Pharm 341 exam 6/13
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
b-Receptors
A family of adrenergic receptors with three known subfamilies: b1, b2, and b3.
b1 Receptor Sensitivity
Isoproterenol > Epinephrine = Norepinephrine
b2 Receptor Sensitivity
Isoproterenol > Epinephrine >> Norepinephrine
b3 Receptor Sensitivity
Isoproterenol = Epinephrine > Norepinephrine
Effect of b1 Receptor Agonist
↑heart rate, ↑muscle contraction, ↑renin secretion
Effect of b2 Receptor Agonist
Smooth muscle relaxation, bronchodilation, vasodilation, Glycogenolysis
Effect of b3 Receptor Agonist
Lypolysis
Propranolol
The first of aryloxypropanolamines and the first b-blocker for clinical use.
SAR of b-Blockers: Hydrophobic Groups
Replacement of the two –OH groups of the agonists with hydrophobic groups changes a b-agonist into a b-blocker.
SAR of b-Blockers: –OCH2- Group
The incorporation of the –OCH2- group increases potency.
SAR of b-Blockers: Hydroxyl Group Configuration
The carbon bearing the hydroxyl group is “S” configuration to be active, mimicking that of epinephrine and norepinephrine.
SAR of b-Blockers: Isopropyl or t-butyl Group
Isopropyl or t-butyl ( -C(CH3)3 ) group for b-receptor selectivity (against a-receptors).
SAR of b-Blockers: Substituents at the para- Position
Introduction of long substituents at the para- position of the aryl group offers selectivity to the b1-receptor.
Esmolol
Shortest elimination half life of 9 minutes, rapid onset, short duration of action. Effect disappears within 20-30 min after the infusion is discontinued.
Non-selective b-blockers
ortho and/or meta substitution
β1-selective b-blockers
para substitution
b-blockers with Intrinsic activity
H-bond donor at meta and/or para position
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE)
Glycoprotein in circulation, ~60kD. Protease stored in kidney. Cleaved by Renin.
Zn++
Binds to and activates the amide carbonyl for cleavage during ACE Catalysis
Captopril
First ACE inhibitor in US market
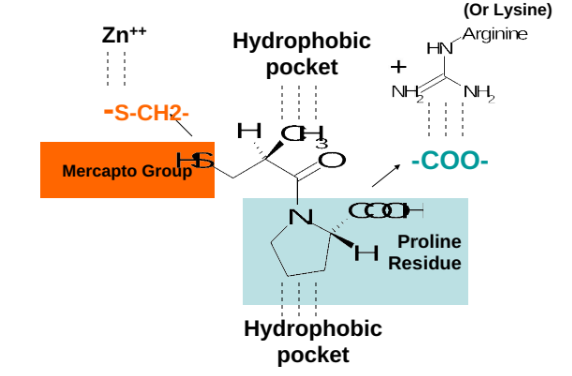
Negatively charged carboxylate group of Captopril
Binds to a positively charged lysine residue or arginine residue of ACE.
Deprotonated, negatively charged mercapto group (pKa ~ 7) of Captopril
Binds to a positively charged Zn++ ion of ACE.
Mercapto group
Replaced with a carboxylate group in new ACE inhibitors to bind to the Zinc (Eg. Lisinopril, Enalaprilat).
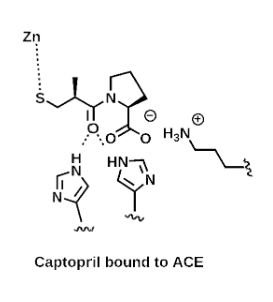
Binding of Captopril to ACE
Involves the interaction between the negatively charged carboxylate and mercapto groups of Captopril with the positively charged residues and Zn++ ion in the active site of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE).
ACE Inhibitors without Sulfur
lisinopril and enalapril, which utilize carboxylate groups for activity.
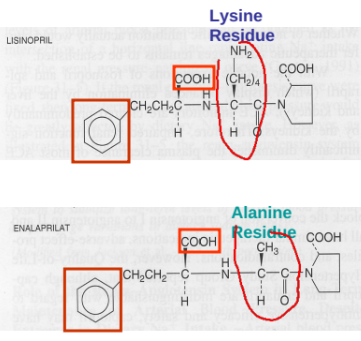
Enalaprilat
Used for i.v. injection when oral administration is not appropriate.
