mutations/everything after the quiz we had in the dogs unit
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
what causes changes in organisms?
genetic mutations ig?
why are mutations the only source of new genetic material (alleles)?
Mutations are the only way to create new genetic material because they change the DNA sequence, leading to new alleles that didn’t exist before. Other processes like recombination and gene flow only mix or spread existing alleles, but they don’t make new ones. Mutations happen naturally due to DNA copying errors, radiation, or chemicals, creating the raw material for evolution and genetic diversity.
how does resistance to antibiotics demonstrate how mutations are connected to evolution?
a mutation can occur that makes something resistant to something else, and it will therefore survive and reproduce as other things die
beneficial
Rarely, a mutation causes a change of function that increases survival and is known as a beneficial mutation. for example, a fish mutated with bigger gills so it survives better
lethal/deleterious
Most mutations occur in non-regions of DNA and do not affect function. When a mutation occurs in a coding or regulatory region, most mutations are harmful (deleterious or lethal).
molecular clock
the molecular clock works by counting how many mutations (changes in DNA) have happened over time. Since mutations occur at a steady rate, scientists can look at the genetic differences between two species to estimate how long ago they split from a common ancestor. The more mutations, the longer the time since they were last related.
mutation
any change to the DNA sequence
you get this change randomly (you can’t like eat something and then get a mutation)
