Urea Cycle Disorders -BioChem Genetics
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
The Urea Cycle
6 Major Enzymatic reactions that occur in the liver within the Hepatocytes: the mitochondria + cytoplasm
2 Major functions
removal of nitrogenous waste (produced mainly from protein catabolism) → Ammonia incorporated into Urea for Excretion
Synthesis of amino acids: Arginine, Ornithine and Citrulline (become ESSENTIAL A.A. in deficiencies of the UREA CYCLE ENZYMES)
Major presentations of Urea Cycle Disorders:
Severe Neonatal Hyperammonemic encephalopathy (exception: Argine deficiency + late/mild onset variants)
All Autosomal Recessive except for Ornithine transcarboxylase deficiency (OTC):
OTC is X-Linked Recessive → only affects Males
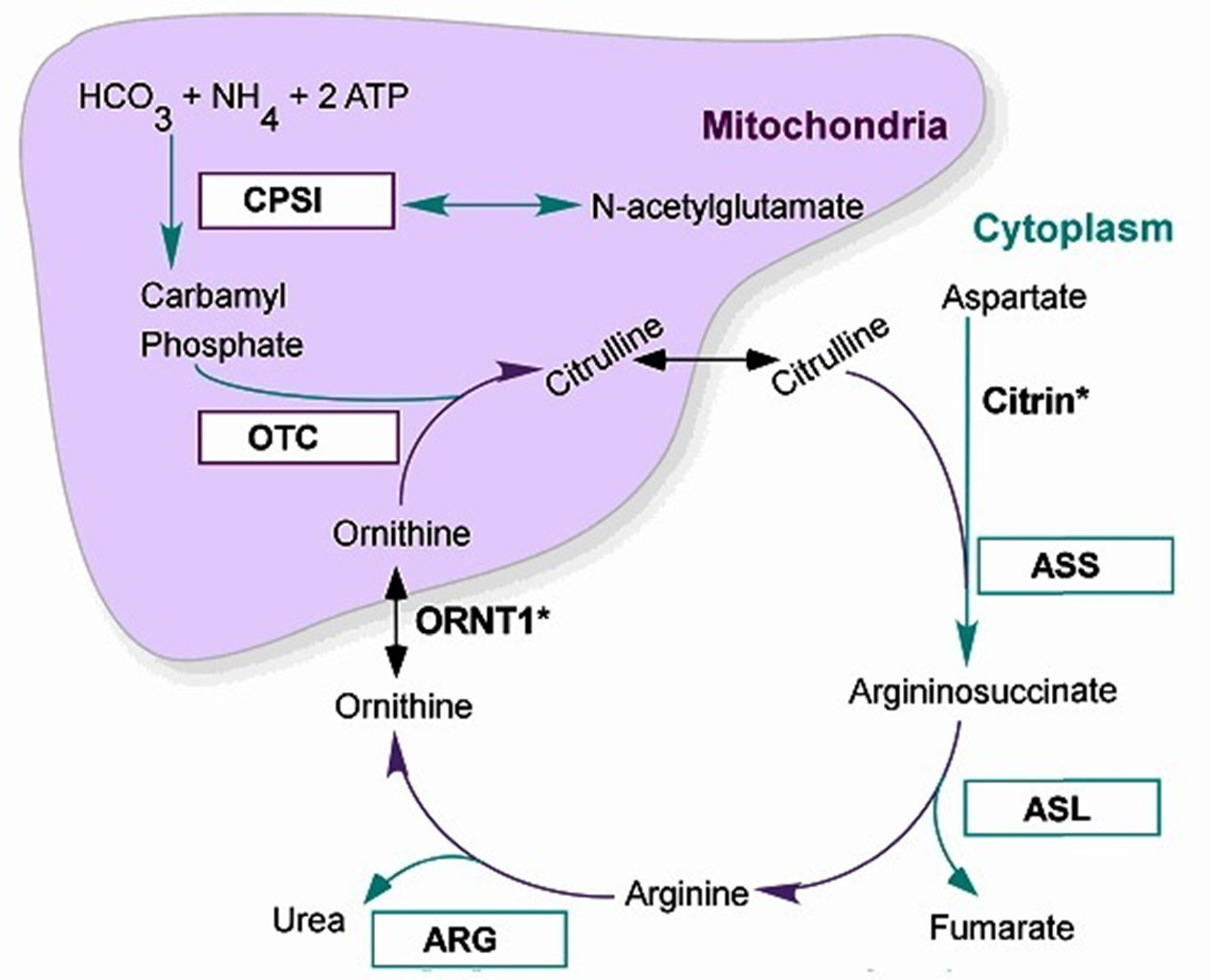
The 6 Urea Cycle Disrders
Correspond to the 6 steps of the Urea Metabolic cycle: taken individual relatively uncommon, but all together 1:8-35,000
N-Acetyl Glutamate Synthetase Deficiency
Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase (CPS1) Deficiency
****Ornithine Transcarbamylase (OTC) Deficiency****—> *****MOST COMMON*****
Arginosuccinic Acid Synthetase I (ASS1) Deficiency → also called Citrullinemia I
Arginosuccinic Acid Lyase (ASL) Deficiency
Arginase (ARG) Deficiency
Ammonia (NH3)
Ammonia is the product of the metabolism/catabolism of protiens/amino acids
Normal serum ammonia levels
Adults <35 mmol/L
Neonates <100 mmol/L (immature liver cells + increased tissue catabolism surrounding delivery)
