Geophysical systems D1.2
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Distribution of hazards
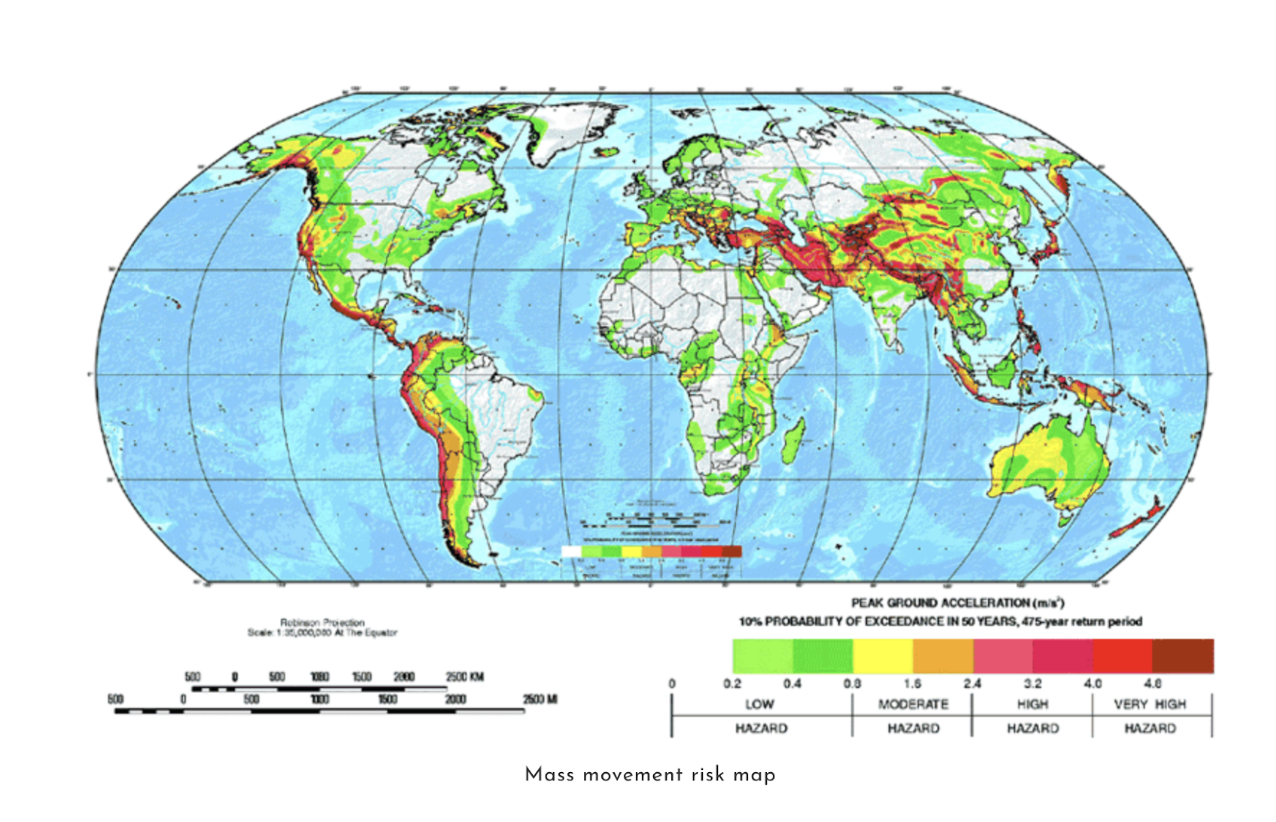
What is used to measure earthquakes
Used to use Richter scale
Now they use the moment magnitude scale
Moment magnitude - current + more accurate measurement
Interpret and record a broader segment of seismic systems
How are recurrence intervals of earthquakes useful for risk management?
Recurrence interval = the average time interval that occurs between two recorded events of seismic activity, of equal magnitude, along the same fault.
