Holocaust
1/189
Earn XP
Description and Tags
midterm 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
190 Terms
4 major claims long:
holocaust was an event of global proportions with worldwide repercussions. any effort to grasp it in its entirety must begin with recognition of that massive scope
happned step by step. occured over time as a process with no easily determined begining or end
intertwined with WWII , the holocaust needs to be understood in the context of conflict. without the war the holocaust wouldnt. or couldnt have happened.
Jews were the primarty targets of nazi german destruction but their fates were linked with those of other victim groups.ppl with disabilities, roma and sinti, polish elite soviet pow and homosexual men
4 major claims:
hocoause was global event
holocaust happened step by step
intertwined with WWII
jews were the primary targets but fates link with others
Integrated approach
scholors incoporate both perpetrator and victim sources to produce a synthetic account or narrative of the past
henry friedlander
famous holocaust scholor who advocated an inclusive jolocause scholorhsip
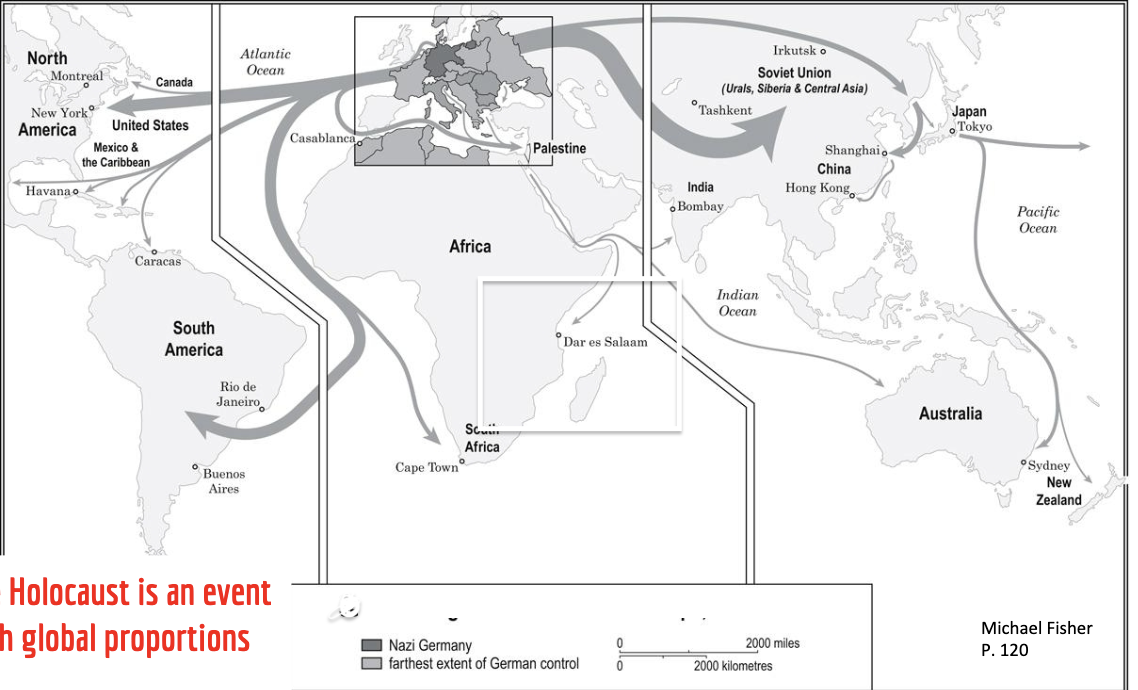
jewish refugees and exiles from europe 1933-1941
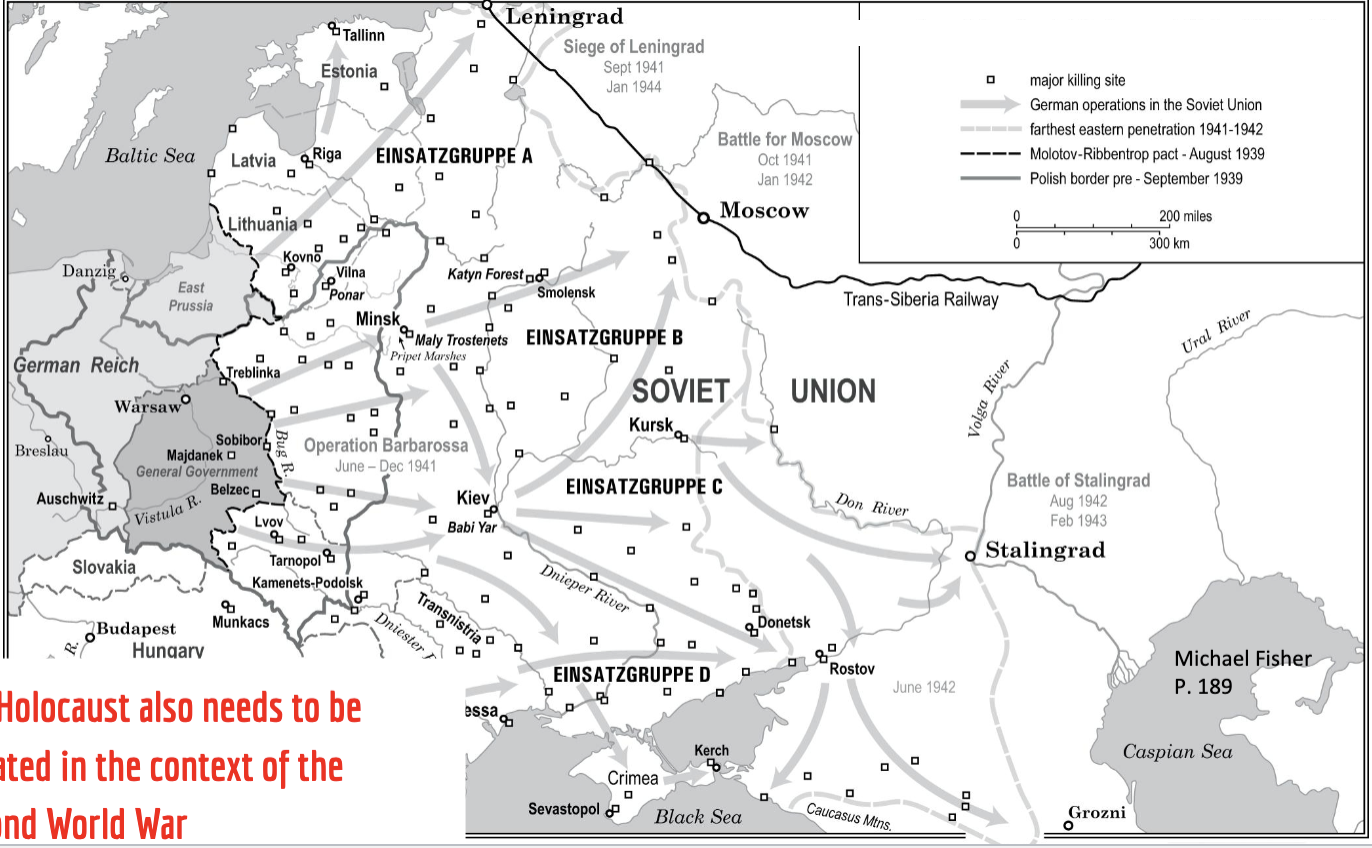
Invasion of soviet union and major killing sites
prisoner marking
begingin in 1937-1938 SS created this for prisoners in conctration camps
orgins of nazi violence
nazi antisemtism and racism
eugenics
europena/german imperialism and colonialism
lebensraum(living space)
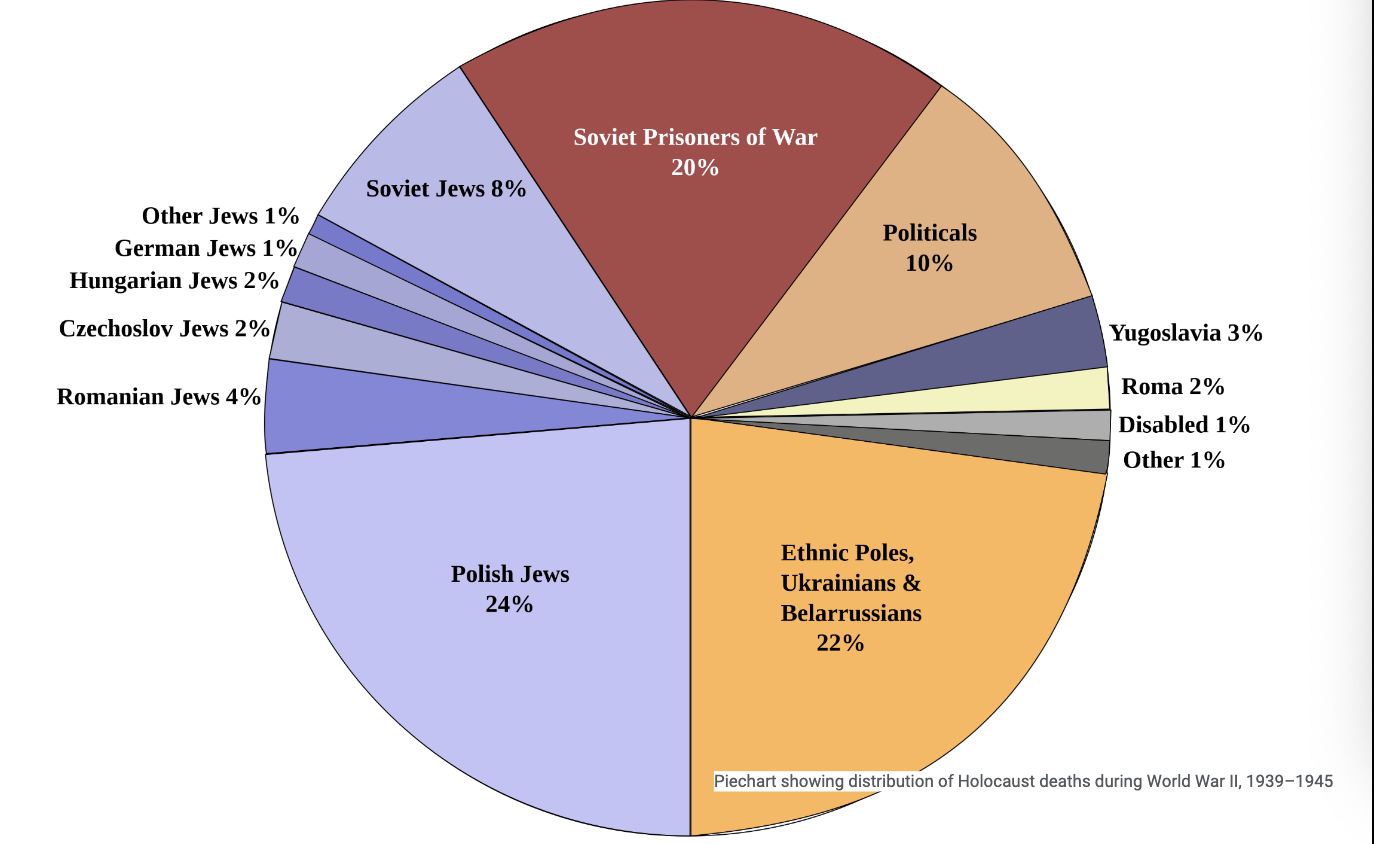
death during WWII
what is anti semetism
crusades
ghettoization
labeling
expulsion
inquisition
new modern antisemitism
preconditions:
enlightment and jewish emancipation
antisemitism coined in 1879 by wihelm marr
hidden dimension: imperialism and colonialsims
part of broader underluong ideologies that structured european thinking inclduig anti black racism, anti slavic and anti roma and sitin also homophobia and misongyny
gigure of the jew is consitutent with invention of races sexuality and gender
nazi innovation and antisemitism
fusion of radical racial approach to jewish otherness and that of other undersirables who were conceieved as jewish
biologization of politicall subervsion of judebolshevism
eugenics
The science of improving a human population by controlled breeding to increase the occurrence of desirable heritable characteristics
A "good birth" defined by white supremacist ideologies
since late 19th century racial anthropology were disciplines that had been well established in western universities
nazism
fusion of eugencis with racism
T4 operation
