Week 7 - Interpreting Qualitative Data
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Qualitative Data Analysis
An inductive approach that analyzes:
Words and phrases
Symbols
Techniques are not standardized
Analysis begins during data collection
Compared to quantitative, where analysis begins after
Similarities between qualitative and quantitative data analysis
Analysis is based on comparions
Document data collection
Looks for patterns regarding social life
Differences between qualitative and quantitative data analysis
Qualitative data is less standardized
Difference in epistemology - interpretivism vs. positivism
Qualitative - starts during data analysis (e.x after the first interview or observation)
Quantitative - starts after the entire data set is in
Iterative
Repeated steps
The repetition of certain steps within the analytical model
Reflexive
The consideration of the resarcher’s influence over their data
Biases, prejudices, holes within methods
Process where a researcher considers their role, and the role of their data
Self-criticism displays trustworthiness in the accuracy of the subject information
Roadmap to analysis (Qualitative)
Test Initial Explanations ——→ Deconfirm Evidence ——→ Redifine Concepts ———> Collect New Data
Iterative Process
Fracturing the Data
To “pull apart”, re-organize, and reassemble the data
Do it in a systematic way
Going through data in a methodical way to look for themes
Outline themes and ideas
Coding
The categorization of data in a systematic process
Put data into categories
e.x. Categorize groups of text, media, etc, and assign a term to describe it
e.x. table of contents
Time-consuming and complex, such as 200 pages of text
Deductive Coding
Predetermind themes (theory and literature)
Analysis of text to look for concepts that stem from these themes
Inductive Coding
Building themes or theories based on the data
Ground-up approach, analyze multiple pages of data, and identify themes
Codebook
A roadmap that includes a set of codes as well as definitions and examples
Usually stems from iterative processes
Takes a hefty alot of time, but reliable and consistent
Components (themes) include:
Code names - Ethnic Superiority
Definition - the belief that one’s own ethnicity is superior to others
Example - Podcaster A said to Podcaster B that he believes there is a racial hierarchy, and that his ethnicity sits up top
