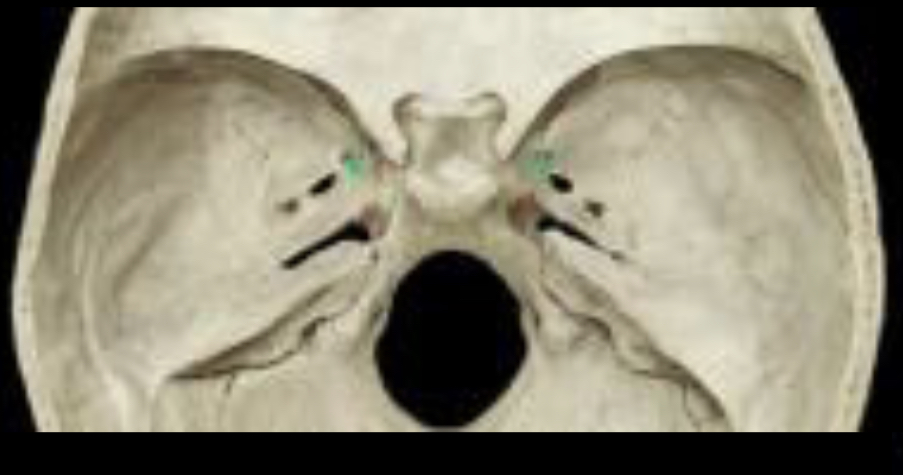
82
New cards
Sphenoid foramina Foramen ovale
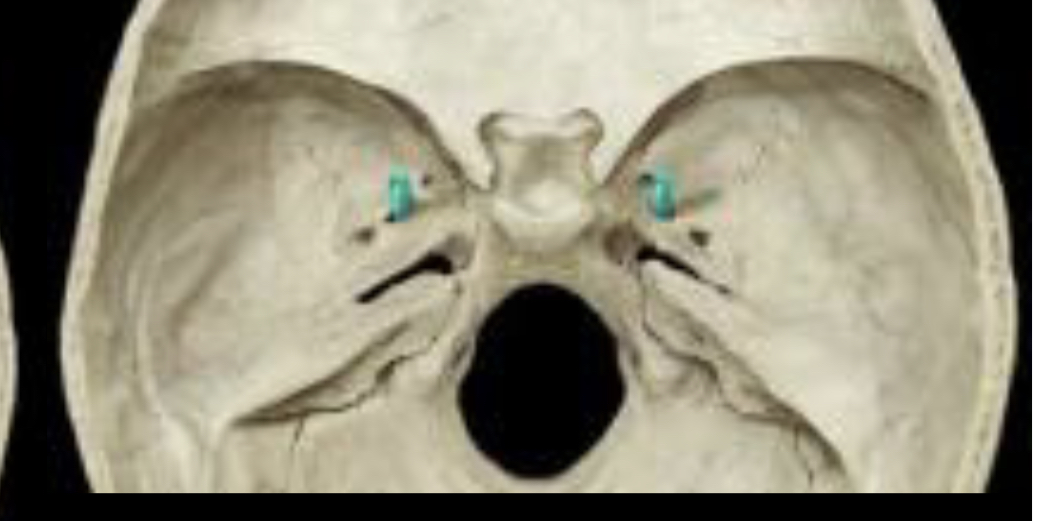
83
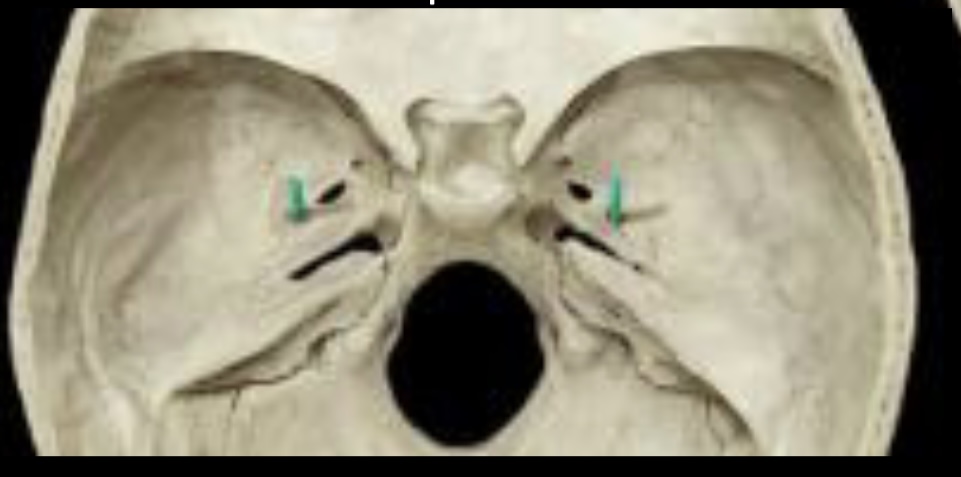
New cards
