Unit 1 - Thinking Geographically
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Five Themes of Geography
- Place
- Location
- Interaction
- Region
- Movement
Reference Maps
People refer to them for general info about places
Three types of RM's are: Political, Physical, & Road maps
Political Maps
Human created boundaries and designations like countries, cities, etc
Physical Maps
Show & label natural features like rivers, mountains, etc
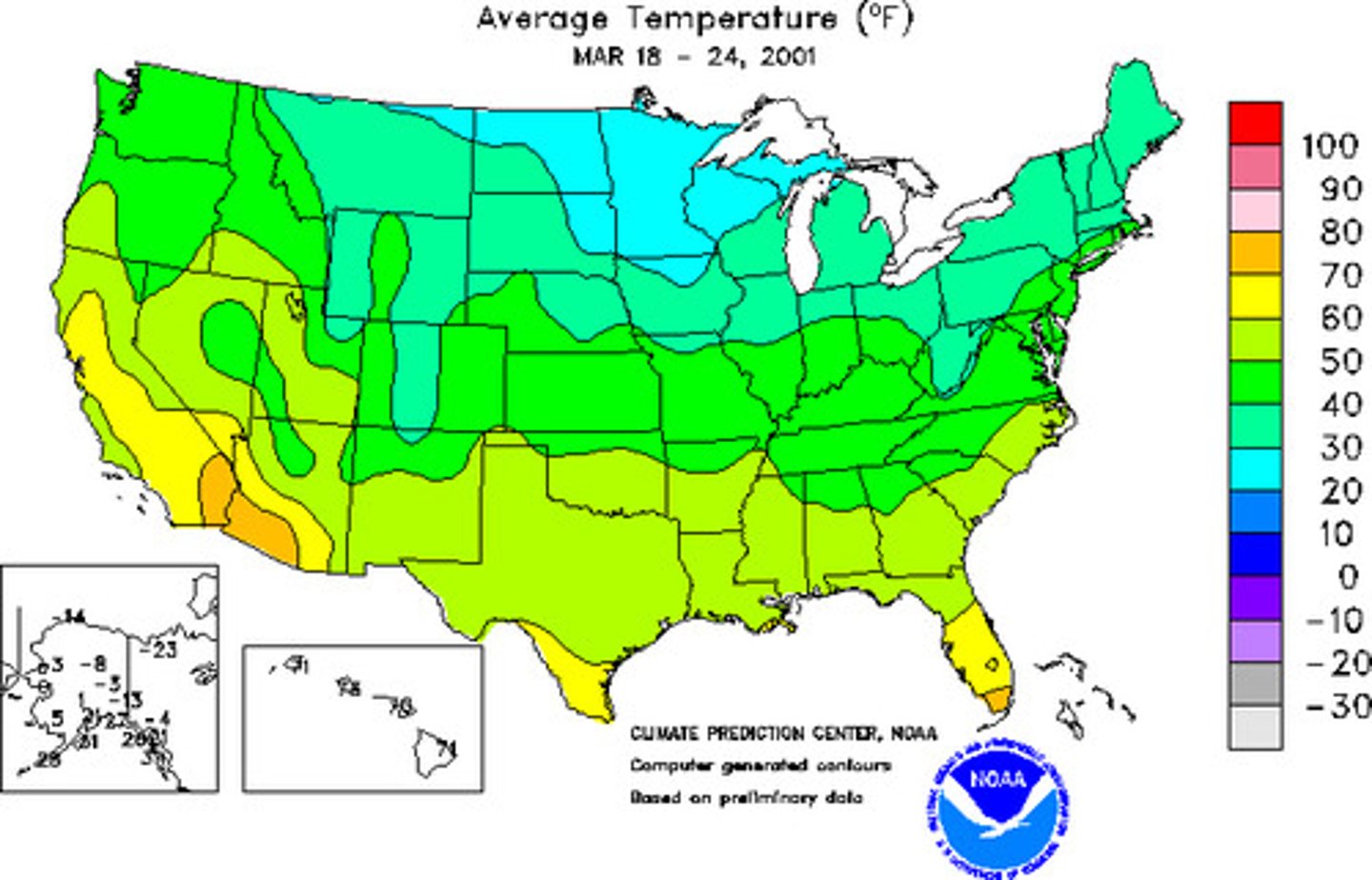
Thematic Maps
Show spacial aspects of info or of a phenomenon
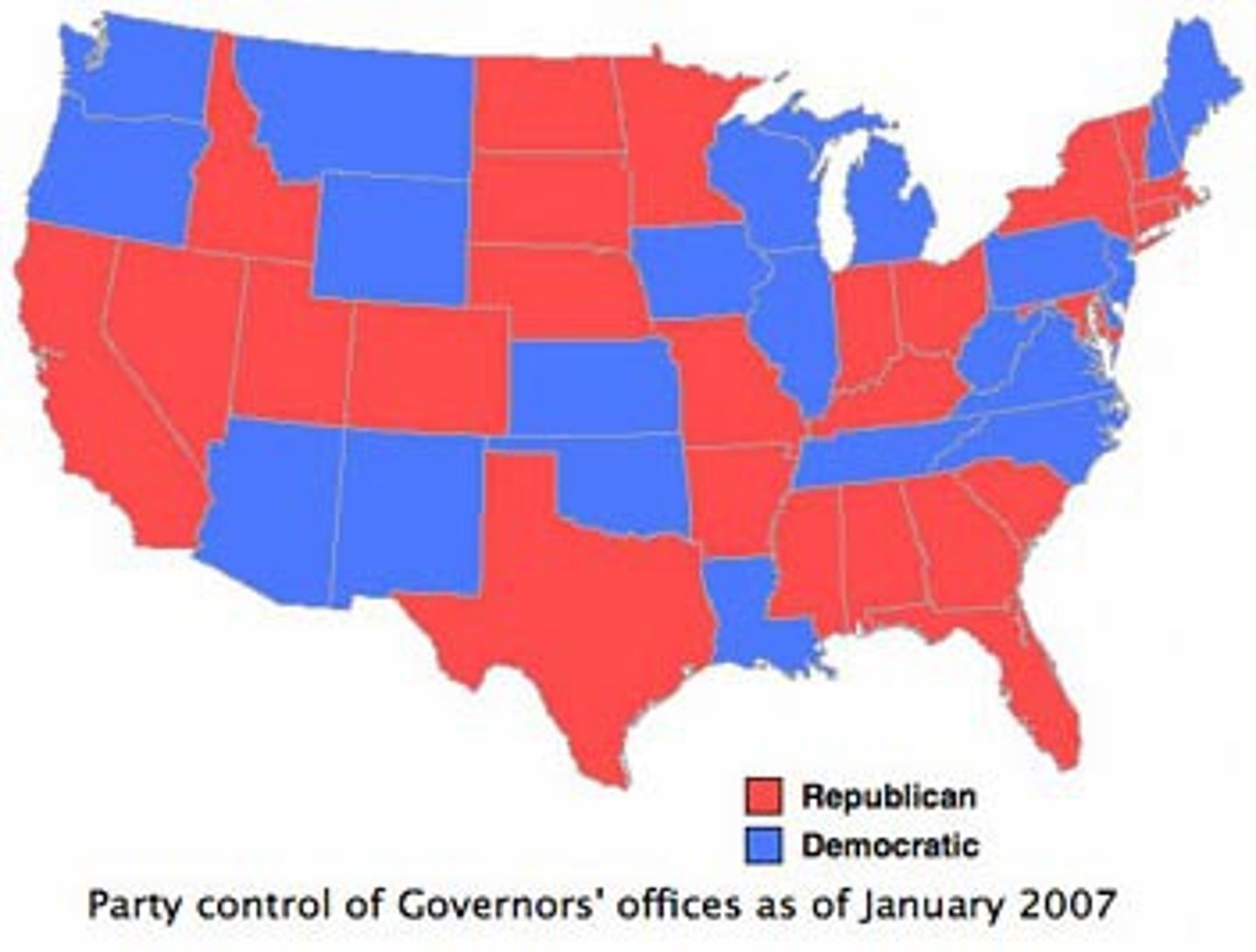
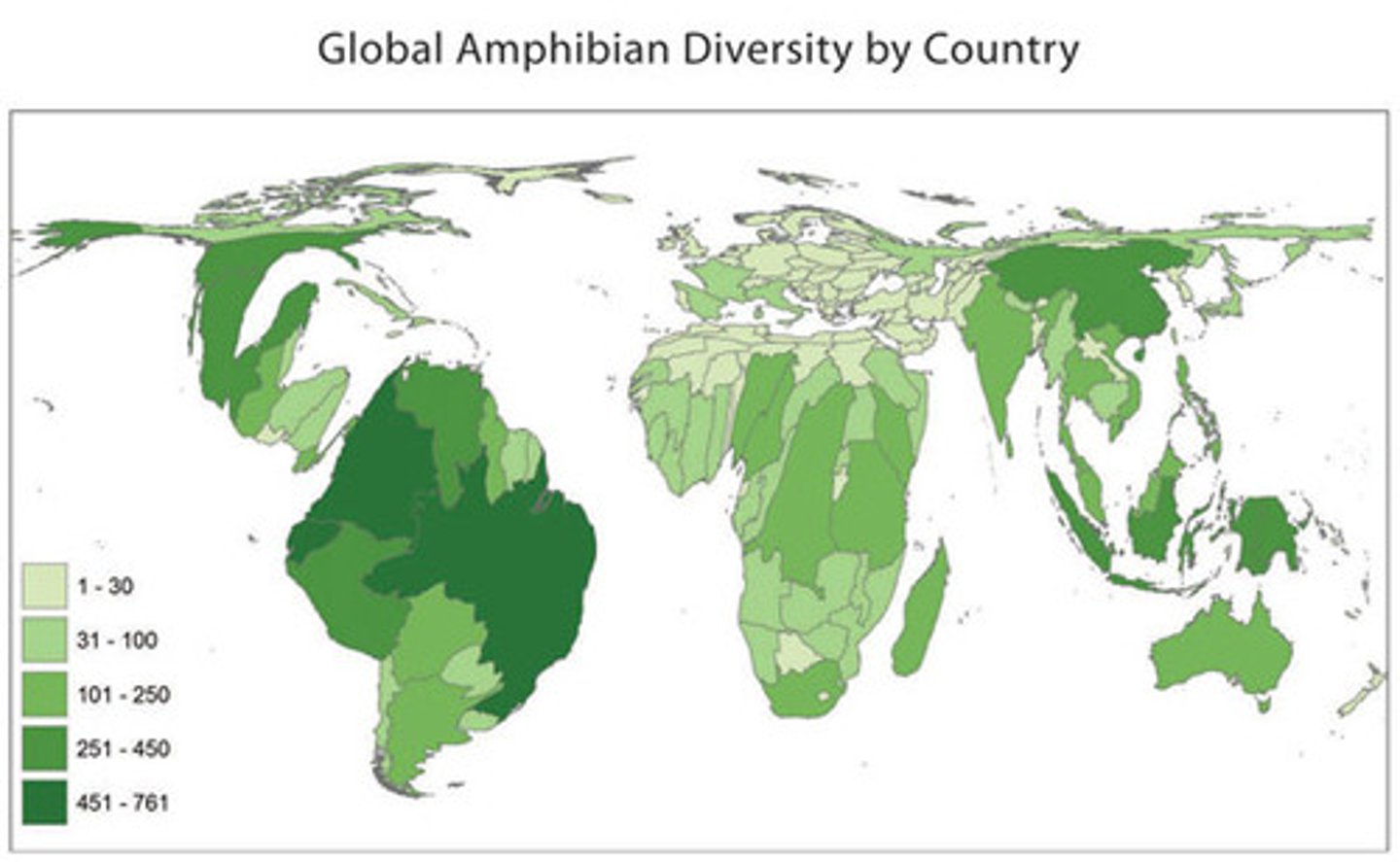
Cloropleth Maps
- Use various colors, shades of one color, or patterns to show location and distribution of data
- Usually, the darker the color, the higher the statistical value
- Always look at the key!
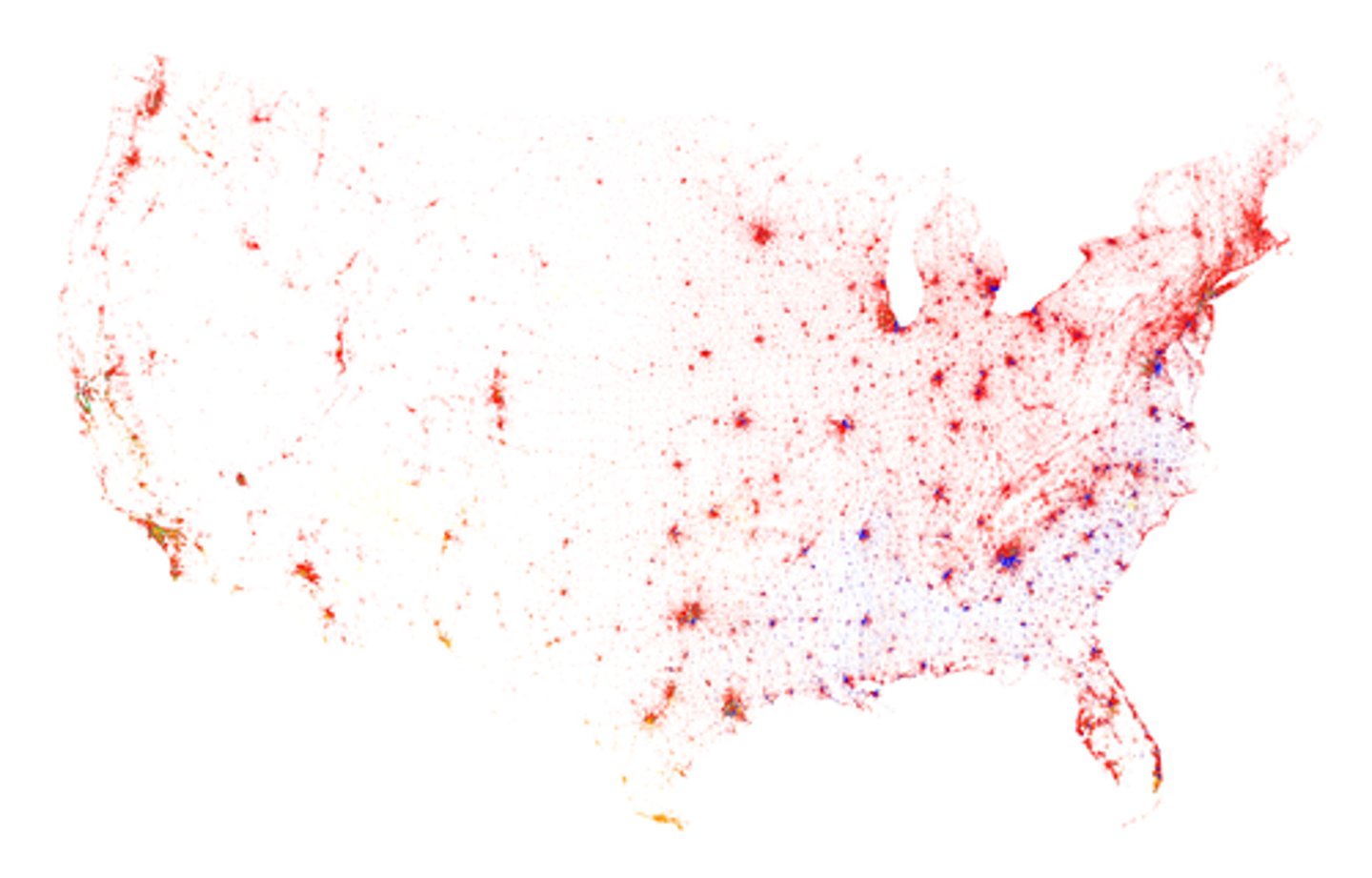
Dot Maps
