Animal responses (6)
1/123
Earn XP
Description and Tags
done
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
What is the T-test formula?

What is the role of the nervous system in the fight or flight response?
1) The sympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system is activated
2) It signals to the adrenal glands to release adrenaline from the adrenal medulla.
What is the role of the hormonal system in the fight or flight response?
1) The pituitary gland releases the hormone ACTH
2) ACTH acts on the adrenal glands, stimulating the release of steroid hormones (e.g. cortisol) from the adrenal cortex.
What does the posterior part of the pituitary gland do?
It stores and releases hormones made by the hypothalamus eg ADH
Explain why glucose is required for the contraction of skeletal muscle
For respiration to produce ATP
ATP is needed for breaking cross-bridges between myosin and actin
ATP is needed for active transport of calcium ions back into sarcoplasmic reticulum
What does the ganglia do?
It connects organs around the body to the CNS.
What must a communication system enable?
Detection of changes in the environment
Cell signalling to occur between all parts of the body
Coordination of a range of effectors to carry out responses to the sensory input
Suitable responses
What is a response?
A change in behaviour resulting from a stimulus
Give examples of stimuli?
Threat of predation
Abiotic stresses e.g extreme temp, insufficient water
Internal stimuli→ need to find food to increase survival
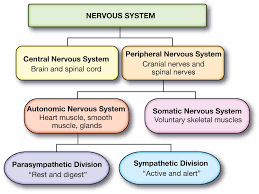
What is the structural organisation of the nervous system?
Central nervous system- brain, spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system- receptors, sensory neurones, motor neurones
What is the PNS composed of?
Sensory and motor neurones
Role of the peripheral nervous system
