ApHug Exam study guide
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/258
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:24 AM on 4/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
259 Terms
1
New cards
Chapter 1: Geography Its Nature and Perspectives
Chapter 1: Geography Its Nature and Perspectives
2
New cards
What are the origins of geography?
Study of earth
3
New cards
What is the purpose of scale? What are 3 types of scale?
Ratio or Fraction Scale: Ex. 1:24,000 or \n 1/24,000
\
Written Scale: Ex. 1 inch equals 1 mile
\
Graphic Scale: Usually consists of a bar line \n marked to show distance on Earth’s surface
\
The purpose of a scale is so we can use it to create accurate maps.
\
Written Scale: Ex. 1 inch equals 1 mile
\
Graphic Scale: Usually consists of a bar line \n marked to show distance on Earth’s surface
\
The purpose of a scale is so we can use it to create accurate maps.
4
New cards
Distortion is especially severe on which types of maps?
Small scale maps
5
New cards
What is the purpose of remote sensing?
Detecting and monitoring the physical characteristics of an area by measuring its reflected and emitted radiation at a distance
6
New cards
Explain GIS - How would a geographer use GIS?
A geographic information system (GIS) is a \\n computer system that captures, stores, queries, \\n analyzes, and displays geographic data. And to produce different types of more detailed maps
7
New cards
What system determines a location using mathematical location?
Global Positioning System (GPS)
8
New cards
What term do geographers use to describe a location relative to other objects?
Relative location
9
New cards
What term do geographers use to identify a place by unique physical characteristics?
Site
10
New cards
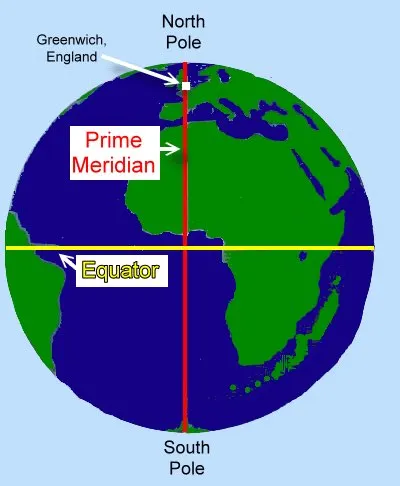
From what degree is Greenwich Mean Time measured?
(0º longitude).
11
New cards
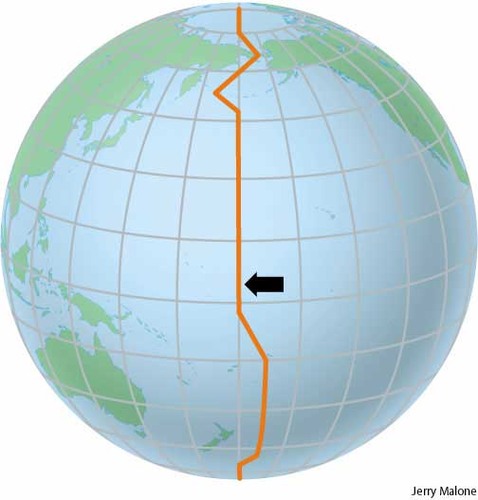
From what degree is the International Date Line measured from?
(180º longitude)
12
New cards
What was the result of the U.S land Ordinance of 1785?
Set up a standardized system whereby settlers could purchase title to farmland in the undeveloped west. Divided into townships
13
New cards
What are the 3 different types of regions?
\-Formal(uniform): Midwest is considered the corn belt because corn is a distinctive
\
\-Vernacular(perceptual): people think sweet tea when they think of the south, perception of an area
\
\-Functional:(nodal area with focal point): area of Chicago that receives the Chicago tribune
\
\-Vernacular(perceptual): people think sweet tea when they think of the south, perception of an area
\
\-Functional:(nodal area with focal point): area of Chicago that receives the Chicago tribune
14
New cards
Explain the idea behind Possibilism
The theory that the physical environment may set limits on human actions, but people have the ability to adjust to the physical environment and choose a course of action from many alternatives.
\
EX Making it snow in Dubai UAE
\
EX Making it snow in Dubai UAE
15
New cards
Explain the idea behind Environmental determinism
A philosophy of geography that stated that human behaviors are a direct result of the surrounding environment.
\
EX
The continuously warm weather of subtropical regions leads to underdeveloped, more tribal societies.
\
EX
The continuously warm weather of subtropical regions leads to underdeveloped, more tribal societies.