first stage of biologicaracial exermination carried out by nazism
mass killing of mentally ill and certain other categories of ppl deemed handicapped and disablled
90k victims
directly connected to mass killing of jews
German imperisalism and colonialism
genocide of hereor and nama
practices of retaliation, the drive towards total victory and enxiety about any kind of rebllion left a brutal legacy and would resurface both in WWI and even more in WWII
herero and Nama
1904-1908
first genocide of 20th century
The Herero and Namaqua Genocide was the massacre of approximately 50,000 – 65,000 Herero and 10,000 Nama between 1904 and 1907 by German military forces in German South West Africa
Lebensraum- Living Space
fusion of social darwinsim and imperialist geopolitics and stemmed from a vision of world s a space to be colonized by biologically superiror races and aspiring the extiniction of inferior ones
hitler compared the german war on the eastern front to colonial wars
geerman settlr colonism in the east
Hitler and the nazi party
joseph goebbels: minister of propaganda
hermann goring: commander in cheif of the lutwaffe, 4 year plan\heinrich himmler: head of SS and main architect of holocaust
Joseph goebbels
minister of propaganda
hermann goring
commander in cheif of the lutwaffe
in charge of 4 year plan
heinrich himmler
head of ss
main archietect of holocaust
failed beer hall putsch
novemrber 1923
was a failed coup d'état by Nazi Party leader Adolf Hitler, Generalquartiermeister Erich Ludendorff and other Kampfbund leaders in Munich, Bavaria, on
great depression
hitler uese to apeal to germans that were unelplyed to see him as a savior
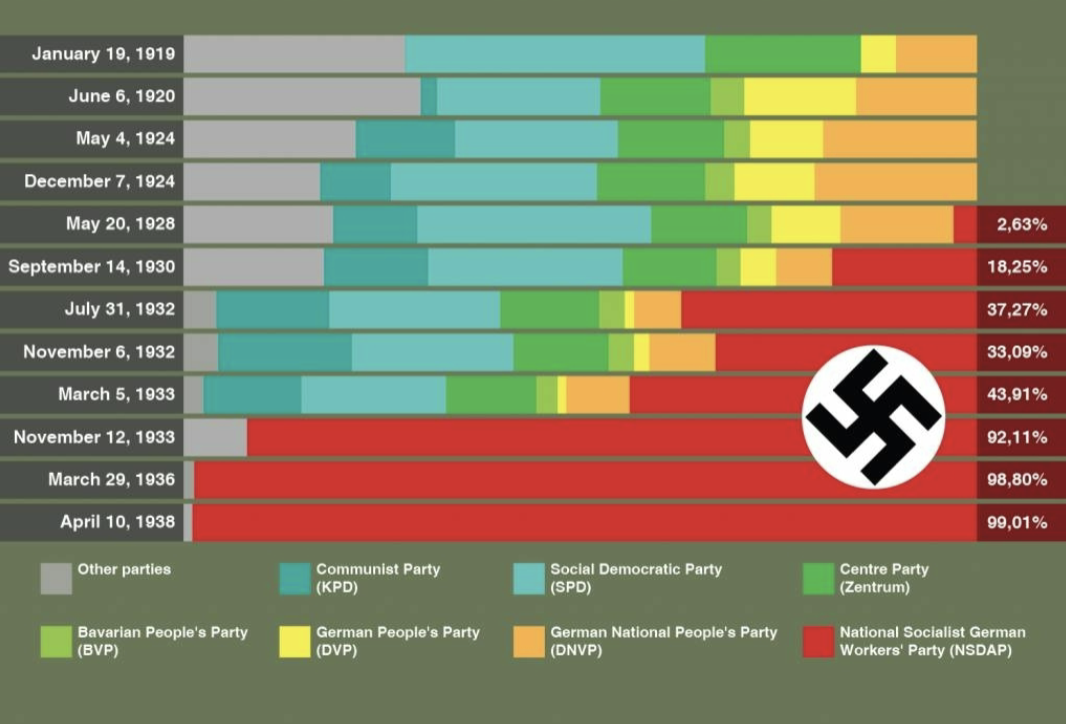
results of german federal elections 1919-1938
january 30 1933
president hindeburg named hitler as chancellor
convicned to do so by conservite elites and industrialist in order to ousr the sucess of the german communist party
early phases
revolutionizing germany 1933/34
routinizing nazism 1934-1938
lebensraun and open agression 1938/1939
1933 hitlers cabnet
only two nazi party memebrs beside himself
goring as minister without portfolio
frick as minister of interior
Monday, 27 February 1933
4 weeks after hitler sworn in
reichstag fire
Reiechstag fire
Monday, 27 February 1933
was an arson attack on the Reichstag building, home of the German parliament in Berlin,
Nazis attributed the fire to a group of Communist agitators, used it as a pretext to claim that Communists were plotting against the German government,
induced President Paul von Hindenburg to issue the Reichstag Fire Decree suspending civil liberties, and pursue a "ruthless confrontation" with the Communists.