- Show the specific loction and distribution of info across territory
- Each dot represents a specified quantity
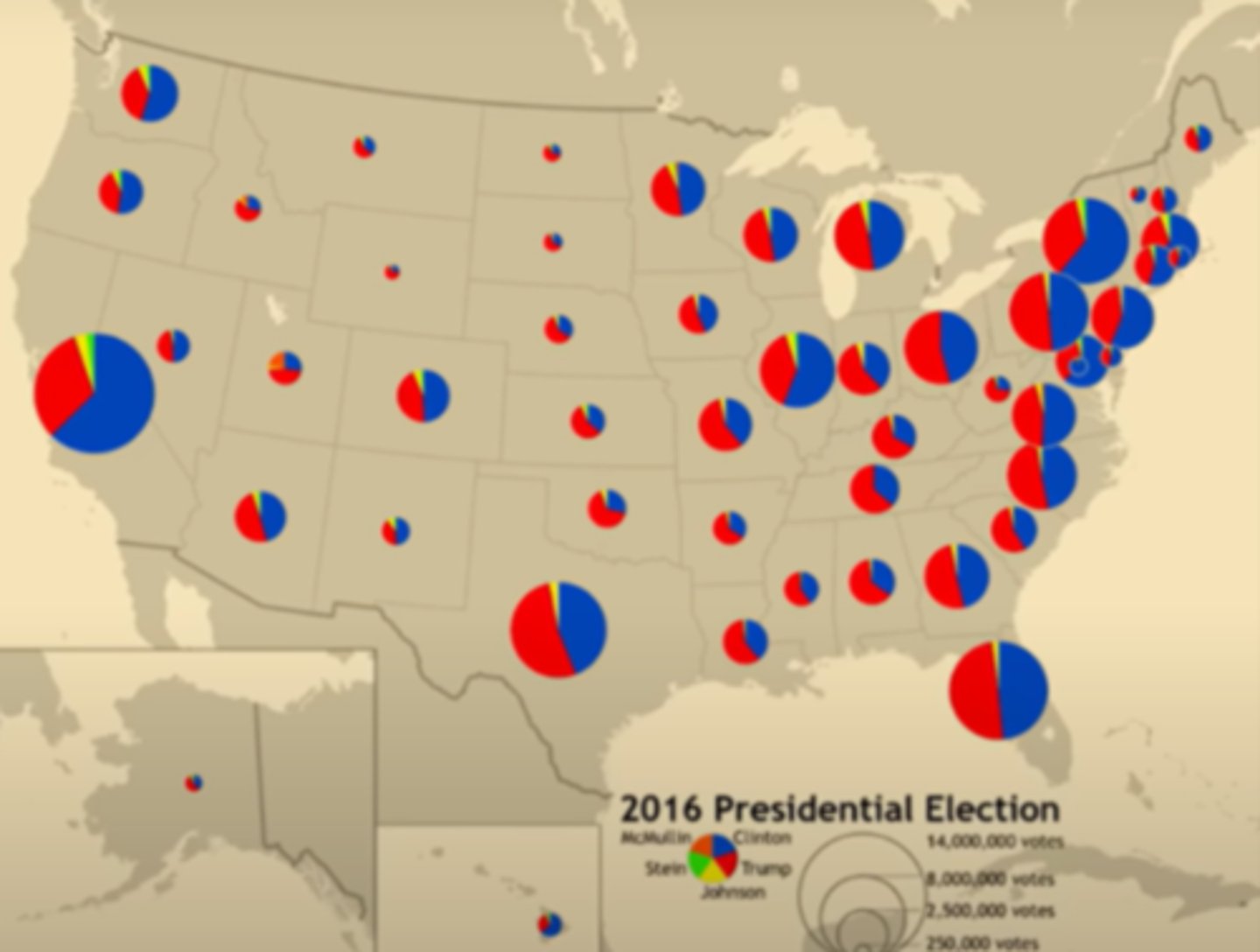
Graduated (proportional) Symbol Maps
Use symbols of different sizes to indicate different amounts of what is being mapped
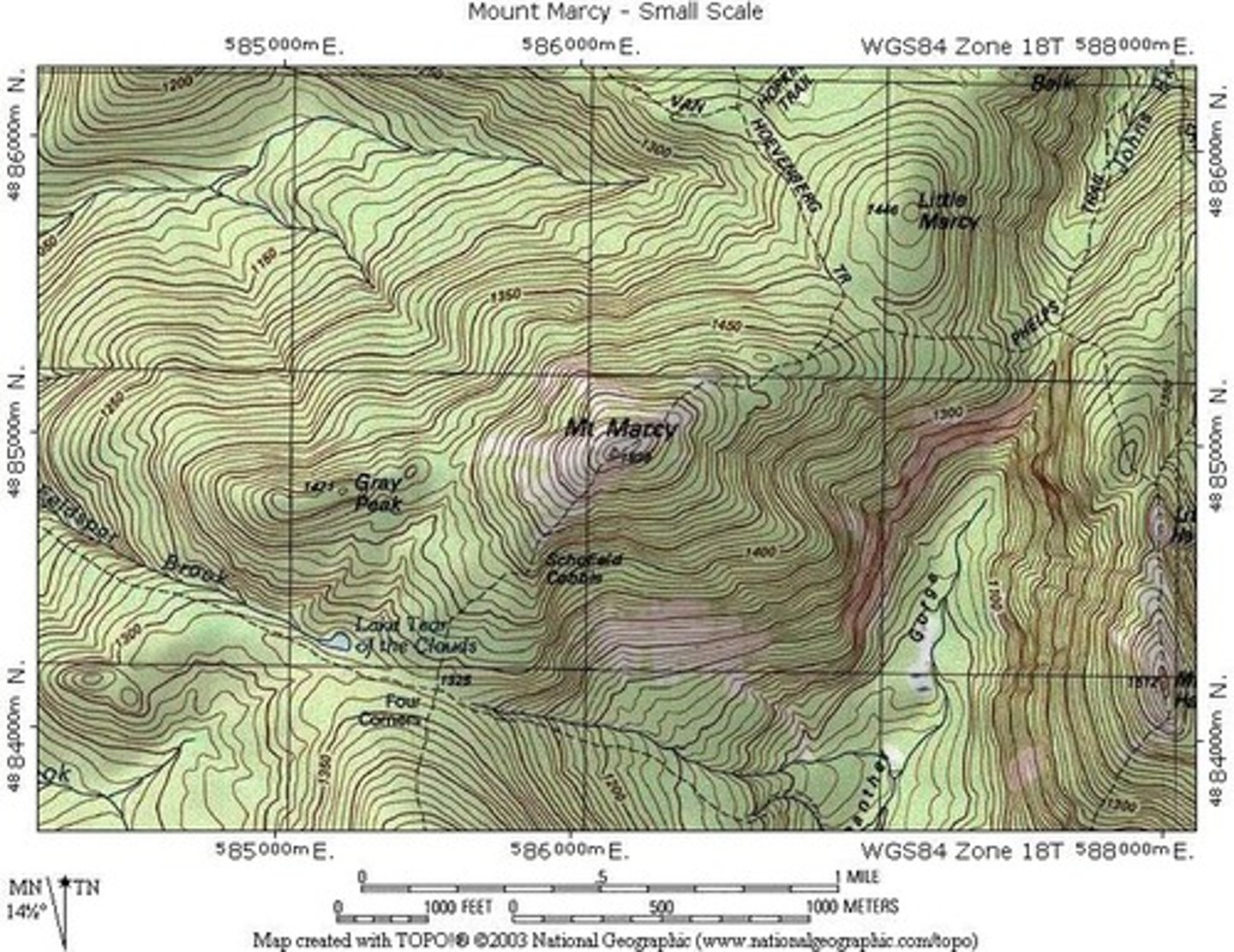
Isoline Maps
- Use lines that connect points of equal value to show variations in data
- Where lines are close together, change is rapid
