Hole's Anatomy and Physiology: Chapter 2: Chemistry
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Isotopes
-atom with the same atomic numbers but with different atomic weights
-atoms with the same number of protons and electrons * but a different number of neutrons*
Ion
-an atom that gains or loses electrons to become stable
-an electrically charged atom

Ionic Bond
A chemical bond resulting from the attraction between oppositely charged ions.
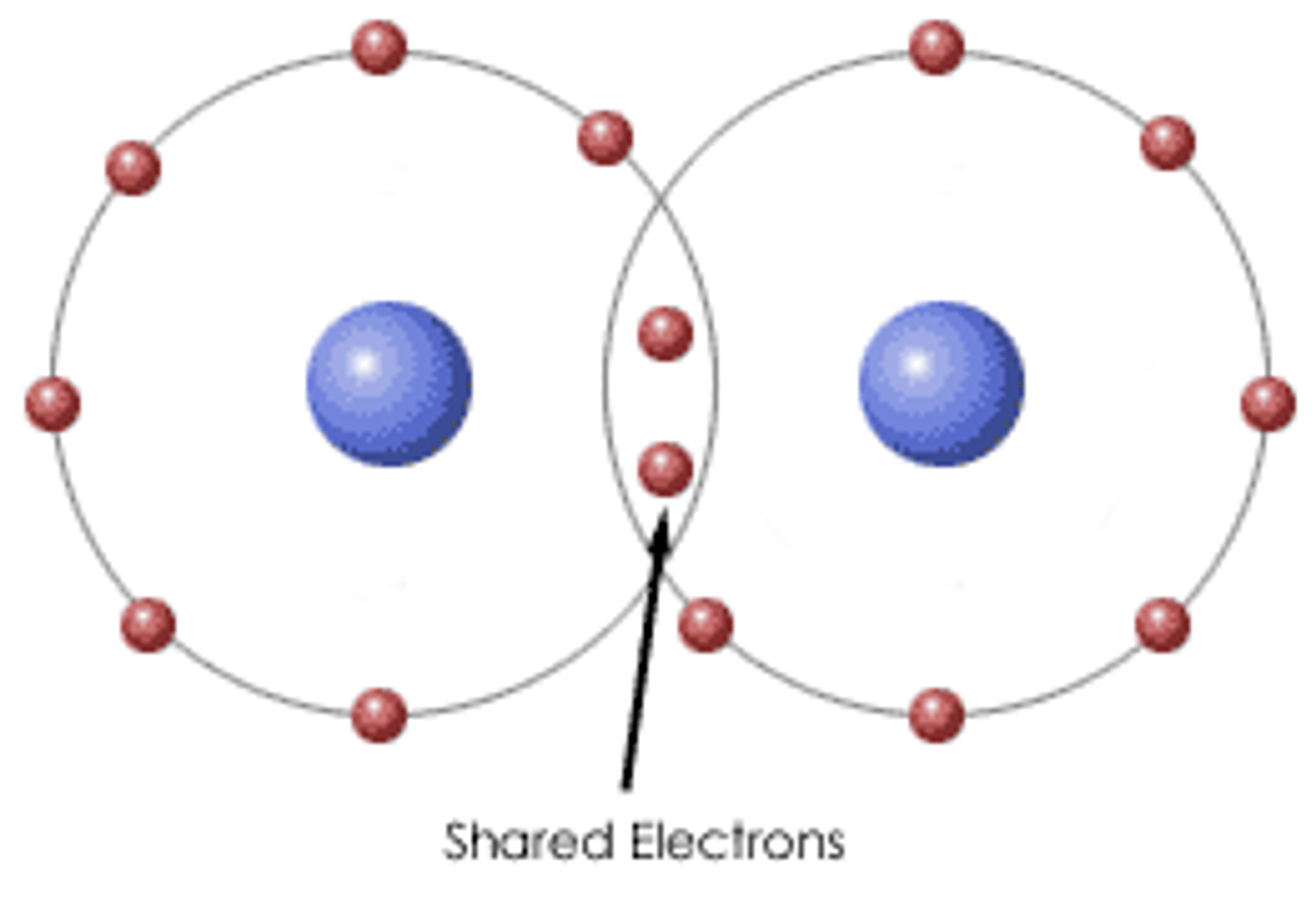
Covalent Bonds
formed when atoms share electrons
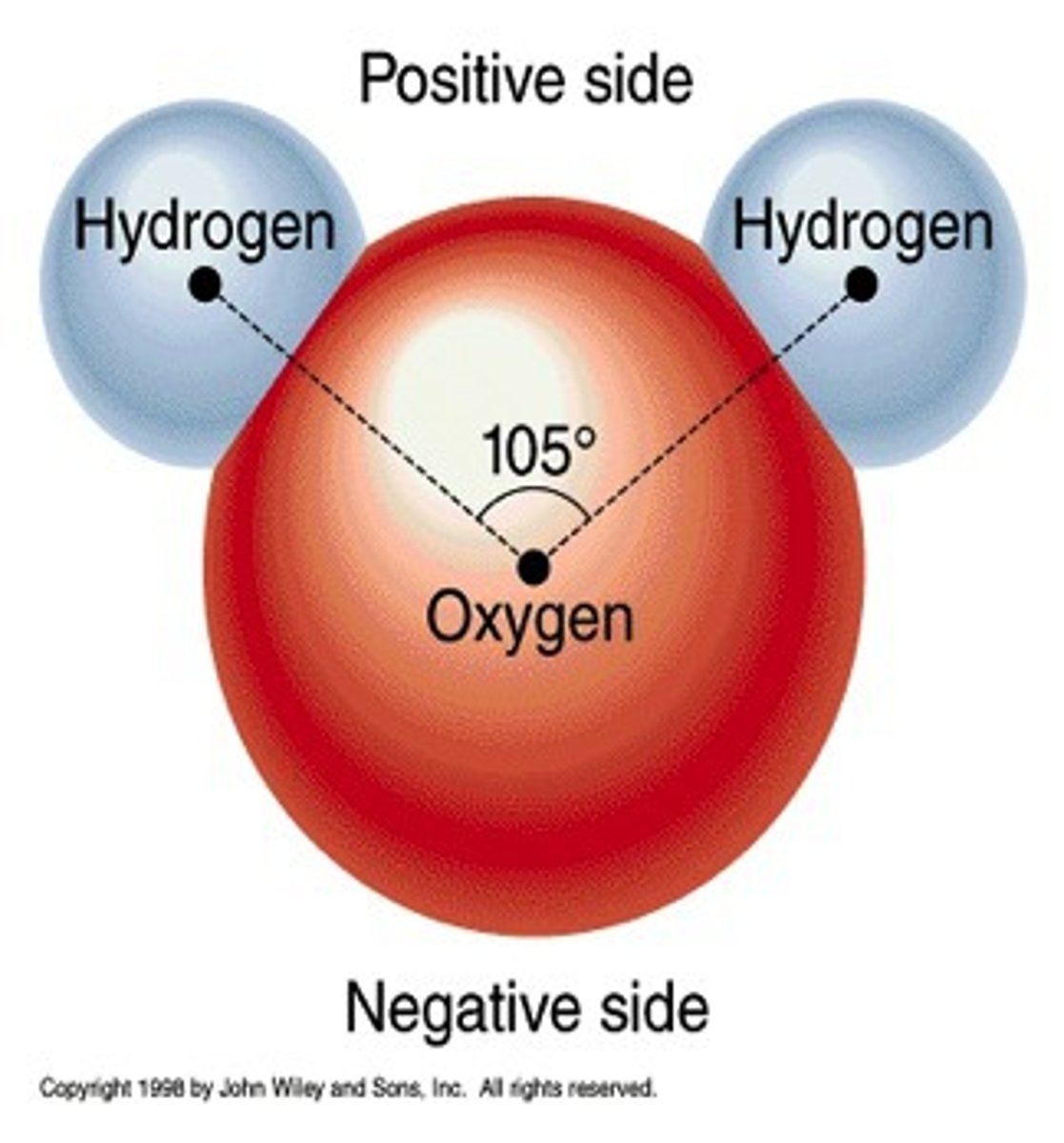
Polar molecules
-molecules with a slightly negative end and slightly positive end
-Result when electrons are not shared equally in covalent bonds
pH scale
indicates the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution

Acidic
pH less than 7, indicates a greater concentration of H+
Basic or alkaline
pH greater than 7, indicates a greater concentration of OH-