Sphenoid foramina Foramen spinosum
84
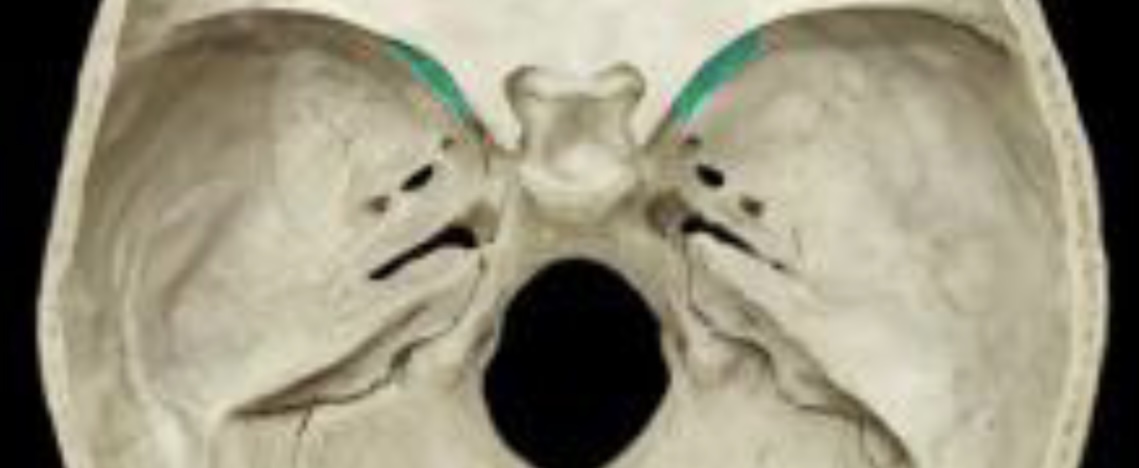
New cards
Superior orbital fissure Sphenoid foramina
85
New cards
Optic canal