Grounded Theory (Both a method and theory)
Ground-up approach that uses constant comparison and coding procedures to create a theory from the ground up
Rooted in empirical observation
Data collection, then constructing a theory based on data
Theory - an explanation for a phenomenon going on in the world
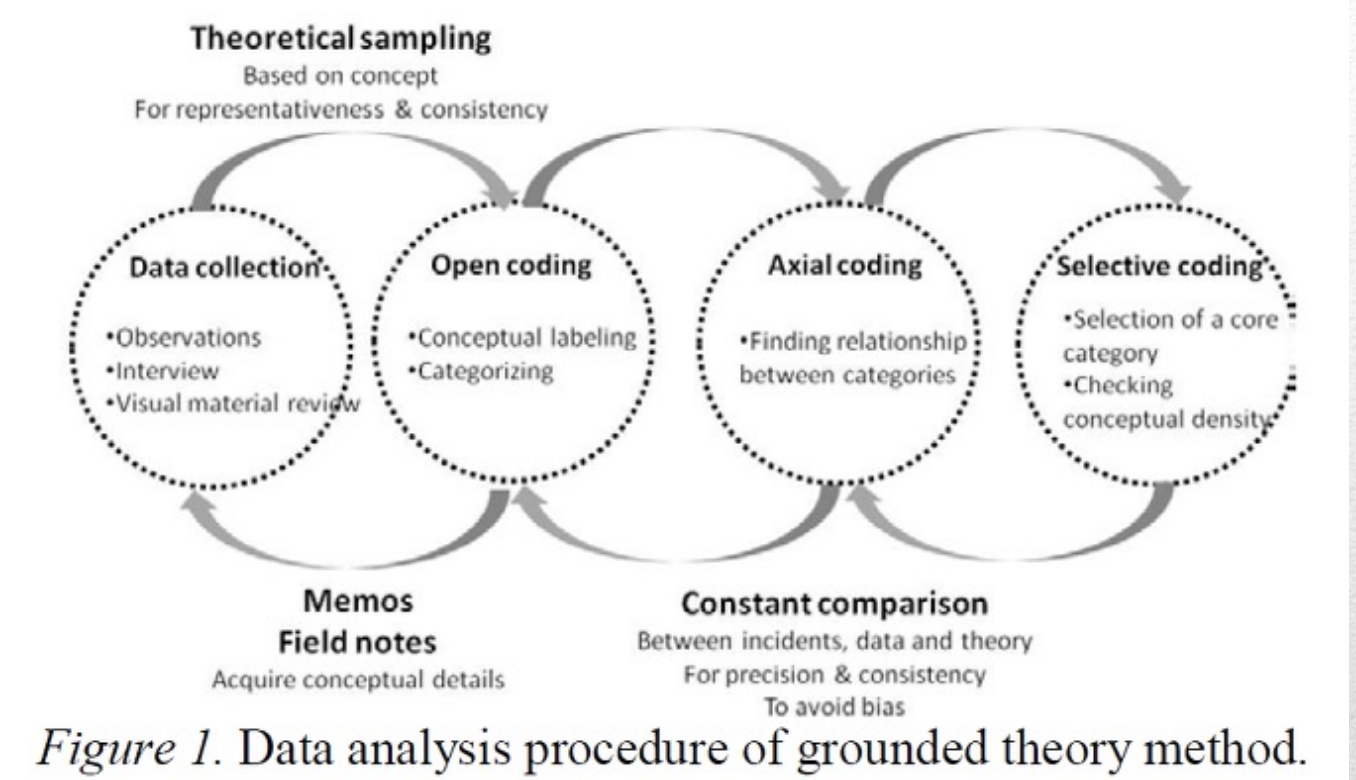
Elements of grounded theory
Iterative process - repeat the data breakdown and categorization process
This cycle gradually builds up to a theory
Involves constantly going back to analytical memoes, codi,ng and diagrams
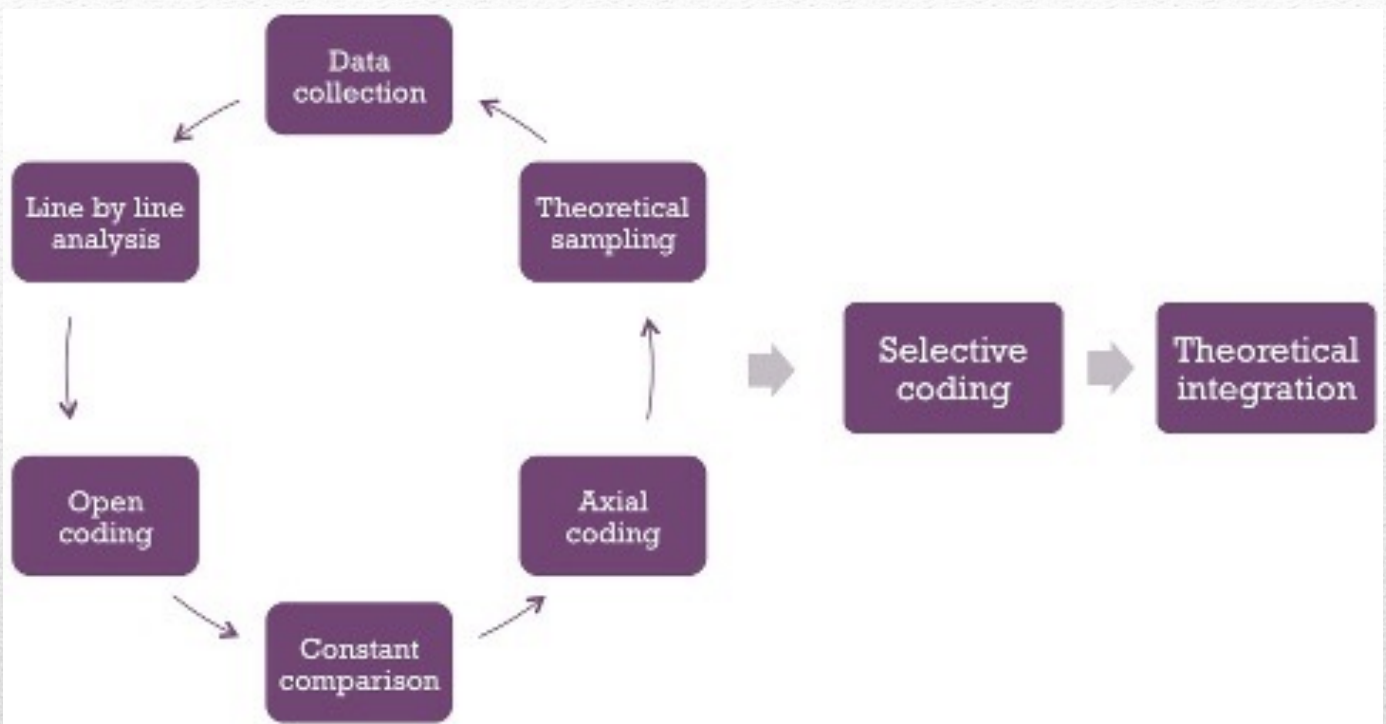
3 Steps of Grounded Theory
Open coding - Identifying codes
Axial coding - Combining Codes
Selective Coding - Develop a theoretical explanation
Open Coding
First step - first encounter with data
Identify and collect data for the framework
Essentially label topics & events
Create themes/codes
Initial framework for analysis
Detail of the themes depends on the data richness
Don’t concern yourself about making connections, just form codes
Axial Coding
Second step - combine codes
Combine codes to form thematic categories
Draw connections between codes
Looks at the relationship between codes
Codes - themes/categories that we organized blocks of text into
Axial coding involves creating larger categories based off of the smaller categories (codes)
Temporal Sequencing - If A happens, this causes B to happen, then C
Selective Coding
Last stage for coding
Once categories of code are complete, develop a theoretical explanation for these codes
Develop a central concept
A primary code that explains other codes
Coding process example - Teens Coming Out as Gay
Open coding - themes include: living a double life, fear of change, and familial love
Axial Coding - Drawing a connection between these themes (e.x. familial characteristics, anxieties, possible outcomes)
Selective Coding - the overarching theme of identity
Coding True Crime Podcast - Example
Portrayal of co-victims of intimate partner violence on true crime podcast
Deductive - used the 6 stages of grief as a theme
What stage was most highlighted?
Each podcast was chosen based on the theme of a male perpetrator looking at domestic violence amongst adults
Qualitative Content Analysis of the True Crime Podcast