To ensure rapid communication between the sensory receptors, the CNS and the effectors
Splits into the somatic and autonomic nervous system
How is the peripheral nervous system further divided?
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
About the somatic nervous system
It controls conscious activity.
Conducts action potentials under voluntary control.
What is the autonomic nervous system?
Controls the involuntary motor activities of the body
It splits into the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems
\
* Sympathetic system
About the parasympathetic system
Decreases activity; conserves energy
Its neurotransmitter is acetylcholine
Most active during sleep or relaxation
Decreases heart rate, constricts pupils and reduces ventilation rate
About the sympathetic system
It increases activity- prepares for activity
The neurotransmitter is Noradrenaline
Its most active during times of stress
It increases heart rate, dilates pupils and increases ventilation rate
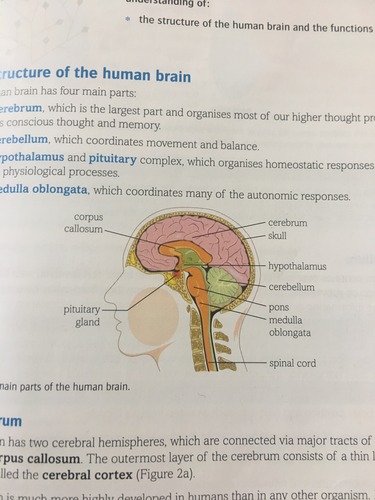
Name the main parts of the human brain
Cerebrum
Cerebellum
Medulla oblongata
Hypothalamus
Pituitary gland
Pons
Corpus callosum
\
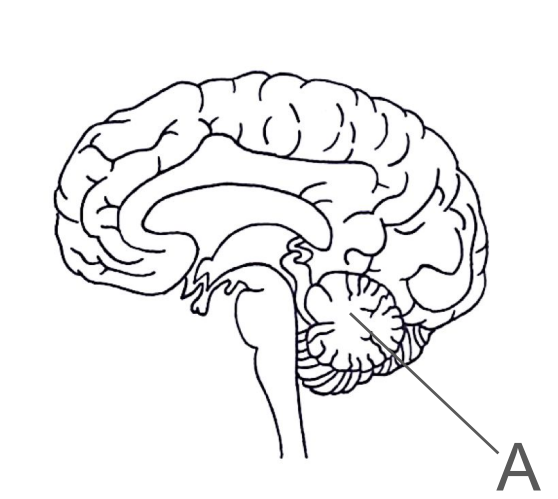
* The cerebellum
\
* The Medulla Oblongata
\
* The Hypothalamus & pituitary complex
About the cerebellum
Coordinates muscular movement and balance
It’s important for muscle coordination, posture and coordination of balance
About the Medulla Oblongata
Coordinates many of the autonomic responses- breathing, heart rate
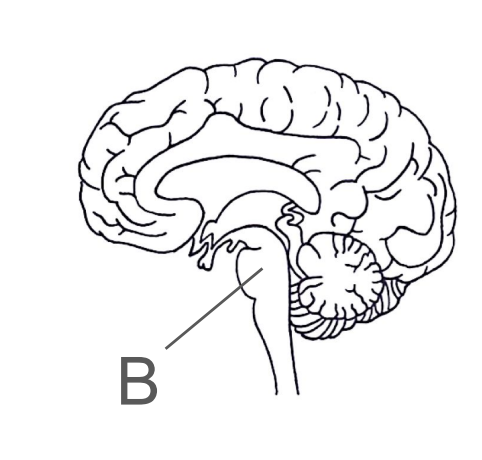
About the pituitary gland
Its controlled by the hypothalamus
It releases hormones and stimulates other glands
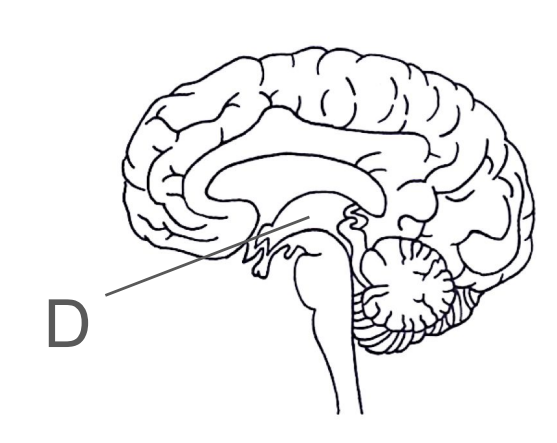
About the cerebrum
The largest part of the brain
It divides to 2 cerebral hemispheres which are connected via the corpus callosum.
