Corso 1
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
what class of NT is endorphin?
peptide
what class of NT is glutamate?
amino acid
what class of NT is endocannabinoids?
retrograde
what class of NT is dopamine?
biogenic amine
what class of NT is ATP?
purigenic
list the biogenic amine NTs
dopamine (DA)
norepinephrine (NE)
epinephrine (Epi)
5-HT (serotonin)
histamine
melatonin
list the amino acid NTs
glutamate (Glu)
glycine (Gly)
GABA
list the purigenic NTs
adenosine
ATP
ADP
diadenosine
UTP
list the peptide NTs
encephalins
endorphins
substance P
neuropeptide Y
VIP
what NT is this?
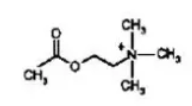
acetylcholine (Ach)
what NT is this?
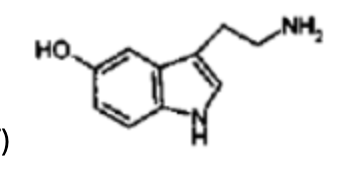
serotonin (5HT)
what NT is this?
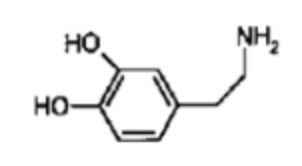
dopamine (DA)
what NT is this?
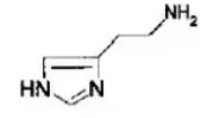
histamine
what NT is this?
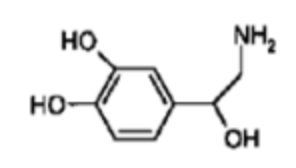
norepinephrine (NE)
what NT is this?
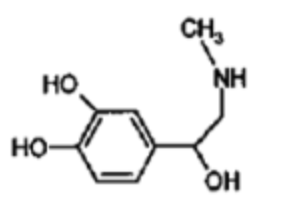
epinephrine (epi)
what NT is this?
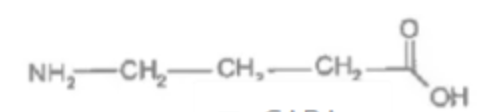
GABA
what NT is this?
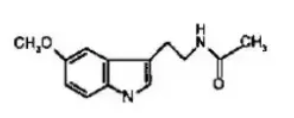
melatonin
what NT is this?
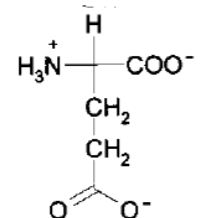
glutamate (Glu)
what NT is this?
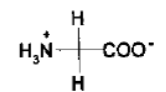
glycine (Gly)
where is dopamine found?
substantia nigra
where is serotonin found?
raphe nuclei
where is melatonin found?
pineal gland
where is histamine found?
hypothalamus
where is ACh found?
nucleus basalis
where is norepinephrine found?
locus ceruleus
where is epinephrine found?
adrenal gland
acetylcholine is most associated with which areas of the nervous system?
nucleus basalis projecting to the hippocampus
neuromuscular junction
POST-ganglionic PARAsympathetic neurons projecting to target organs
autonomic PRE-ganglionic neurons projecting to the autonomic ganglia
norepinephrine is most associated with which areas of the nervous system?
locus ceruleus projecting to the cortex
POST-ganglionic SYMpathetic neurons projecting to target organs
serotonin is most associated with which areas of the nervous system?
raphe nucleus projecting to the cortex
what are the three different classes of cells found in the brain?
blood vessels
glia
neurons
what are the 3 different types of neurons in the brain?
multipolar
bipolar
pseuodunipolar
which of the following types of cells are multipolar neurons? (SATA)
a. cerebellar purkinje cells
b. pyramidal cells
c. granule cells
d. astrocytes
e. spinal motor neurons
a
b
c
e
________ are the junctions between neurons
synapses
what are the “branches” of axon?
terminal arborization
what is grey matter?
a. cell body
b. myelin
a.
what is white matter?
a. cell body
b. myelin
b.
what receives information?
a. dendrites
b. axon
a.
what conducts signal away from cell body?
a. dendrites
b. axon
b.
which 2 types of glia cells create the myelin sheaths around axons?
schwann cells
oligodendroglia
which cell type lines the BBB with its “feet”?
astrocytes
what type of glia cells are phagocytic cells that degrade dead cells and debris in the CNS (brain and spinal cord)?
a. microglia
b. ependyma
c. satellite cells
d. astrocytes
a.
what type of glia cells forms the surface layer of cells for the brain, spinal cord, ventrical and central canal?
a. microglia
b. ependyma
c. satellite cells
d. astrocytes
b.
what type of glia cells protect pseudounipolar cell bodies in the sensory dorasal root ganglia (outside the CNS)?
a. microglia
b. ependyma
c. satellite cells
d. astrocytes
c.
what type of glia cells wrap CNS axons with myelin?
a. oligodendroglia
b. schwann cells
a.
what type of glia cells wrap PNS axons with myelin?
a. oligodendroglia
b. schwann cells
b.
Guillain–Barré syndrome is an acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, an autoimmune disorder affecting the peripheral nervous system. What type of cells would be mostly affected?
a. ependymal cells
b. schwann cells
c. astrocytes
d. oligodendrocytes
b.
what is the movement from axon terminal to cell body?
a. retrograde transport
b. anterograde transport
a.
what is the movement from cell body to axon terminal?
a. retrograde transport
b. anterograde transport
b.
what is a hydrogen ion ATPase primary active transport that pumps protons in?
a. proton transporter
b. vesicular transporter
c. dense core vesicles
d. synaptic vesicles
a.
what is a hydrogen ion neurotransmitter secondary active transport antiporter (hydrogen ion out and NT in)?
a. proton transporter
b. vesicular transporter
c. dense core vesicles
d. synaptic vesicles
b.
what are synaptic vesicles that contain peptide NTs?
a. proton transporter
b. vesicular transporter
c. dense core vesicles
d. synaptic vesicles
c.
what contain small molecule NTs?
a. proton transporter
b. vesicular transporter
c. dense core vesicles
d. synaptic vesicles
d.
what kind of neurons are sensory cells (incoming pain, touch, and temperature info)?
a. pseudounipolar
b. bipolar
c. multipolar
a.
what kind of neurons are special sensory cells (vision, hearing, balance)?
a. pseudounipolar
b. bipolar
c. multipolar
b.
what kind of neurons are motor cells (outgoing info) and interneurons (communication between cells)?
a. pseudounipolar
b. bipolar
c. multipolar
c.