Hyperammonemia: happen with great degree with IEMs of Urea Cycle But also seen with other metabolic disorders like Organic Acidemias (excess acid decreased Urea Cycle activity, lesser extent that UCDs)
Causes Neuronal excitotoxin increased extracellular glutamate +overexcitation of NMDA receptors→ Cell death and Cerebral Edema
Clinical Consequence
Acute severe elevation: seizures, coma, death
Mild chronic elevations: Brain atrophy, cognitive impairment
Classic UCD Presentation: Early
Neonatal Hyperammonemia Encephalopathy
In utero: protected my maternal urea Cyle activity of liver cells
At Birth in first 48hours: Ammonia levels rise quickly
Decreased feeding w/ vomiting
Lethargy
Tachypnea (rapid breathing)
Seizure activity
Followed by Rapid
Encephalopathy/Coma
Respiratory Failure
Cerebral Edema and Death
Late-Onset UCD Presentations
Variable age of onset and severity of Chronic and/or recurrence/Fluctuating symptoms:
Headache, Vomiting Ataxia and incoordination
Psychiatric/Behavioral disturbance: Delirium, ASD, ADD/ADHD, Manic episodes
Cognitive impairment: DD/MR, executive processing defects, early dementia
Often exacerbated/precipitated by:
Fever, Illness, fasting, post-partum, protein load (self restrict protein)
STILL AT RISK FORM HYPERAMMONEMC ENCEPHALOPATHY:
even if previously asymptomatic, can still be fatal
Mutiple Etiologies for Hyperammonemia
Things besides UCDs (MOST COMMON CAUSE) that can also cause the accumulation of excess ammonia:
Generalized Liver Deiasie (Acute or Chronic)
Non-genetic Causes: infections, Toxins, Trauma, Ischemia etc.