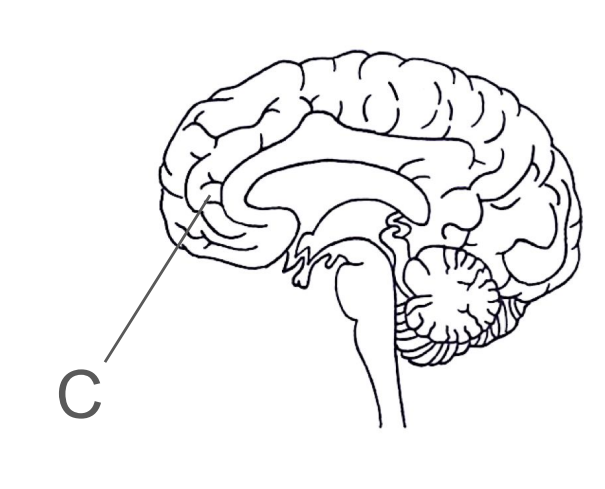
What higher brain functions does the cerebrum control?
Voluntary action
Conscious thought
Conscious actions
Emotional responses
Intelligence, reasoning, judgement and decision making
Memory
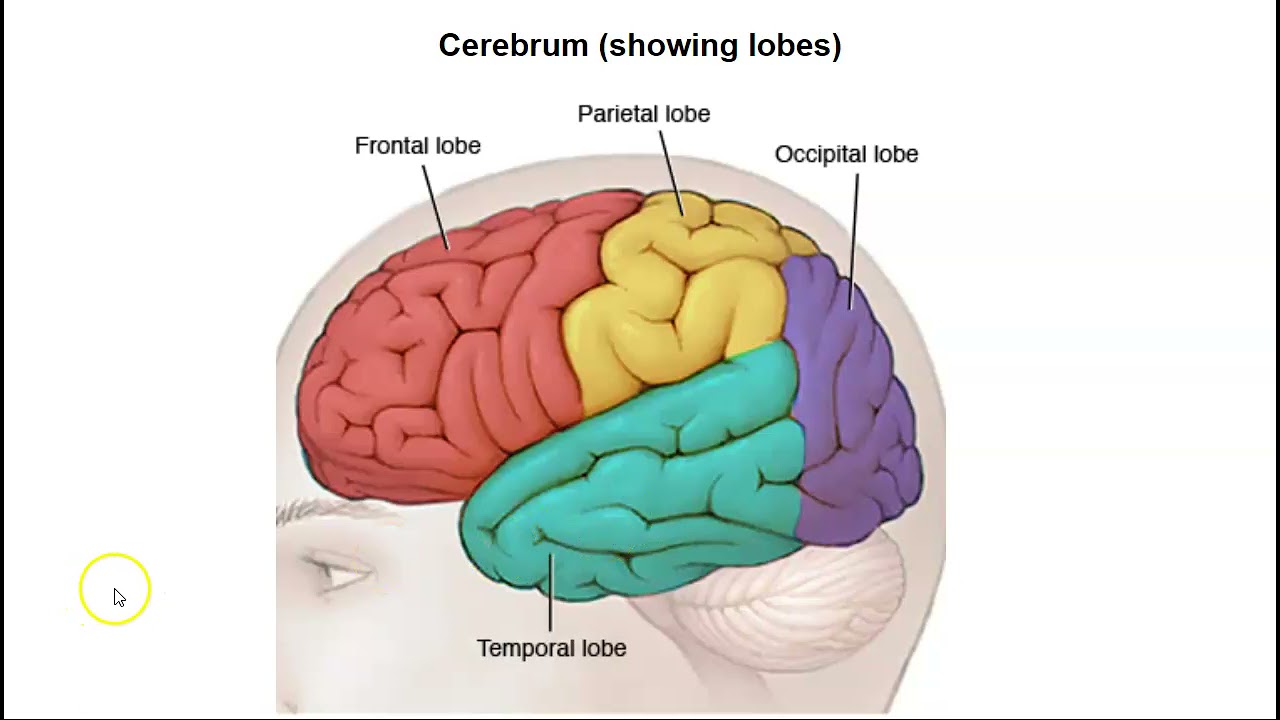
What areas is the cerebral cortex subdivided into?
Sensory areas
Association areas
Motor areas
\
* The balance organs in the inner ear
\
* Spindle fibres in the muscles which give info about muscle length and the joints
What muscular movements does the cerebellum finely control?
Maintaining body position and balance
Judging the position of objects and limbs while moving about
Tensioning muscles in order to use tools and play musical instruments effectively
About the hypothalamus
It contains its own sensory receptors
It’s the main control of the autonomic nervous system
It monitors our internal environment and produces hormones to coordinate them at a stable level
Involved in thermo and osmoregulation
It produces hormones that control the pituitary gland
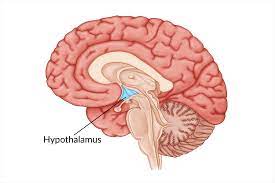
Describe the role of the hypothalamus in temperature regulation
1) It detects changes in core body temperature
2) It also receives sensory input from temperature receptors in the skin
3) It will initiate responses to temp change that regulate body temperature within a narrow range
Describe the role of the hypothalamus in osmoregulation
1) It contains osmoreceptors that monitors the water potential in the blood
2) When the water potential changes, the osmoregulatory centre that bring about a reversal of this change
\
* The anterior lobe
Name 3 centres in the medulla oblongata
The cardiac centre
The vasomotor centre
The respiratory centre
These centres receive sensory info and coordinate vital functions by negative feedback
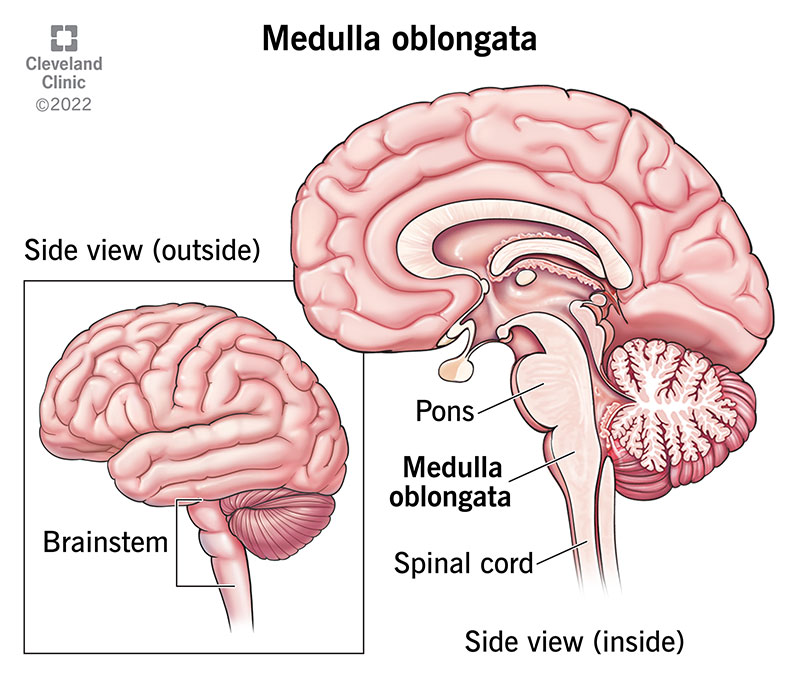
What does the cardiac centre do?