Buffers
homeostatic mechanisms help regulate pH
-chemicals which act to resist pH changes
Organic molecules
-contain C (carbon) and H (hydrogen)
-usually larger than inorganic molecules
-dissolve in water and organic liquids
-carbohydrates, proteins, lipids,and nucleic acids
Inorganic molecules
-generally do not contain C (carbon) and H (hydrogen)
-usually smaller than organic molecules
-usually dissociate in water, forming ions
-water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and inorganic salts
Water
-most abundant compound in living material
-2/3 of the weight of an adult human
-major component of all body fluid
-medium for most metabolic reactions
-important role in transporting chemicals in the body
-absorbs and transport heat
Oxygen (O2)
-used by organelles to release energy from nutrients in order to drive cell's metabolic activities
-Necessary for survival
Sources of neccessary ions
(Na+, Cl-, K+, Ca2+, )
bio- (biochemistry)
life
di- (dissacharide)
two
lip- (lipids)
fat

mono- (monosaccharide)
one
poly- (polysaccharide)
many
sacchar- (monosaccharide)
sugar

Biochemistry
chemistry of living organisms
carbohydrates
-provide energy to cells
-supply materials to build cell structure
-water-soluble
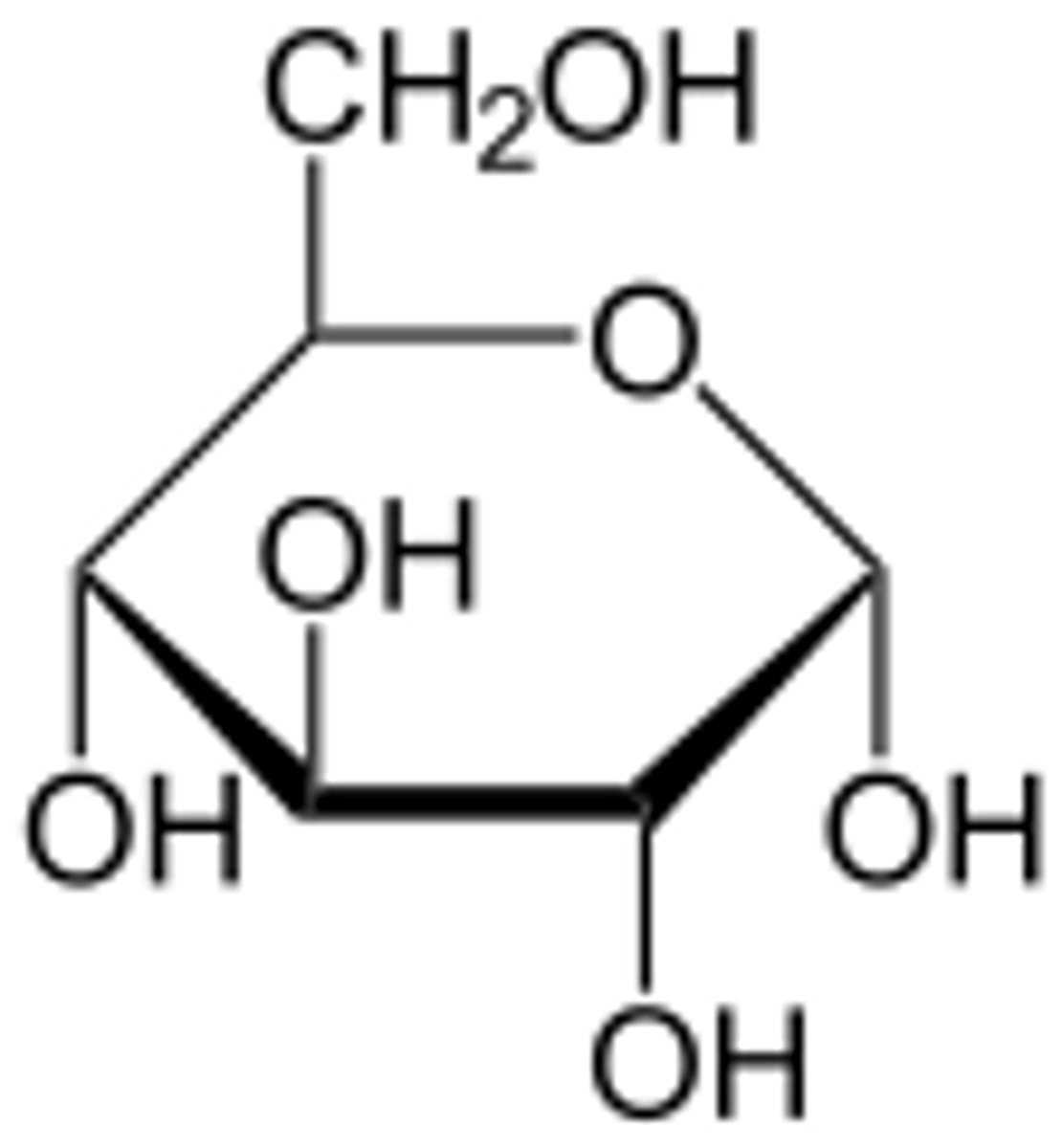
Carbohydrates contain
C (carbon) H (hydrogen) and O (oxygen)
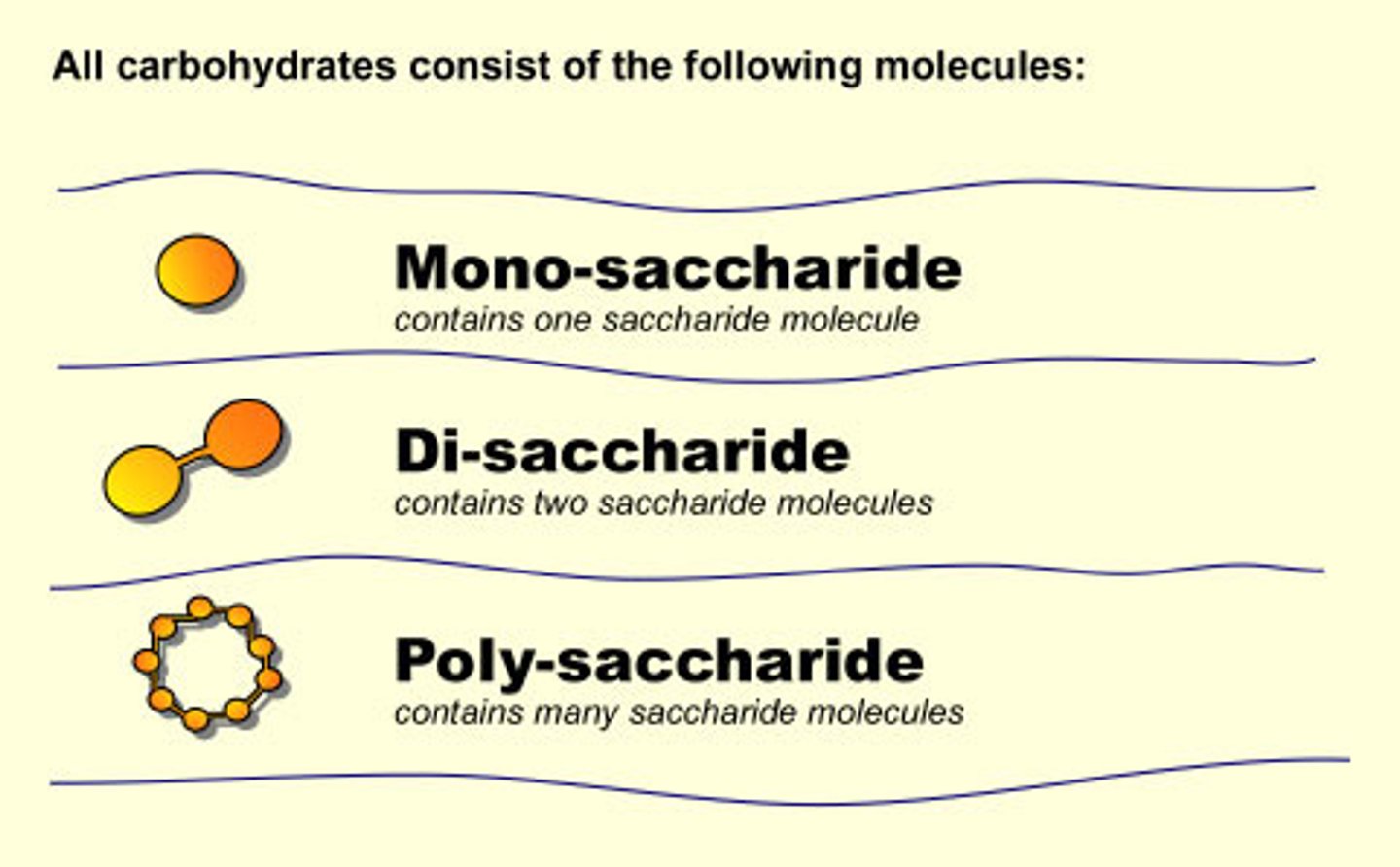