16
New cards
How is arithmetic density calculated? If the population of the U.S. is 300 million, and the land area is 9 million square kilometers, what is the arithmetic density of the U.S.?
Dividing the total population or number of people, by the total area.
\
34 people per square kilometer
\
34 people per square kilometer
17
New cards
Expansion diffusion (Hierarchical, Stimulus, Contagious)
Examples
18
New cards
Hierarchical diffusion
hierarchical diffusion - the spread of an idea through an. the established structure usually from: □ people of/with power to people of/with less/no power
\
Hydroflask water bottles
\
Hydroflask water bottles

19
New cards
Stimulus diffusion
When an idea diffuses from its cultural hearth outward, but the original idea is changed by the new adopters.
\
When Chicken tikka masala was made in the UK with influence from Indian food.
\
When Chicken tikka masala was made in the UK with influence from Indian food.

20
New cards
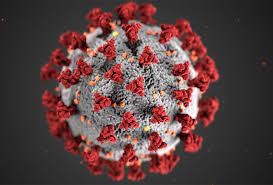
Contagious diffusion
the process of an idea being spread rapidly throughout the population; all places and individuals in the region are affected.
\
Coronavirus
\
Coronavirus
21
New cards
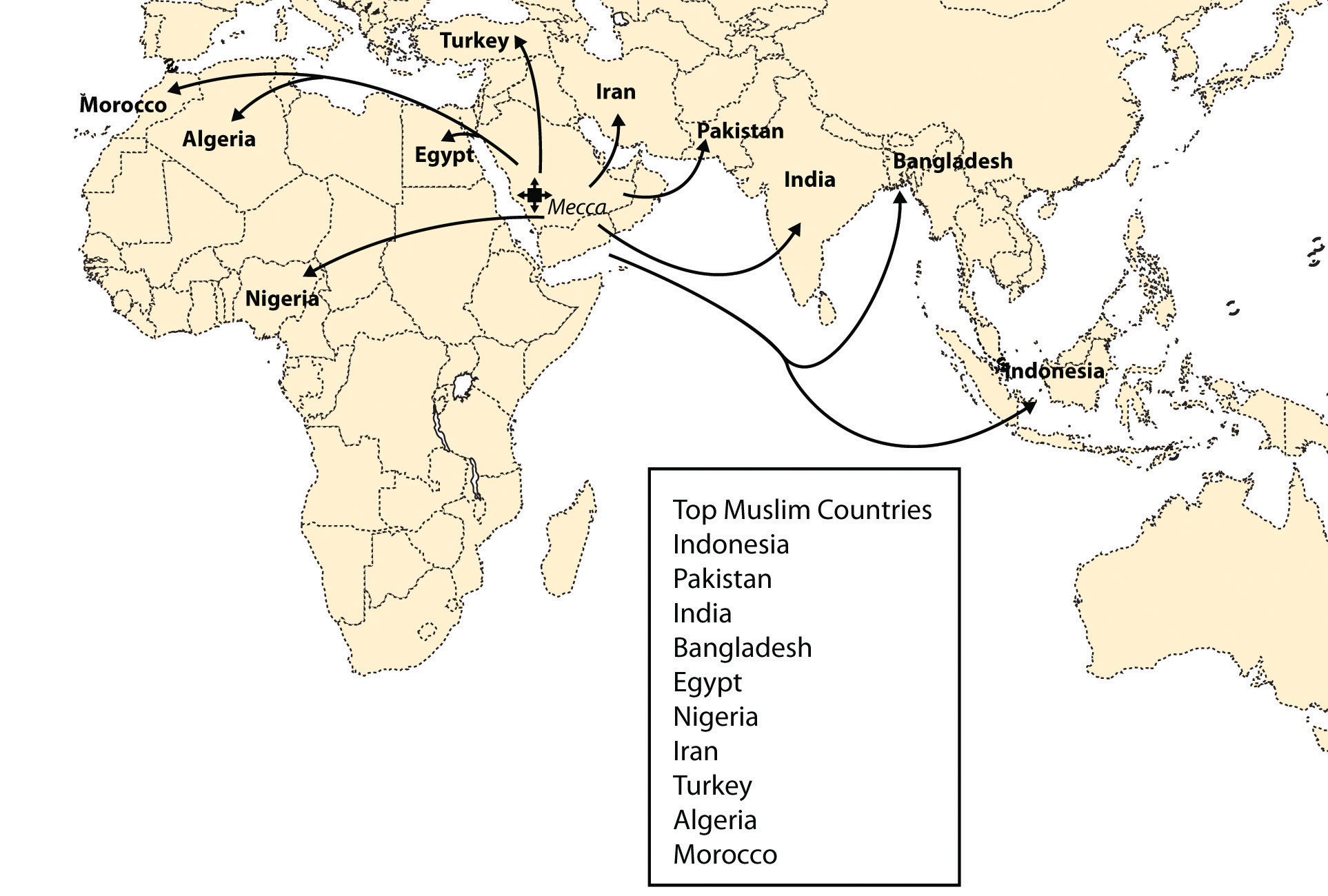
Relocation diffusion
When people move, or relocate, they spread ideas along with them.