San Andreas fault = transform boundary |(no volcanoes formed) - two plates moving at different speeds - build up of pressure -- earthquake
Parkfield section (straight section of the San Andreas fault) = magnitude 6
Many fault lines in california
Recurrence interval = every 20 years
Scientists use computer simulations to work out if there's going to be an earthquake
How wide scale, how many people affected, what areas affected, is there any construction that should not be allowed in an area like this - high risk of damage, eg. airport on this land.
San andreas = big threat to san francisco = less to los angeles
Lower section on fault = recurrence interval is less - 190 years
How to prepare for an earthquake - Short and long term
Short term - What individuals can do
Schools - special session on what to do if earthquake
In japan - earthquake prepare drill
Families - first aid kits, water and food, radio
Long term
Reinforce building codes - accentuated
Power lines - reinforce and redundancies
Avoid building highways that collapse - redesign the roads
Hazard zoning
What is used to measure magnitude of volcanoes
VEI = Volcanic explosivity index - 0 to 8 scale
Amount of erupted tephra
Eruption column height
Eruption type
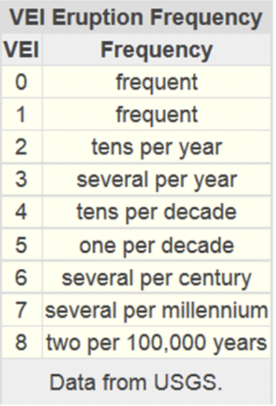
VEI levels and examples
0 = trickle of lava - Hawaiian volcano of Kilauea - not tallest part of island but erupts more actively - shield volcano
1 - gentle eruption - italy stromboli = erupted for almost - Strombolian volcano
2 - several mild explosions - indonesia mount sinabung has been erupting since 2013
3 - catastrophic - lassen peak northern california
4 - happen every other year - 2010 iceland Eyjafjallajokull - high in air
5 - things more dramatic - mt vesuvius + mt st helens - blue top + lost altitude + erupt out of side - Volcanion
6 - colossal eruptions - krakatoa - triggered tsunami - 1883
7 - every 1000 years - indonesia mt tambora
8 every 50,000 - yellowstone caldera would reach this level if it were to erupt again - us - national park - so massive that people don't understand it is a volcano - supervolcano - if it erupted = would make big difference - many deaths, people, animals - climate would change. = Plinian
Disaster risk equation
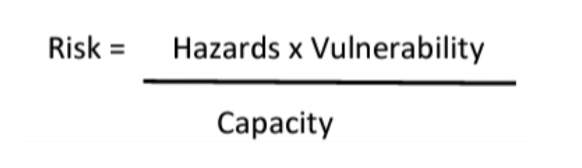
Hazard risk factors - Haiti port au prince 2010

Risk
Risk: To be susceptible to physical or even emotional attack
Capacity
Capacity: The ability of a communtity to absorb and ultimately recover from a natrual disaster
Resilience
Resilience: The ability of a community to bounce back after hazardous event
Affected by income of country
Japan = better than Haiti
Hazard
Hazard: The exposure of people to hazardous event which make present a potential threat to people or their possessions including buildings and structures
Vulnerability
Vulnerability:
Characteristics + circumstances of community, asset or system that make it available to the damaging effects of a hazard.
Aspects of vulnerability:
Physical
Social
Economic
Environmental
Examples:
Poor design and construction of buildings - due to governance
Linadequate protection of asset - people who choose to hold money under bed rather than a bank account - hazard will destroy this
lack of public information and awareness,
limited official recognition of risks and preparedness measures, and
disregard for wise environmental management.