Benazepril, enalapril, fosinopril, moexipril, perindopril, quinapril, ramipril, and trandolapril
Are relatively inactive until converted to their corresponding di-acids.
Prodrugs
Hydrolyzed by liver esterases during oral absorption (first-pass metabolism)
Most metabolites are slowly excreted (renal or renal/fecal) with a half life of more than 10 hours
The major reason of slow elimination seems to be the tight binding of the inhibitors to ACE
Food, Antacids, Diuretics, NSAIDS, Iron salts (captopril), Tetracycline (quinapril)
An ACE inhibitor interaction
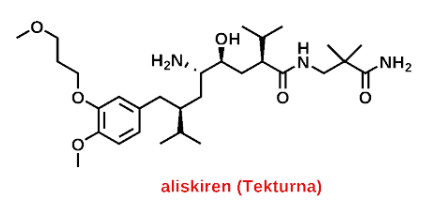
Aliskiren (Tekturna)
Renin inhibitor that reduces blood pressure by inhibiting the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). It is used in the treatment of hypertension.
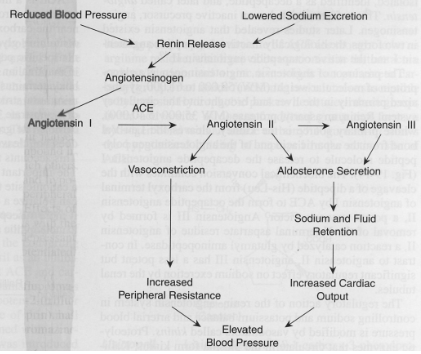
ATII Blockers and nitrates
Blockers and nitrates are the main focus.
Effects of ATII Blockers and Nitrates
Reduced Blood Pressure, Renin Release, Lowered Sodium Excretion, Vasoconstriction, Aldosterone Secretion, Sodium and Fluid Retention, Increased Peripheral Resistance, Increased Cardiac Output, Elevated Blood Pressure
Renin metabolism pathway
A biochemical pathway that regulates blood pressure, controlling the conversion of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I, and then to angiotensin II, influencing vascular tone and fluid balance.
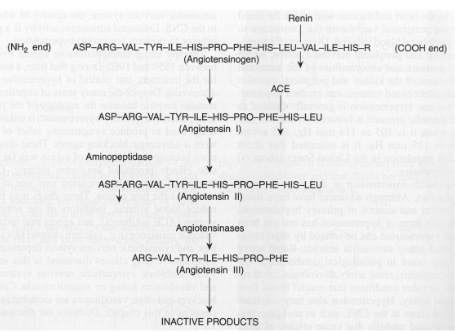
Angiotensin I
ASP-ARG-VAL-TYR-ILE-HIS-PRO-PHE-HIS-LEU
Angiotensin II
ASP-ARG-VAL-TYR-ILE-HIS-PRO-PHE-HIS-LEU
Angiotensin III
ARG-VAL-TYR-ILE-HIS-PRO-PHE
ARB Mechanism
ARB bind and inhibit angiotensin II (ATII) type 1 receptor (AT1).
AT1 Activation
causes vascular smooth muscle contraction, sodium and water retention, and aldosterone secretion.
ARBs Uses
ARBs are used to treat hypertension, heart failure, diabetic nephropathy and for patients who cannot tolerate ACE inhibitors.
Examples of ARBs
EXP3174, Valsartan, Telmisartan, Candesartan, Olmesartan, Azilsartan, Irbesartan
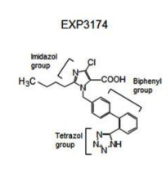
ARB SAR
Imidazole ring mimics His6 in angiotensin II. Butyl/propyl substituent mimics Ile. Biphenyl group has ortho acidic substituent (tetrazole is best).
Losartan
a Prodrug that is converted to its active form, EXP3174, in the liver. It is primarily used for hypertension and to protect against kidney damage in diabetic patients.