This made the fire pivotal in the establishment of Nazi Germany.
first concentration camp
March 1933
capacity of 5k
houses communist
phase 1: revolutionizing germany 1933/934
reichstag fire
nazi majority
first concentration camp
cordination
Purge of SA
Cordination
leagure of german girls
hitler youth
positve image
peoples community
aryan only
Militarty cordination
SA: strumbteilung- storm division
SS: schutztaffel- protection squadren
allgemine SS- general SS
Waffen SS- armed SS
SS totenkentokpfverbande- Death head unites
Getstapo- secret police
Sircheheistends: intellegent agency
SA Sturnmabteilung: Storm division
orgininal paramllity wing of nazi party
played significant role in hitlr rise to power in the 1920s until rohim pitsh in 1934
provided protection for nazi rallies assemlblies distrutiong the meeting of and fighting against the paramility units of opposing parties
SS Schutzstaffel- Protection Squadron
major paramilitary organisation in nazi germany and later througout german occupied europe
between 1933-1945 was the foremost agency of security mass survallance and state terrorism withing germany and german occupied europe
allegience SS
genral ss
responsible for enforicing the racial policy of nazi germany and gerneal policing
Waffen SS
armed SS
comabt units
SS-totenkopfverbande
deaths head unit
ran concentration and extermination camps
The Night of Long Knives
june 30-july 2 1934
rohm putsch
in an attempt to wipe out leaders in the SA and reinforce his power.
Phase 2: routinization 1934-1938
centralization of power
ritualization
legalization
routinization
centralization of power
put hindeburnbg in war memorial instead of family plot
when president hidenburg died wotht he aproval from the militarty hitler and his cabnet aboloshied the title of president
combined the offices of president and chancellor and made hitler have all pwoer
legalization
nurember laws
law for protection of german blood and honor and reich citenship law
reich citenship law
only pure germans are allwoed to be german citenship
he remainder were classed as state subjects without any citizenship rights
law for the protection og german blood and german honor
forgbade marrigens and sex between jews and german
employemnt og germans in jewish houselhold femalse had ot be over 45
who is jeiwsh according to nuremberg laws
a person with ¾ jewish grandparents
mischlinge
neither german nor jewish
1-2 jewish grandparents
mixed
Dolchstoblegende/ Stab in the back myth
anti semtic/ anti communit conspiracy theory that was widely believed promulgated in weimar and nazi germany
maitined imperial geerman army did not lose WWI on the battlefiedl in 1918 but was instead betrayed on the hme front by jews and revolutionary spcialist who formented strikes and labar unrest
fuhrerprinzip/ leader principle
the basis of executive authority in the government of nazi germany
placed hitler above al written law and meant that government policies decision and officials all served to realize his will
enabbling act
Enabling act
cornerstorn of hitlers dictorship
ability for reich chancellor the ability to pass laws without consulting goverment
routinization
stab in the back
leader principle
synchronization/gleichshaltung
Gleichshaltung/synchronization
nazification of german society follwoing nazi seizure of power in 1933
sought to cordinate all politcal, social and cultural institions with nazi state
national unity
state enforced cordination from top down
single party state
selbgleichslautung: gemans bottom up cordination
Phase 3: lebensrasum and open agression
Kristallnacht/Night of Broken Glass
flight
war against poland
expansion
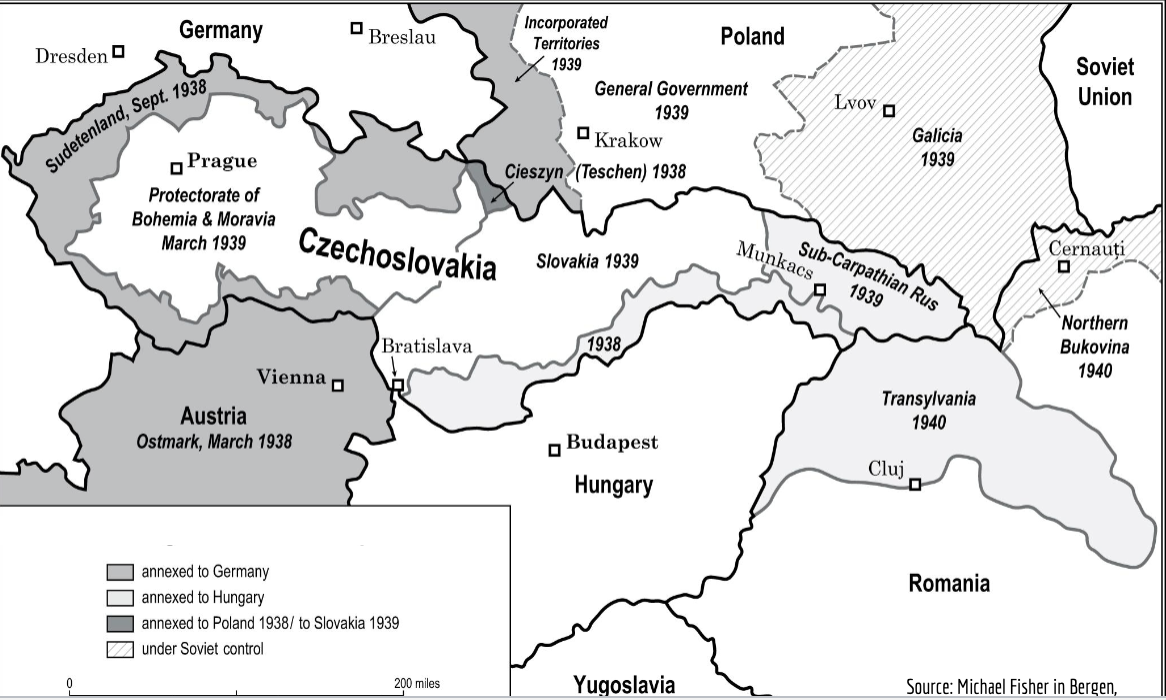
border changes in central europe 1938- 1940
Herschel Grynszpan
shot german diplomant Ernst von Roth in the german embassy in paris
novemebr 7 1939
bron in germany to polish jews who imigrated
used assisnation to start progroms
9–10 November 1938
knristalnach
prelude to the Final Solution
flight
ppl tried to leave
cuban denied pasager
so did us
German-Soviet Pact
August 1939.
It paved the way to invade and occupy Poland that September.
agreement of convenience between two bitter enemies.
It permitted them to carve up spheres of influence in eastern Europe, while pledging not to attack each other for 10 years.
