Lab 2: The Endocrine System and Blood
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
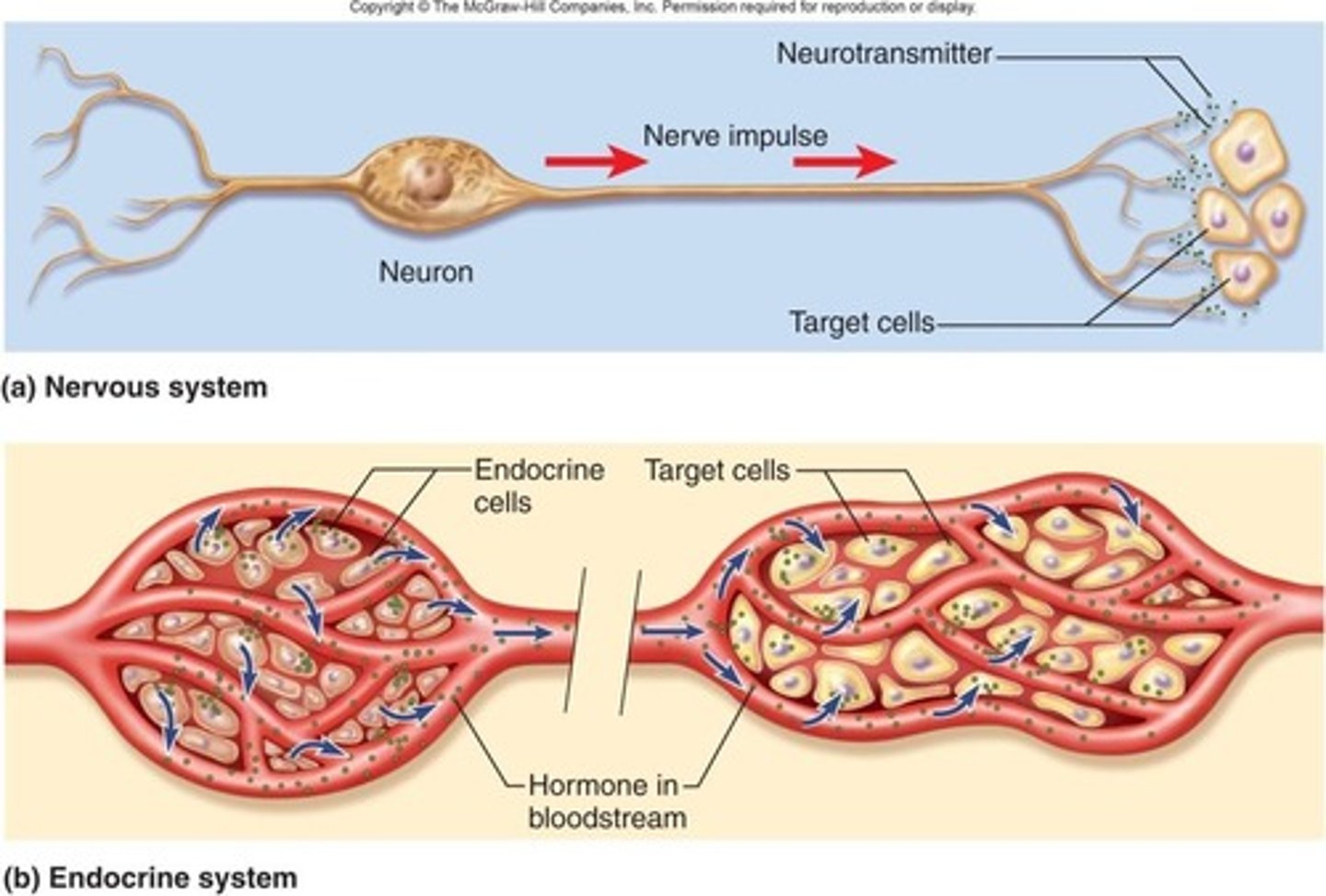
Endocrine glands
Glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream.
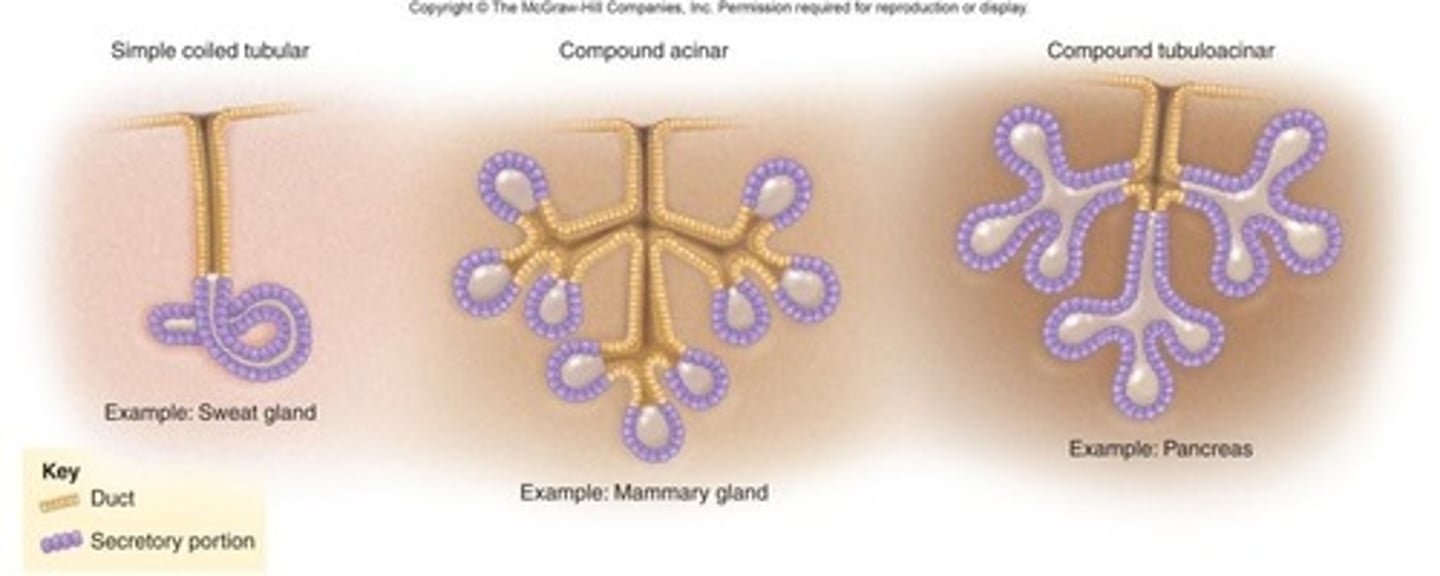
Exocrine glands
Glands that secrete substances through ducts to the outside of the body.