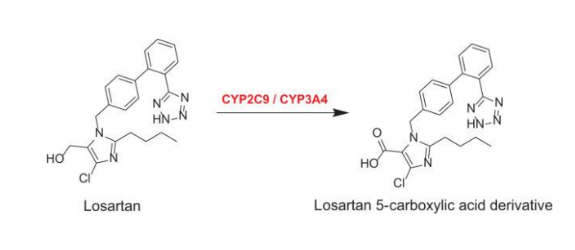
Metabolite of Losartan
Losartan 5-carboxylic acid derivative
ARBs Requiring Hydrolysis (Prodrugs)
Olmesartan medoxomil, Candesartan cilexetil, Azilsartan medoxomil
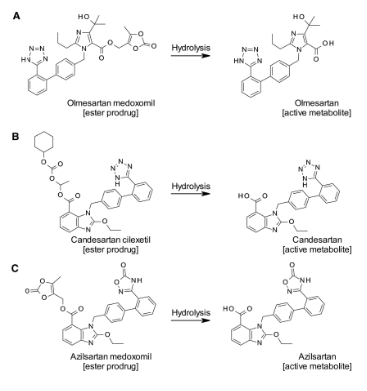
Active Metabolite ARBs
Olmesartan, Candesartan, Azilsartan
ARBs Characteristics
Highly variable bioavailability, high protein binding, primarily fecal elimination unchanged, Interactions with other antihypertensive drugs, contraindicated in pregnancy/nursing.
Organic nitrates
Nitroglycerin, Isosorbide dinitrate, Pentaerythrityl tetranitrate, Isosorbide mononitrate, Amyl nitrite, Sodium nitroprusside, Nicorandil
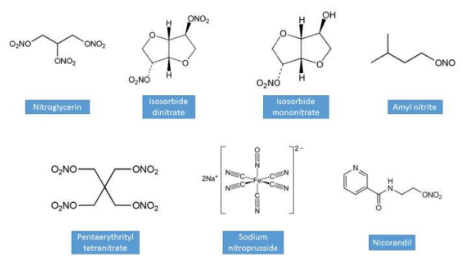
Organic nitrate mechanism & use
Prodrugs for nitric oxide (NO). Causes relaxation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Decreases cardiac preload and increases coronary blood flow. Used for treating angina (prophylactic and acute), hypertension, and heart failure. Nitrate tolerance can develop.
Organic nitrates Characteristics
Lipophilic nitrate esters, are very well absorbed, has a wide variety of dosage forms, metabolically activated to deliver NO and has interactions.
Big Picture
These drugs act on renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system (RAAS) or generate nitric oxide directly. DDIs with each other or diuretics can be beneficial or harmful. They have similar mechanism-based DDIs
Ejection Fraction
The percentage of blood pumped out of the left ventricle with each contraction; normal is around 60%.
cardiac myocyte contraction and relaxation
are influenced by various factors including calcium levels, neurohormonal activation, and heart rate.
myocytes during contraction
extracellular Ca enters cardiac myocyte through calcium voltage channels
this triggers calcium release from sarcoplasmic reticulum
increased calcium concentration causes myofibril contraction with the actin-troponin-tropomyosin system.
myocytes during relaxation
sodium/calcium channels extrude calcium from the cytosol by using the Na gradient.
sodium pump maintains sodium gradient my extruding sodium and entering potassium into the cell, keeping the cells HYPERPOLARIZED
sarco-endoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase pump is activated by intracellular calcium and reuptake into SR. this pump helps maintain free cytoplasmic calcium at very low levels during diastole by pumping calcium into the SR
pathophysiology of heart failure
refers to the functional changes and mechanisms in the heart that lead to its inability to pump blood effectively, often due to structural heart disease, abnormalities in myocyte function, and neurohormonal activation.
vicious cycle of heart failure progression
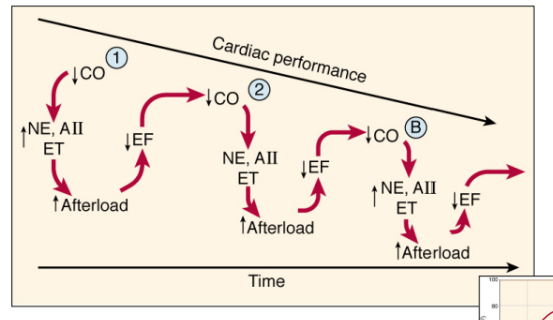
Preload
The volume of blood coming into the ventricles (EDV).
Afterload
Resistance to left ventricle ejection (increased in vasoconstriction).
Cardiac Output (CO)
Volume of blood pumped out (ejected) by heart each minute. CO = SV x HR.
Stroke Volume (SV)
The volume of blood pumped out of the ventricle in a single beat.
positive inotropic effects
Increased force of heart contraction, improving cardiac output.