Three categories of CHOs
-monosaccharides
-disaccharides
-polysaccharides
Monosaccharides
glucose
fructose
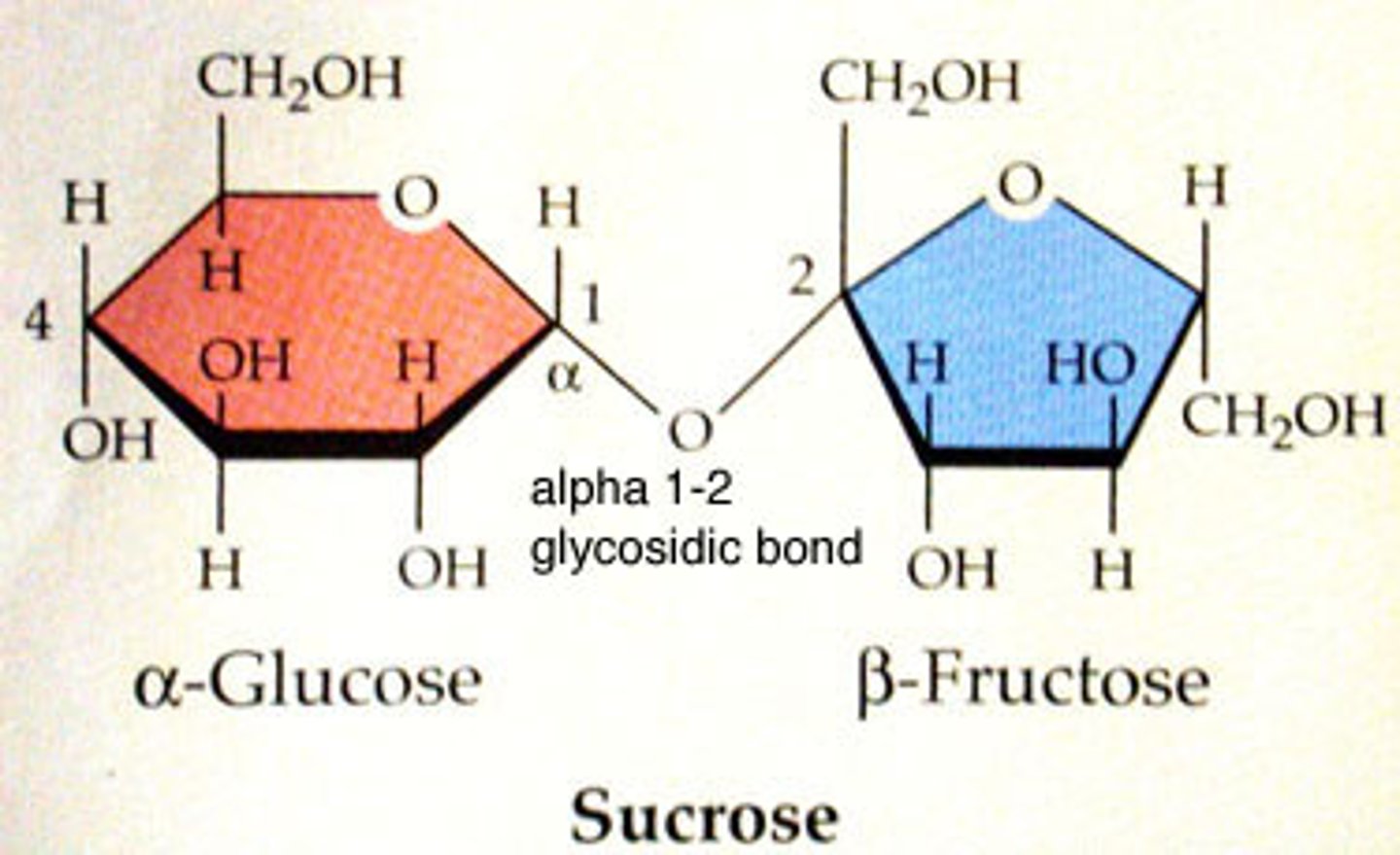
Disaccharides
sucrose
lactose
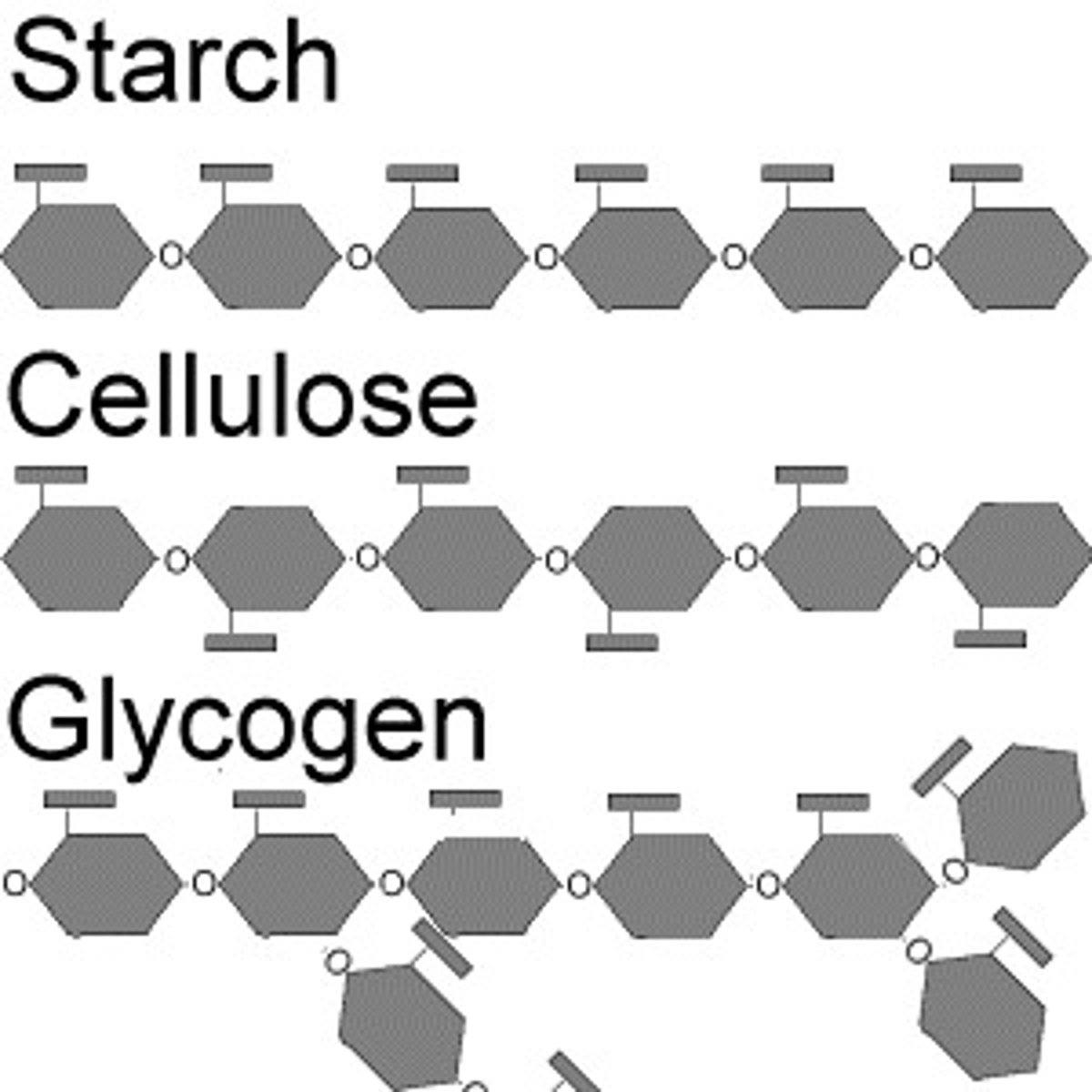
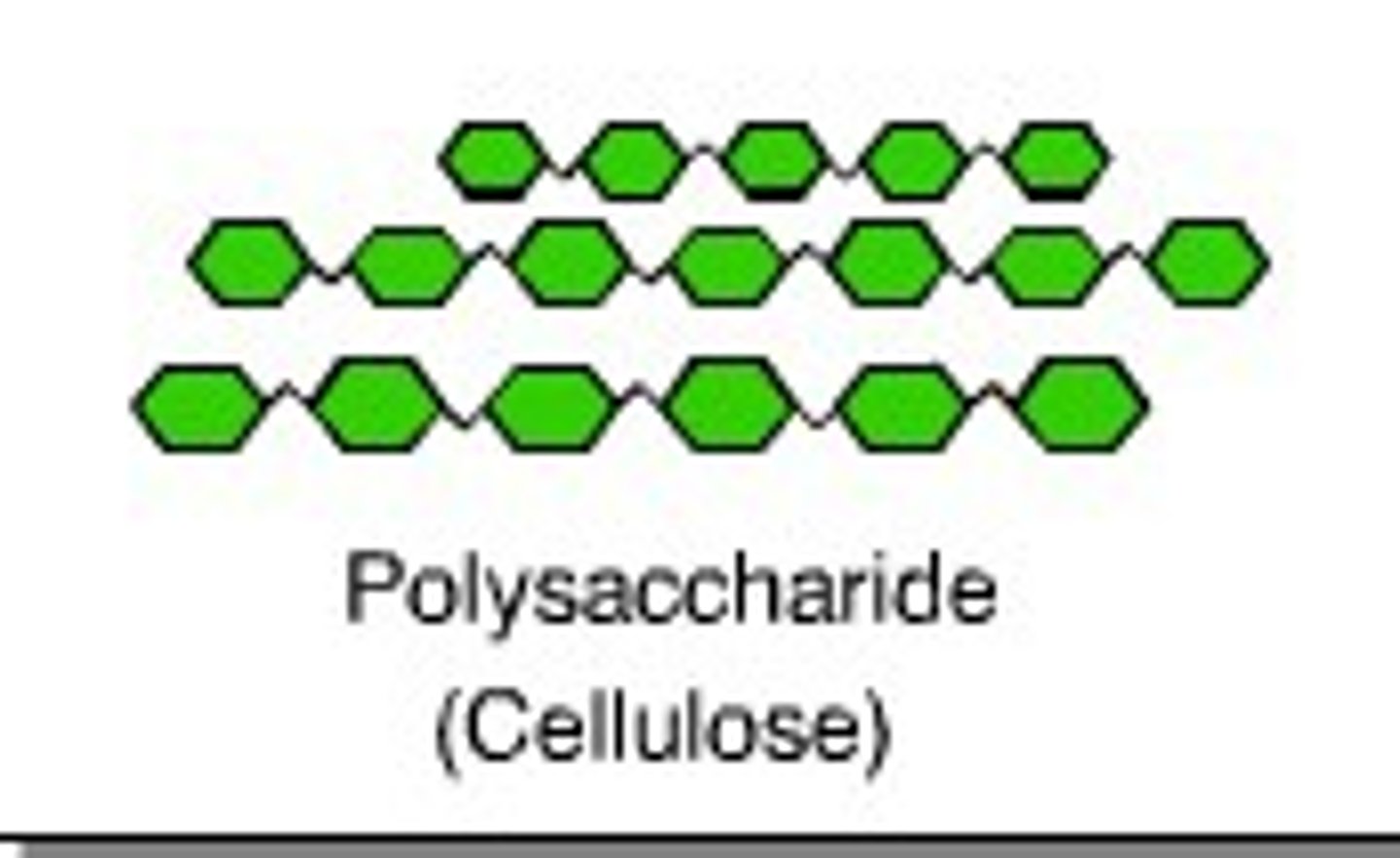
Polysaccharides
glycogen (animals)
starch (plants)
cellulose
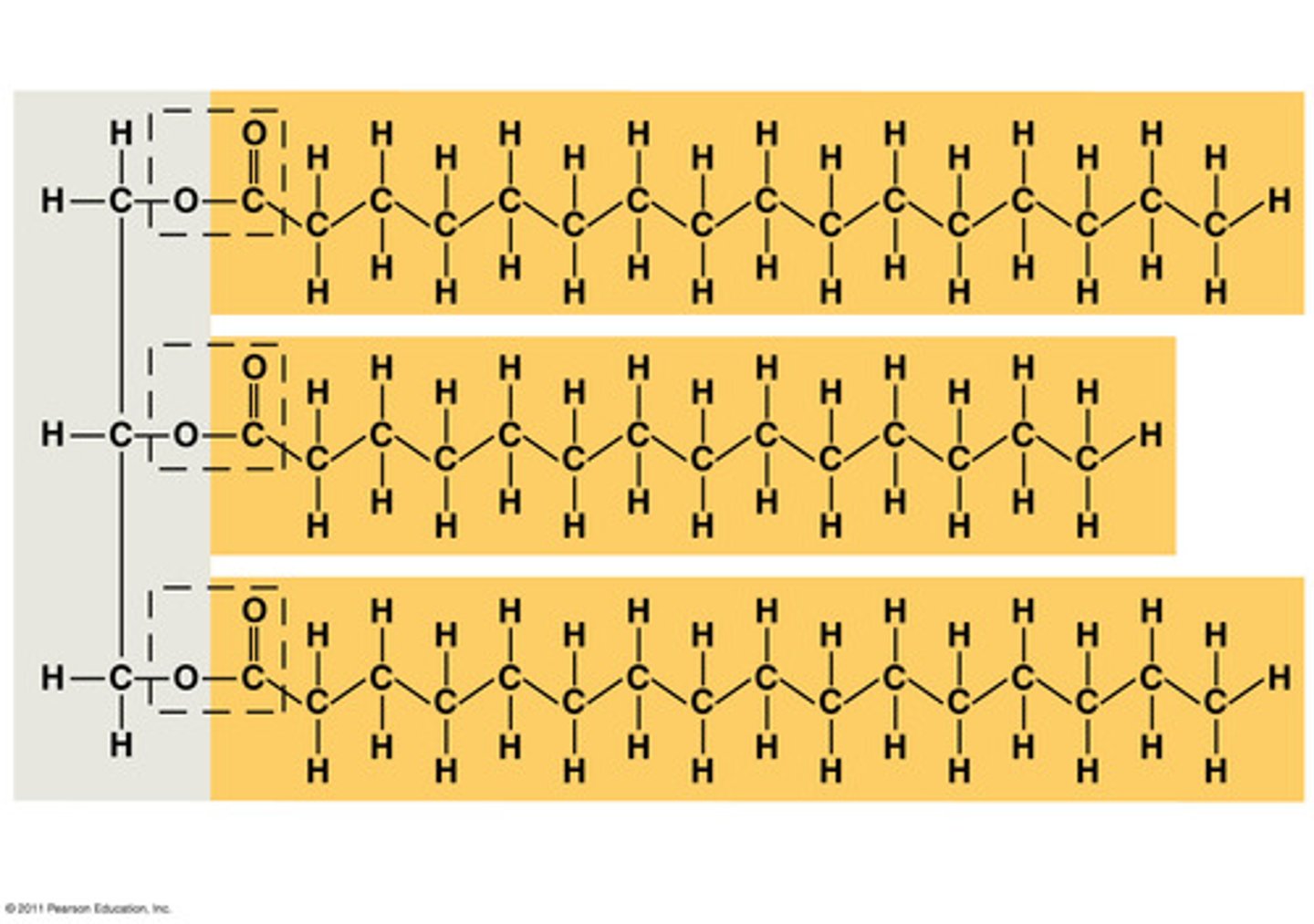
Fats (triglycerides)
used primarily for energy
-most common lipid in the body