Deductive approach - used the 6 stages of grief as a framework
Used these pre-existing codes and applied them to the podcast
Looked at each podcast for these themes
What could be classified as a stage of grief?
Coding Findings (True Crime Podcast Example)
All 6 stages of grief were present, but…
2 stages were commonly portrayed:
Acceptance
Meaning
2 Stages were the least common:
Anger
Depression
Limitations of the True Crime Podcast Study
The victims talked about on the podcast aren’t representative of all crime victims
Podcasts disproportionately focus on white, heterosexual murder victims
Ignores many marginalized victims
Certain themes and quotes are cut
Coding Terrorist Social Media Posts
Asked about the motivations for terrorists who use social media
Looked at 153,119 tweets, coded 563
Classification stemmed from previous analysis of terrorist tweets, used as a guide
(Inductive Coding)
Findings about terrorist tweets
Terrorists basically tweet for the same reasons as everyone else:
Religious Instruction - explaining their religion
Reporting from the battlefield - info about battles
Communication
Tourism - basically, everyday things
Threats against the West
Discourse Analysis (EXAM)
By Foucault
Examining how knowledge & meaning are created through the usage of language and context
Emphasizing how and why something is talked about
Naming = power
Latent and manifest understandings of knowledge
You must acknowledge body language, emotion, etc, in the context of discourse
Looks at words (manifest) and the bigger picture (latent)
What do they mean? What are they trying to accomplish with their words? What does it say about their culture, feelings, or sense of power
Critical Discourse Analysis
Looks at the social implications of how power is attributed through language.
How power is created through the perception of roles and mastery
Example: A Teacher Says, “Boys are better at math than girls.”
Why did the teacher say this (Context)
Where does this idea come from? (Rationale)
How might this make the students feel
Does this give more power to one group?
CDA looks for hidden meanings and power imbalances in language
e.x. Racism, Sexism, etc
Foucault on Language
Language to Foucault is a social practice, with power being created and recreated through language
Defines social problems
Outlines powerful state & non-state actors