Cosmology
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What are the characteristics of quasars?
Emit mostly infrared and radio light
large optical red shifts, they emit 10^ 38-42 watts of energy (luminosity) but are very distant
Not much bigger than a star in size
What are quasars?
An active galactic nucleus; type of supermassive black hole surrounded by a disc of matter resulting in jets of radiation to be emitted from its poles.
They are the most distant measurable objects in the universe.
What is the Big Bang Theory?
A theory for the origin of the universe. It says that if time were to be reversed, the universe must have orignated from an extremely hot and dense point (singularity) and has been expanding since.
Now, the universe is expanding and decreasing in density and cooling down.
Evidence for the big bang theory
(also known as HBB - hot big bang theory)
Hubble’s law; galaxy’s recessional velocity is directly proportional to its distance from Earth implying that the universe expands from a common starting point
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
Explains the abundance of hyrdogen and helium in the universe
Proof and causes of the rate of expansion of the universe
rate of expansion is increasing
measurements of supernovae do not agree with predictions from Hubble’s law; supernovae are less bright than expected
there is no known energy source causing rate of expansion to increase
What is cosmic microwave background radiation?
High energy radiation that is isotropic; comes equally from all directions in the Universe
Fits a black-body curve with peak wavelength corresponding to a temperature of 2.73K
Tiny variations in temperature, corresponding to tiny variations in density of the Universe.
What do variations in CMBR temperature imply?
Some regions of the universe would be more dense, therefore leading to gravitational collapse and the formation of galaxies.
What is the doppler effect?
The apparent change in frequency of a wave due to the relative motion between the source of the wave and the observer.
What is redshift?
occurs when the source moves away from the observer
waves spread out; apparent increase in wavelength and decrease in frequency (red light has low frequencies)
the more distant an object, the greater its redshift
What is blueshift?
occurs when the source moves towards the observer
the waves compress; apparent decrease in wavelength and increase in frequency (blue light has high frequencies)
What does each sign mean in the doppler shift equation?
change in lambda: apparent wavelength emitted by moving source - emitted wavelength of stationary source
v: relative speed between the source and the observer
change in f: apparent frequency emitted by moving source - emitted frequency of stationary source
What happens in the doppler formula if the source is moving away?
apparent wavelength > stationary wavelength
change in wavelength > 0
v is negative, associated with recession therefore redshift
What happens in the doppler formula if the source is moving away?
apparent wavelength < stationary wavelength
change in wavelength < 0
v is positive, therefore blueshift
What is a binary star (system)?
A system of two stars orbiting each other around a common centre of mass.
When can doppler formula be used?
When v is MUCH smaller than c (v << c)
What are Spectroscopic binaries?
Systems whose binary nature is revealed by from the periodic shift observed in absorption lines. Each star has its own set of absorption lines
occurs when the stars are too close to be resolved by a telescope
Doppler shifts of each star must be used to resolve them
What can be calculated using doppler (spectrocsopic binaries)
angular velocity of each star (doppler shift gives v, v = wr)
The period of rotation of each star (w = 2pi/T)
The distance between the two stars (v = wr)
What is Hubble’s law?
the recession velocity of a galaxy is directly proportional to its distance. i.e. more distant galaxies are moving faster than closer galaxies.
The constant of proportionality is also known as the Hubble constant (H0/H)
What are the units for hubble’s constant?
kms-1Mpc-1 (kilometers per second per mega parsec)
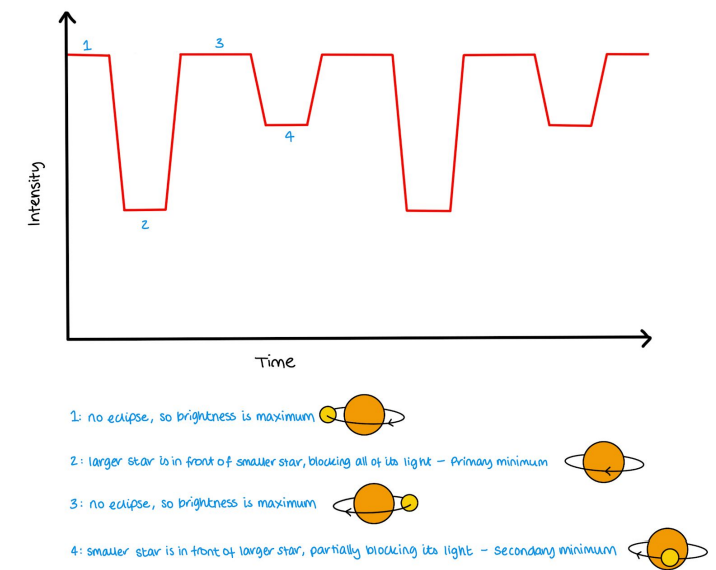
What is an eclipsing binary?
When the plane of orbit of the stars is in the line of sight from Earth to the system; the stars cross in front of each other.
Describe the light curve of an eclipsing binary
When stars are not eclisped, there is a constant intensity (1,3)
when the fainter star eclipses the bright star, there is a significant decrease of intensity (2)
when the brighter star eclipses the fainter star, there is a small decrease of intensity (4)
What are exoplanets?
Planets outside of our solar system that orbit other stars
Why are exoplanets difficult to detect?
Because they are obscured by their star’s light
What is the radial velocity method?
A method for detecting exoplanets
star and planet orbit a common centre of mass resulting in a Doppler shift in the light received from the star
the time period of the planet’s orbit is equal to the time period of the Doppler shift
(similar to spectroscopic binaries)
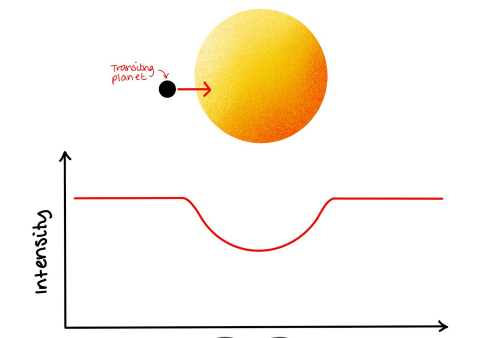
What is the transit method?
a method for detecting exoplanets
The intensity of the light emitted by a star is measured
If a planet transits (crosses in front of a star) the intensity reduces. If the intensity reduces regularly, it indicates the presence of an exoplanet
size and orbital period can be determined by the change in intensity and duration of the reduction respectively
Disadvantage of the transit method
it only works if the line of sight of the star is in the plane of the planet’s orbit. This is more likely for planets with small orbits.
Most orbits are inclined
Light curve of a star with a transiting planet
see image