Genetic Causes
Non-IEM: Alpha-1 Antitrypsin (accumulation in liver=chrossis), Alagille syndrome etc
Non-UCD IEM
Aminoacidopathies: Tyrosinemia Type I
Organic Acidemia: elevated Lactic acid which inhibit NAGS
Primary Mitochondrial disorders
Fatty Acid oxidation Defects: Reye-Like syndrome
Carbohydrate Metabolic defects: Galactosemia, Fructosemia
Metal Processing defects WILSONS DIEASE, hemochromatosis
Primary UCDs
OTC Deficeiny Metabolism
X-Linked Recessive Form
Within the Mitochondria of Liver Cell:
Carbamyl Phosphate + Ornithine → Citrulline via Ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) activity: a Block at OTC = decreased Citrulline, increased Arginine and Aringnosuccinate (along the cycle)
Ammonia + Orotic Acid also increased (run-off product of carbamyl phosphate NOT becoming citrulline, not usually accumlated)
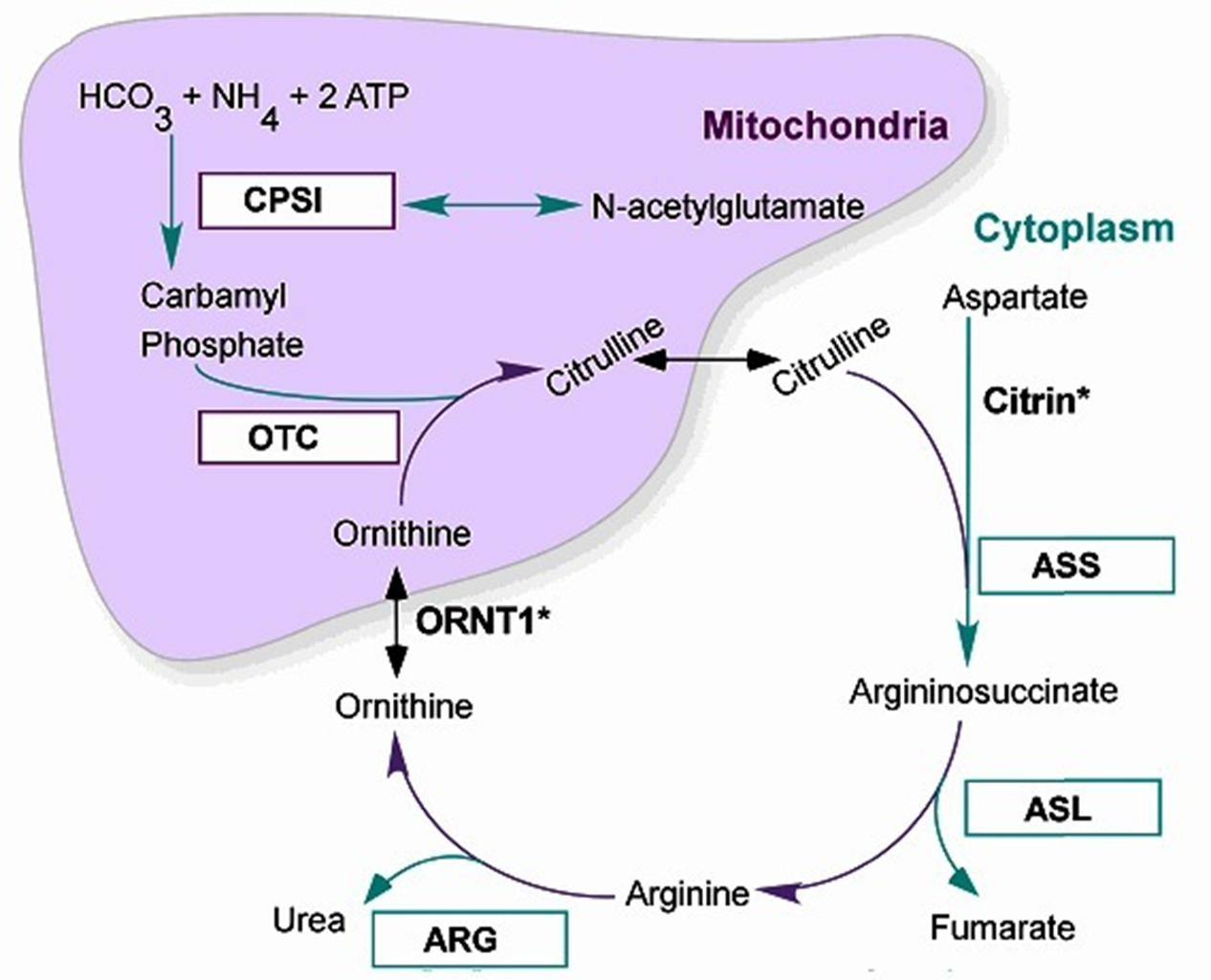
OTC Deficiency
Orthine Trancarbamylase (OTC) Deficiency:
Most Common UCD
X-Linked Recessive Inheritance
Incidence 1:56,000 (not increased in any specific group)
Genetic Defect: Orthine Transcarbamylase (OTC) Gene mutation
High Orotic Acid + Ammonia : Low Cirtrulline+ASS+ARGE
Female carriers most common, with symptomatic male probands
Non-carrier females: 3-4% germline mosaicism rate (apprecaible)
Untreated OTC Deficiency
Classic (usually males, only very rarely females)
At Birth to 24/48 Hours: Asymptomatic
2-3 Days old: Progressive hyperammonemia Encephalopathy
Poor feeding
Vomiting
Lethargy
Hyperventilation
Seizures
By 1 week Old: Lethal hyperammonemia Encephalopathy
Cerebral edema
Hypothermia
Coma
Respiratory failure
Death
MILD (Mild mutation males/symptomatic Females - 15%)
Episodic hyperammonemia Symptoms: ranging form mild to life-threatening
Chronic symptoms
Protein avoidance
recurrent headache
neuropsychiatric difficulty
Diagnosing OTC Deficiency
Newborn Screening: not done in all states (like NY) but ME, MAN,RI,VT
LOW CITRULLINE
Diagnostic Evaluation
Ammonia Level: symptomatic >100, Encephalitic >200
Blood gas/Metabolic profile/lactic acid levels: exclude other IEMs
Plasma Amino Acid Profile + Urine Organic Acid Profile
High glutamine/alanine + citrulline/ASA/ARG low in blood
High Orotic acid in urine
****Allopurinol given to female carriers can expose OTC by preserving Orotic Acid and show Orotic Acidemia****
Confirmatory Testing
Enzyme activity analysis: needs liver biopsy and not 100% in females due to x-inactivation in the liver
OTC genotyping via sequencing +del/dup analysis: 60-90% detection
Treating OTC Deficiency
Acute Encephalopathy treatment
Radpidly remove ammonia: hemodialysis/hemofiltration