Hormone
Chemical messengers that act on target cells, tissues, or organs.
Endocrine gland
Glands that release hormones directly into the bloodstream.
Exocrine gland
Glands that secrete substances through ducts.
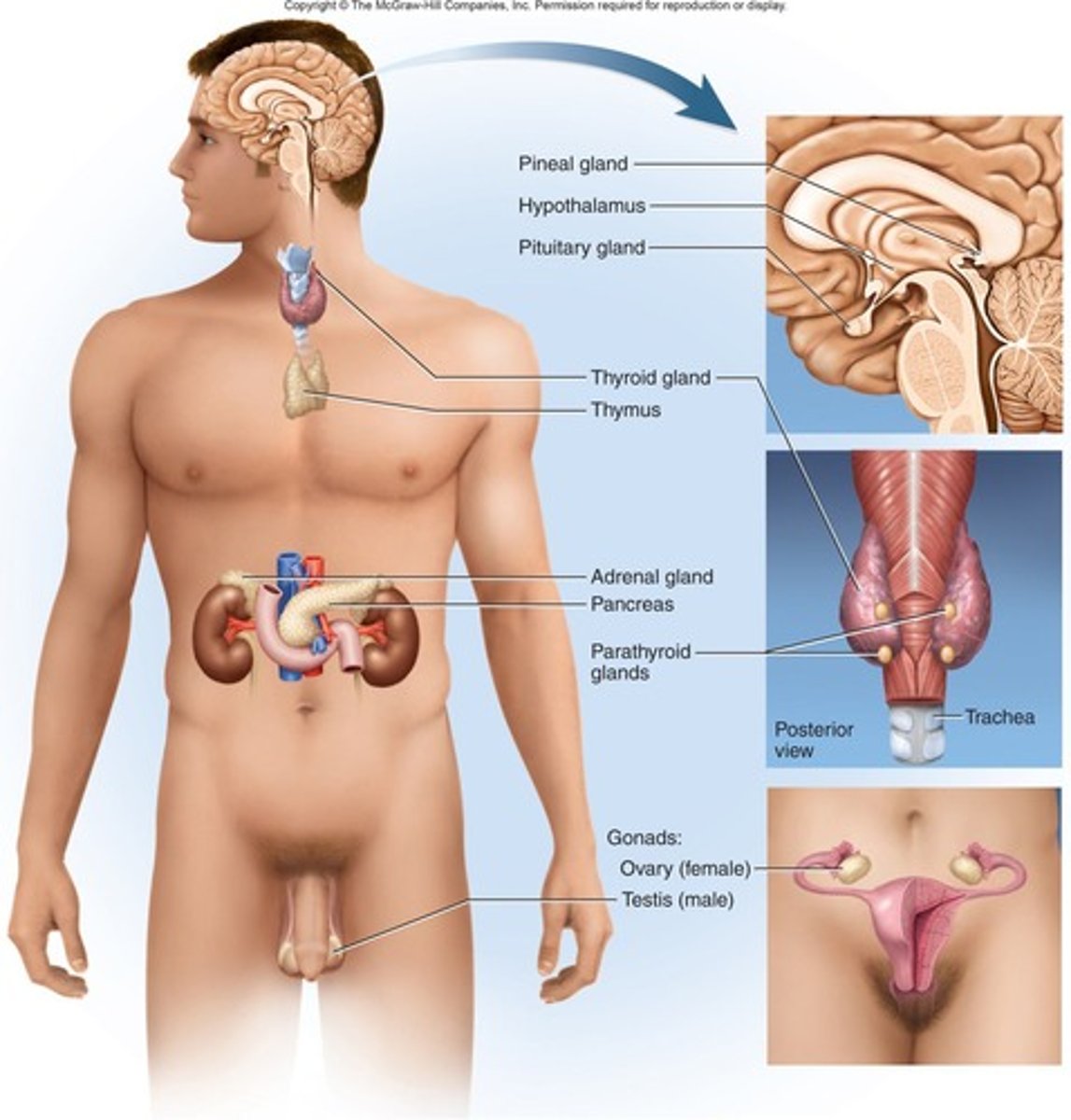
Pineal Gland
Produces melatonin.