Regulates heart rate
What does the vasomotor centre do?
Regulates circulation and blood pressure
What does the respiratory centre do?
Controls the rate and depth of breathing
\
* They do not involve any processing in the brain to coordinate movement
Outline what happens in a simple reflex arc
1) Receptor detects stimulus
2) Sensory neurone
3) Relay neurone in CNS coordinates response
4) Motor neurone
5) Response by effector
\
* It is a reflex arc as it begins and ends in the eye
Describe the process of the blinking reflex
Sensory nerve endings in the cornea are stimulated by a stimuli (touch)
A nerve impulse is sent along the sensory neurone to a relay neurone in the CNS
The impulse is then passed from the relay neurone to the motor neurones
The motor neurones send impulses to the effectors- the orbicularis oculi muscles that move the eyelids
These muscles contract causing the eyelids to close quickly to prevent eyes being damaged
What is a Consensual response?
Both eyelids close even though only one may be irritated
What is a Cranial reflex?
A reflex that occurs in the brain
What type of reflex is the knee jerk reflex?
A spinal reflex
The nervous pathway passes through the spinal cord rather than through the brain
What does the patella tendon do?
It connects the patella to the lower leg bones at the front of the knee
Describe the process of the knee jerk reflex
Stretch receptors in the quadriceps muscle detect that the muscle is being stretched
A nerve impulse is passed along a sensory neurone
The sensory neurone communicates directly to a motor neurone in the spinal cord
The motor neurone carries the nerve impulse to the effector (quad muscle)
This causes it to contract so the lower leg moves forward quickly
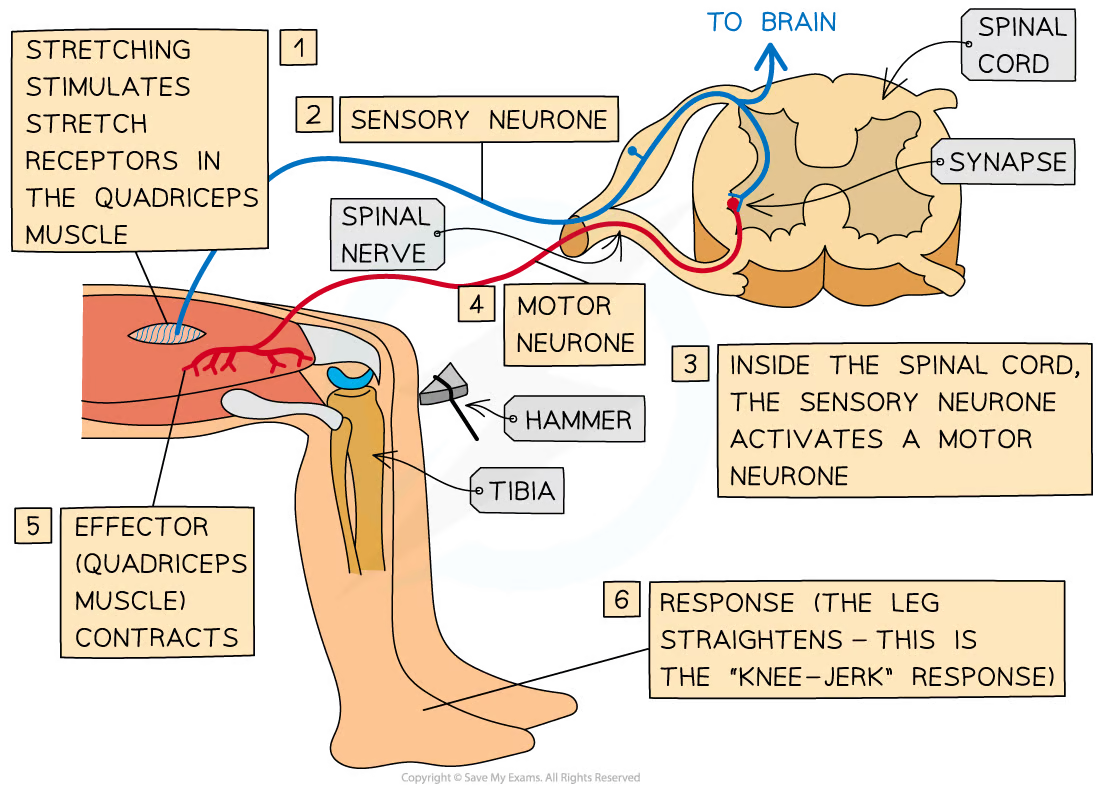
What neurones are involved in the knee jerk reflex nervous pathway?