Reduce production: protein cessation 12-24hours, decrease nitrogenous waste
Prevent Catabolism: high calorie, protein free - IV glucose + lipids and IVE arginine (become essential AA b/c it cannot be synthesized ‘like normal’)
Provide other ammonia removal agents: IV ammonia scavengers Sodium-Benzoate + Sodium-Phenylbutyrate
Chronic Treatment: after acute encephalopathy has resolved
Protein restriction + essential AA formula
Oral cituralline or arginine and ammonia scavenrs (Sodium-Benzoate + Sodium-Phenylbutyrate provide alternative pathways for ammonia excretion)
Avoid Valproic Acid, fasting, Fever, steroid, protein load
Liver transplant: only if neurologically intact after EPISODE + poor response to chronic treatment
OTC Deficiency Outcome
Outcome with Treatment: Variable
Neurocongtive delvepmn depens on intiala hyperammoneicm encephalyopth udration and control of subsquent amonia/glutamate leves
Ofente ID, ADHA, executive defcits, brain attrophy (even in midl males and symptomatic females)
OTC Carrier Screening + Prenatal Diag
Carrier Screening:
Molecuelar if mutation known in proband
Allopurinol Loading test show Orotic Acid elevations
Prenatal implantation: No enzyme/metabolite testing is useful, activity of OTC contained to liver cells
Arginosuccinic Acid Synthetase I (ASS1) Deficiency
A block at the next part of the cycle after OTC: Arginosuccinic Acid Synthetase I
where citrulline + Aspartate → Arginosuccinate
Increased Citrulline levels - Called Citrullinonemia
Increased levels of Ammonia, Orotic Acid (not quite as high as in OTC)
Decreased Arginaine, Arginosuccinatic Acid
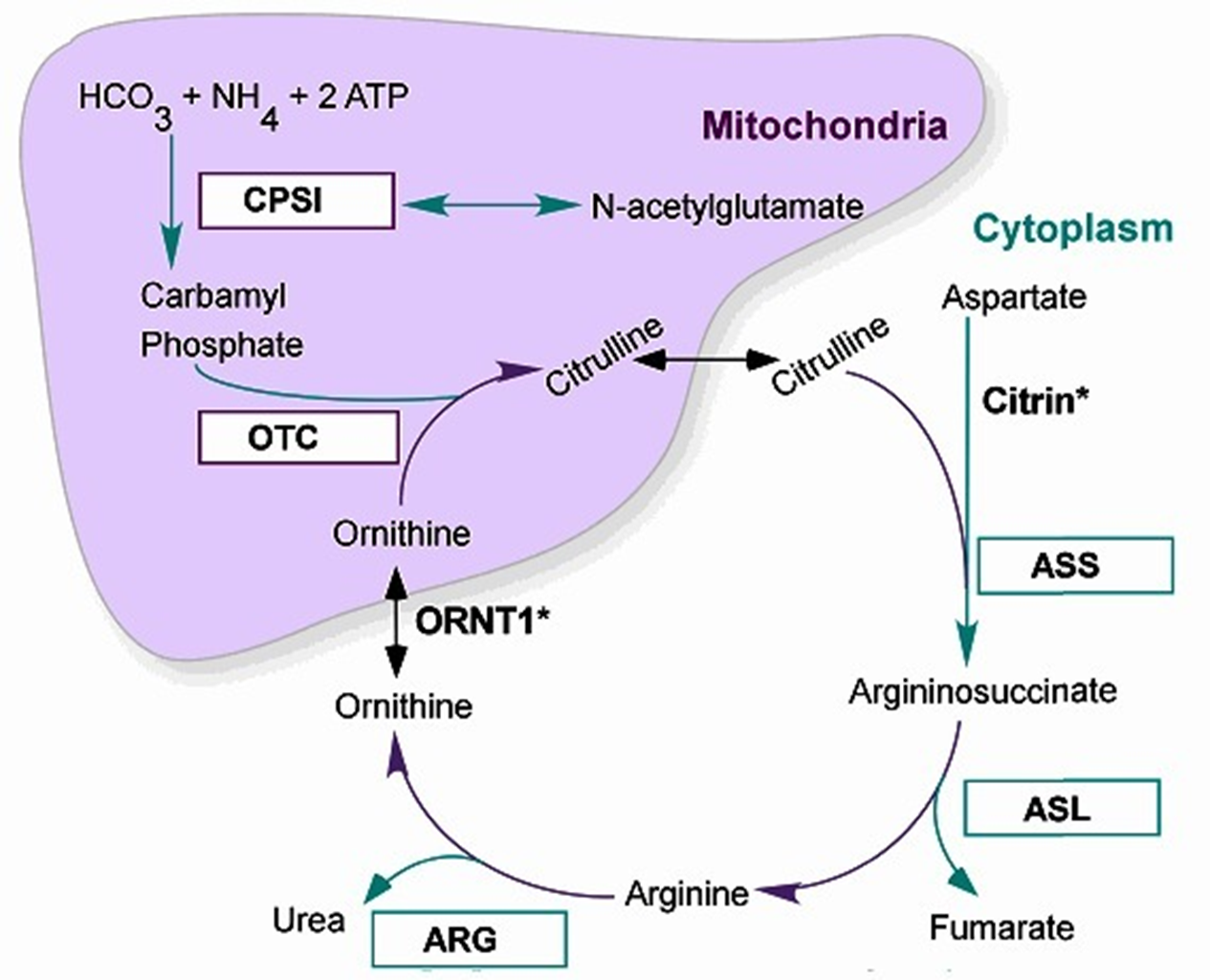
Citrullinemia Type I
Arginosuccinic Acid Synthetase I (ASS1) Deficiency
Inheritance Autosomal Recessive
Incidence: 1:200,000 (no increased in any particular group)
Genetic Defect Arginosuccinic Acid Synthetase I (ASS1) Gene
Increased Citrulline
Decreased Arginnine,
High Ammonia and Orotic Acid levels
***ANOTHER DEFECT in Citrin Gene (a transporter) causes Citruallenmia type II/III → MILDER***
Untreated Citrullinemia I
Classic
At birth to 48hours : Asymptomatic
By 4-7 days old: progressive hyperanomieic encephalopathy
Poor feeding
Vomiting
Lethargy
Hyperventilation
Seizures
By 1-2 weeks old: Lethal hyperammonemic Encephalopathy (slightly slower progression than OTC deficieny)
Cerebral edema
hypothermia
coma
respiratory failure
death
Late-Onset Forms (milder)
Episodic hyperammonemic symptoms
Chronic symptoms
protein avoidance
recurrent headache
neuropyshciatric difficulty
only a few cases with liver failure
Diagnosing Citrullinemia I
New Born Screening