Hypothalamus
Controls hormone release by secreting stimulating and/or inhibiting hormones.
- Also controls non-endocrine functions such as pH, hunger, thirst, etc...
Pituitary Gland
Also known as Hypophysis; connected to the hypothalamus by the infundibulum.
- Anterior lobe: endocrine tissue
- Posterior lobe: nervous tissue
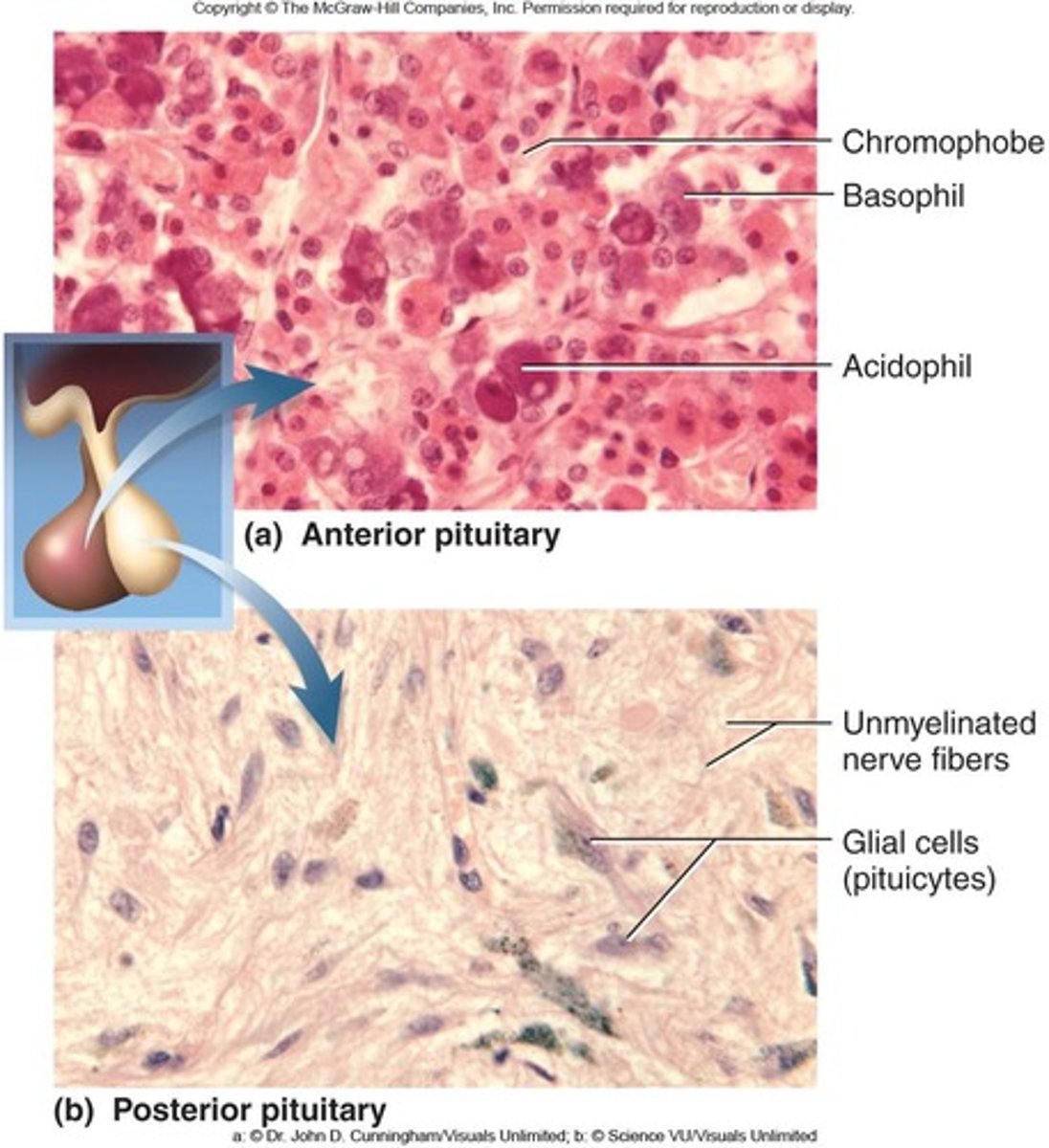
Adenohypophysis
Anterior lobe of the pituitary gland; composed of endocrine tissue (simple cuboidal).
Neurohypophysis
Posterior lobe of the pituitary gland; composed of nervous tissue.