Phosholipid have
hydrophilic end and hydrophobic end
Major component of cell membranes
phospholipids
Proteins functions/uses
-structural material
-energy source
-hormones
-receptors
-enzymes
-antibodies
amino acids
Protein building blocks are _____
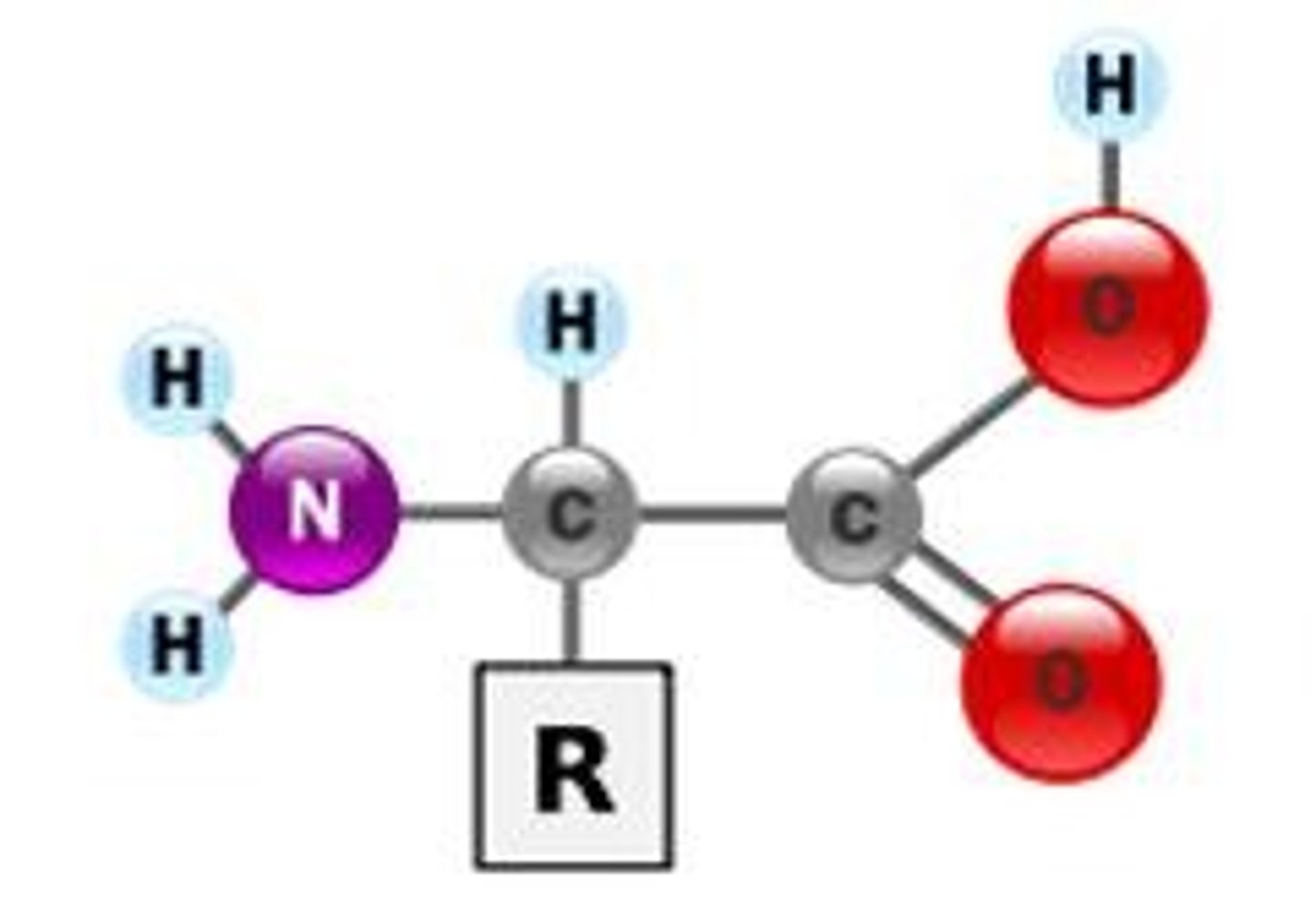
Peptide bonds
amino acids held together
Proteins are
complex three dimensional shapes
-shape activates and determines function
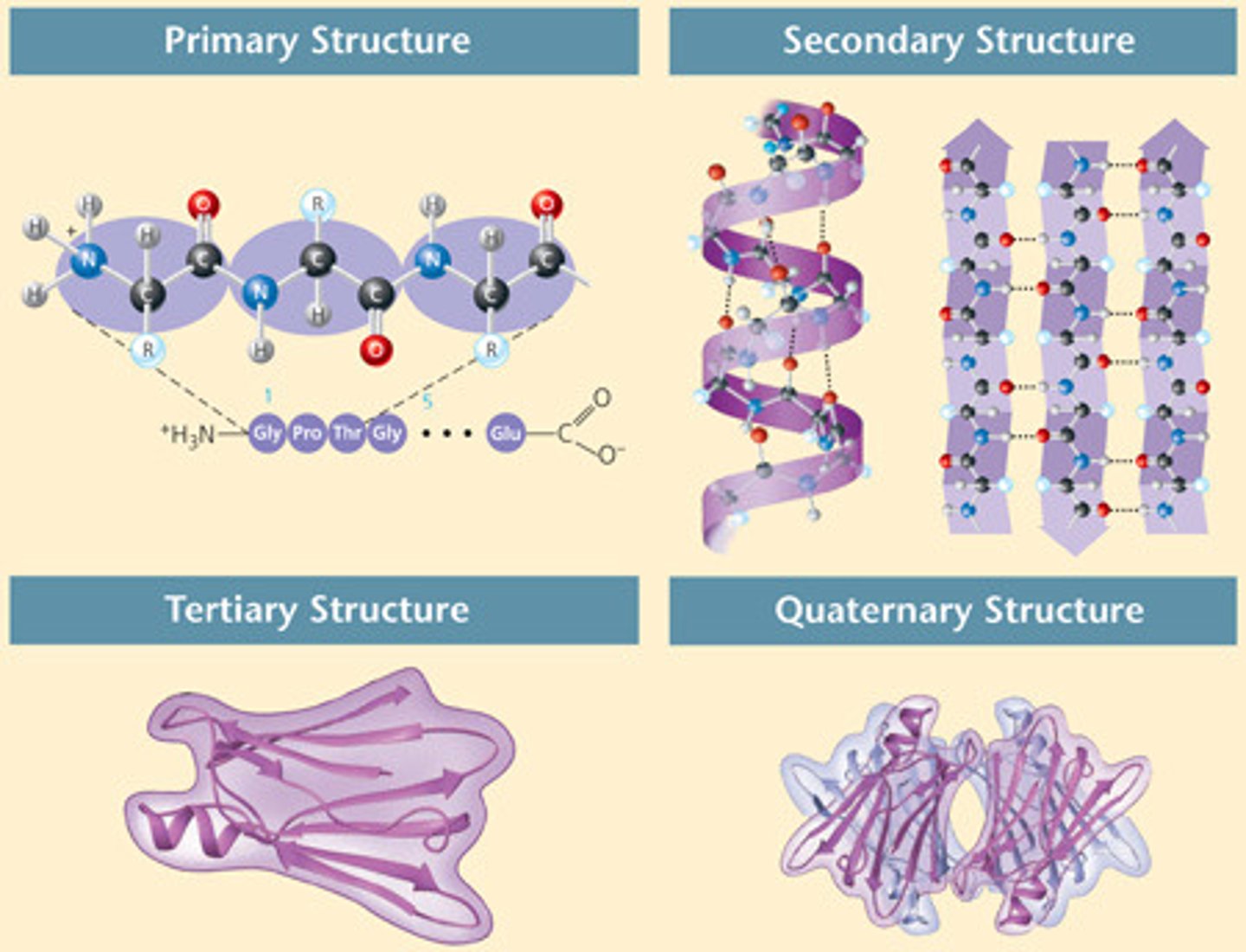