Less than two years later, however, Hitler launched an invasion of the Soviet Union
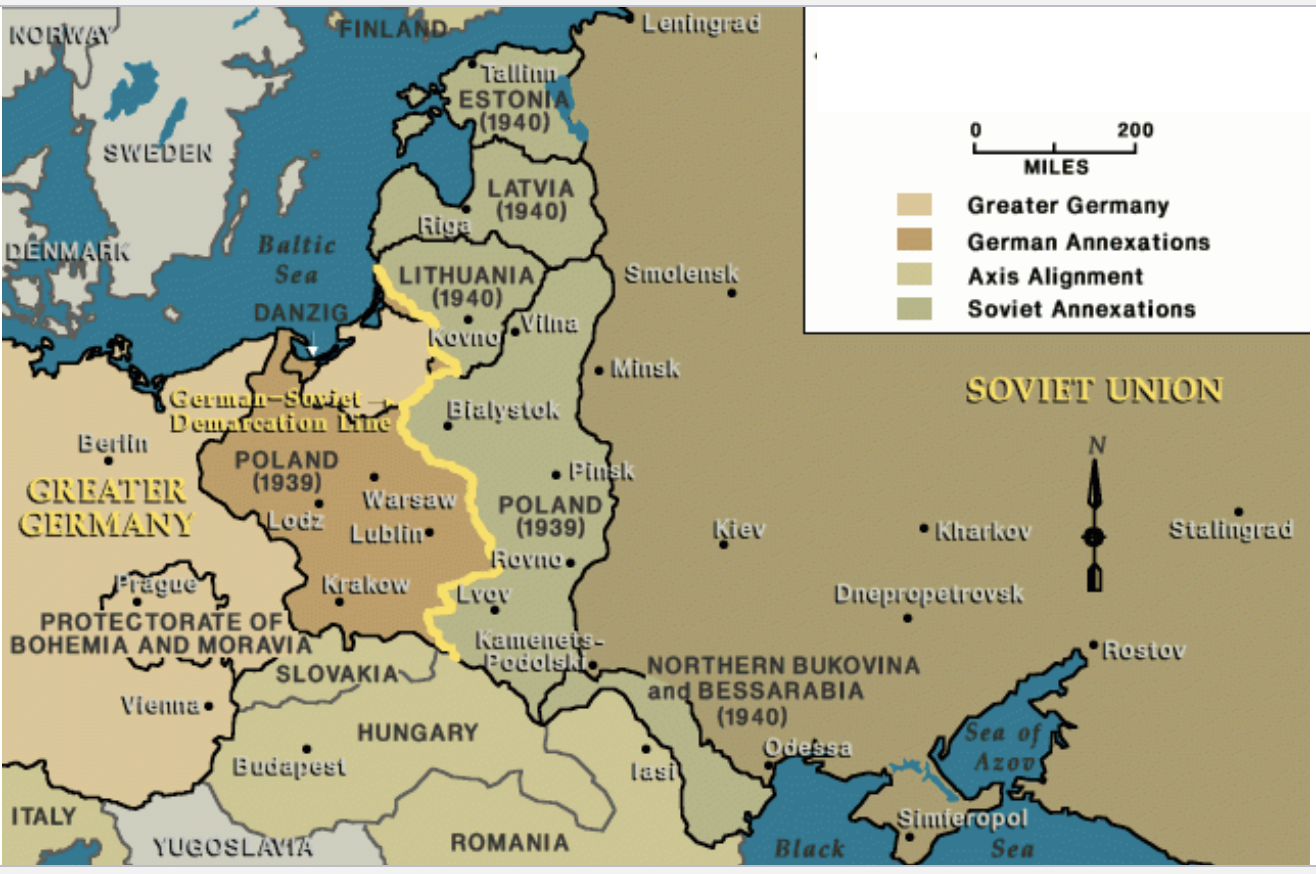
eastern european after the german sovviet pack
1939-1940
Radio station figth
German-Polish border : gleiwitz
August 31, 1939
staged mock attack
fabricated proof that poles were to blame
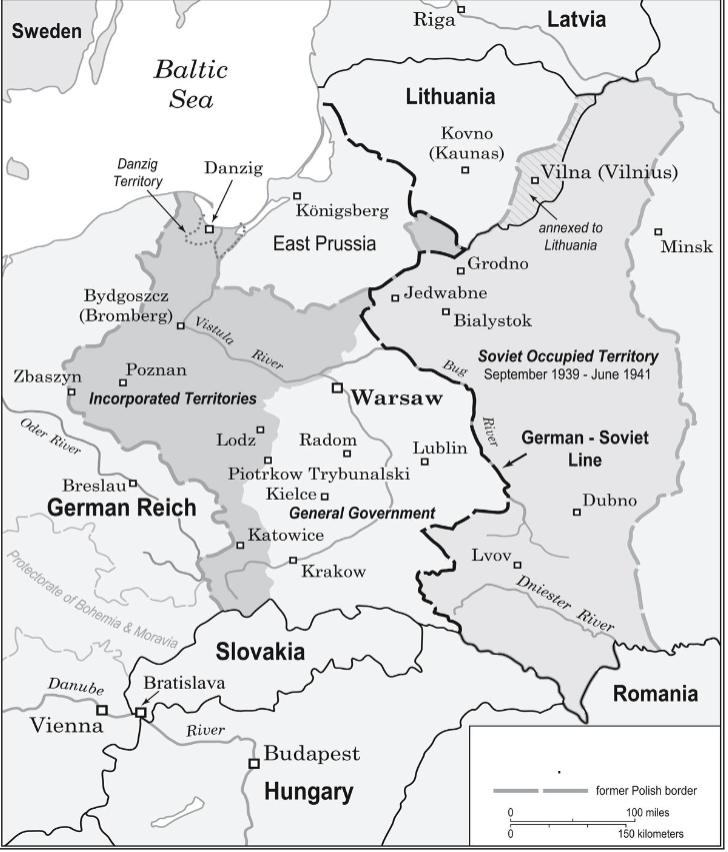
division of poland septemnber 1939
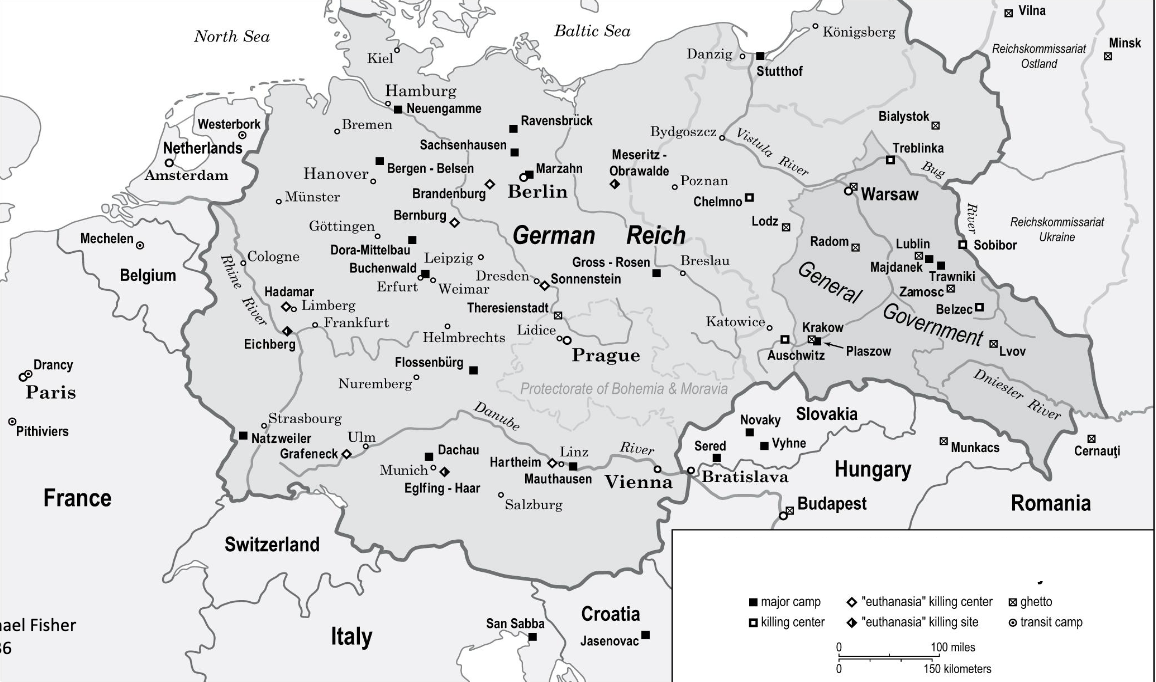
euthansia and killing center, major camps and ghettos in greater germany
particular featurs of polish situation
half of the jews murdered in nazi era were polish
major killing centers were located in conqued ploish terrioty
chronology
ideologogy
demography
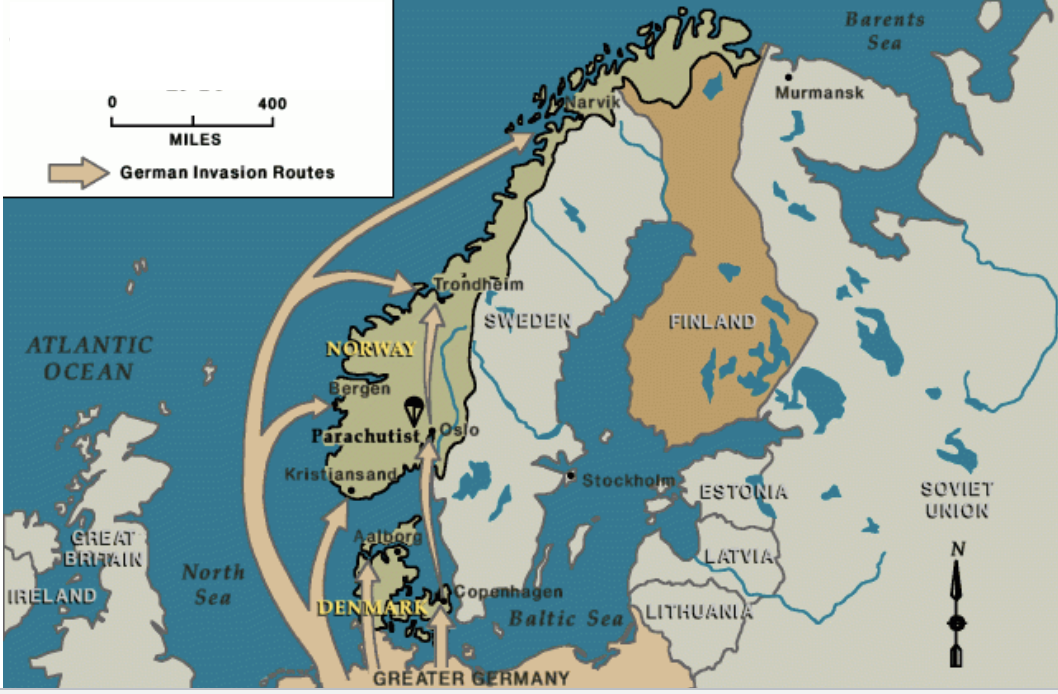