reading frame
The reading frame is the way DNA or RNA is read in sets of three letters (called codons) to make proteins. Each codon codes for one amino acid.
In simple terms, the reading frame determines how the sequence of nucleotides (DNA or RNA letters) is grouped into sets of three, which are then "translated" into proteins. If the reading frame is shifted (by adding or deleting a letter), it can change the entire sequence of amino acids, leading to a different protein. This is called a frameshift mutation.
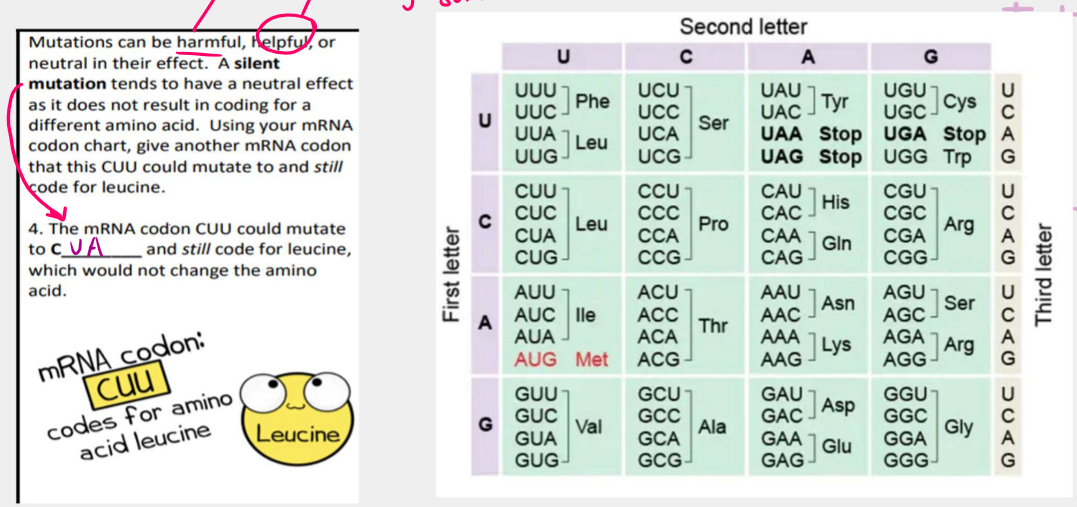
silent/neutral
if a mutation causes no change to the chemical structure of the amino acid, it is said to be silent or neutral
because you have a triplet coding for one amino acid, changing one letter out 3 doesn’t have effects sometimes
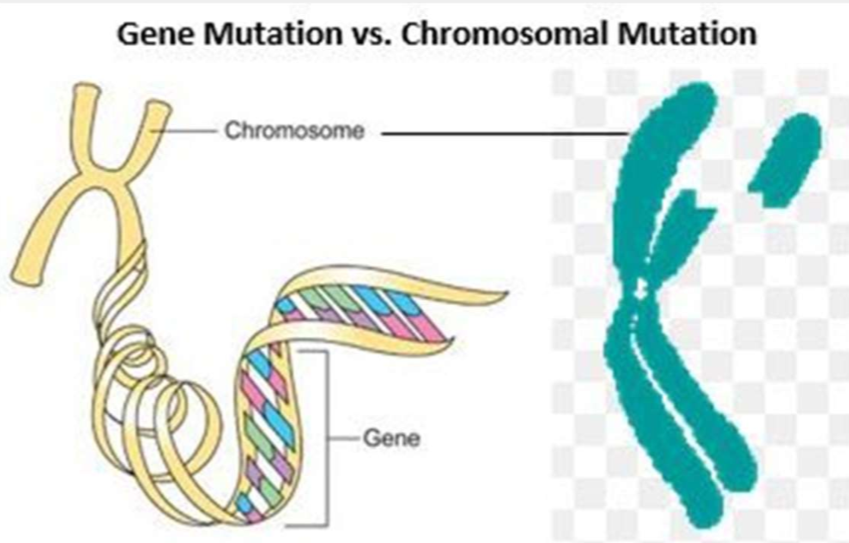
chromosomal mutations vs gene mutations
Gene mutations are localized changes to the DNA base sequence. Chromosomal mutations are changes to whole sections of the chromosome.
a gene mutation is an alteration of the nucleotide sequence of a gene
changes to a single gene
two main types of changes: substitution and frameshift
if a single nucleotide changes, it’s called point mutation
a chromosomal mutation is an alteration of the structure or number of chromosomes
affect longer sections of DNA
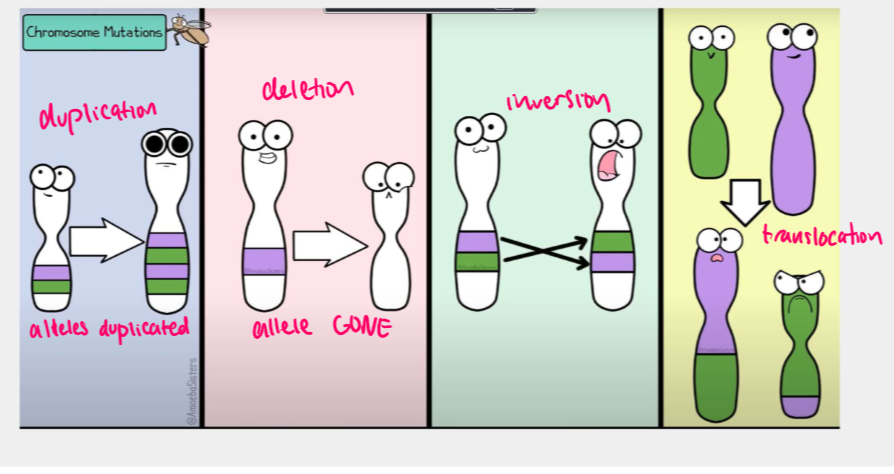
types: deletions, duplications, inversions, translocations
what do many genetic diseases come from?
Many genetic diseases are the result of mutations to recessive alleles like Cystic Fibrosis, but they can also be caused by dominant or codominant alleles as in the case of Huntington's disease and Sickle Cell Disease respectively.
how can mutations occur?