- Hormones stored here are synthesized in the hypothalamus
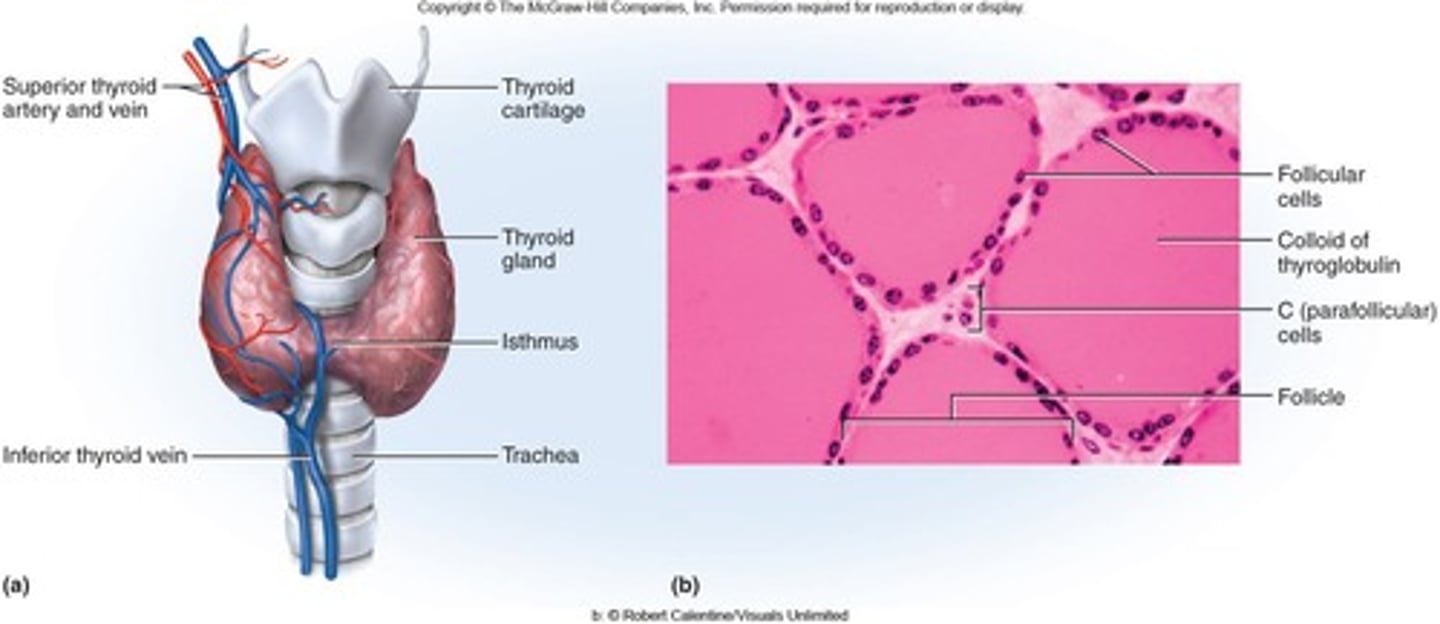
Follicular cells
Produce T3 and T4, dark cells surrounding thyroid follicles
Thyroid Gland
Produces thyroid hormone (T3 and T4) and calcitonin.
Function of thyroid hormones
regulate metabolism
Function of calcitonin
- Lowers blood calcium levels
- Increase bone density
Mainly in children
T3
triiodothyronine
T4
thyroxine (tetraiodothyronine)
Isthmus (thyroid)
tissue connection between right and left thyroid lobes
Parafollicular cells
AKA "C cells"
- Produce calcitonin (lower blood calcium)
- Located outside the thyroid follicles
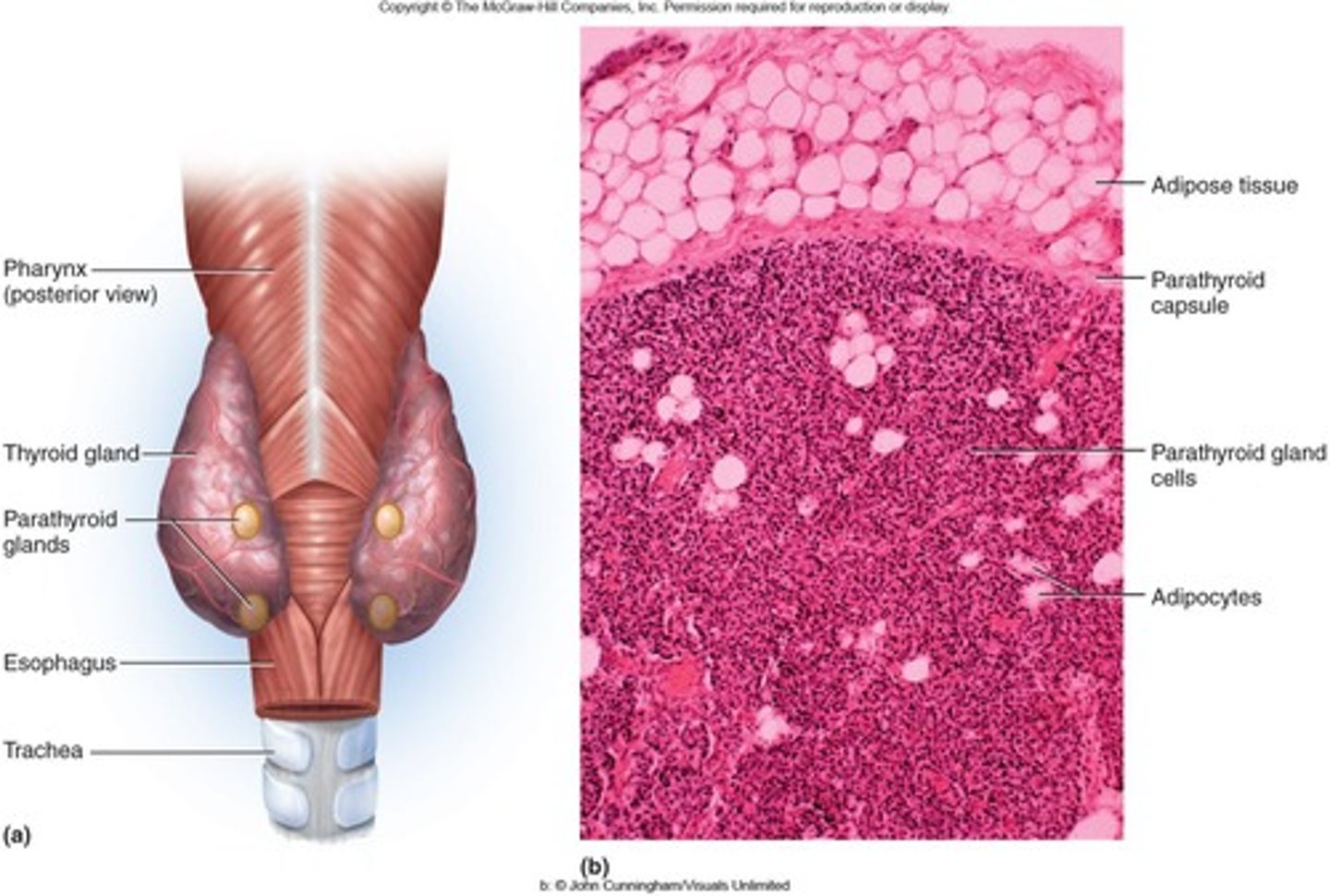
Parathyroid Glands
Usually 4 glands located bilaterally on the posterior of the thyroid gland that produce parathyroid hormone.