\
Muslims relocated, taking Islam with them.
\
Muslims relocated, taking Islam with them.
22
New cards
Chapter 2 - Population
Chapter 2 - Population
23
New cards
Where in the world does the most rapid growth occur?
Sub-Saharan Africa
24
New cards
How do geographers describe overpopulation?
Too many people compared to resources.
25
New cards
The area on earth that is made up of permanent human settlement is called?
Ecumene
26
New cards
What is the most populous country in the world?
China
27
New cards
What four regions make up 2/3 of world population?
East Asia
South Asia
Southeast Asia
Europe
South Asia
Southeast Asia
Europe
28
New cards
What regions do humans avoid and why?
High lands, too hot, too wet, too dry, too cold, because you can't grow crops and live easily.
29
New cards
What does physiological density measure? Why would it be useful
Measures the total number of people and divides them between the total amount of farmable land, helps people to know where to live and where crops can be gown = economic prosperity.
30
New cards
If country has more land then farmers is agricultural density high or low?
It would be low since each farmer has more land and meaning less clustered.
31
New cards
What conclusion can you make if a country has a larger physiological density than the arithmetic density?
Farmland being used by more people (higher population)
32
New cards
What can you conclude about India and the United kingdom having the same arithmetic density?
Similar size in population according to land.
33
New cards
What caused the annual global population growth rate to increase ten thousand years ago?
The agricultural revolution.
34
New cards
What caused the annual global population growth rate to increase two hundred years ago?
The industrial revolution
35
New cards
Explain the four stages of the demographic transition model.
\-1.) preindustrial: CBR and CDR are close keeping population level \n
2\.) urbanizing/industrial: improvements in healthcare, drop-in CDR but CBR same, increasing population \n
3\.) mature industrial stage: decreasing in CDR, economic development bring CBR down \n
4\.) post-industrial stage: population growth levels (evens out) because CBR and CDR reduce
2\.) urbanizing/industrial: improvements in healthcare, drop-in CDR but CBR same, increasing population \n
3\.) mature industrial stage: decreasing in CDR, economic development bring CBR down \n
4\.) post-industrial stage: population growth levels (evens out) because CBR and CDR reduce
36
New cards
The lowest crude birth rates are found in countries in which stage of the demographic transition model?
Stage 4
37
New cards
The highest crude death rates are found in countries in which stage of the demographic transition model?
Stage 1
38
New cards
Highest natural increase rates are found in which stage of the demographic transition model?
Stage 2
39
New cards
If Country X has a crude birth rate of 40 and a crude death rate of 15, while country X has a crude birth rate of 20 and a crude death rate of 9, which country has a higher natural increase rate? Why?
Country x because the difference is greater compared to Country y.
40
New cards
How would a country deal with a large aging population?
Increasing retirement age.
41
New cards
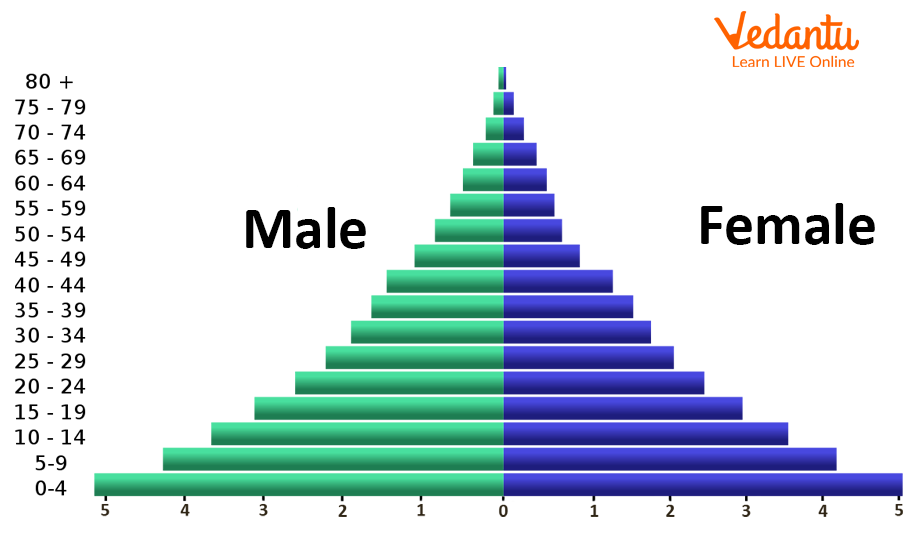
What primarily determines the shape of a country's population pyramid?
