Developmental Psych Research Methods
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What makes a particular test a good measure of development?
Must be both reliable (consistent results) and valid (actually measure what it should)
Reliability
Does the test give consistent outcomes each time?
Validity
Does the test really measure what it is supposed to measure?
- relies on operational definitions
Case studies
Method of collecting data that involves creating a detailed record of an individual/groups development
Advantages and Limitations of case studies
Advantages - can provide rich and unique data
Limitations - Lack of generalizability (difficult to make comparisons when based specifically on an individual)
Self report measures
Method of collecting data through structured interviews or questionnaires using standard questions (same questions or inventory for every child)
Advantages and Disadvantages of Self Report Measures
Advantages - researcher has the flexibility to ask follow up questions in clinal settings
Limitations - not very useful for young children who can't banshee questions about themselves as well as may have questionable honesty due to the desirability bias + amplified as children tell us what they think we want to hear, interpretation of questions can be difficult depending on ages
Way to get around the disadvantages of miscommunication in self report methods
Use rating scales adjusted for children Ex. An emoji scale for emotions
Physiological methods
Method of collecting data using by measuring physiological reactions to stimuli Ex. Heart react monitors, fMRI, eye tracking - can show what infant is interested in or recognizes, EEG - can show surprise to use of wrong word for object
Disadvantages of Physiological Measures
Very expensive, hard to determine what exactly caused the response
Observational methods
Method of collecting data by systematically watching behaviour in either a naturalistic or structured observation setting - designed to illicit a desired behaviour
Disadvantages of observational research
observer bias/influence, may be difficult to draw causal conclusions
Observation to Connectedness in Peer Social Play
Utterances between two children playing in the vicinity of each other were coded to determine whether they were topically connected
- had to be connected to same topic and had to respond within five seconds to be counted
Developmental designs
Used to compare across different age groups or across time
cross-sectional, longitudinal, sequential
Cross sectional design
research design that examines children of different ages at the same time
- is most common as is the most cost effective and easy (are opposed to longitudinal)
Disadvantages of Cross sectional design
Cohort effects - if there is something different about one cohort (age group) Ex. Covid 19 causes difference in socialization based on what age it was experienced
Sampling error - happen to get a sample that shows more variability (always more possibility in the in-between subjects designs)
What is a cohort?
A group of individuals of the same age who are exposed to similar cultural experiences/historical events
Longitudinal design
research design in which one group of children is studied over a long period of time
Disadvantages of longitudinal design
Practice effects - skills change due to experience over time
Selective Attrition - have to get participants to come back multiple times may cause CERTAIN people to drop out
Cross generational problem - the longer the study goes on the more society changes which limits generalizability to new time periods
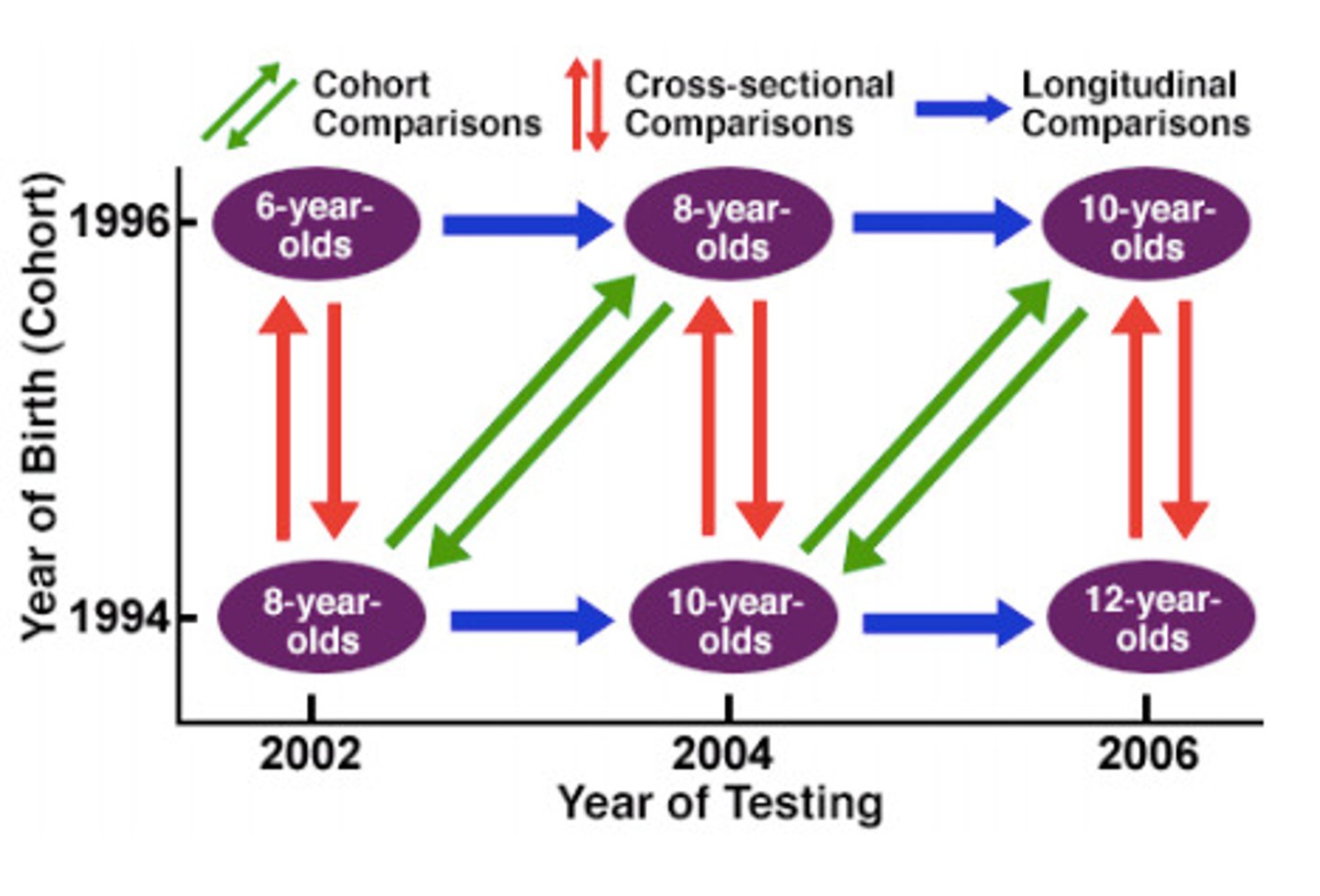
Sequential Design
Combination of cross-sectional and longitudinal designs involving repeated study of different cohorts (cross sectional) at different points in time (longitudinal)
Correlational design
research design that examines the extent to which two variables are related with no experimental manipulation
- can't determine cause and effect
What is r (correlation)
Index of strength and direction of relation between two variables
- ranges from -1 to +1
- strength indicated by absolute value (closer to 1 is stronger than closer to 0)
positive correlation
A correlation where as one variable increases, the other also increases, or as one decreases so does the other (Both variables move in the same direction)
negative correlation
the relationship between two variables in which one variable increases as the other variable decreases (goes opposite directions, an inverse relationship)
Goal of an experimental design
To determine whether a causal relationship exists
An experiment needs
an independent variable - manipulated by researcher
a dependent variable - measure used to collect data (DEPENDs on independent variable)
Quasi-experimental design
Measures the impact of a naturally occurring event - conditions are not manipulated by researchers (can make casual conclusions)