- Raise blood Ca2+ levels
Thymus
Known as the 'shrinking' gland; produces thymosins.
- Huge in childhood, shrinks at adulthood
Thymosins
Part of the immune system
Hormone produced by the thymus responsible for T-lymphocyte development and function
Pancreas
Located posterior to the stomach
Has both endocrine and exocrine functions:
Endocrine: (produces insulin and glucagon)
Exocrine: (produces pancreatic juice for digestion).
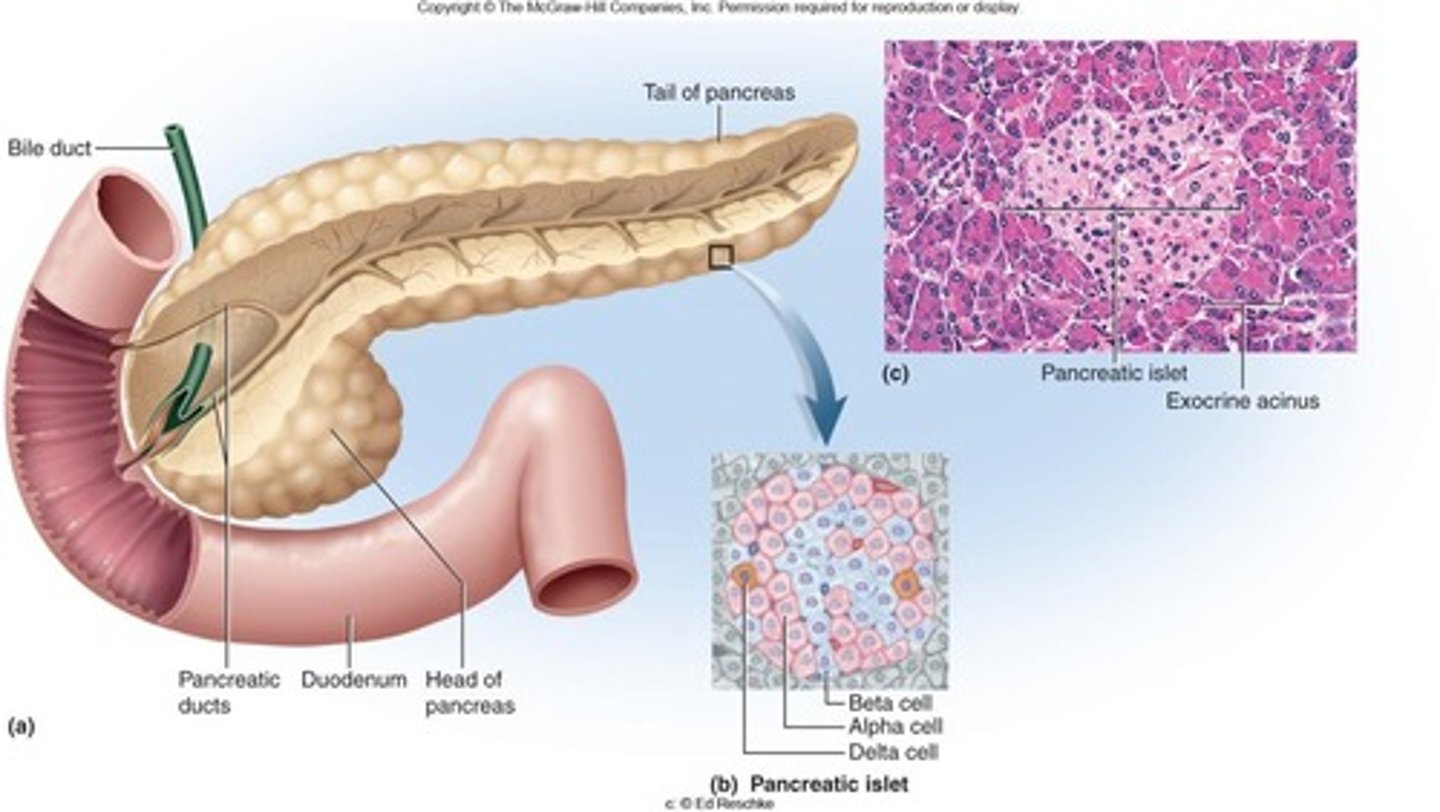
Pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans)
Endocrine cells that produce insulin and glucagon in the pancreas
Acinar cells
Exocrine cells that secrete digestive enzymes through ducts in the pancreas
- Dumps juice into the small intestine
Adrenal Glands
Composed of cortex (external) and medulla (internal).