german invasion of denmark and norway
1940
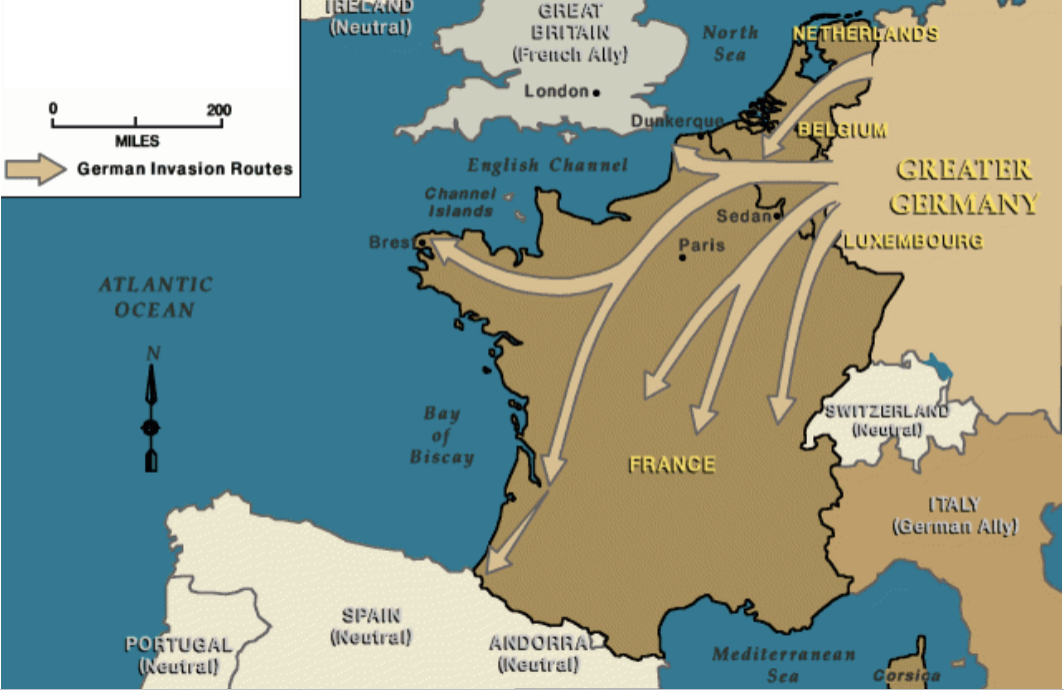
german invasion of western europe 1940
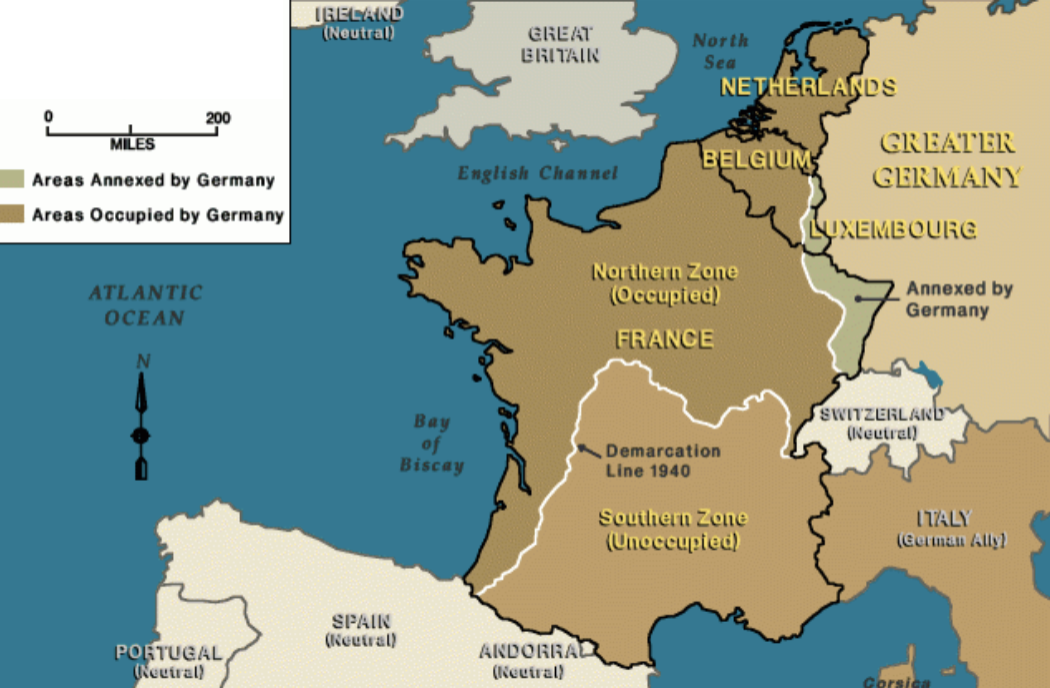
occupation of western europe
1940
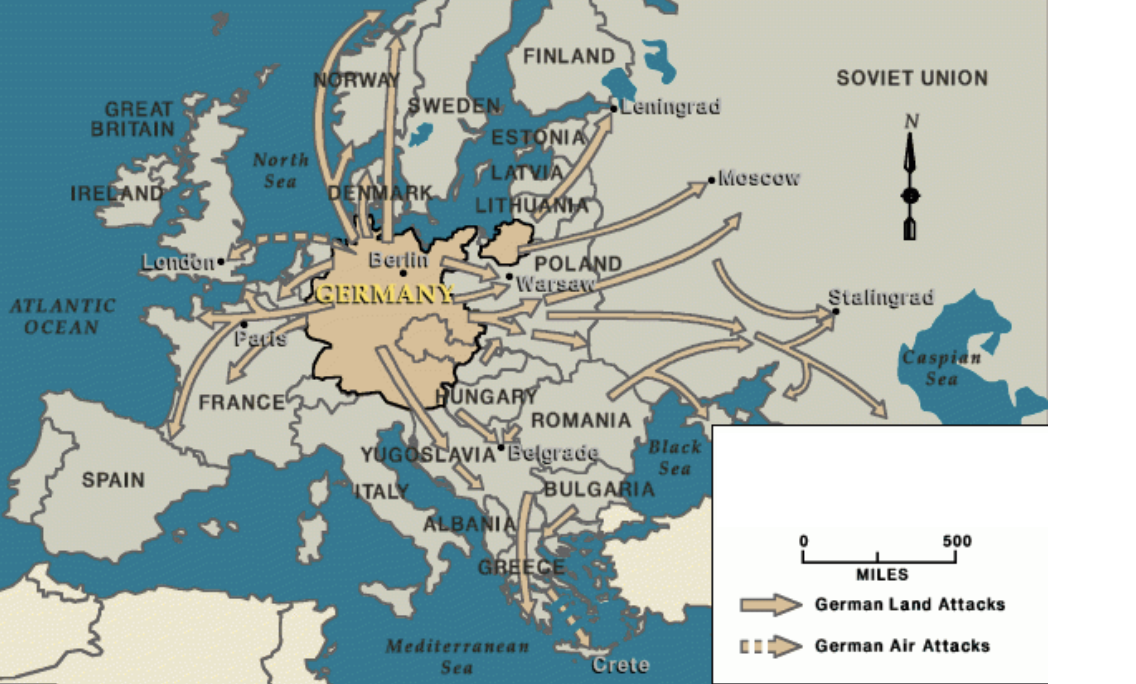
german conquest in europe
1939-1942
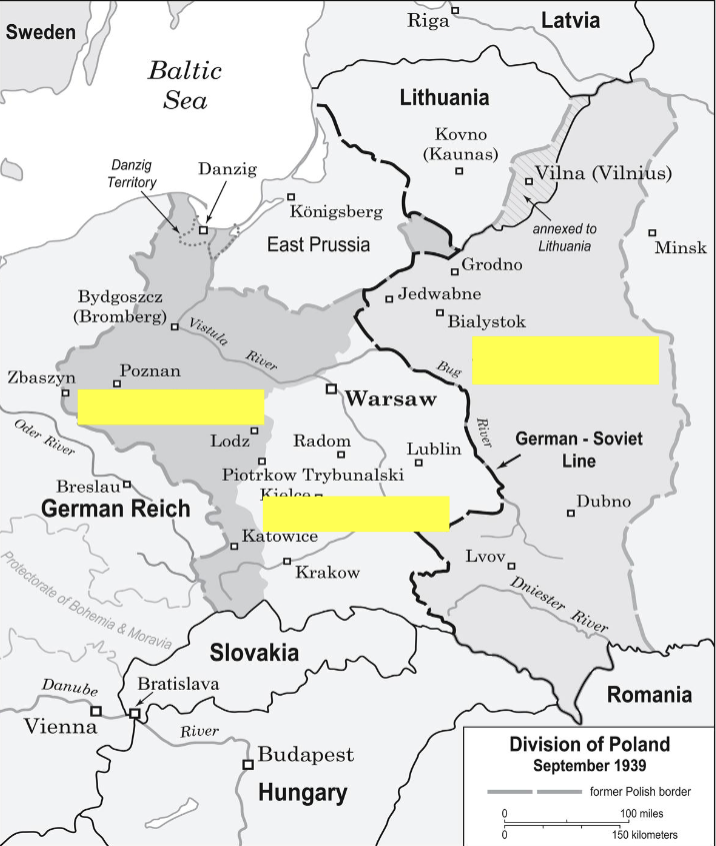
incoported terretories
general goverment
soviet occupied territory
september 1st 1939
nazi germany invades poland
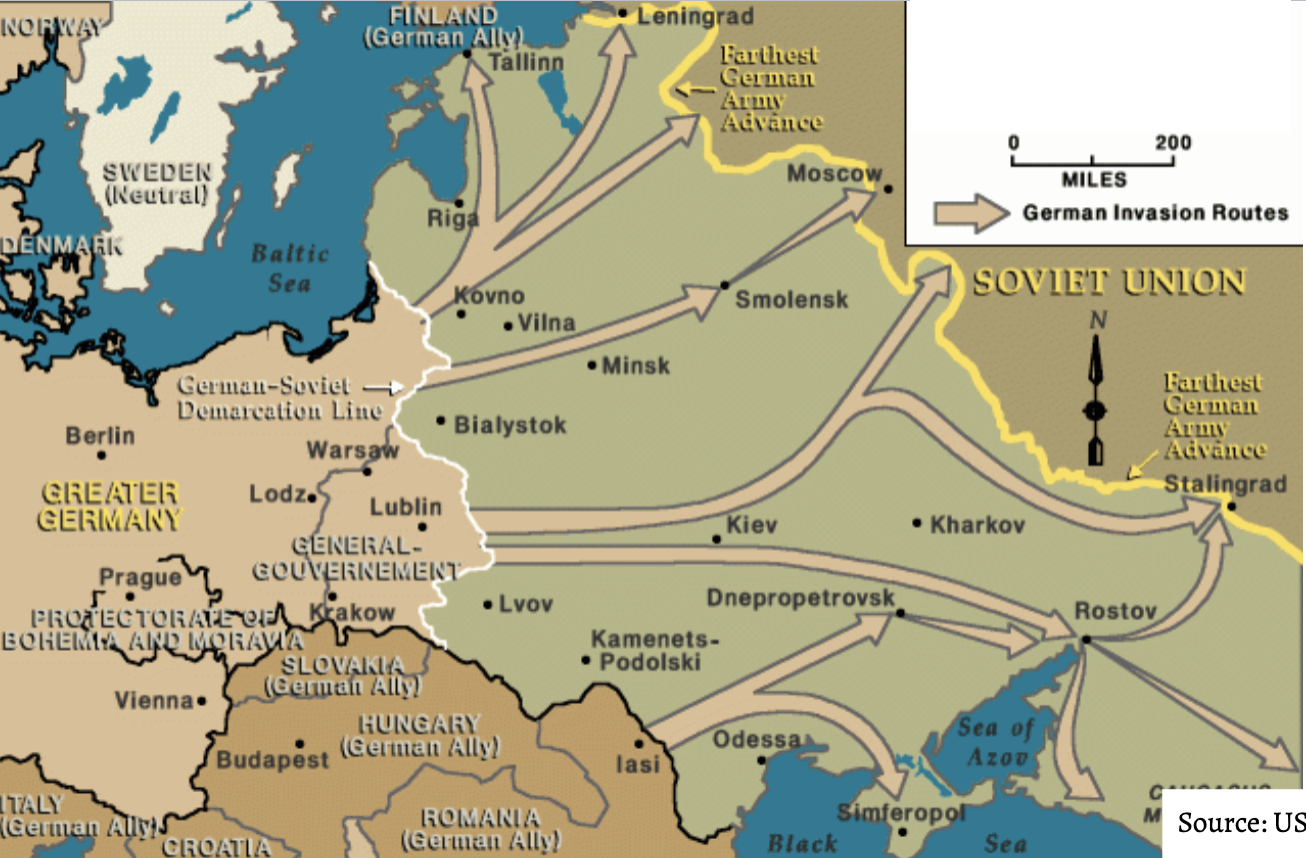
invasion of the soviet union
1941-1942
blizkrieg of 1941
the sustained campaign of aerial bombing attacks on British towns and cities carried out by the Luftwaffe (German Air Force) from September 1940 until May 1941.
war of annihilation against the soviet union