Vulnerability varies across communities and within communities - also over time
4 aspects of vulnerability
4 types of vulnerability:
Physical vulnerability
Aspects
population density
Remoteness of a settlement
Site
Design and materials used for infrastruatire/housing
Example:
Wooden homes are less likely to collapse in earthquake - more vulnerable to fire
Social vulnerability
Aspects
Inability of people/organisations/societies oto withstand impacts due to:
Inherent social interactions/instituions/systems of cultural values
Linked to level of well being
Levels of literacy and education
Existence of peace and security + acess to basic human rights
Systems of good fovernance
Social equity
Positive traditional values
Customs and ideological beliefs
Overall collective organisational systems
Example:
When flooding occurs some citizens - children/elderly/differently-able - unable to protect themselves or evacuate if necessary
Economic vulnerability
Aspects
Economic status of individuals/communities/nations
Poor = more vulnerable to disasters - bc they lack the recoutrse to build sturdy structures and put other enginneering measures in place to protect themselves from being negatively impacted by disasters
Example:
Poorer families may live in squatter settlements because they cannot afford to live in safer (more expensive) areas
Environmental vulnerability
Aspects
Natural resource depletion
Recourse degradation
Example:
Wetlands - Caroni Swamp - are sensitive to increasing salinity from sea water, and pollution from stormwater runoff containing agriculture
Progression of vulnerability
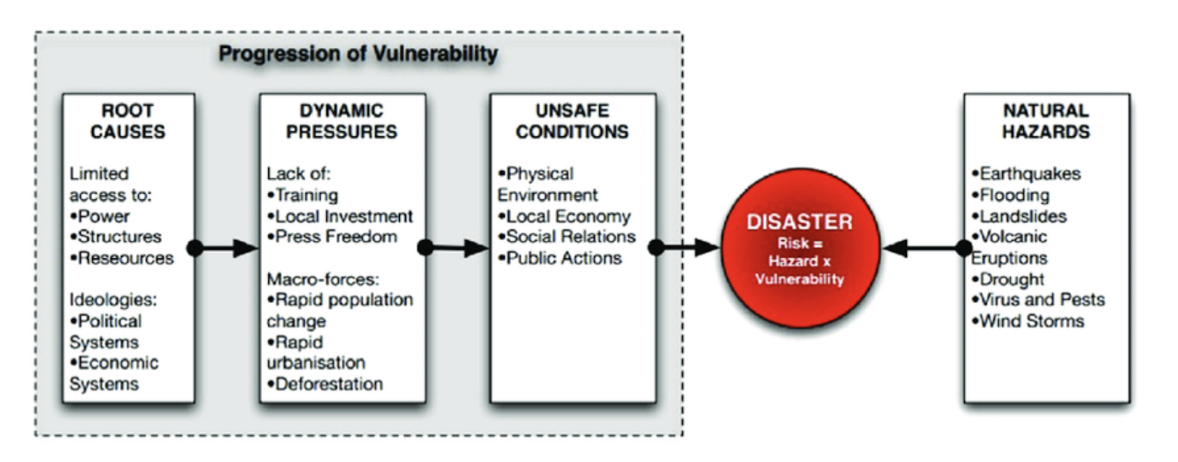
People who are more vulnerable than others
Poor
Children
Disabled
Elderly
Females - Carer role
For example, according to an Oxfam survey, four times as many women than men were killed in Indonesia, Sri Lanka, and India during the 2004 tsunami because men were taught how to swim and climb trees at young ages, while women were not.
Urban populations can have better access to healthcare and their needs can be more easily met following a disaster.
Initiative that could be taken to reduce vulnerability ro natural disasters
Increase level of preparedness - emergency kits - education
building prevention in hazard areas
Improve quality of housing and infrastructure
What geographic factors contribute to geophysical hazards becoming disasters?