Age and sex structure of the population.
42
New cards
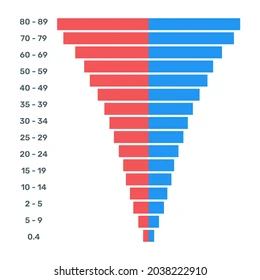
What would an "upside-down" population pyramid represent about a country?
Large amounts of old people compared to the younger population.
43
New cards
What is the current natural increase rate?
1\.2%
44
New cards
What is Thomas Malthus's theory?
Population growth will always tend to outrun the food supply and the betterment of humankind is impossible without strict limits on the reduction of population.
45
New cards
Chapter 3: Migration
Chapter 3: Migration
46
New cards
What does it mean if a country has a net-in migration?
A lot of people migrate ==to== the country.
47
New cards
What does it mean if a country has a net-out migration?
A lot of people migrate ==out== of the country
48
New cards
What are the 3 types of migration push and pull factors?
Social
\
Political
\
Economic
\
Political
\
Economic
49
New cards
Refugees migrate because of which type of push factors?
Political (War)
50
New cards
What push factor led to the migration of the Irish in the 1840s?
Religious conflicts, lack of political autonomy and dire economic conditions.
51
New cards
What are the 3 largest groups of refugees?
Palestinian, Iraqi, Afghan (according to U.S)
52
New cards
What is the most important pull factors for migrants to North America?
Economic \~ opportunities for better employment, higher wages, facilities, better working conditions.
53
New cards
Which factor is most common for voluntary migration?
Economic
54
New cards
Which factor is the most common for forced migration?
Physical or environmental factors.
55
New cards
The greatest number of foreign-born residents can be found in what country?
The United States.
56
New cards
What caused migration rates to decline in the United States in the 1920s?
In 1921, Congress passed the Emergency Quota Act, which drastically scaled back the number of entries to the country and assigned new birthplace quotas.
57
New cards
What impact did the U.S. quota laws from 1920s-1960s on immigration?
Ensured the majority of migrants continued to be from Europe.
58
New cards
Explain the "brain drain" phenomenon.
The emigration of highly trained or intelligent people from a particular country.
59
New cards
Current U.S immigration policies?
Family-based (spouse, child, parents, etc.) \\n -skills-based (Ph.D., blue-collar jobs that other Americans don't want) \\n -quotas \\n -most Asian refugees are in America \\n -US has largest annual amount of incoming immigrants.
60
New cards
What country do the majority of illegal immigrants come from?
Mexico
61
New cards
What was the outcome of the 1986 immigration reform and control act?
This act introduced civil and criminal penalties to employers who knowingly hired undocumented immigrants or individuals unauthorized to work in the U.S.
62
New cards
What caused large levels of interregional migration in the U.S?
Opening up of the western territories.
63
New cards
What direction has the U.S. center of population moved over time?
Westwad
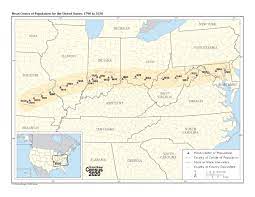
64
New cards
What is the current interregional trend in the U.S?
Cities to suburbs.
65
New cards
What is the most prominent type of intraregional migration in the world?
Rural areas to urban areas.
66
New cards
What is the most common environmental threat to people?
Too much or too little water.
67
New cards
Chapter 4 Folk and Popular Culture
Chapter 4 Folk and Popular Culture
68
New cards
What is the difference between a habit and a custom?
The difference is that traditions and customs are practiced over a long period by many people.
\
A habit is more informal and is usually limited to one person.