sake of advancing german settler colonialism
ethnic cleansing of millions of undersirables and slave lanors
enslaved millions of soviet union who werent jewish
soviet 1945
27 million soviets had been killed
2/3 civilians
2 million of 5 million jews
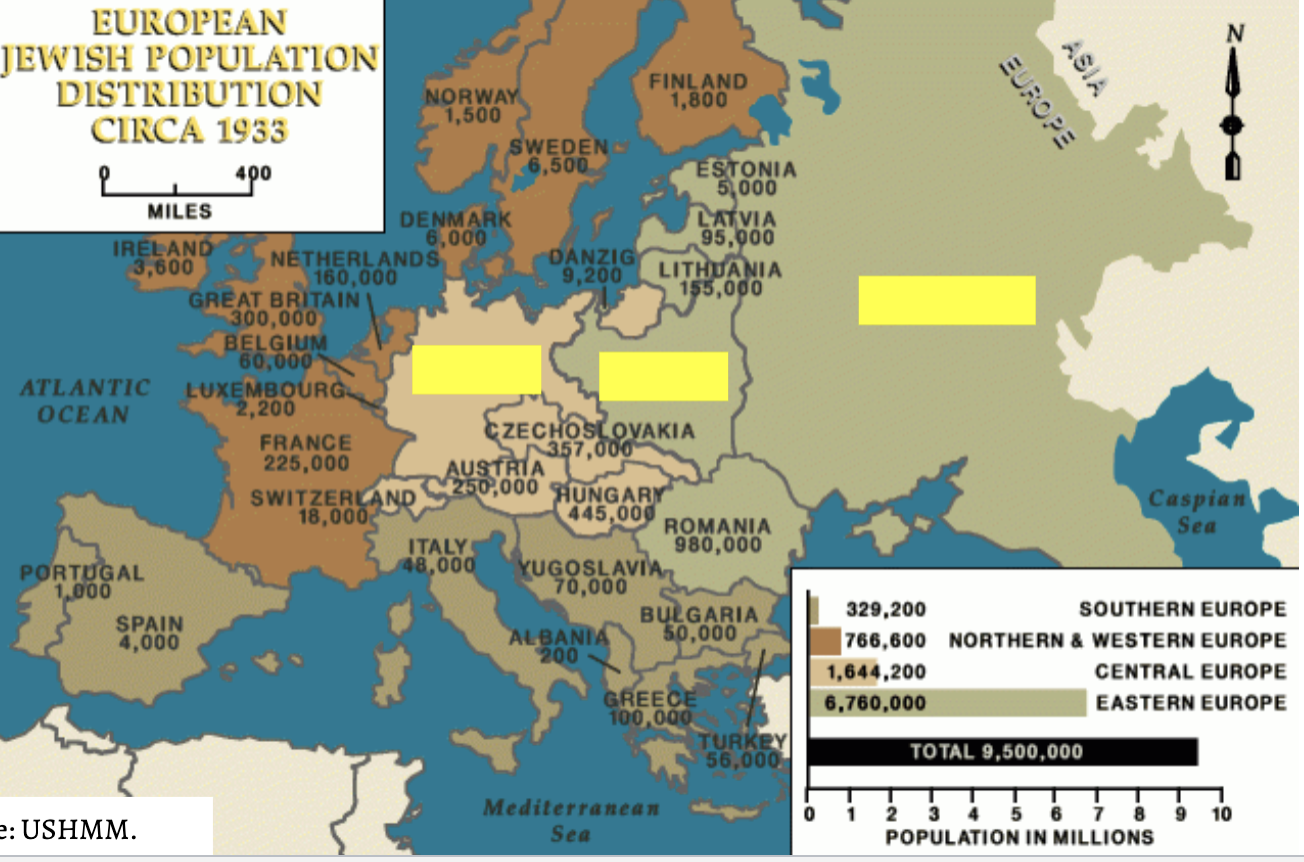
germany: 565,000
poland”:3 milion
Soveit union: 2,525,00
War of anialiation
1941/1942
major porgroms broke out perpertaed by locals non jews
egged on by german forces
soviet pows
between june 22 1941 and end of war took about 5.7million
killed 57% 3.3m
starvation, disease, freezing, shooting, gassing
killed in facility by german militarty but not ss
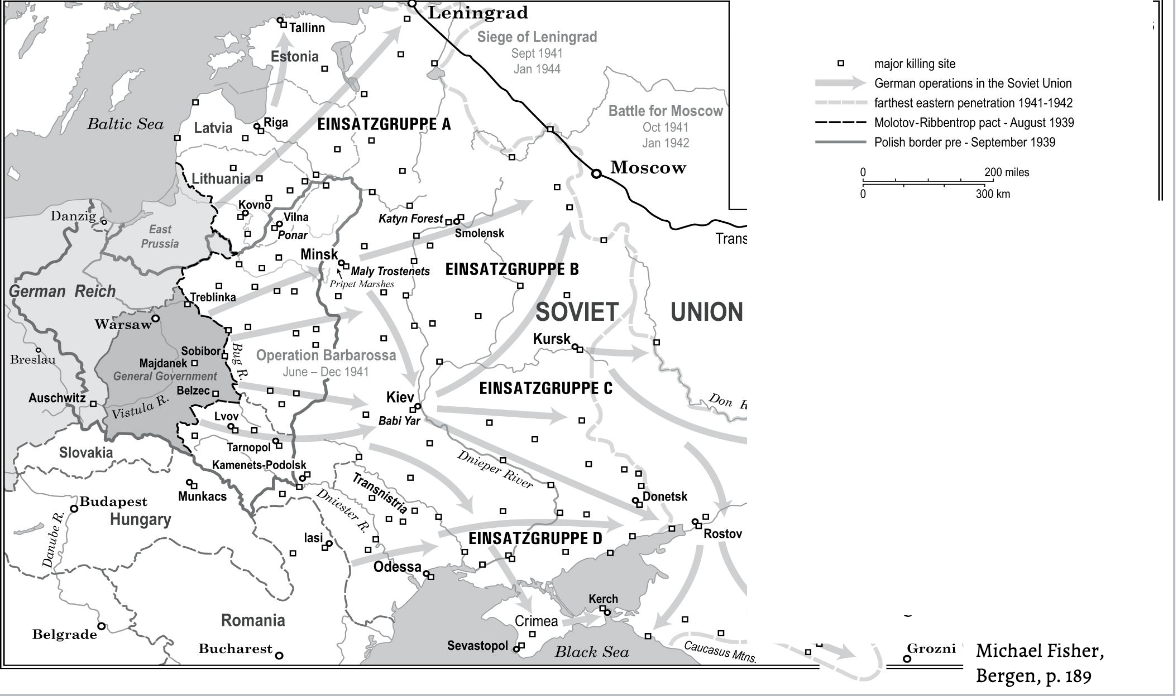
invasion of soviet union and major killing sites
holocaust by bullets