- Geographic factors = physical
Slope
Location - near coast line → create tsunami
Liquefaction = secondary hazard of earthquake
Rural vs urban location
If epicentre in urban location = affect more people
Time of day
Degree of isolation
What geographic factors contribute to geophysical hazards becoming disasters? - examples
2004 Indian Ocean tsunami in Banda Aceh, Indonesia
Altitude - how close to sea level
Location/Direction of the wave = affect land
Relief plane - how flat or hilly
2021 Nyiragongo eruption in Dominican republic of congo
Gradient of slope - influence where lava flow goes
Valleys were affecting flow of lava
Where plumes are - living directly above a plume = must higher risk
Type of eruption - lava erupted from flank of volcano
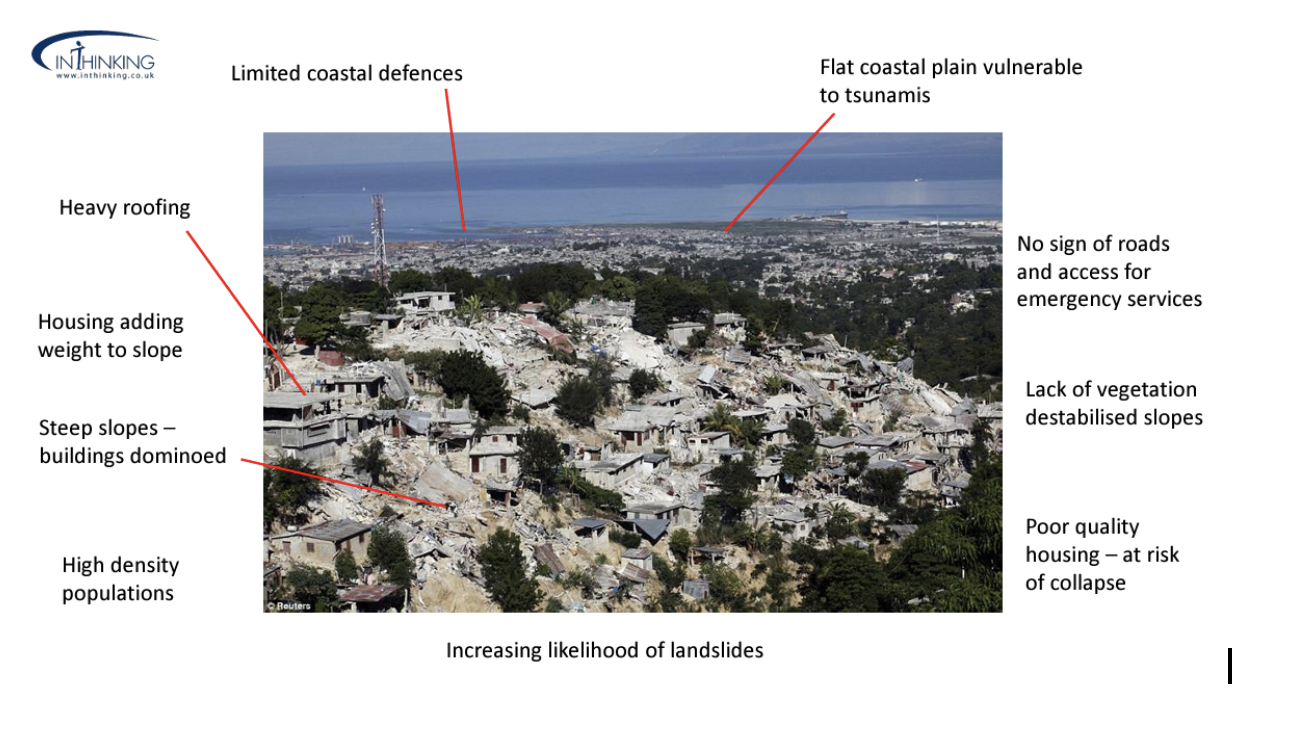
2010 7.0 earthquake in Haiti
Tsunami risk
Slope
Underlying geology that effects shaking ons surface
No liquefaction on hillside but near coast
Relief
2018 in Palu earthquake and tsunami Sulawesi
When tide goes far out it is a sign of the wave - wave = very large
- Epicentre triggered earthquake which then caused tsunami which channelled into that small area - waves became bigger because less space bc is channelled + triggered liquefaction and landslide
- inlet
TIming of event
Most people were asleep - but scientists figured out it is better when they were sleep because if it was during the day thousands of people would have died because of poor infrastructiure
A small matter of what time it occurs can make a huge impact on the exposure to risk.
L'Aquila in italy
Rural vs urban
In urban places - can get help faster in terms of
emergency aid
search and rescue
temporary shelters
In remote/rural areas it is much more difficult to get in the help fast
Local factors
Type of eruption
Altitude
Location relative to the direction of tsunami waves
Inlet
Geology
Soil type