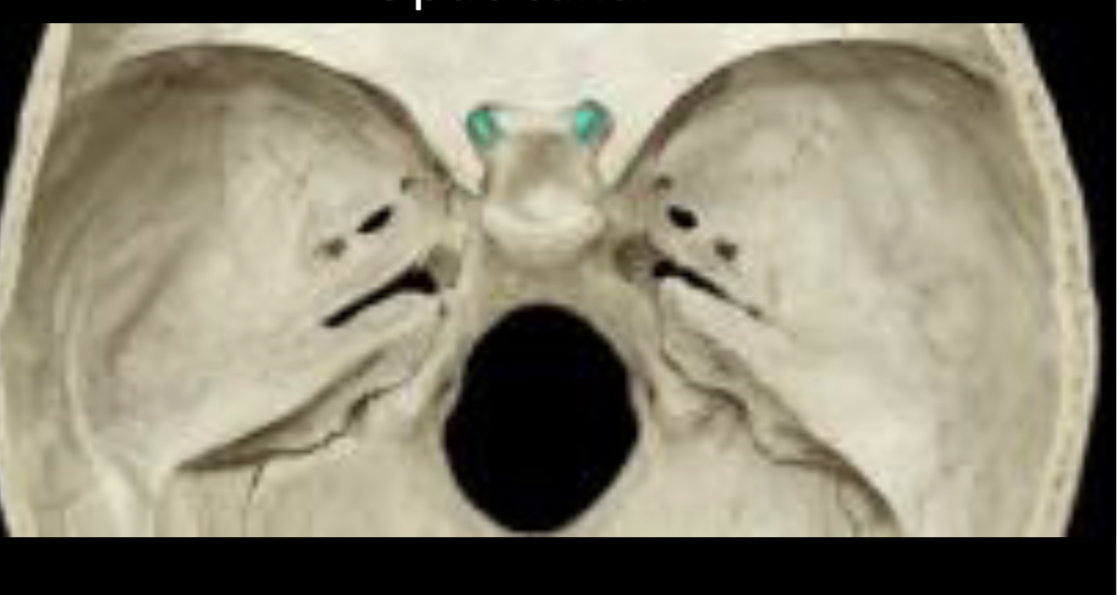
86
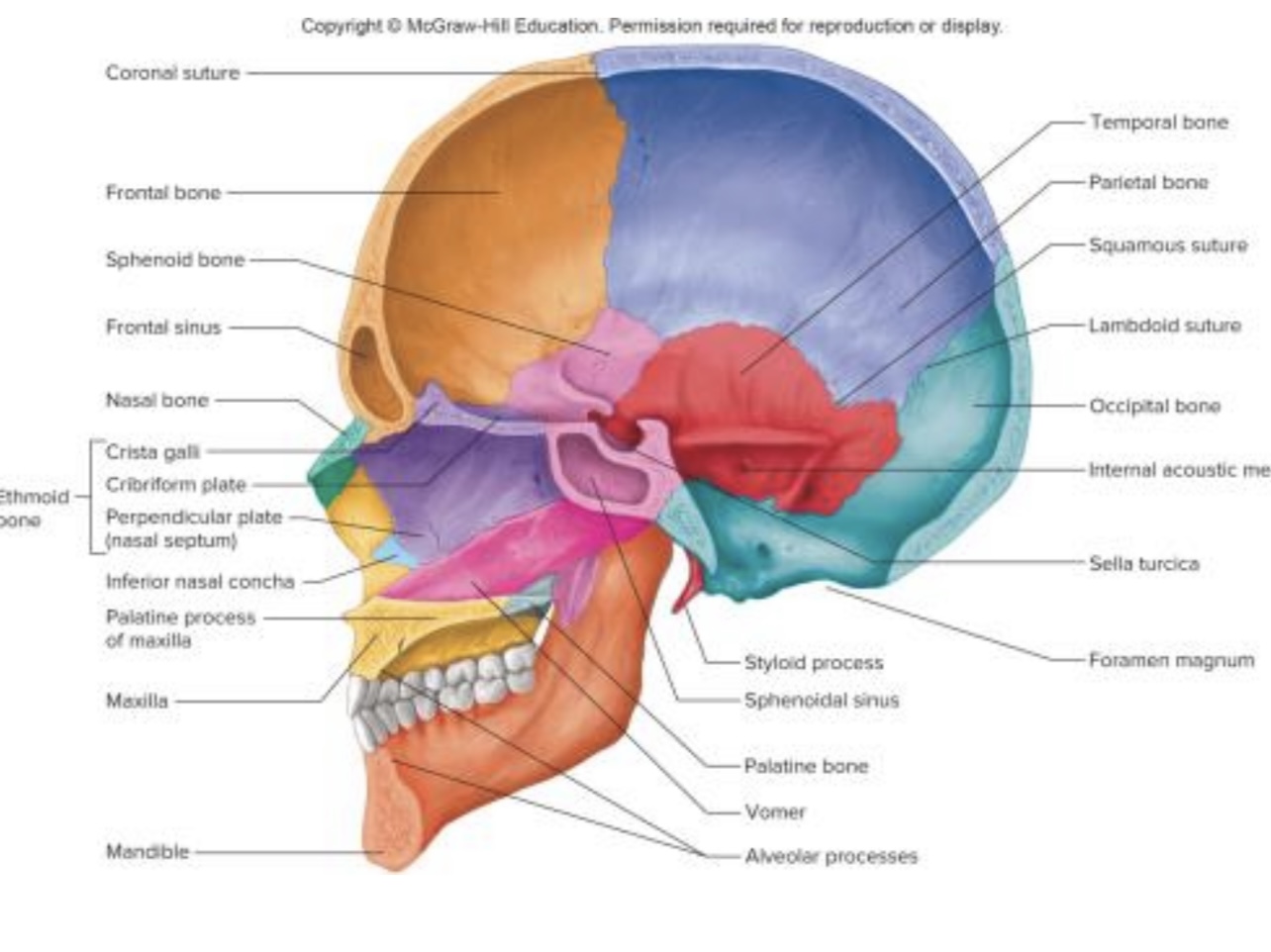
New cards
Sagittal Section of the Skull
87
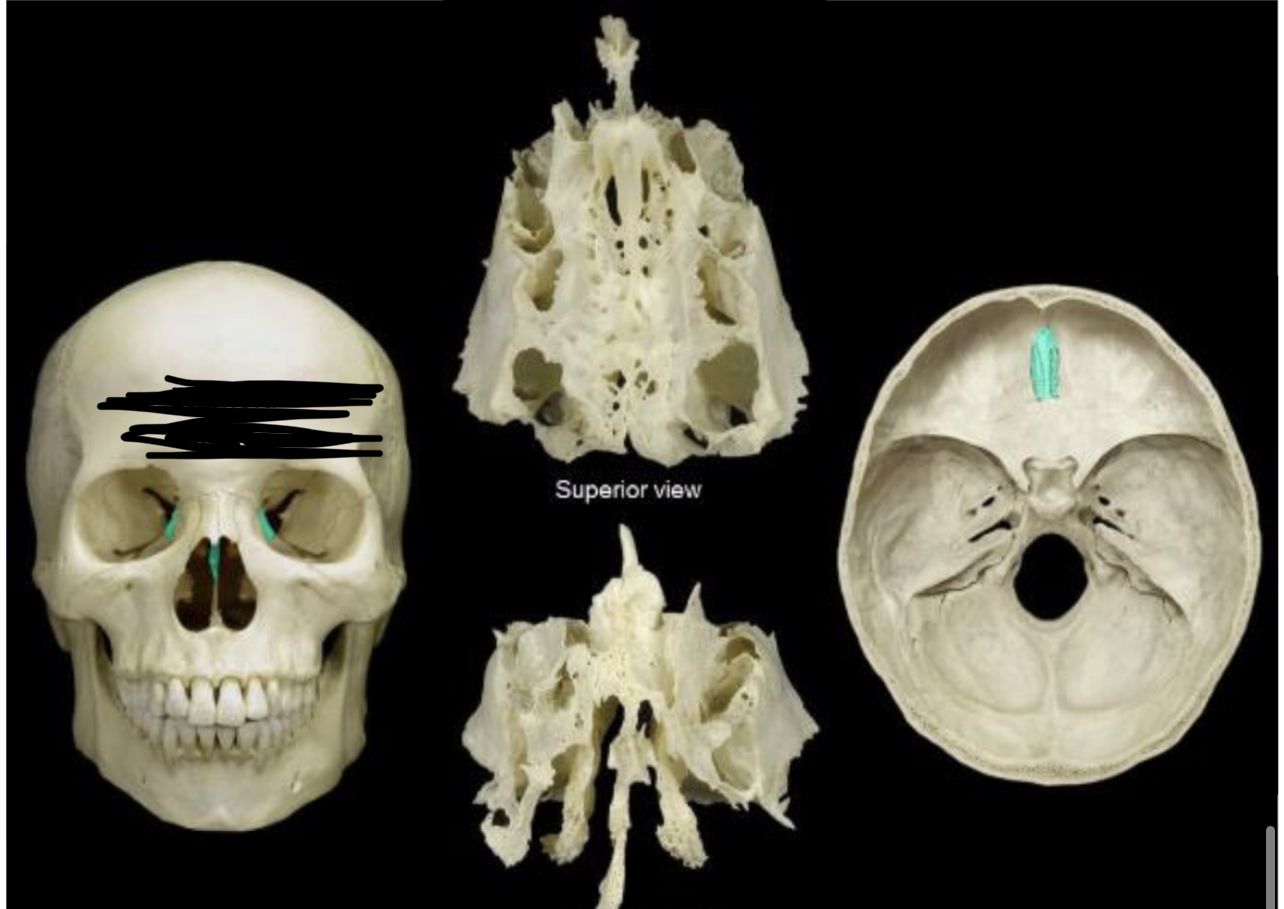
New cards
Ethmoid bone