-Where lines are far apart, the phenomenon is relatively the same
- Most common type: topographic map
Cartograms
Sizes of countries are shown according to some specific statistic
Mercator Map
- ALL land has the correct shape
- Map can be used for oceanic navigation
- Size of land is MASSIVELY distorted
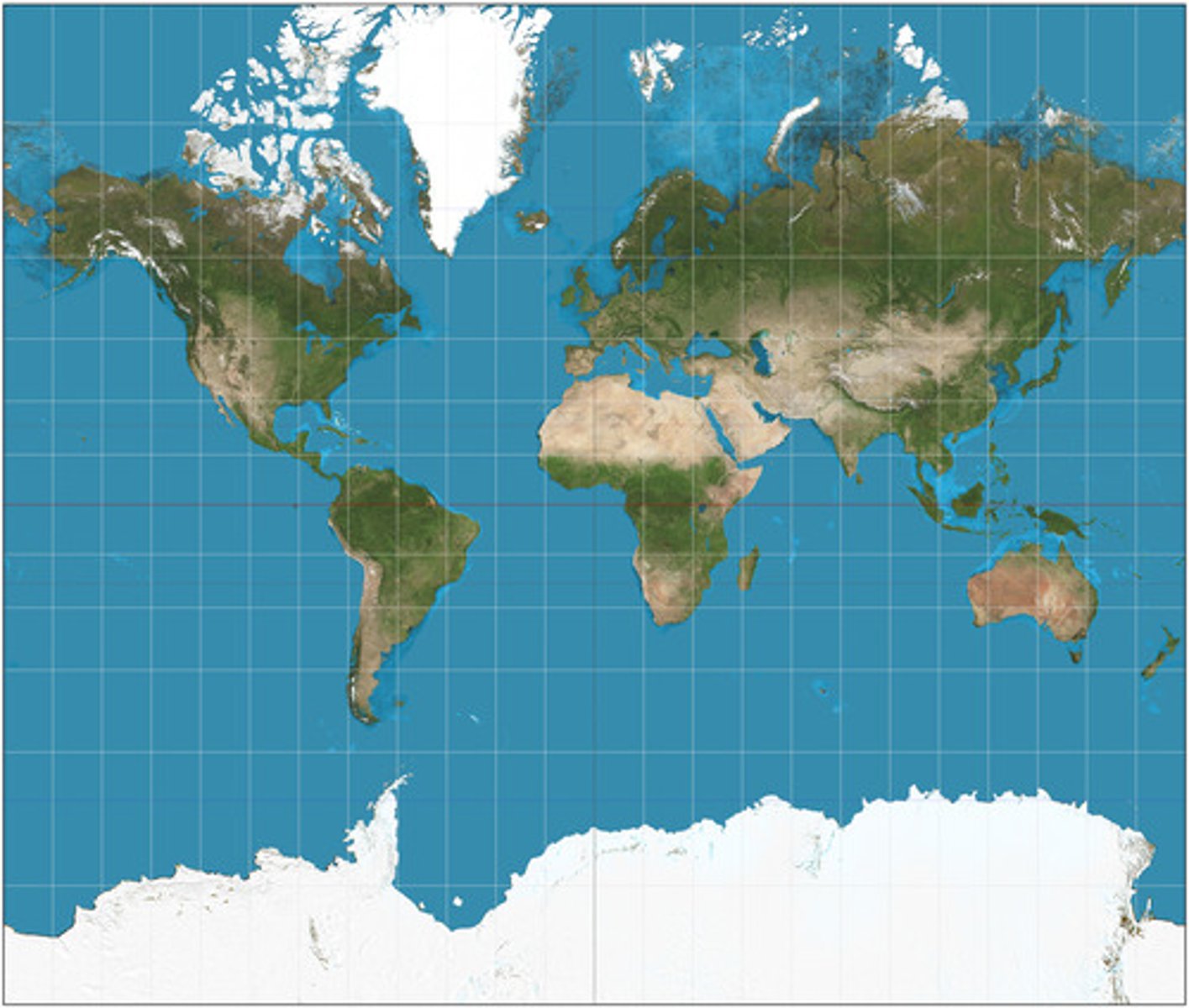
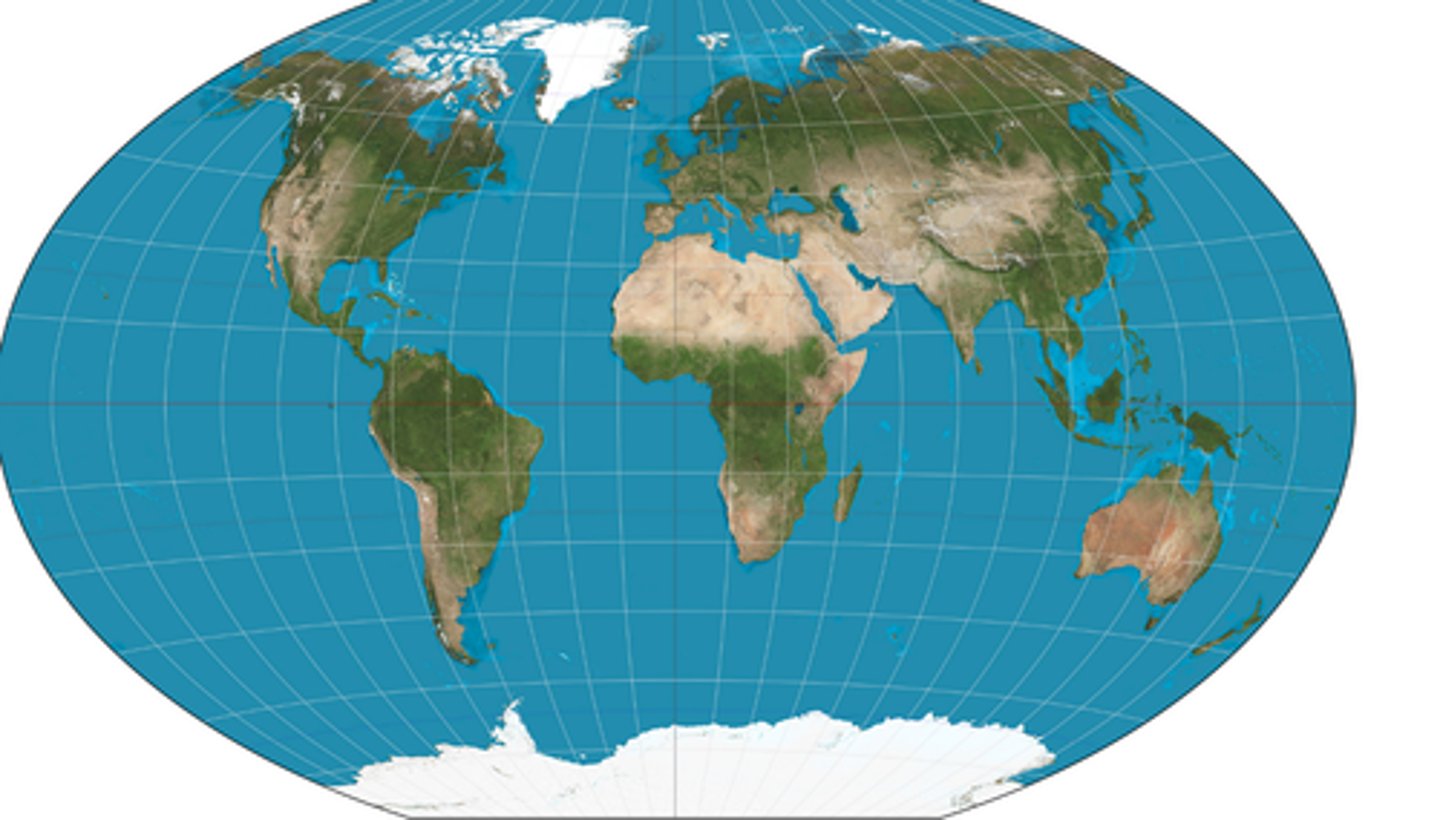
Goode's Map
- Minimizes distortion of the size & shape of land masses
- Land masses appear large compared to oceans