Sensory neurone and motor neurone
This makes the response quicker
What happens to an organism when they detect a threat to survival?
‘fight or flight response’
It leads to a range of physiological changes that prepare the body for activity
Name some physiological responses involved in the fight or flight response
Pupils dilates
Heart rate and BP increases
Arterioles to the digestive system and skin constrict
Arterioles to the muscles and liver are dilated
Blood glucose levels increase
Metabolic rate increases
Erector pili muscles in the skin contract
What is the survival value of the pupils dilating during fight or flight?
It allows more light to enter the eyes
This makes the retina more sensitive
What is the survival value of the heart rate and BP increasing during fight or flight?
Increases the rate of blood flow to deliver more O2 and glucose to the muscles
Removes more CO2 and toxins
What is the survival value of the arterioles to the digestive system and skin constricting during fight or flight?
Diverts blood flow away from the skin and digestive system and towards the muscles
What is the survival value of the blood glucose levels increasing during fight or flight?
It supplies energy for muscular contraction
What is the survival value of the metabolic rate increasing during fight or flight?
Converts glucose into useable forms of energy such as ATP
What is the survival value of the erector pili muscles in the skin contracting during fight or flight?
Makes the animal look bigger
What occurs during 'fight-or-flight' response?
Sensory receptors detect environmental changes.
Sensory neurones carry action potential to CNS
The nerve impulses from the sensory neurones arrive at the hypothalamus
This activates both the hormonal system and the sympathetic nervous system
What happens when the sympathetic nervous system is activated during fight or flight?
Adrenaline is released from the medulla region of the adrenal gland
What systems does the control of heart rate involve?
The nervous and hormonal system
How does the nervous system help control the heart rate?
The SAN generates electrical impulses that cause the cardiac muscles to contract
The rate at which the SAN fires is unconsciously controlled by the medulla
What are the pressure receptors in the heart called?
Baroreceptors
About the baroreceptors in the heart
They’re found in the aorta and the vena cava
They’re stimulated by high and low blood pressure
What are the chemical receptors called?
Chemoreceptors
About the chemoreceptors
Found in the aorta, carotid artery and the medulla
They monitor the oxygen, CO2 and pH levels
Describe what happens when high blood pressure is detected by baroreceptors?
Impulses are sent to the medulla
The medulla sends the impulses along the vagus nerve
This secretes acetylcholine.
Acetylcholine binds to receptors on the SAN
The result of this is the heart rate slowing down, returning bp to normal
Describe what happens when low blood pressure is detected by baroreceptors?
Impulses are sent to the medulla
The medulla sends impulses along the accelerator nerve
This secretes noradrenaline which binds to receptors on the SAN
This causes the heart rate to speed up, increasing bp to normal
Describe what happens when high blood O2, low CO2 or high pH levels are detected by chemoreceptors?
Impulses are sent to the medulla
The medulla sends impulses along the vagus nerve
This releases acetylcholine which binds to receptors on the SAN
This causes the heart rate to decrease, which returns O2, Co2 and pH levels back to normal
Describe what happens when low blood O2, high CO2 or low pH levels are detected by chemoreceptors?
Impulses are sent to the medulla
The medulla sends impulses along the accelerator nerve
This secretes noradrenaline which binds to receptors on the SAN
This causes the heart rate to increase. returning O2, CO2 and pH levels back to normal
Describe how the cerebrum uses sensory input to coordinate a suitable response.