\
Custom India - bowing down to elders
\
Habit - studying every night
\
A habit is more informal and is usually limited to one person.
\
Custom India - bowing down to elders
\
Habit - studying every night
69
New cards
How does folk culture and pop culture differ from one another?
Pop culture is often used to refer to popular music, movies, and TV shows.
\
Folk culture is used to refer to the traditions and customs that make up the cultural identity of a local group of people.
\
Folk culture is used to refer to the traditions and customs that make up the cultural identity of a local group of people.
70
New cards
What type of culture varies from place to place at a given time?
Folk culture
71
New cards
What type of culture varies from time to time at a given place?
Pop culture
72
New cards
Folk culture is primarily spread by?
Relocation diffusion
73
New cards
Pop culture is primarily spread by?
Through rapid electronic communications and transportation networks.
74
New cards
Where does folk culture originate?
Unknown or multiple origins.
75
New cards
Where does pop culture originate?
Popular culture is most often a product of the economically more developed countries (MDCs), especially North America, Western Europe, and Japan.
76
New cards
How do folk songs differ from popular songs?
Folk songs often have content about the stages and events and life and is often transmitted orally.
77
New cards
How does a group of people maintain their cultural diversity?
By preserving traditions and rituals and speaking the language, Will help keep culture alive.
78
New cards
A taboo against pork is the characteristic of which two monotheistic religions?
Islam and Judaism

79
New cards
What type of culture will result in a uniform landscape?
Popular culture
80
New cards
How does global diffusion from pop culture threat folk culture?
As more pop culture spreads more people forget about they’re own culture resulting in the culture slowly dying.
81
New cards
Chapter 5 - language
Chapter 5 - language
82
New cards
What tribes were included in the Germanic invaders of England?
Angles
\
Jutes
\
Saxons
\
Jutes
\
Saxons
83
New cards
Why are there different dialects in England?
Because different tribes invaded different parts.
84
New cards
How are British and American English different?
They are different in pronunciation and spelling. American English is different from British English because of American isolation.
85
New cards
What is a isogloss?
An “isogloss” is a boundary line between two distinct linguistic regions.
\
US Canada border divided up American english and canadian english
\
US Canada border divided up American english and canadian english
86
New cards
What happens when a group of people speak the same language but are isolated?
Since the changes wont be shared amongst the languages both of them will develop slowly forming their own distinct language.
87
New cards
What is the difference between language family, branch, and group?
A language family is a group of different languages that all descend from a particular common language.
\
Language branch A collection of languages related through a common ancestor that existed several thousand years ago.
\
Language group A Collection of languages within a branch that share a common origin in the relatively recent past and display relatively few differences in grammar and vocabulary.
\
Language branch A collection of languages related through a common ancestor that existed several thousand years ago.
\
Language group A Collection of languages within a branch that share a common origin in the relatively recent past and display relatively few differences in grammar and vocabulary.
88
New cards
Origins of English
Language family - Indo-European
\
Language branch - Germanic languages
\
Language group - West germanic
\
Language branch - Germanic languages
\
Language group - West germanic
89
New cards
What is the largest language family?
Indo-European
90
New cards
What is the second largest language family?
Sino-Tibetan
91
New cards
What is the most widely spoken language in Brazil?
Portuguese

92
New cards
What is a creolized language?
A creole is believed to arise when a pidgin, developed by adults for use as a second language, becomes the native and primary language of their children – a process known as nativization.
93
New cards
What is the most widely spoken indo-european language?
English
94
New cards
Russian is part of which language branch
Eastern branch of the Slavic family of languages.
95
New cards
What is a revived language?
A language that has been revived from extinction or almost dying.
\
Example Hebrew
\
Example Hebrew

96
New cards
What does the survival of language depend on?
The key to survival is that two languages must be spoken by enough people to begin with and they must be sufficiently similar.
97
New cards
What is a lingua franca?
A language that is adopted as a common language between speakers whose native languages are different.
98
New cards
What type of language has no native speakers?
Pidgin languages have no native speakers.
99
New cards
Chapter 6 - Religion
Chapter 6 - Religion
100
New cards
What are branches denominations and sects?
Branch (Religious Branch) A large and fundamental division within a religion.
\
Denomination. A division of a branch of a religion that unites a number of local congregations in a single legal and administrative body.
\
Sect a relatively small breakaway from a religion.
\
Denomination. A division of a branch of a religion that unites a number of local congregations in a single legal and administrative body.
\
Sect a relatively small breakaway from a religion.