Elevated citrulline: but not specfic to Citrullinemia I
Citrullinemia II/III (Citrin Deficiency) Arginosuccinic Acid Lyase (ASL) deficiency, Pyruvate Carboxylase deficiency
False positive
Confirmatory Testing
Ammonia Level: symptomatic over 100, encephalopathic over 200 (often 1000s)
Blood gas/metabolic progile/lactic acid level: exclude metabolic acidosis indicating other IEM
Plasma Amino Acid + Urine Orgnic acids
Plasma: Elevated citrulline/glutatmine/allaine + Decreased Arginosuccinate/Arginine/Ornithine
Urine: Increased orotic acid
ASS1 Activity in Fibroblasts, liver, CVS or aminocytes
ASS1 Genotyping
gene sequecing + del/dup analysis 96% detection
genoype/phenotpye correlation not 100%
Treating Citrullinemia I
Acute Encephalopathy treatment
Rapidly remove ammonia: hemodialysis/hemofiltration
Reduce production: protein cessation 12-24hours, decrease nitrogenous waste
Prevent Catabolism: high calorie, protein free - IV glucose + lipids and IVE arginine (become essential AA b/c it cannot be synthesized ‘like normal’)
Provide other ammonia removal agents: IV ammonia scavengers Sodium-Benzoate + Sodium-Phenylbutyrate
Chronic Treatment: after acute encephalopathy has resolved
Protein restriction + essential AA formula
Oral citrulline or arginine and ammonia scavengers (Sodium-Benzoate + Sodium-Phenylbutyrate provide alternative pathways for ammonia excretion)
Avoid Valproic Acid, fasting, Fever, steroid, protein load
Liver transplant: only if neurologically intact after EPISODE + poor response to chronic treatment
Citruellemia Type I Outcome
Depends on how quickly the hyperammonemia encephalopathy is dealt with + the control of subsequent ammonia/glutamate levels (LIKE OTC DEFICENCY)
Even with reatment: Often ID, ADHA, executive deficits, brain atrophy
Citrullinemia Type 1
Carrier Screening: if you know the muration
PRenatal.Preimplation diagonsis
if mutation is known, it can be detected via screening
ASS1 enzyme activty can be measured on CVS or Amniocentisis
Arginosuccinic Acid Lyase (ASL) Metabolic Pathway
Arginosucinate → Arginine + Fumarate (by product) via Arginosuccinic Acid Lyase
Elevated Ammonia, Argininosuccinate, Citrulline (Mild orotic acid)
Decreased Arginine
Arginosuccinic Acid Lyase (ASL) Deficiency
Similar to other UCD plus
Brittle hair
Hypertension
Inheritance Autosomal Recessive
Incidence: 1:220,000 (no increased particular population)
Genetic Defect
Arginosuccinate Lyase (ASL) Gene
Increased Citrulline and ASA
Decreased Arginine, Ammonia
Mild to no Orotic Aciduria
Untreated ASL Deficieny
Classic
At birth to 48hours : Asymptomatic
By 4-7 days old: progressive hyperanomieic encephalopathy