1) Inputs feed into the sensory centres in the cerebrum
2) The cerebrum passes signals to the association centres
3) If a threat is recognised, the cerebrum stimulates the hypothalamus
4) The hypothalamus increases activity in the sympathetic nervous system
5) This stimulates the release of hormones from the anterior pituitary gland
Describe the mechanism of adrenaline action
1) Adrenaline binds to the adrenaline receptor on the plasma membrane
2) A G protein on the inner membrane is stimulated to activate adrenal cyclase
3) Activated adenylyl cyclase catalyses the production of cyclic AMP from ATP
4) cAMP causes an effect inside the cell by activating enzyme action
5) The precise effect depends upon the cell that the adrenaline has bound to
Describe the process of releasing hormones from the anterior pituitary.
1) The hypothalamus secretes releasing hormones into the blood
2) These pass down a portal vessel to the pituitary gland
3) This stimulates the release tropic hormones from the anterior part of the pituitary gland
4) These stimulate activity in a variety of endocrine glands
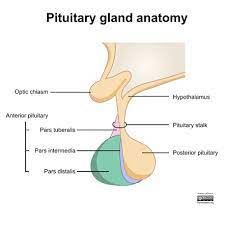
What does CRH from the hypothalamus cause?
It causes the release of ACTH
What does ACTH do?
It passes around the blood system
It stimulates the adrenal cortex to release steroid hormones (e.g. cortisol)
What do glucocorticoids such as cortisol do?
They regulate the metabolism of carbohydrates
This results in more glucose being released from glycogen stores
What does TRH do?
It causes the release of TSH
What does TSH do?
It stimulates the thyroid gland to release more thyroid hormone (thyroxine)
What does thyroxine do?
It increases the metabolic rate making cells more sensitive to adrenaline
What is heart rate controlled by at rest?
The SAN- it has a set frequency
What does the cardiovascular centre in the medulla oblongata do?
Alters the frequency of excitation waves
How does the cardiovascular centre affect the frequency of contractions?
Nerves from the CV centre supply the SAN
Action potentials sent down the accelerants nerve causes the release of noradrenaline at the SAN - increases heart rate
Action potentials sent down the vagus nerve causes release of acetylcholine- reduces heart rate
What do chemoreceptors in the aorta, brain and carotid arteries do?
They monitor the pH of the blood
Chemoreceptors detect change in pH and send AP’s to the CV centre
Low pH detected= increase heart rate
What is high blood pressure detected by?
Stretch receptors in the walls of the carotid sinus
What is skeletal muscle made up of?
Muscle fibres
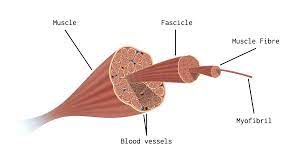
Describe the structure of muscle fibres
Sarcolemma - cell membrane
Sarcoplasm- cytoplasm
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Lots of mitochondria
Multinucleate (many nuclei)
Lots of myofibrils
About the sarcolemma
Bits of it fold inwards across the muscle fibre and stick into the sarcoplasm
These folds are called transverse tubules
The transverse tubules help spread electrical impulses throughout the sarcoplasm so they reach all parts of the muscle fibre
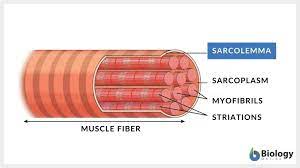
What does the sarcoplasmic reticulum run through?
The sarcoplasm
About the sarcoplasmic reticulum
It stores and releases calcium ions that are needed for muscle contraction
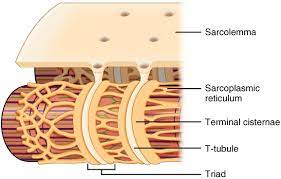
What are myofibrils made up of?
Proteins that are highly specialised for contraction
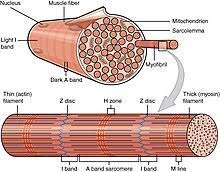
What can skeletal muscle also be called?
Striated, striped or voluntary muscle
What do myofibrils contain?
Bunches of thick and thin myofilaments
These myofilaments move past each other to make muscles contract
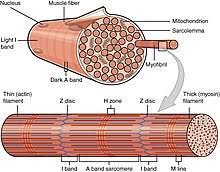
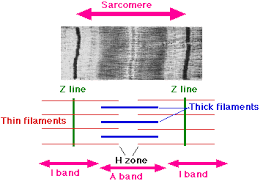
About sarcomeres
The ends of each sarcomere is marked with a Z-line
The middle of each sarcomere is an M-line which is in the middle of the myosin filaments
Around the M-line is the H-zone which only contains myosin filaments