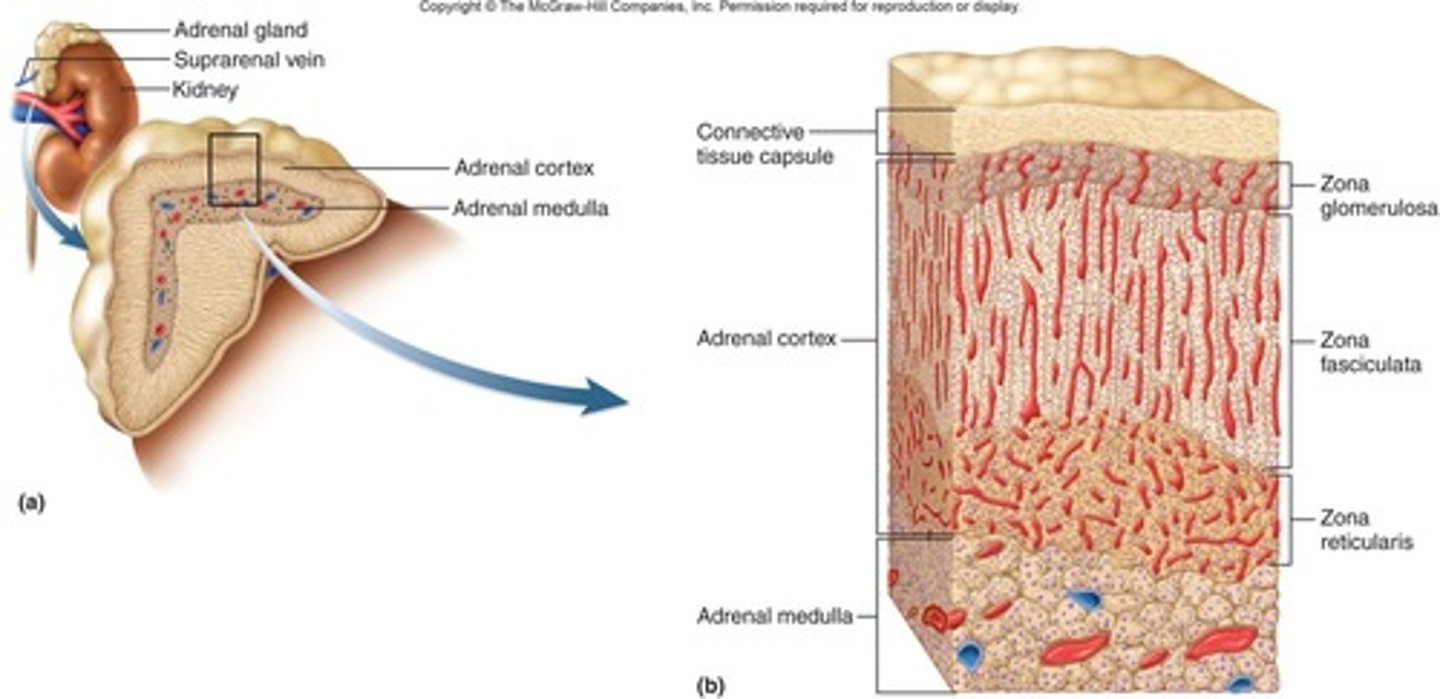
Adrenal Cortex
Produces corticosteroid hormones for water and electrolyte balance and metabolism. Also produces androgens and estrogens
Adrenal Medulla
Produces epinephrine and norepinephrine for stress response.
Testes
Have endocrine (produce testosterone) and exocrine functions (produce sperm).