Poor feeding
Vomiting
Lethargy
Hyperventilation
Seizures
By 1-2 weeks old: Lethal hyperammonemic Encephalopathy (slightly slower progression than OTC deficieny)
Cerebral edema
hypothermia
coma
respiratory failure
death
Late-Onset Forms (milder)
Episodic hyperammonemic symptoms
Chronic symptoms
protein avoidance
recurrent headache
neuropyshciatric difficulty
****LIVER FAILURE OFTEN****
*****Brittle HAIR****
****Hypertension****
Diagnosing ASL Deficiency
New Born Screening
Elevated citrulline: but not specific to ASL defeciney
Citrullinemia II/III (Citrin Deficiency), Pyruvate Carboxylase deficiency
False positive
Confirmatory Testing
Ammonia Level: symptomatic over 100, encephalopathic over 200 (often 1000s)
Blood gas/metabolic progile/lactic acid level: exclude metabolic acidosis indicating other IEM
Plasma Amino Acid + Urine Organic acids
Plasma: Elevated citrulline/glutamine/alanine/Arginosuccinate + Decreased Arginine/Ornithine
Urine: Increased orotic acid
ASS1 Activity in Fibroblasts, liver, CVS, amniocytes AND red blood cells
ASL Genotyping
gene sequencing + del/dup analysis 90% detection
genotype/phenotype correlation not 100%
Treating ASL Defecieny
Acute Encephalopathy treatment
Rapidly remove ammonia: hemodialysis/hemofiltration
Reduce production: protein cessation 12-24hours, decrease nitrogenous waste
Prevent Catabolism: high calorie, protein free - IV glucose + lipids and IVE arginine (become essential AA b/c it cannot be synthesized ‘like normal’)
Provide other ammonia removal agents: IV ammonia scavengers Sodium-Benzoate + Sodium-Phenylbutyrate
Chronic Treatment: after acute encephalopathy has resolved
Protein restriction + essential AA formula
Oral citrulline or arginine and ammonia scavengers (Sodium-Benzoate + Sodium-Phenylbutyrate provide alternative pathways for ammonia excretion)
Avoid Valproic Acid, fasting, Fever, steroid, protein load
Liver transplant: only if neurologically intact after EPISODE + poor response to chronic treatment
ASL Defeciney Outcomes
Depends on how quickly the hyperammonemia encephalopathy is dealt with + the control of subsequent ammonia/glutamate levels (LIKE OTC DEFICENCY)
Even with treatment: Often ID, ADHA, eventual liver failure and hypertension (UNRELATED TO HYPERAMMONEMIA LEVELS→ even with good control, liver failure and hypertension happen)
****Trichorrhexis Nodosa (brittle hair) resolves on Arginine****
ASL Deficiency Screening
Carrier screening: look for specific mutation if found in the proband
Prenatal/preimplantation diagnosis
If mutation known
ASL enzyme can be measured on VS/Amniocentesis