- Can't be used for oceanic travel
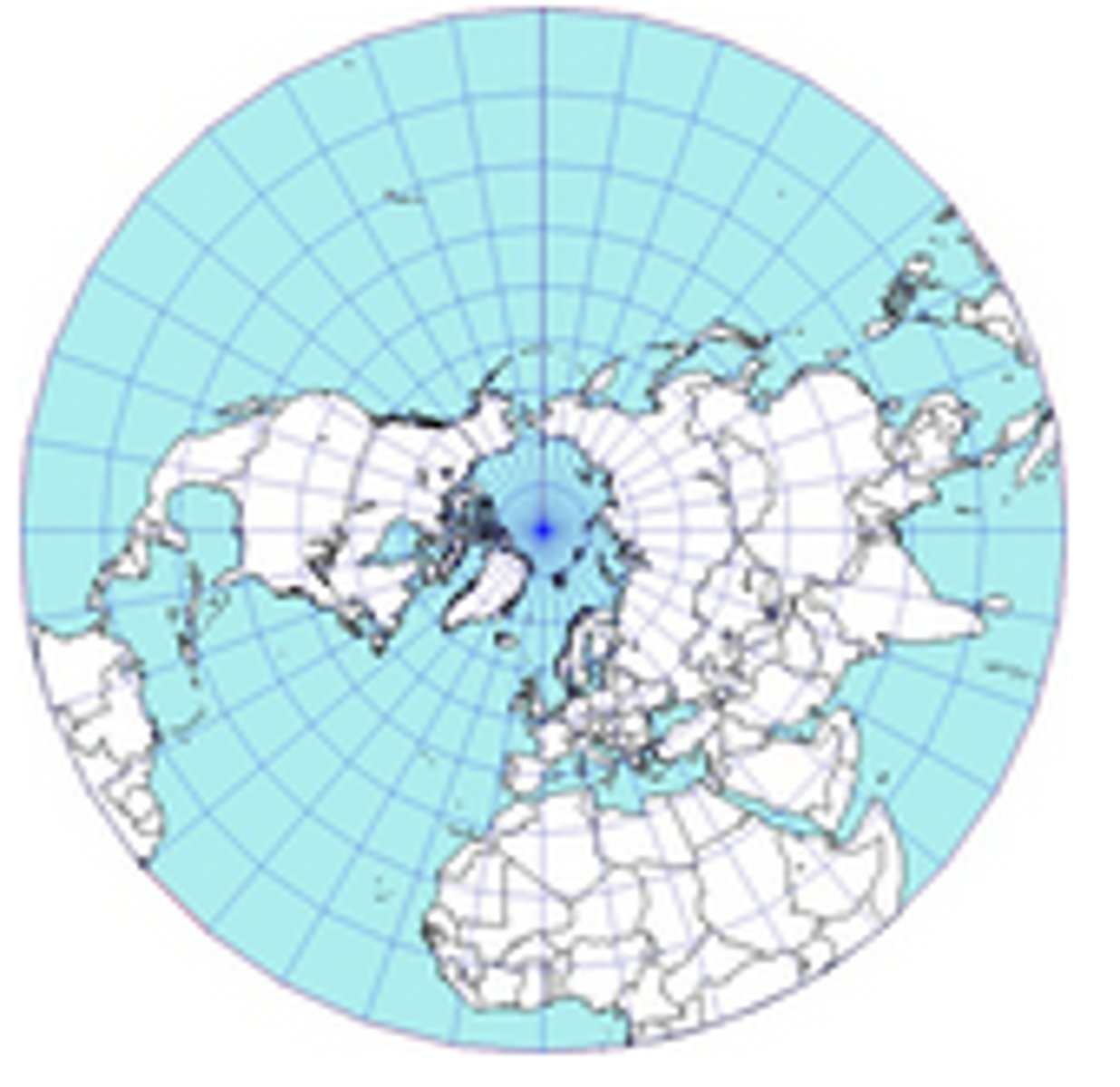
Polar Map
- Accurately displays BOTH polar regions
- Size of continents are realistic
- Distortion increases as you move away from the poles
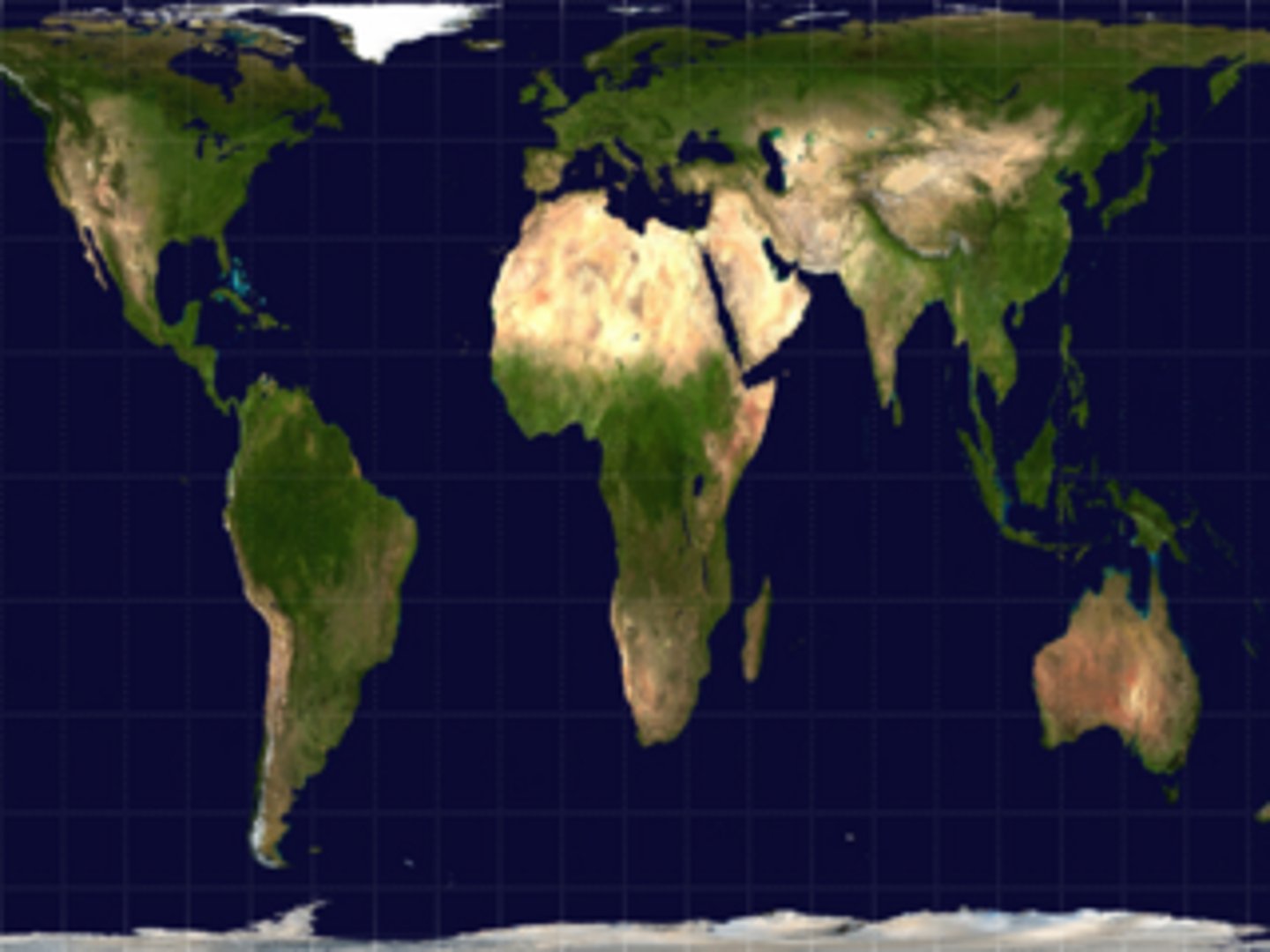
Gall Peters Map
- Size of land masses is accurate
- More accurately depicts the size of developing countries (they are small in the mercator projection)
- Shape of land is INACCURATE!!