88
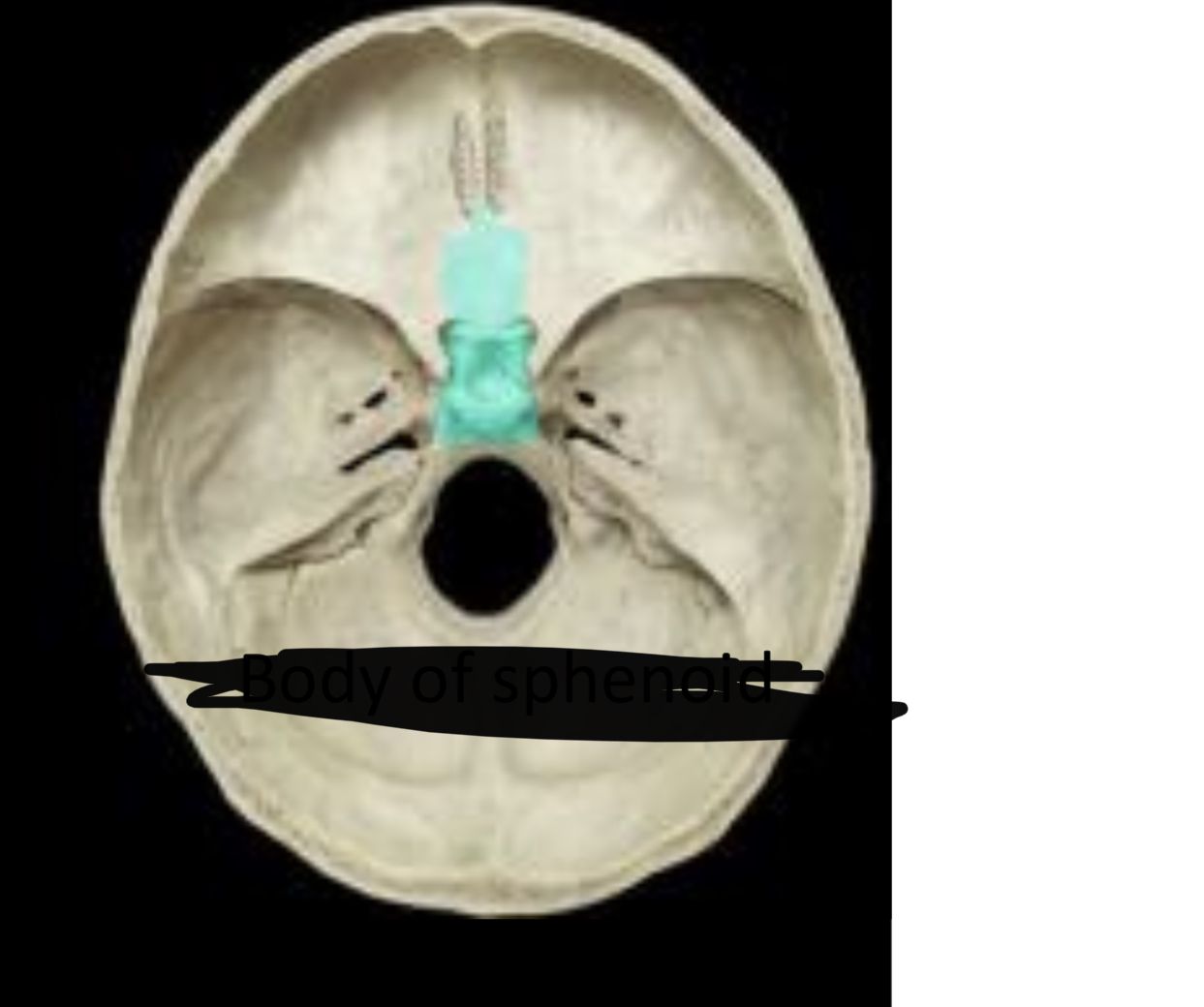
New cards
Body of sphenoid
89
New cards
Sella turcica
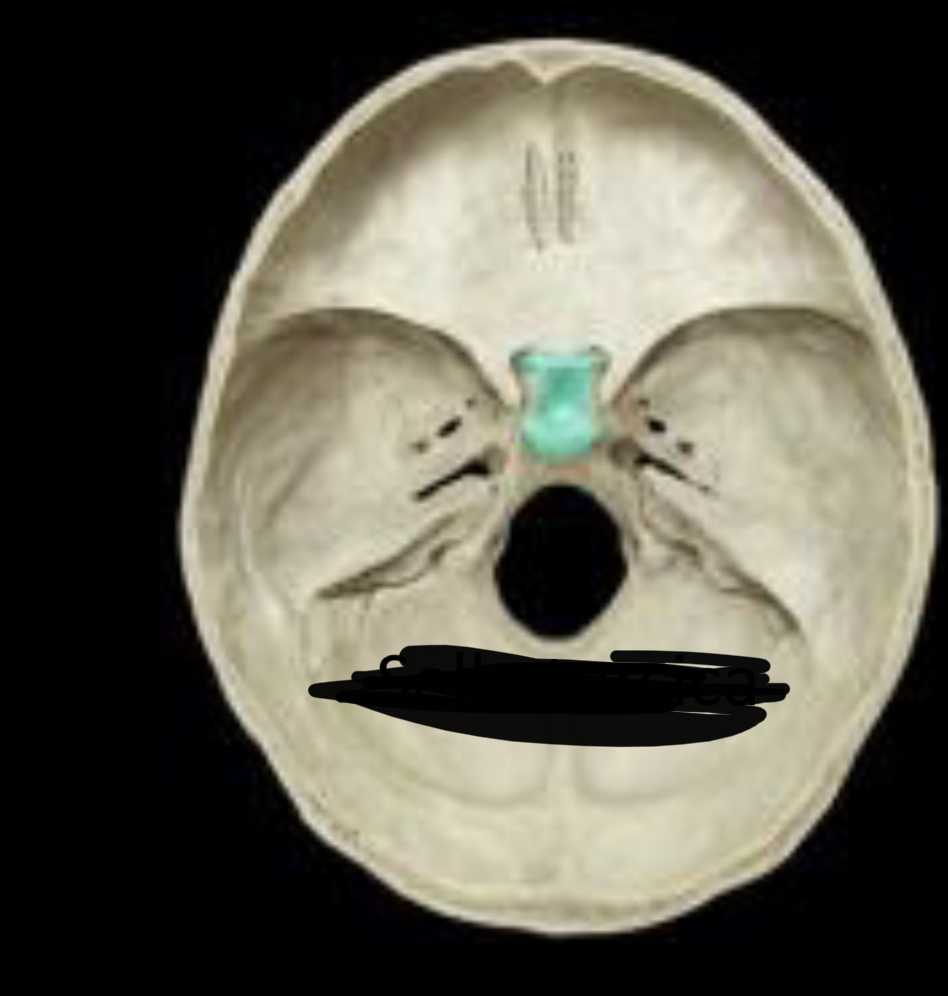
90
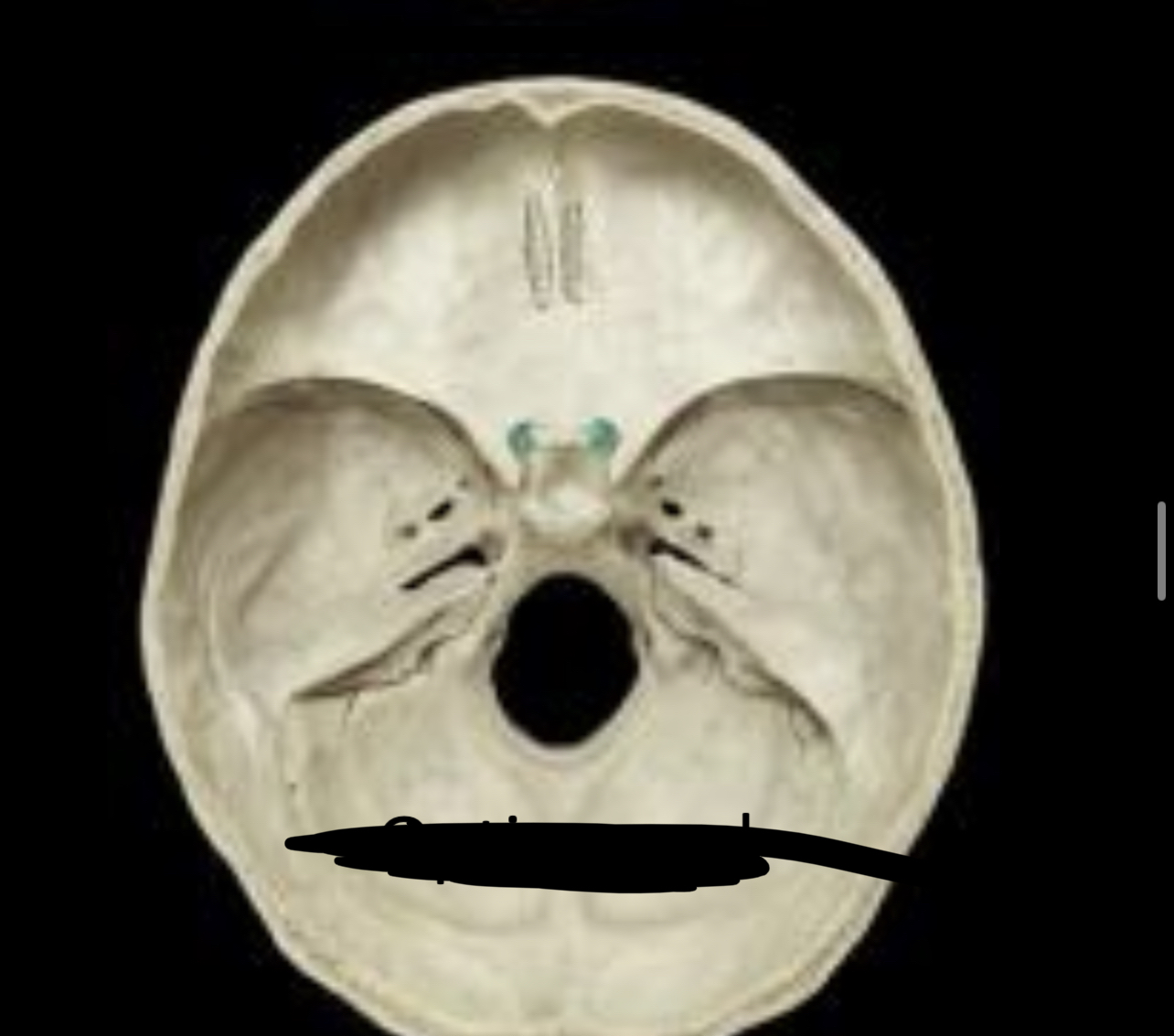