external—something from the environment affects an organism’s DNA, like carcinogens (UV, chemicals, burnt food)
internal—errors made during DNA replication
substitution gene mutations
when the DNA template strand to make the mRNA protein strand, that mRNA will then make a protein sequence using triplets of the mRNA sequence
if the template strand has a substitution mutation, one of the letters will be changed, which will change the mRNA sequence—this may or may not have an effect depending on the amino acid
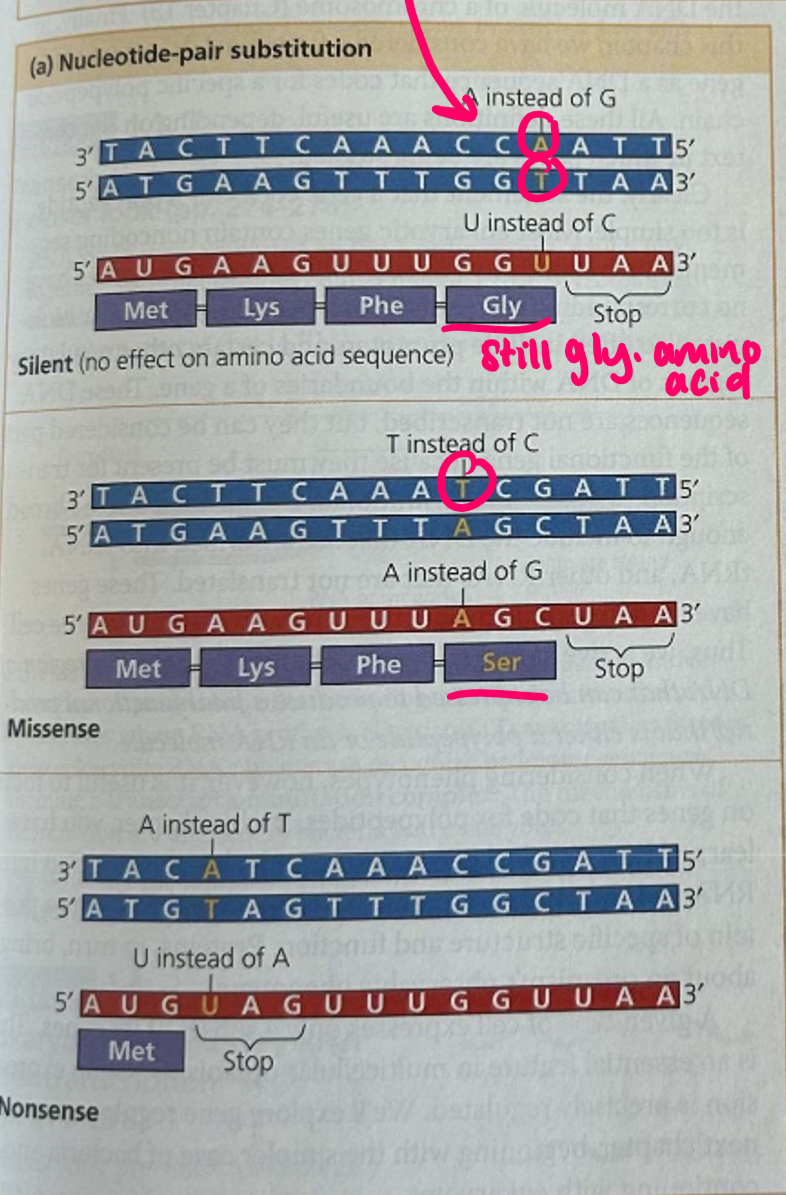
frameshift gene mutations
an extra letter is found in the template strand or there is a missing letter in the template strand which completely alters the animo acid combination from then on
sometimes 3 nucleotides will be deleted so there will be one less animo acid

different chromosome mutations
are all mutations passed down
no, only preexisting mutations in the genome and mutations that occur during meiosis can be passed on to offspring
why can it be advantageous to be heterozygous for a disease?
if you are a carrier of the disease, you could have both the disease and healthy cells in your body, which means that you can better resist it
if you are a carrier for sickle cell disease, for example, you can have partial protection against malaria which increases ur chance of survival
what do pedigrees do
they are maps of inheritance that allow scientists to track traits through families and see how likely they are to appear
how to read a pedigree?
circles are females and squares are males
if you have two possible genotypes (Hh or HH) you should list them both, and put the lettering for a person below their circle or square
line between parents is the marriage line
shaded shapes is what we are tracking
roman numerals represent generations
autosomal dominant
unless someone from outside the family shows up, it cannot skip a generation
two affected parents could not have an unaffected offspring EVER unless both parents are heterozygous (HH and HH or HH and Hh could not have an unaffected child, but Hh and Hh could)
wouldn’t favor a particular gender
autosomal recessive
can skip generations
two unaffected parents could not have an affected offspring unless they are both heterozygous
x-linked dominant
remember to express using X^hY or whatever
sex linkage cannot be confirmed but we make estimates
x-linked traits typically favor a gender
100% of daughters having the trait if the father has the trait probably means x-l dominant
x-linked recessive
if a mother is affected and all of her sons are as well its probably xl recessive
what affects can mutations have
mutation will alter protein and damage its affect (misfolded, no protein, to many