instructions from reichssicherheitshauptamt SS and cheif of reichssicherheitshauptamt reinhard heydrich, einstazruggene had to kill jews, primient communsit and anyone suspected of sabatoge/anti germnt
summer of 1941 massacure of all jews, roma, disabled
einsatzruppen
eployment groups';[1] also 'task forces')[2] were Schutzstaffel (SS)
paramilitary death squads of Nazi Germany that were responsible for mass murder, primarily by shooting, during World War II
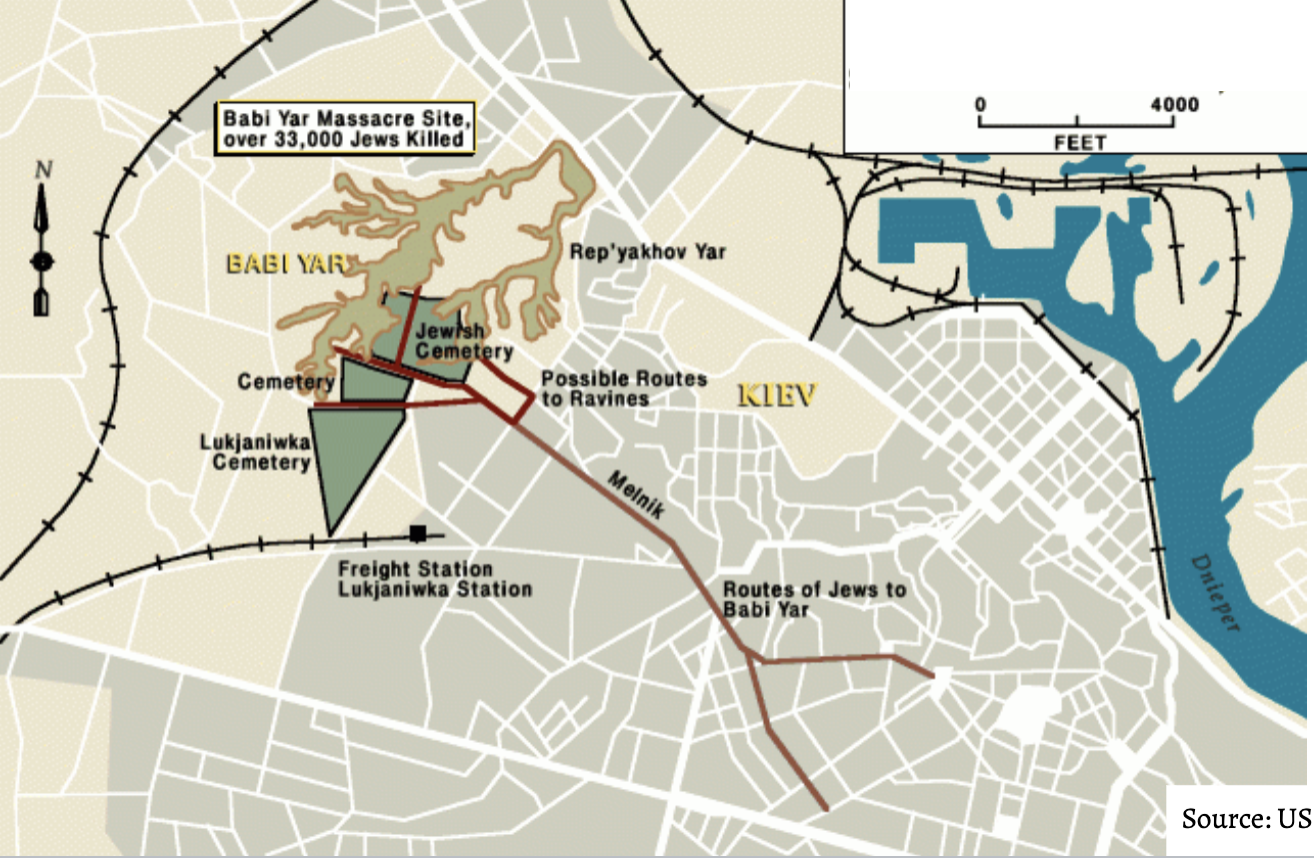
babi yar massacer in kiev september 29 and 30 1941
Babi Yar Massacre
kiev ukrain
septemerb 29/30, 1941
33,771 Jews were murdered.
Other victims of massacres at the site included Soviet prisoners of war, communists and Romani people.