New cards
Optic canal
91
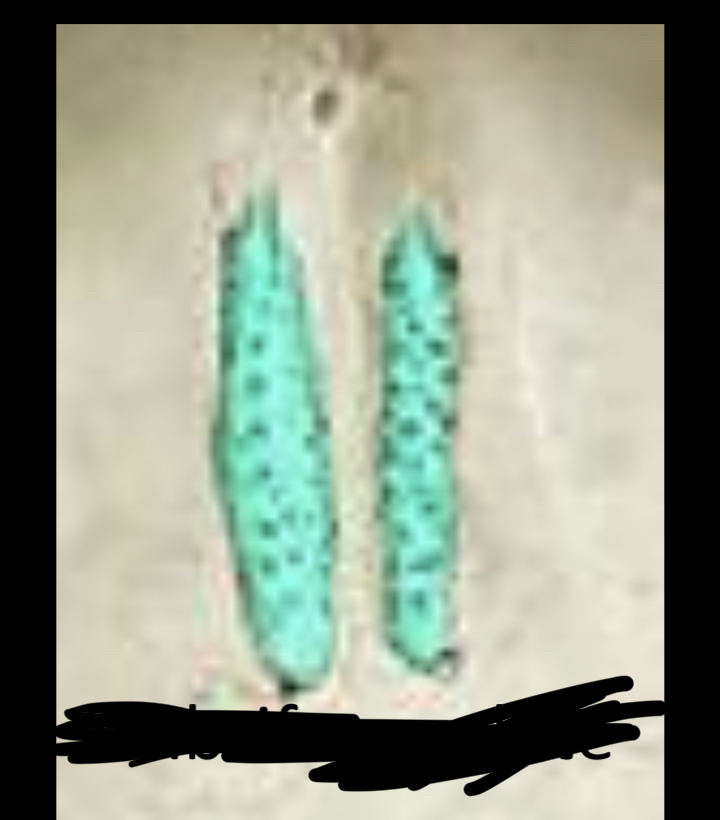
New cards
Cribriform plate

92
New cards
Crista gali
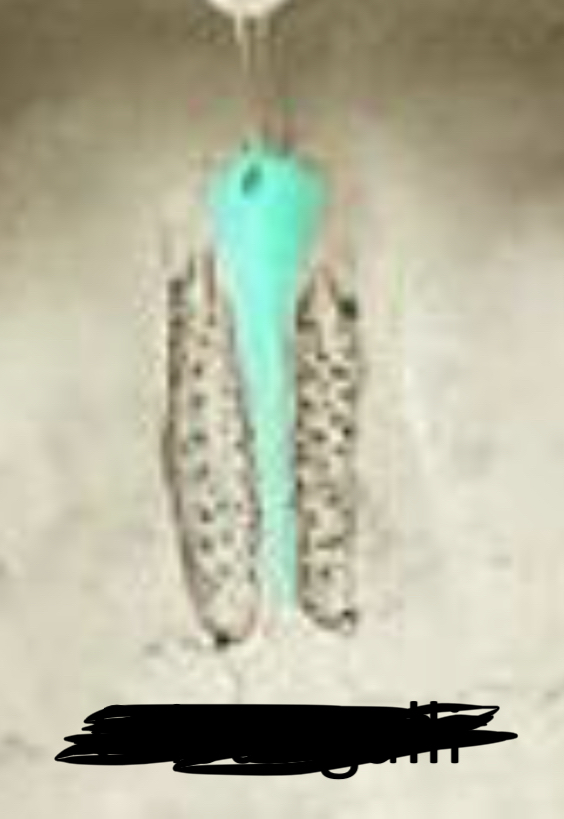

93
New cards