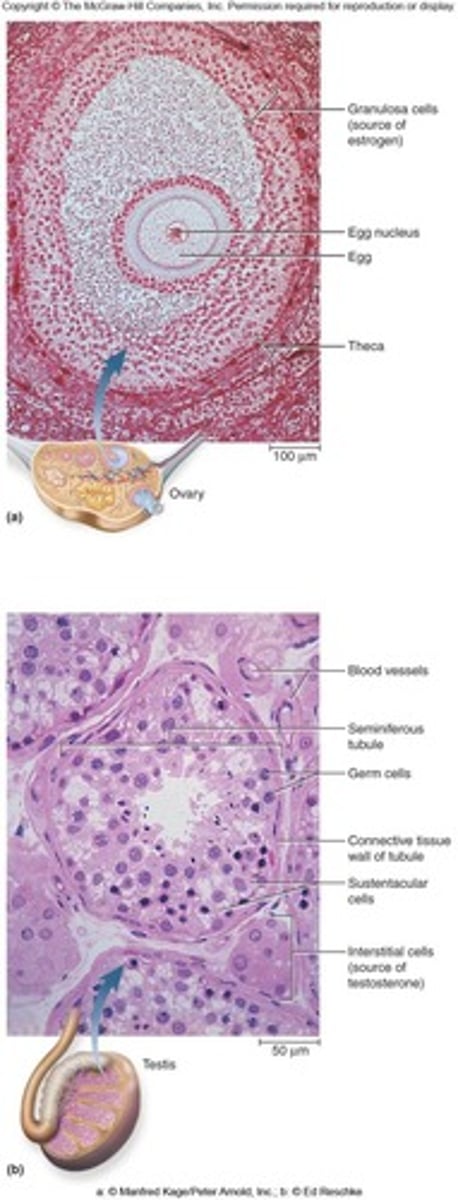
Seminiferous tubules (testes)
Exocrine glands that produce sperm
- Large circular structures that contain many individual tubules
Interstitial cells (testes)
Endocrine cells that produce testosterone
- Smaller circular structures located outside the semin. tubules
Ovaries
Have endocrine (produce estrogen and progesterone) and exocrine functions (produce follicles which contain eggs (oocyte)).
Ovarian follicle
developing sac enclosing each ovum (egg) within the ovary
- Contain granulosa cells which produce estrogen and progesterone
Granulosa cells
Endocrine cells in an ovary surrounding the egg that produces estrogen and progesterone
Mixed glands
Testes, ovaries, and pancreas
- Both endocrine and exocrine
Blood
Connective tissue with a pH of 7.35-7.45, composed of plasma (~55%) and formed elements (~45%).
Blood Alkalosis
blood pH above 7.45
Blood Acidosis
Blood pH below 7.35
Blood Plasma
Over 90% water
10% proteins such as albumin, globulin, and fibrinogen, along with electrolytes, hormones, gases, nutrients, and wastes.
Function: Transport of plasma components and formed elements
Which protein found in blood plasma is key in coagulation?
Fibrinogen
Blood formed elements
erythrocytes, leukocytes, thrombocytes
Erythrocytes (RBC)
Red blood cells containing hemoglobin; average count is 4.2-6.2 million/uL.
Shape:
- biconcave (due to lack of nucleus)
non-nucleate
- This causes RBC's to be the smallest formed element
Function:
- Transport oxygen to body cells (key in ATP synthesis)
- Picks up CO2 for disposal
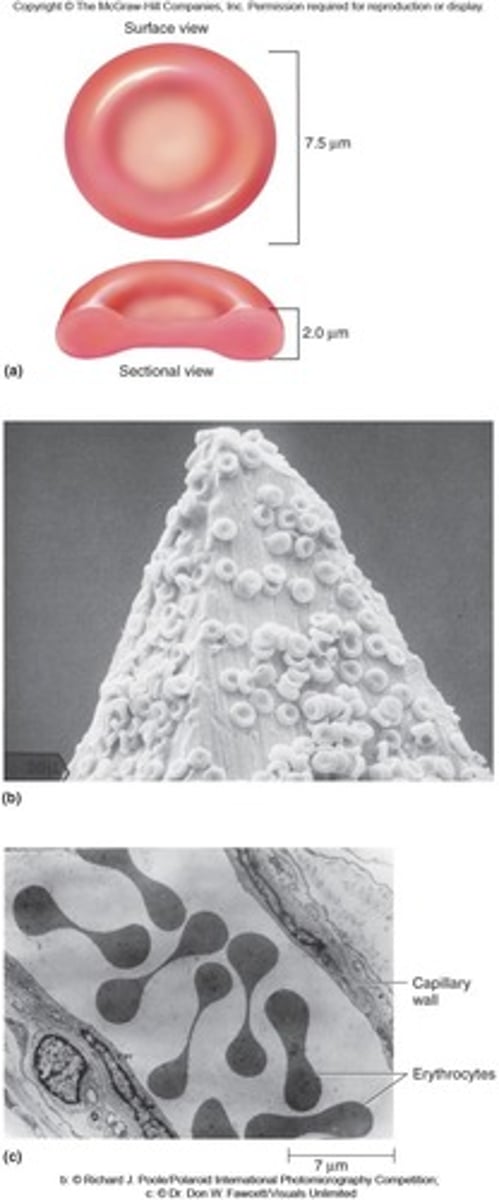
Thrombocytes (platelets)
Average count is 150,000-360,000 per uL
Function:
- Blood coagulation
Non-nucleate
- Cells fragments
Leukocytes (WBC)
White blood cells; average count is 5,000-10,000 per uL.