Protein misfolding can cause disease
-cystic fibrosis
-spongiform encephalopathies
-mad cow (disease)
-alzheimer disease
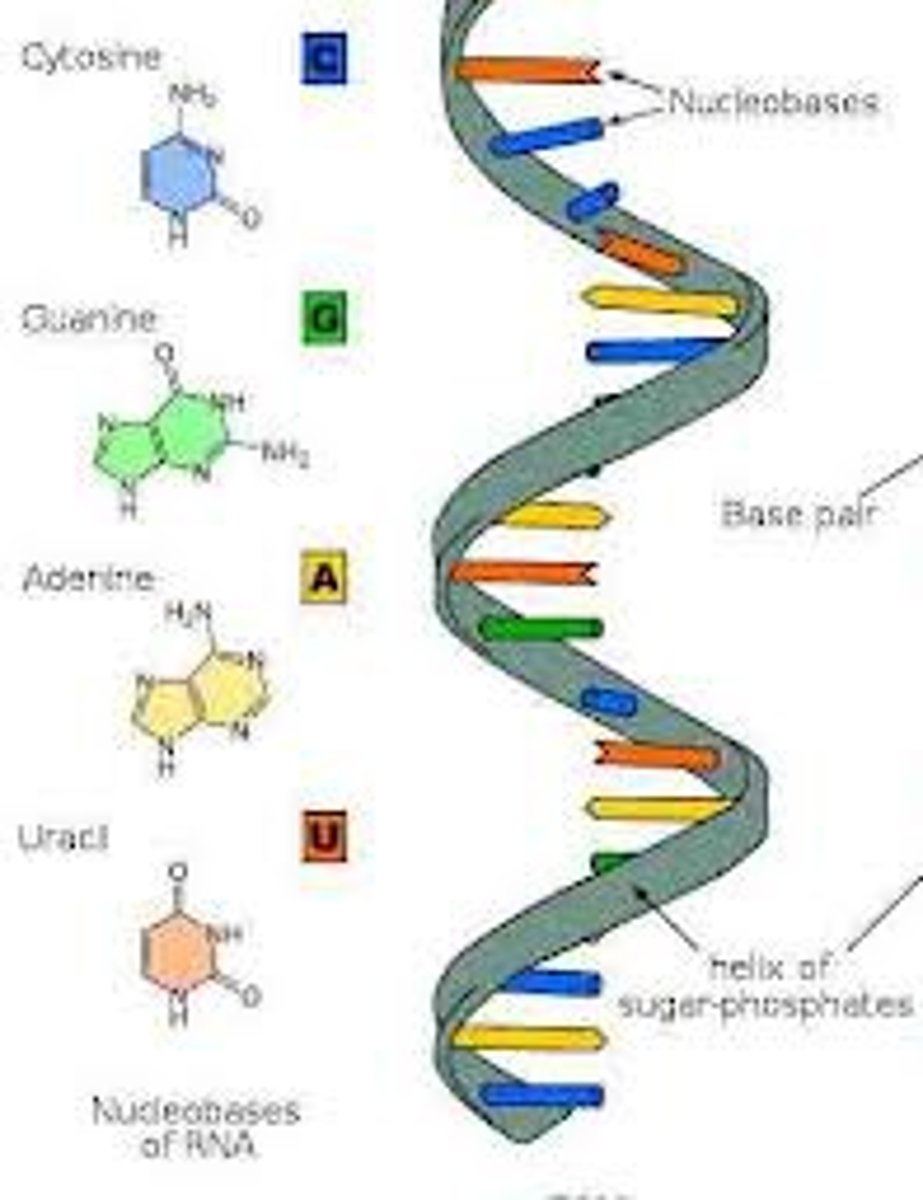
Nucleic acids
encode amino acids sequences of proteins
-DNA
-RNA
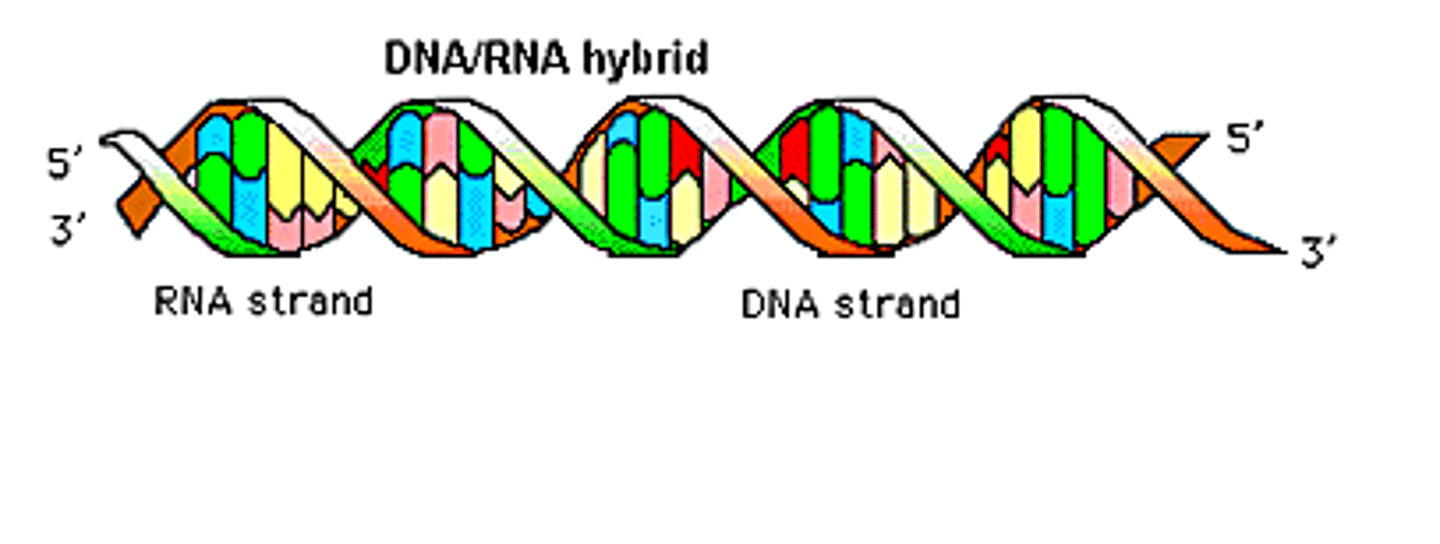
nucletiodes
building blocks of nucleic acids
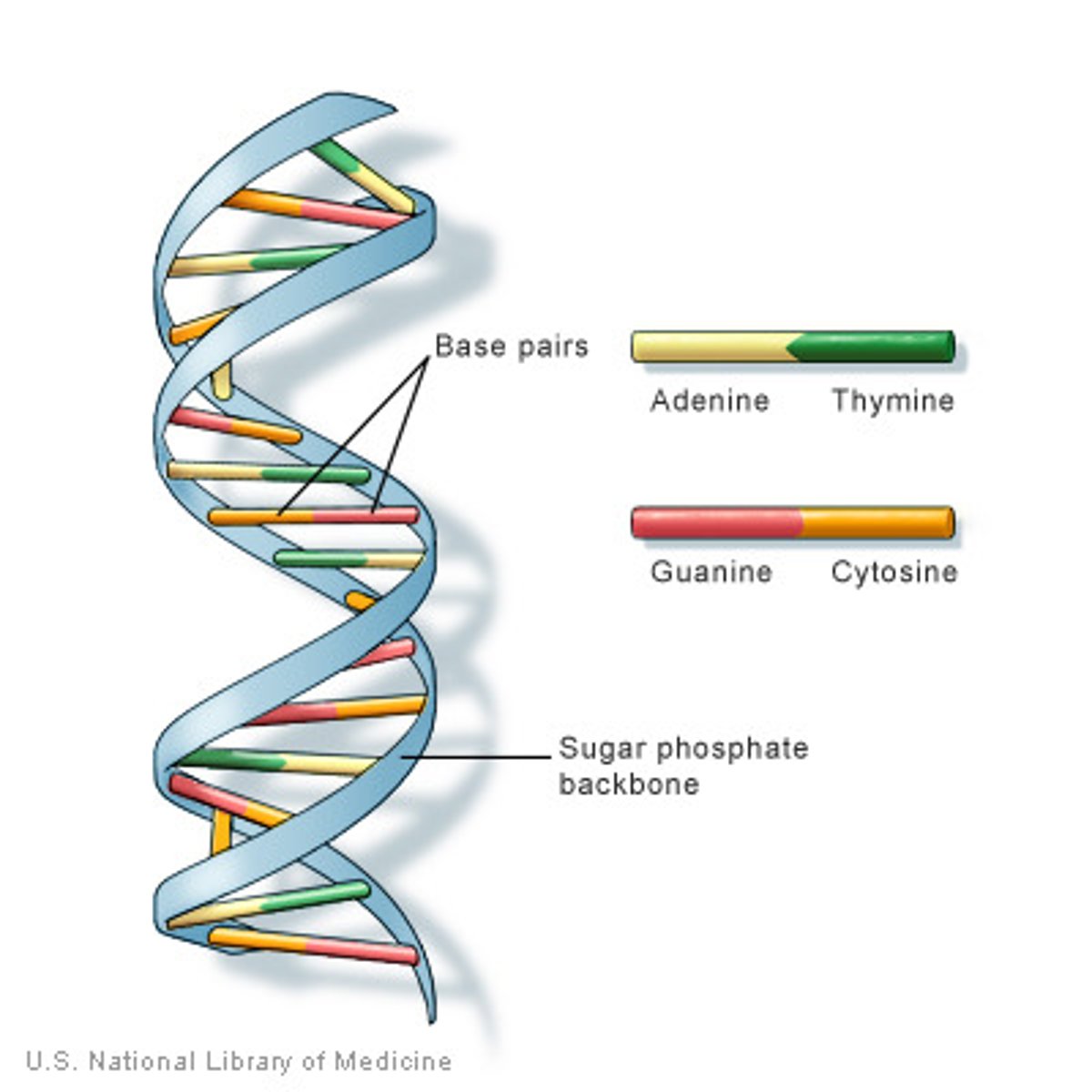
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
double polynucleotide
RNA (ribonucleic acid)
single polynucleotide