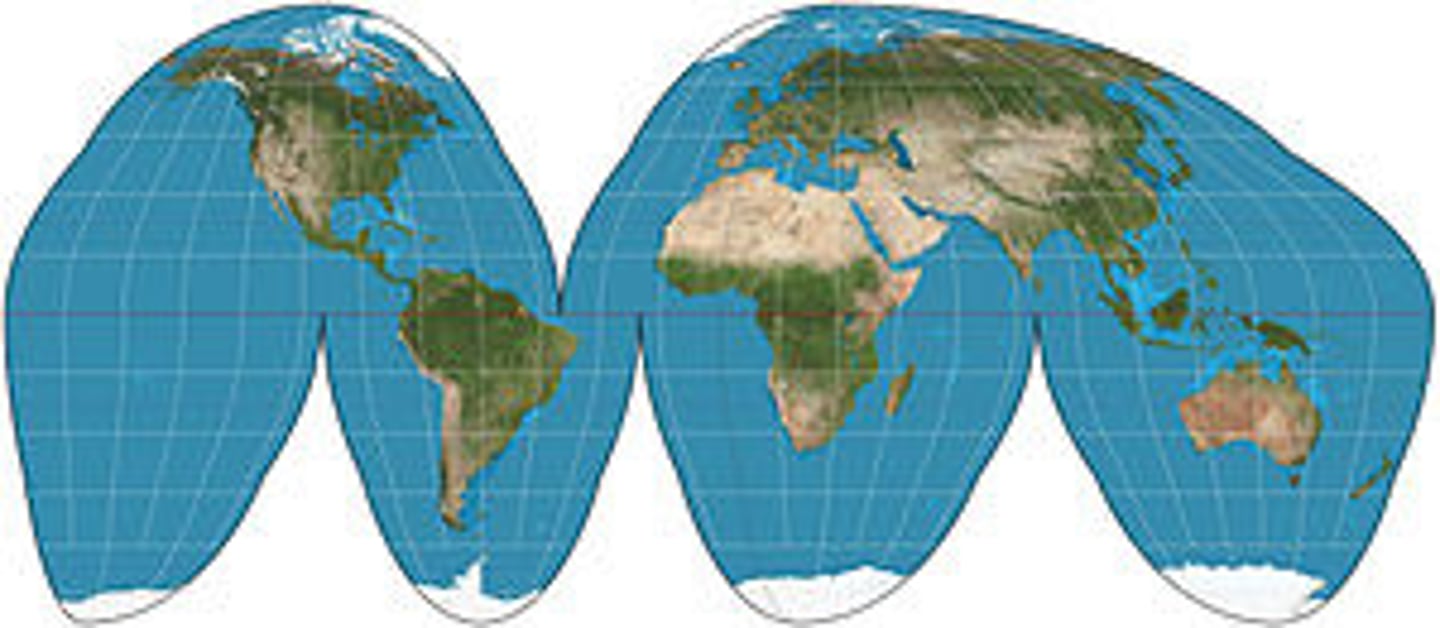
Winkel (Johnson) Map
- NO major distortion
- Oval shape appears more like a globe than does a rectangle
- Area, shape, size and direction are all slightly distorted
Formal Region
- An area united by one or more traits
- Has a defined border
ex.
Physical - Sahara Dessert
Cultural - Northern Belgium where people speak Flemish
Functional Region
- Organized around a focal point (node)
- Defined by an activity that occurs across region
ex.
Pizza delivery area (pizza store is the node)
Sports team fanbase
Newspaper circulation (the same guy prob delivers both you and your friends amazon packages)
Perceptual/Vernacular Region
- Defined by the informal sense of place people give to them
- Boundaries vary widely (people have a different sense what defines this region)
ex. - The American "South", "Upstate" NY
Geographic Info Systems (GIS)
- Computer system that can store, analyze, and display info from multiple digital maps
- Uses include: Analysis of crime data, urban planning, transportation & time analysis
Global Positioning System (GPS)
- GPS receivers use locations of multiple satellites to determine exact location
- Uses include: navigating ships, aircraft, & cars; locating borders
Remote Sensing
- Use of cameras mounted on aircraft or satellites to collect digital images
- Uses include: determining land cover and land use; monitoring environmental change
Online Mapping & Visualization
- Websites that provide graphical and text info as maps and databases
- Example: Google Earth
- Uses include: Planning trips, finding landmarks & businesses, plotting storm tracks
Absolute Location
precise spot that never changes latitude and longitude
ex. street addresses
Lines of LATITUDE
- Run parallel to one another
- Center line is 0° (the equator)
- Get shorter as they approach the poles
- Three categories include..
High (60° - 90°)
Mid (30°-60°)
Low (0°-30°)
Lines of LONGITUDE
- Also called meridians
- 0° East & West is the Prime Meridian
- Located in Greenwich, England
- All meet at the poles
- Time zones are approx. 15° apart
Relative Location
- Where something is located in relation to other things
- Changes over time as accessibility changes
ex. ghost towns
Space
a location w/ no cultural meaning
Place
- the specific human & physical characteristics of a location.
- Types of places are sites and situations
Site
characteristics of that location
ex. soil type, climate, human structures, etc.