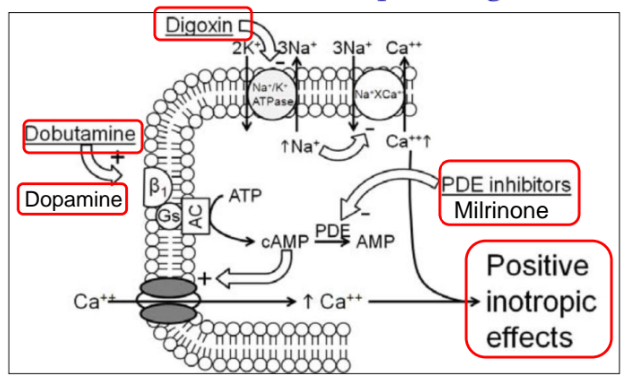
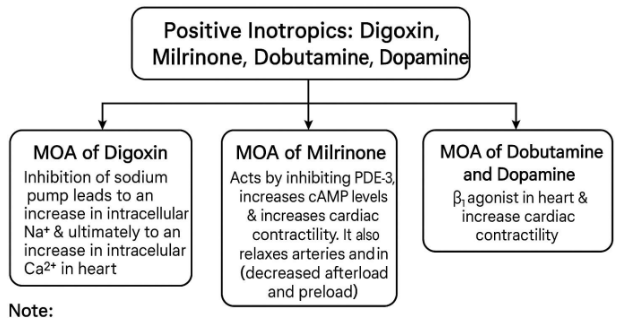
Digitalis (Digoxin)
A positive inotropic cardiac glycoside that inhibits the Na+/K+-ATPase pump, leading to increased intracellular Na+ and Ca2+.
can cause abnormal cardiac automaticity/arrhythmias!
digoxin effects on other organs
affect all excitable tissues, including smooth muscle and CNS
GI effects: anorexia, vomiting, and diarrhea
Milrinone
A phosphodiesterase-3 inhibitor that increases myocardial contractility and causes vasodilation, leading to improved cardiac output and reduced afterload.
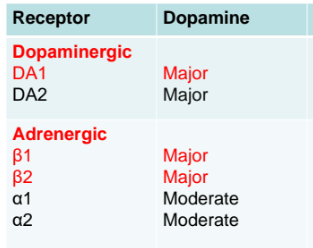
dopamine receptors
are G-protein coupled receptors that mediate the effects of dopamine, influencing cardiovascular function and renal blood flow.
interactions with potassium and digoxin
Potassium levels affect digoxin's action; high potassium can reduce its efficacy, while low potassium increases the risk of toxicity.
affect of hypercalcemia and digoxin
Hypercalcemia can increase digoxin's effects, potentially leading to toxicity and arrhythmias due to enhanced intracellular calcium levels.
interactions with calcium and magnesium with digoxin
Calcium and magnesium levels can influence digoxin's pharmacodynamics; high calcium can increase digoxin effects, while low magnesium can enhance toxicity risk.
Dobutamine
A positive inotropic selective β1 adrenergic agonist that increases cardiac contractility and heart rate.
Dopamine
A positive inotropic adrenergic agonist (β1 and β2) used in acute heart failure to increase cardiac contractility.
Loop Diuretics
Drugs that block the reabsorption of sodium and chloride in the loop of Henle, reducing preload.
ACE Inhibitors
Drugs that reduce angiotensin II production, decreasing peripheral vascular resistance and afterload.
Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs)
Drugs that block the action of angiotensin II, similar to ACE inhibitors, reducing afterload and preload.
Vasodilators (Nitrates)
Drugs that dilate veins, decreasing preload.
Vasodilators (Hydralazine)
A drug that dilates arterioles, decreasing afterload.
Vericiguat
A guanylyl cyclase (GC) stimulator that increases cGMP, promoting vasodilation and positive remodeling.
Beta Blockers
Drugs that slow heart rate, reduce blood pressure, and improve survival in heart failure by inhibiting catecholamine cardiotoxicity.
Sacubitril/Valsartan (Entresto)
A combination drug that inhibits neprilysin and blocks angiotensin receptors, leading to vasodilation and enhanced diuresis.
SGLT2 Inhibitors
Drugs like dapagliflozin and empagliflozin that promote diuresis and natriuresis, reducing blood volume and preload.
Attruby
A transthyretin stabilizer indicated for the treatment of cardiomyopathy of wild-type or variant transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis (ATTR-CM).
Neprilysin
An enzyme responsible for degrading natriuretic peptides.
positive inotropic pathway and mechanism
increased calcium influx that enhances cardiac contractility.