Maxillae
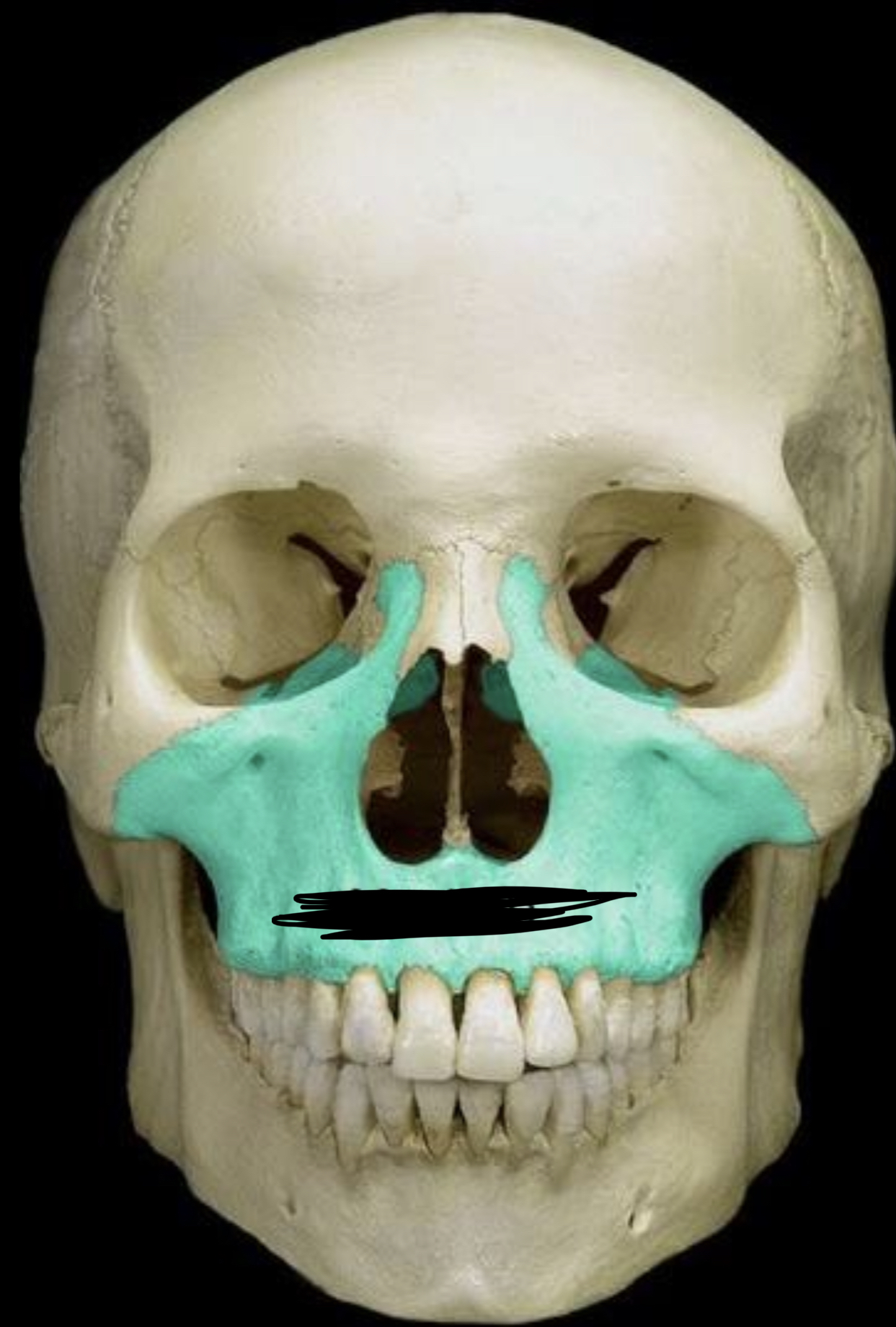
94
New cards
Maxillary teeth
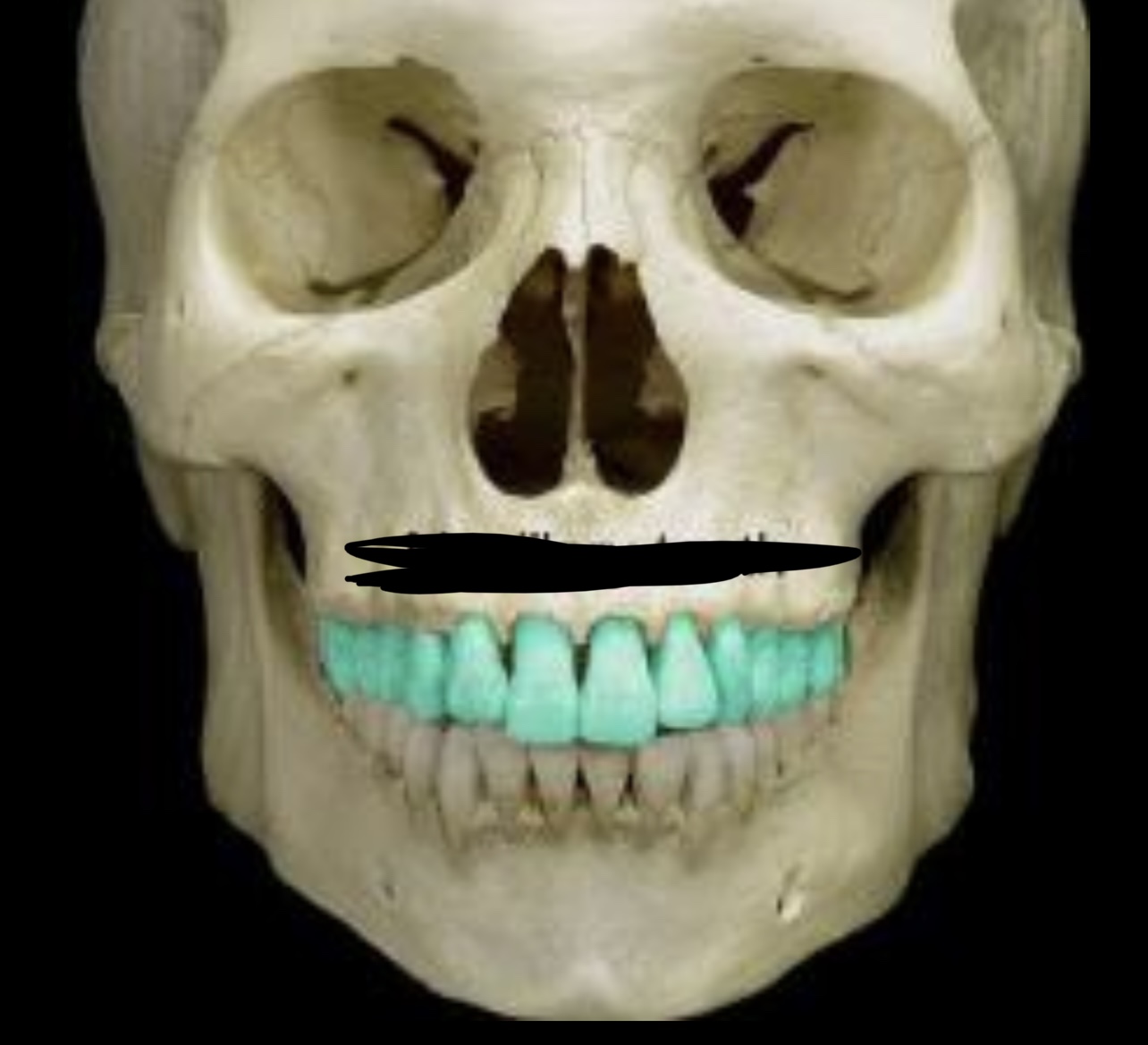
95
New cards
Infraorbital foramina