Arginosuccinic acid levels in amniotic fluid when elevated are suggestive of ASL deficiency
Arginase (ARG) Deficiency Metabolism
Last step of the Urea cycle:
Arginine → Ornithine + Urea (released into urine and expelled) via Arginase activity
Elevated Arginine, Arginosuccinic acid, Citrulline
No elevation of Orotic Acid
Arginase (ARG) Deficiency
***No neonatal Encephalopathy (in contrast to the other UCDs)***
Inheritance Autosomal Recessive
Incidence 1:900,000 (slightly more common in Japan and French Canada)
Genetic Defect
Arginase (ARG1) Gene
increased Arginine
MILD intermittent hyperammonemia
Occasional mild orotic acid elevation
Untreated ARG Deficiency
No Hyperammonemia Encephalopathy
Neo-natal
Birth to 1-3 Years old: Asymptomatic
After 1-3 years old
Growth slows
Motor/cognitive development slows, regression occurs
Spasticity/seizures develop
Adulthood
Severe mental retardation, microcephaly
Short stature
Severe spasticity and joint contracture
Lack of ambulation, bowel, and bladder control
Low risk of hyperammonemic encephalopathy
Diagnosing ARGE Deficiency
Newborn Screening
Elevated Arginine
Confirmatory Testing
Ammonia levels: Normal or less than 150 umol/L (so usually not encephalopathic)
Blood gas/metabolic profile/lactic acid level: exclude metabolic acidosis indicating other IEM
Plasma AA profile + Urine ORgnic Acids
Elevated argienien
Orotic acid normal or minimially elevated
Enzyme active of ARG1: measured in Redblood cells, fetal red blood cells (BUT NOT AMNIOCYTE or CHORIONIC VILLI)
ARG1 Genotyping
gene sequencing + del/dup analysis
Treating ARG Deficiency
Not typically encephalopathic
if it does happen, treat it like the other UCD: dialysis, amonic sacnaer, protien restiction, but NO IV ARGININE: levels already elevated with this condition
Chronic Treatment: after acute encephalopathy has resolved
Protein restriction + essential AA formula
ammonia scavengers (Sodium-Benzoate + Sodium-Phenylbutyrate provide alternative pathways for ammonia excretion)
Avoid Valproic Acid, fasting, Fever, steroid, protein load
Liver transplant: only if neurologically intact after EPISODE + poor response to chronic treatment
ARG Defeicney out come
with treatment, outcome improved but still increased risk of:
intellecuta diablity,
short stature
spascity
joint ocntracture
lack of ambulation
loss of bowl+bladd control
Liver dysfunciton
ARG Deficiency Diagonsis
Prenatal/Preimplantation diagnosis
ARGE enzyme activity only on RBCs: so not via amnio of CVS
Possible to test enzyme activity of fetal blood via ubiclial sample, but rarely done