Situation
- synonym for relative location
- can change over time
sense of place
people perceive characteristics of places based on their personal beliefs
flows
movement of people, things, or info from one place to another
distance decay
- as distance between places increases, interaction between places decreases
-also called friction of distance
time - space compression
- the shrinking "time distance" between locations due to improved transportation and communication
- Global forces now influence culture almost everywhere
- Local diversity reduced
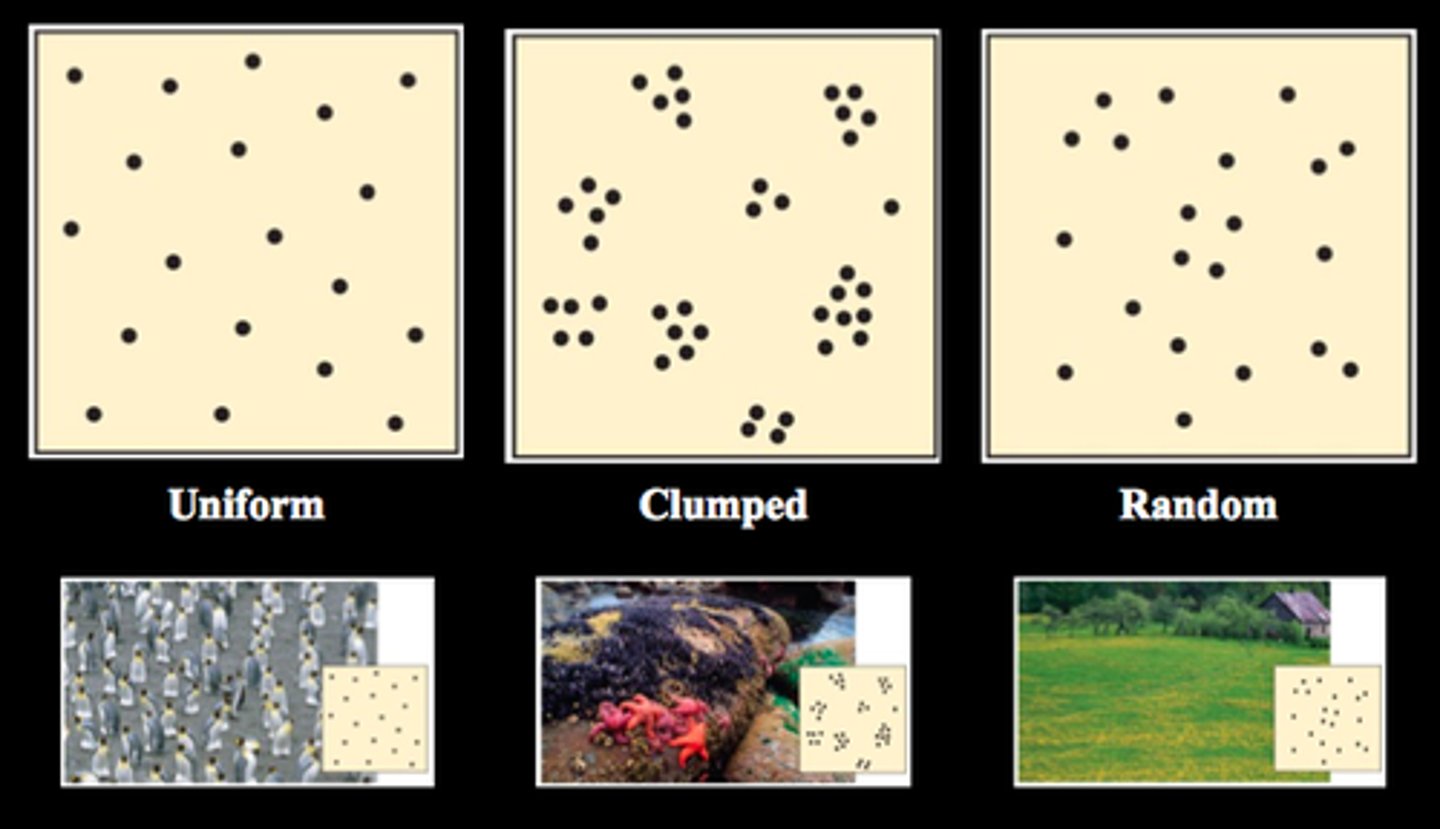
Pattern
- geometric arrangement of things like people, houses, stores, etc
- this arrangement can be CLUSTERED, RANDOM, OR UNIFORM

hierarchical diffusion
occurs when ideas leapfrog from one important person, community, or city to another, bypassing other persons.
ex. trends set by celebrities, spread of fashion from influencers to followers
contagious diffusion
the rapid spread of ideas in the manner of a contagious disease, moving from person to person through close contact
ex. rapid spread of internet memes, spread of cold or flu from person to person
stimulus diffusion
occurs when a specific trait is modified and adapted in new locations to create a new, related trait. the main idea is the base principal.
ex. McDonalds altering it's menu for different countries (they have veggie burgers in india because Hindu's do not eat beef)
Relocation Diffusion
occurs when individuals or groups w/ a particuar idea or practice migrate from one location to another, thereby bringing the idea/practice to their new homeland
ex. immigrants introducing italian food, like pizza, to America & the spread of Christianity via European colonization
Scale is..
How zoomed in/out the map or image is.
zoomed out maps = SMALL!! Less detail
zoomed in maps = HUUGE!!! More detail
scale maps = shows a HUGE area with LESS detail
Global scale
Map of the world
- aggregated at a global level
- almost impossible to use
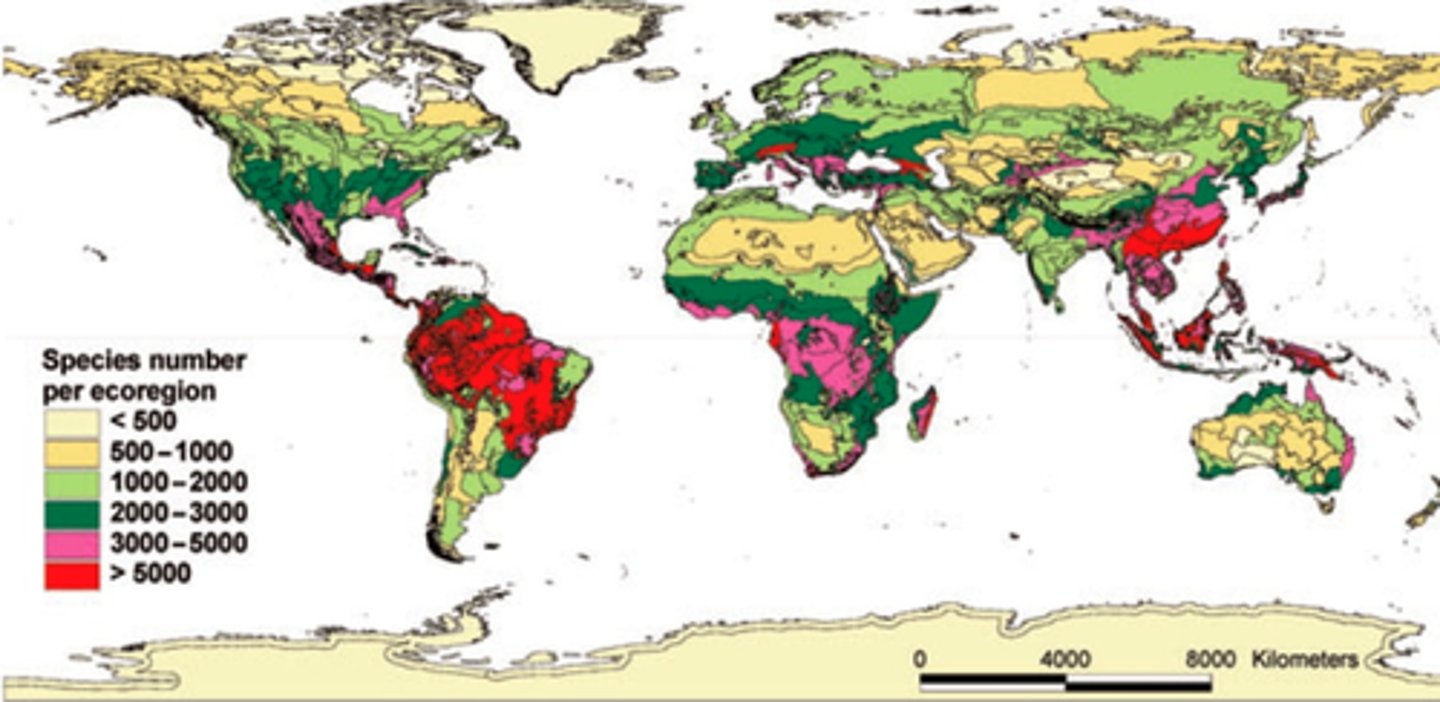
Regional Scale
map of a specific area of the world
- aggregated at regional level
- world regions, continents
(see how certain parts of the map r highlighted?!)