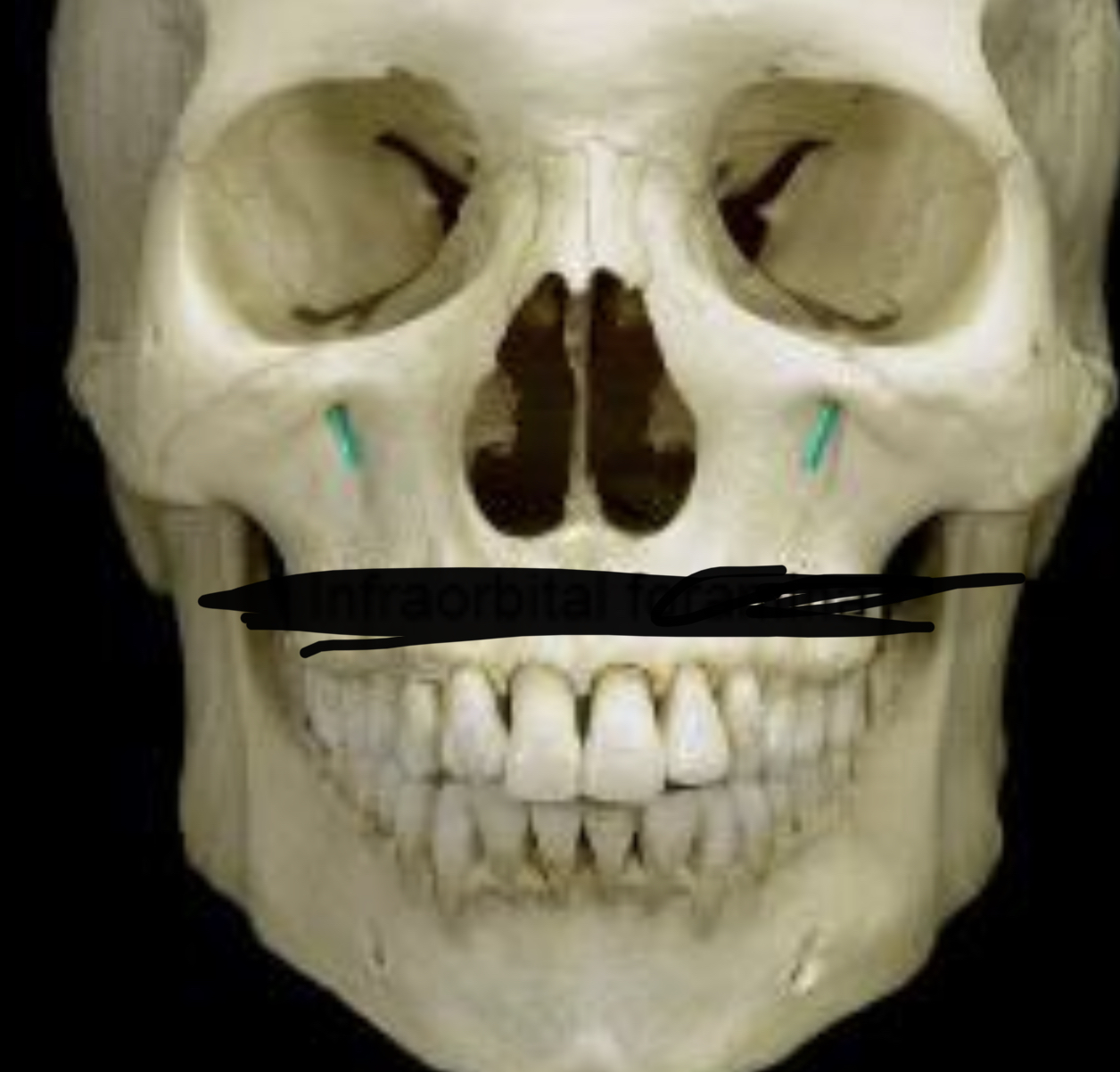
96
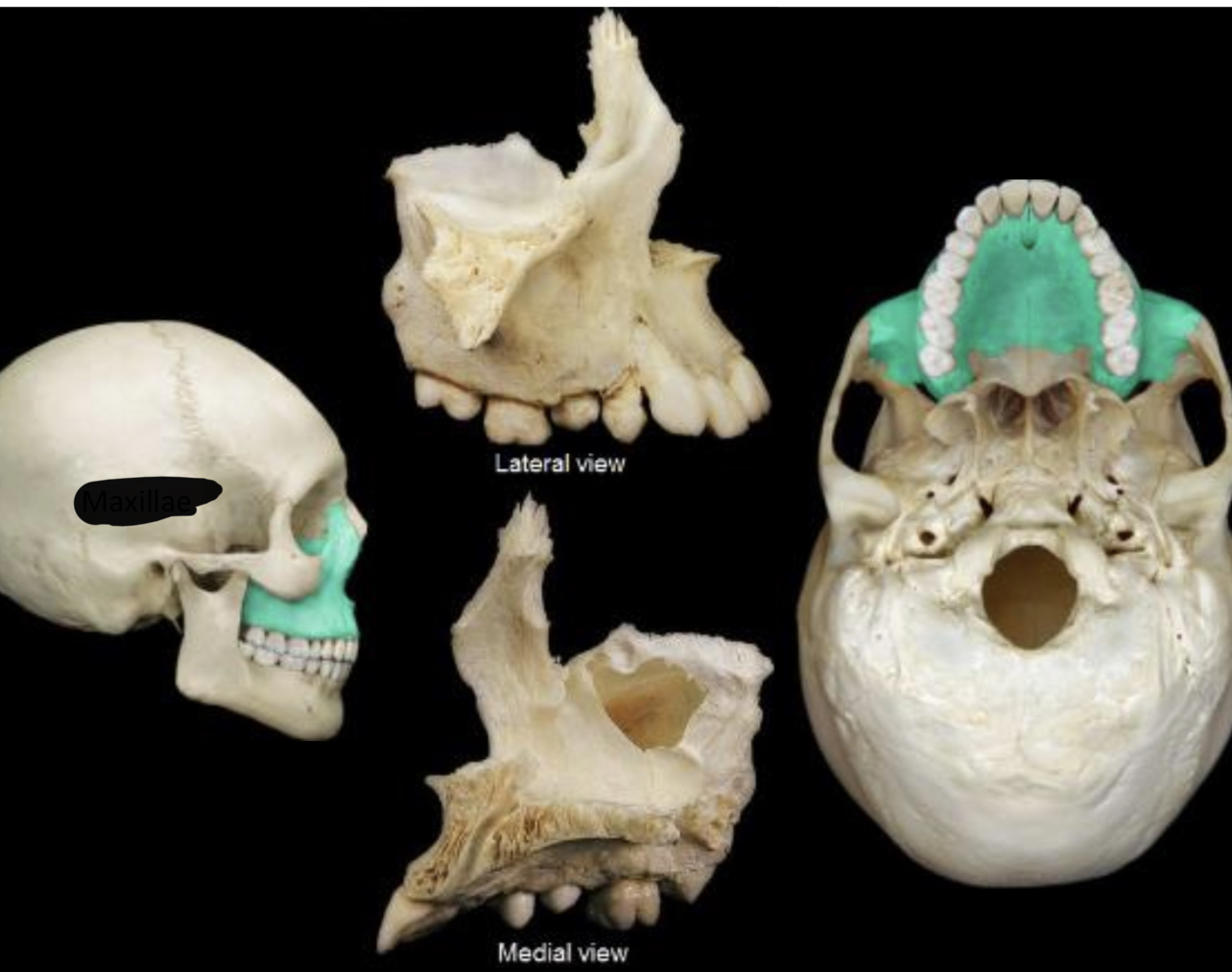
New cards
Maxillae lateral view and medial view
97
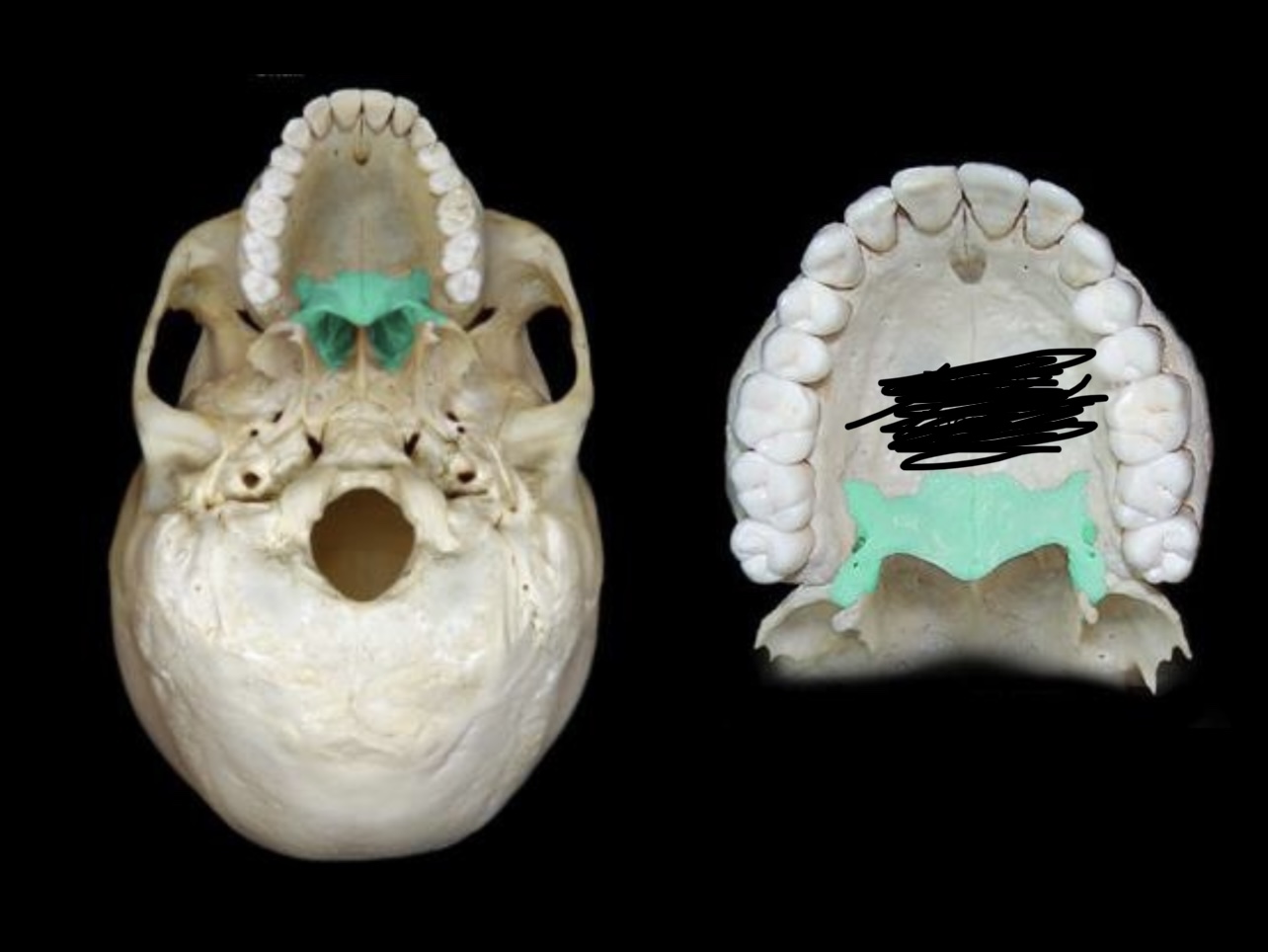
New cards