Cell category types:
- Granulocytes: Visible granules
- Agranulocytes: non-visible granules
5 types:
- Neutrophils
- Eosinophils
- Basophils
- Lymphocytes
- Monocytes
Function:
- Immune support, kill foreign invaders
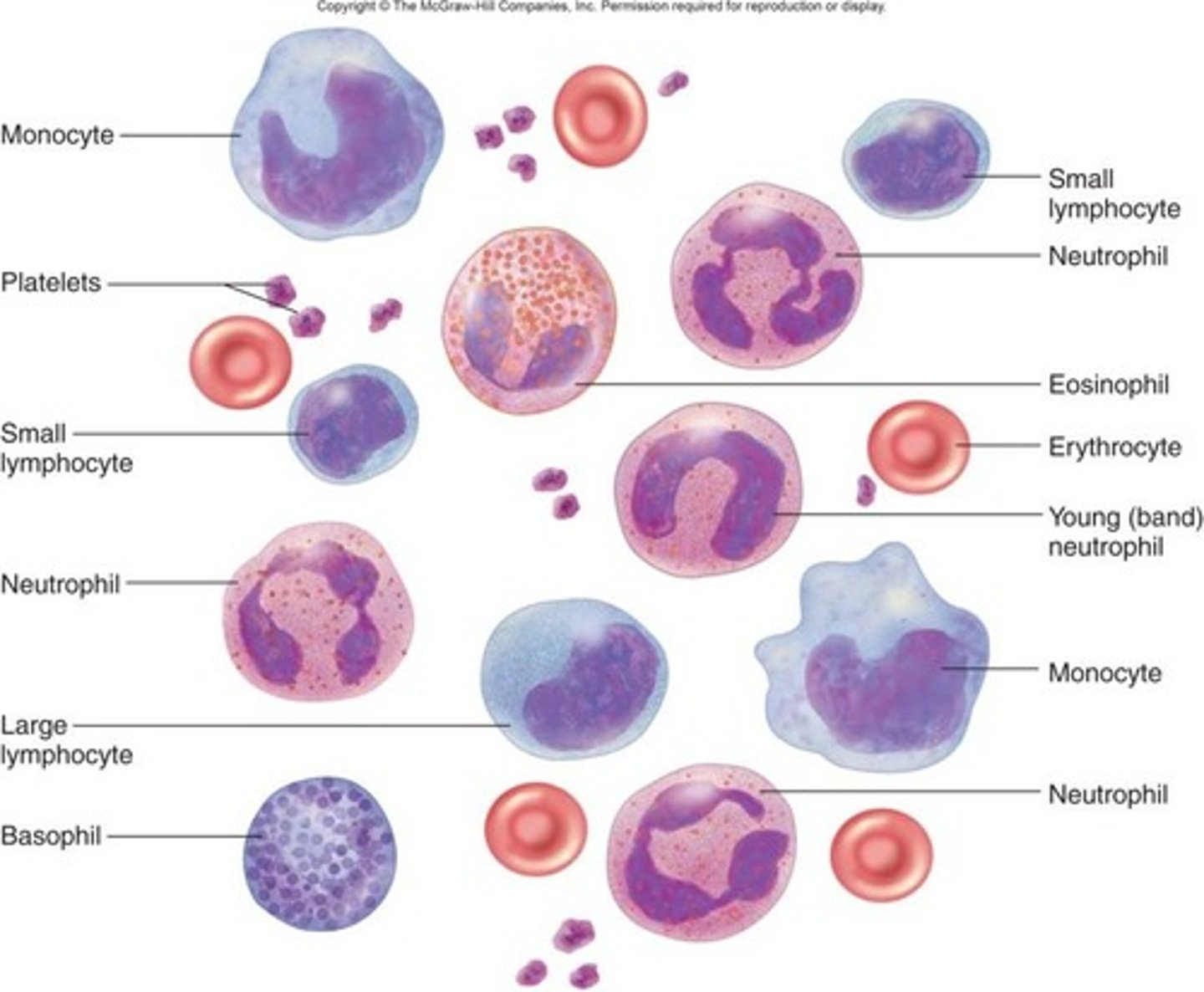
Granulocytes
Type of leukocyte that contain visible granules
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
All end in -phils
Agranulocytes
Non-visible granules
lymphocytes and monocytes
Neutrophils
Most common Granulocyte
Form/identification:
- Always 3-5 lobes/structures inside of nuclei
Function:
- phagocytosis of bacteria
Eosinophils
Granulocyte with red/pink cytoplasm (red granules)
Function
- Fighting parasites and phagocytosis of allergens
Basophils
Most rare granulocyte
Form/Identification:
- Large, dark granules
- Can't see cytoplasm or nucleus
Function:
- secrete histamine and heparin
- allergic and inflammatory responses
Lymphocytes
Agranulocyte, second most common leukocyte
Form/Identification:
- Small cells with large, round nucleus;
Two Types:
- T-lymphocytes (T-cells): destroy foreign cells
- B-lymphocytes (B-cells): produce antibodies
T-cells
Type of lymphocyte (agranulocyte)
Cells created in the thymus that produce substances that attack infected cells in the body.
B-cells
Type of lymphocyte (agranulocyte)
Cells made in the bone marrow that create antibodies
Monocytes
Agranulocyte
Form/identification:
- Large cells with kidney-shaped nucleus;
Function:
- Involved in phagocytosis and become macrophages
Blood pressure
Pressure that your blood exerts on the vessels as it travels
Measured in mmHg; normal resting blood pressure in a young adult is typically around 120/80 mmHg.
Normally measured on the brachial artery
Pulse pressure
Measured in mmHg;
calculated as systolic pressure minus diastolic pressure.
Mean arterial pressure (MAP)
Measured in mmHg;
calculated as (pulse pressure ÷ 3) + diastolic pressure.
or
((systolic - diastolic) / 3) + diastolic
Hypertension
130/80 mmHg beginning, 140/80 mmHg true
Acute hypertension
a short period of elevated blood pressure
Chronic hypertension
persistent high blood pressure, over 140/90 mm Hg
Korotkoff sounds
sounds heard while taking the blood pressure
The first sounds are systolic, last sounds are diastolic