Ibetween 100,000 and 150,000 people were murdered a
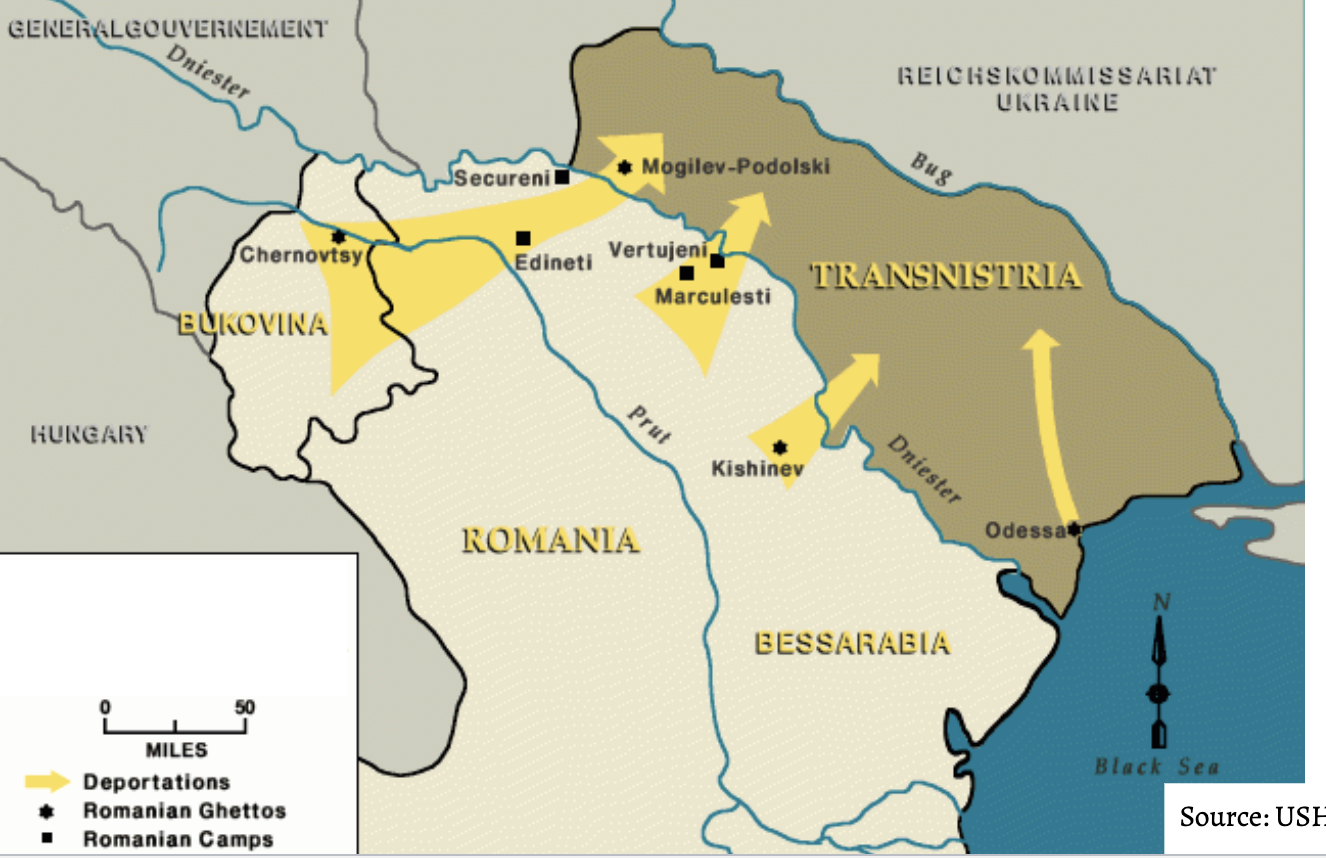
romanian deportation to transnistria 1941-1042
Transistria
became a central location of mass murder of Jews by Romanians during the Holocaust.
As part of Romania’s larger campaign of ethnic cleansing, Romanian authorities deported to Transnistria as many as 200,000 Jews from other parts of the country.
Among those deported there were Jews living in Bukovina and Bessarabia.
Romanian authorities in Transnistria quickly, and somewhat chaotically, adopted measures to persecute Jews
an estimated 280,000 to 380,000 Jews were murdered.
peak years of killing
1942-1943
peak years killing 1942-1943
early this year 75% of jews who would be murdered were still alive
by spring this year 75% of the 6 million who would be killedeed were dead
Wansee confrence date
January 20, 1942
Wannsee Conference
middle levle adminstrators met
discussed how, financials, impletenting a policy design
how to organize
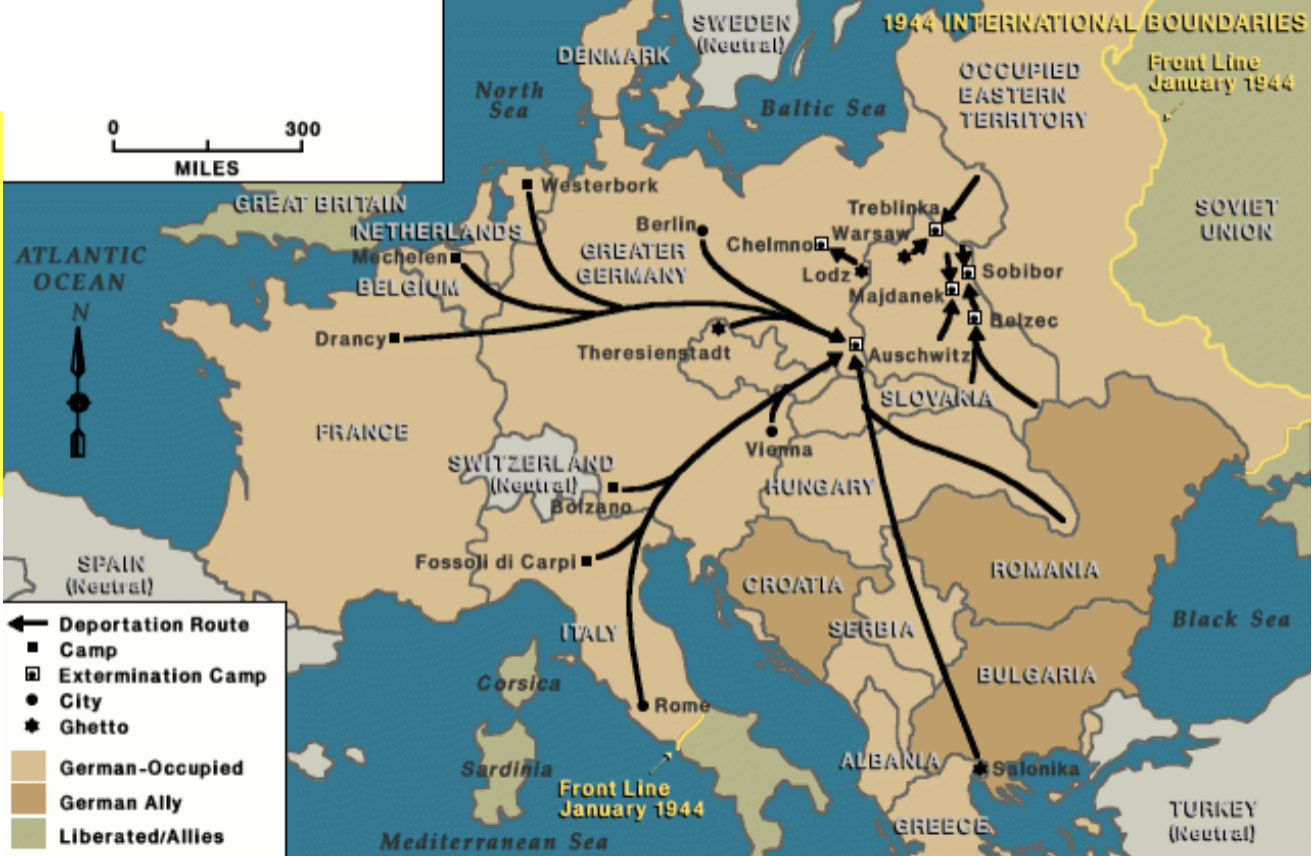
major deportations to extermination camps 1942-1944
Chelmo
which was specifically intended for no other purpose than mass murder,
operated from December 8, 1941, to April 11, 1943, again from June 23, 1944, to January 18, 1945,
145,000 people, primarily Jews
Belzec
killing center on the site of a former labor camp in German occupied-Poland.
It was the second German killing center to begin operation.
It was also the first of three killing centers established as part of Operation Reinhard
400k jews
unkoiwn roma and pole
Operation Reinhard
the fall of 1941, Nazi Germany implemented a plan to systematically murder Jews in the General Government
Belzec, Sobibor, and Treblinka.
deadliest phase of Nazi Germany’s intention to commit genocide against the Jewish people.
gassing
Sobibor
operation reinhard
250k jews form eastern poland
Treblinka
operation reinhard
constructed in the summer of 1942.
900k jews
2k roma
Aushwitz Birkenau
1.1m ppl
1m jews
This is about 2 miles (just over 3 km) from the Main Camp.
The Germans started construction in 1941.
Aushwitz
main camp
brikenu(gas chmabers)
monowitz and other satellite camps
german economics intrest and aniloharting jews
rented out slaves to companies
treaty of versailles
may 7, 1919
war guilt clause
german forced to accept respobility and fincacial burden responsibility for initiating WWI
Stab in back date
november 18 1919
spread by feild marsjal paul von hindeburg
Beer hall putsh date
november 9, 1923
hilter and nazi party attemt to overthrown the weimar rebulic
January 30 1933
hilter appointed chancellor
dueb to nazi parie large presence in goverment