Palatine bones
98
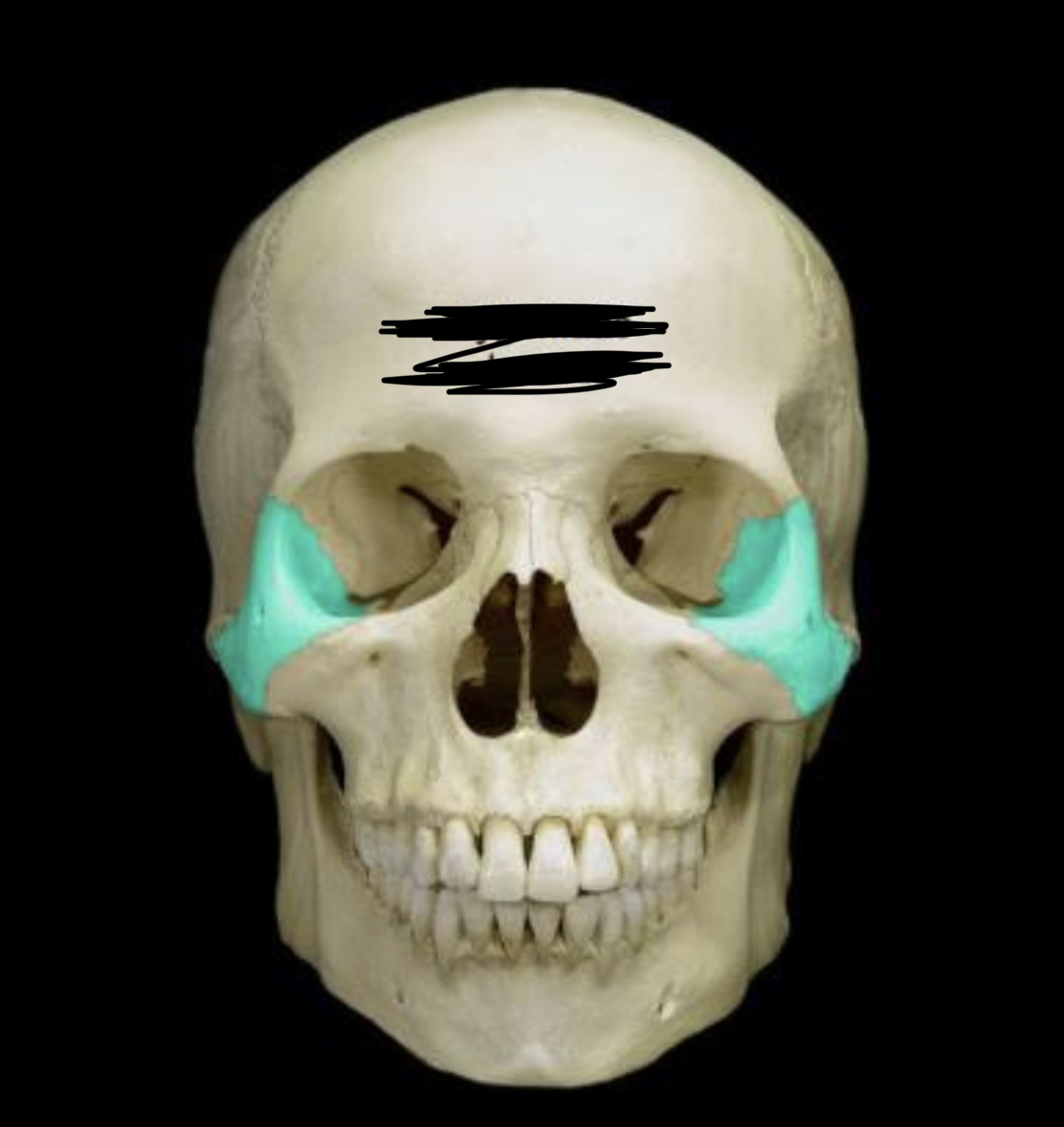
New cards
Zygomatic bones
99
New cards
Zygomatic bones
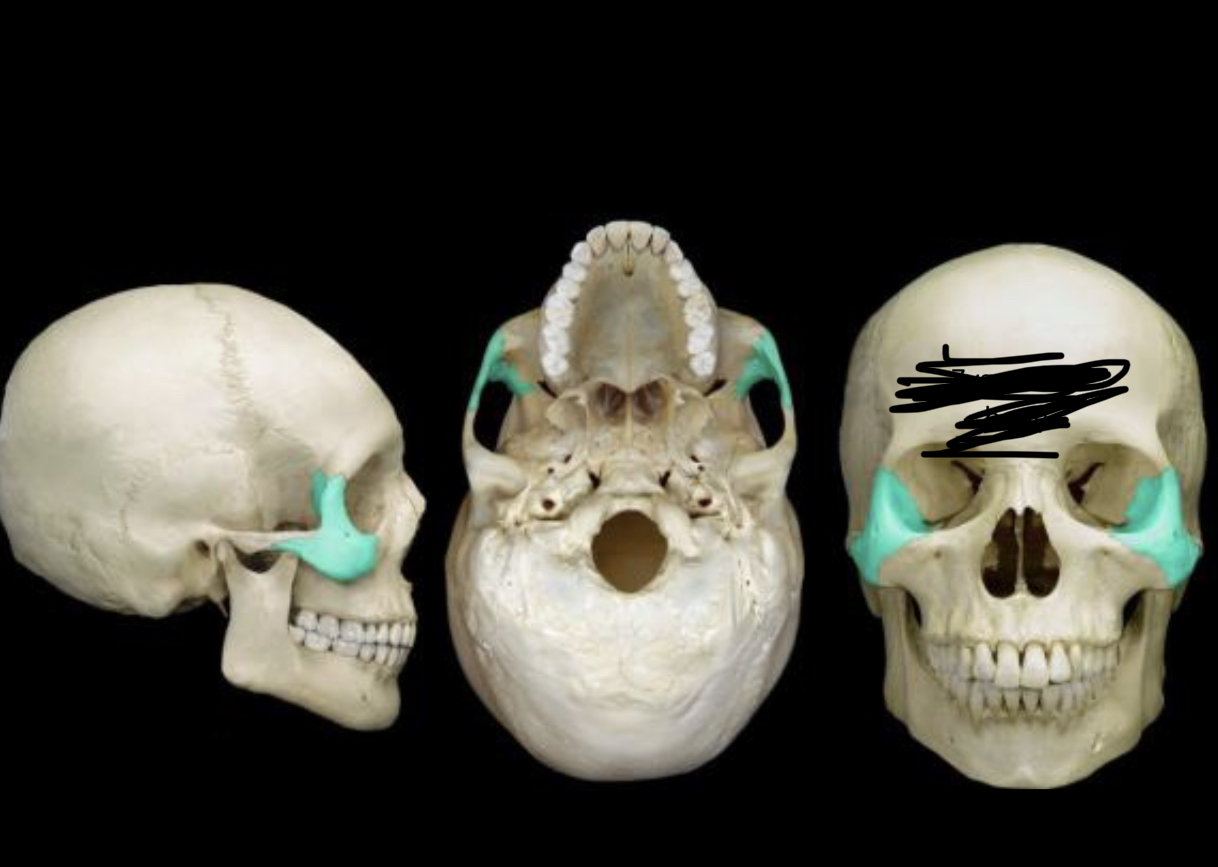
100
New cards
Lacrimal bones