N-Acetyl Glutamate Synthetase (NAGS) Deficiency and Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase (CPS1) Deficiency Metabolic pathways
First steps of the Urea Cycle Pathways
Ammonia + N-acetylglutamate → Carbamoyl Phosphate via Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase (CPS1) activity
Glutamate → N-acetylglutamate via N-Acetyl Glutamate Synthetase (NAGS) activity
Blocks in NAGS or CPS1 = failure of N-acetylglutmate to combine with ammonia
SEVER HYPER AMMENIMA with low level of Carbamyl Phosphate + Citrublline, Arginosuccinaic Acid, Arginine, Ornithine
****NO OROTIC ACID: no Carbamyl Phospate to convert into it***
NAGS and CPS1 Deficiency
Called the Pre-Orotic UCD: the rarest UCD
Same clinical presentation as OTC/ASS1/ALS
Neonatal hyperammonemia encephalopathy
But with NO OROTIC ACIDURIA
Both Autosomal Recessive Inheritance
Genetic Defects
N-AceytlGlutamate synthetase (NAGS) gene
Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase 1 (CPS1) Gene
NAGS and CPS1 Deficiency Diagnosis
Newborn screening: neither are identified on NBS
Diagnostic Evalution
Ammonia level: highest of the UCDs, >1000 at diagnosis, Neonatal Encephalopathy
Blood gas/metabolic profile/lactic acid level: exclude metabolic acidosis indicating other IEM
Plasma AA and Urine Organic Acids
High Glutamine/Alaine
Low Citrulline/ASA/arginine
***NO OROTIC ACID***
Confirmatory testing
Enzyme activity requires liver biopsy
gene sequencing + del/dup analysis
NAGS/CPS1 Deficiency Treatment
Acute Encephalopathy treatment
Rapidly remove ammonia: hemodialysis/hemofiltration
Reduce production: protein cessation 12-24hours, decrease nitrogenous waste
Prevent Catabolism: high calorie, protein free - IV glucose + lipids and IVE arginine (become essential AA b/c it cannot be synthesized ‘like normal’)
Provide other ammonia removal agents: IV ammonia scavengers Sodium-Benzoate + Sodium-Phenylbutyrate
Chronic Treatment: after acute encephalopathy has resolved
Protein restriction + essential AA formula
Oral citrulline or arginine and ammonia scavengers (Sodium-Benzoate + Sodium-Phenylbutyrate provide alternative pathways for ammonia excretion)
Avoid Valproic Acid, fasting, Fever, steroid, protein load
Liver transplant: only if neurologically intact after EPISODE + poor response to chronic treatment
***Carglumic Acid: Synheic N-Acytle gluamate (NAG) for NAGS defeciney****
NAGS/CPS1 Deficiency Outcome
Outcome with treatment variabl
Often intellectual disability, ADHD, executive defects, brain atrophy
NAGS/CPS1 Deficiency Carrier Screening
Molecular: if mutation known in proband or linkage informative
Prenatal/Preimplantation diagnosis:
No enzyme or metabolite testing is useful