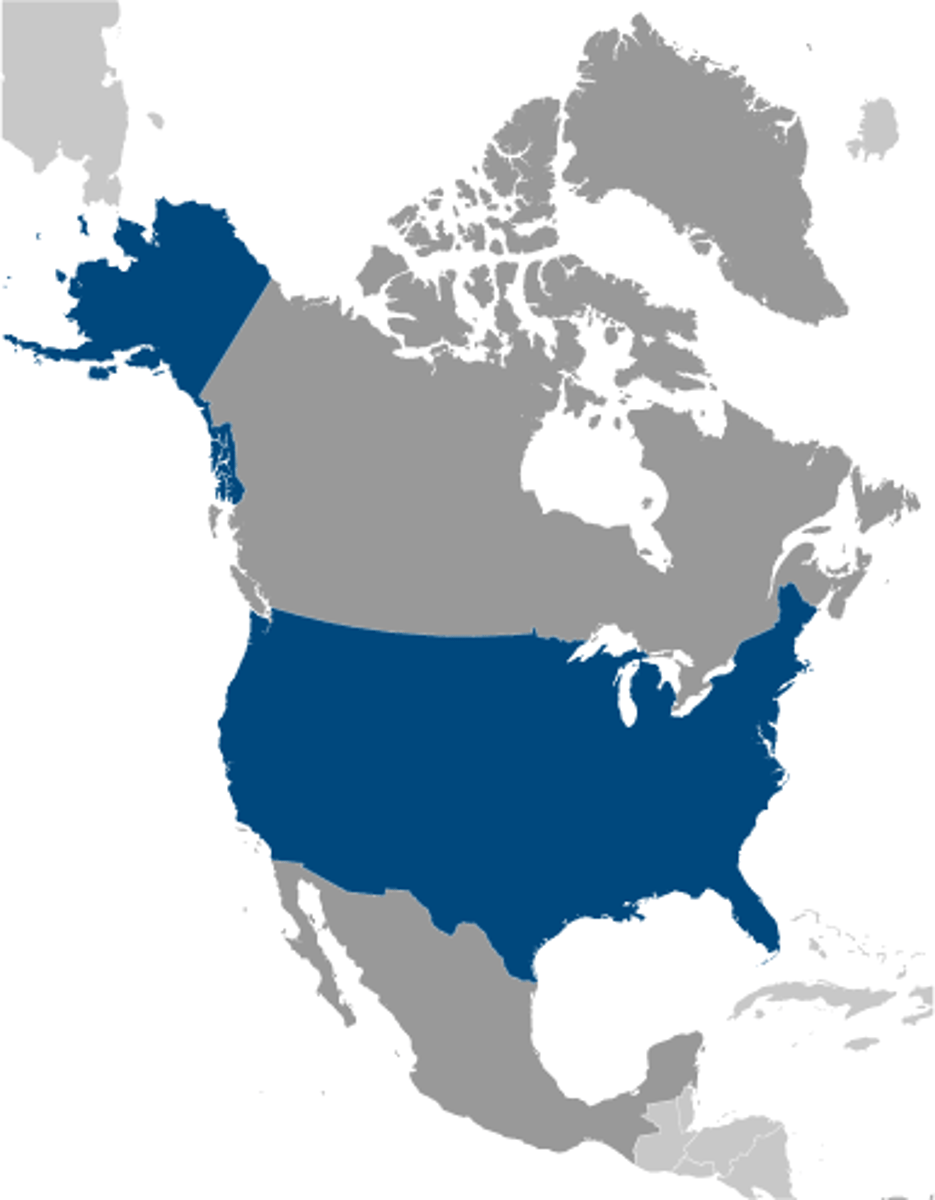
National Scale
map of a specific country
- data is aggregated at a national level
- displays one or more countries
(notice how ONLY USA is highlighted blue)
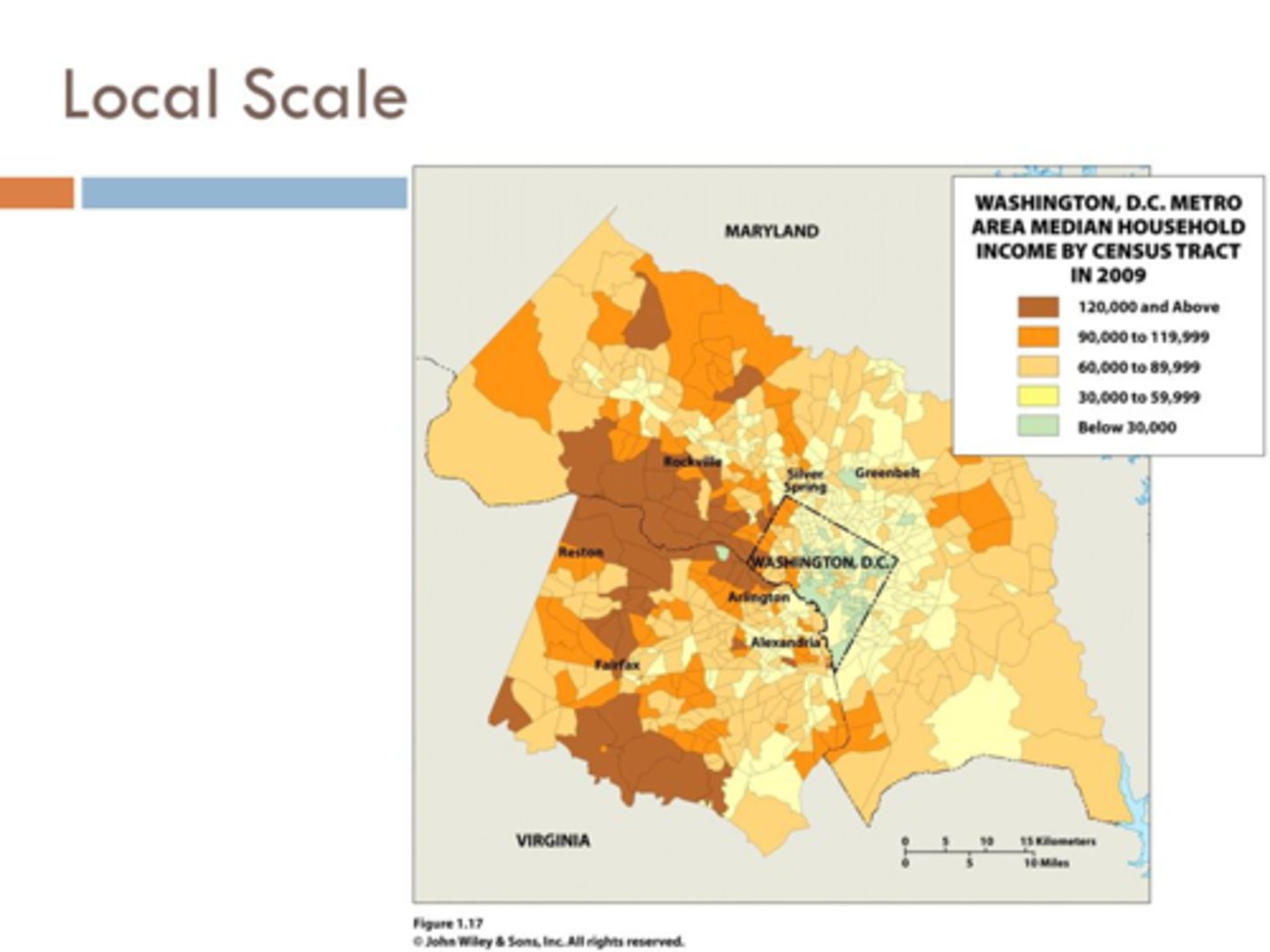
Local Scale
map of a city, state, or country
-data is aggregated at a local level
- shows subregions of a country
scale of analysis
data on a map
when you analyze maps, ALWAYS ask yourself 2 things..
- what's the geographical scale of the map?
- what is the scale of analysis of the map
Why do geographers divide geographic spaces into regions?
To better understand, compare, and analyze areas that share similar characteristics like culture, climate, or landforms
Quantitative Data
- Deals with numbers
- Measurable data
Qualitative Data
- Deals with descriptions
- Non measurable data
Examples of QUANTITATIVE Data
- Census Data
- Geospacial Data
- GPS Coordinates
- Remote sensing
- Thematic Maps
- GIS
Examples of QUALITATIVE Data
- Interviews
- Photographs
- Audio Recordings
- Surveys
- Thematic Maps