15 - Meds for Cardiovascular Life Support
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
causes of bradycardia
increased parasympathetic tone
profound hypoxia
↓C.O.
↓BP
↓O2 delivery
causes of tachycardia
stress
fever
exercise
hypovolemia
hypoxemia
supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)
narrow QRS complexes

ventricular tachycardia (VT)
shockable rhythm
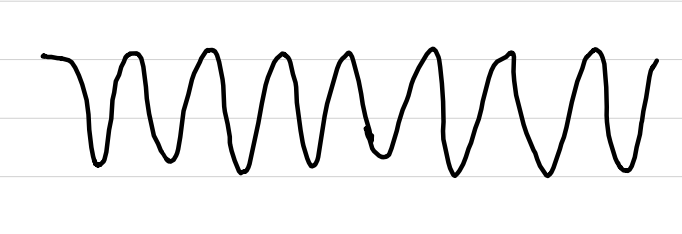
ventricular fibrillation (v-fib)
shockable rhythm
treatment: CPR, de-fib, meds

asystole
NOT shockable
treatment: CPR/AED, epinephrine

pulseless electrical activity (PEA)
NOT shockable
activity in the heart that is not tachycardia nor fibrillation
treatment: epinephrine, continuous compressions, look for causes
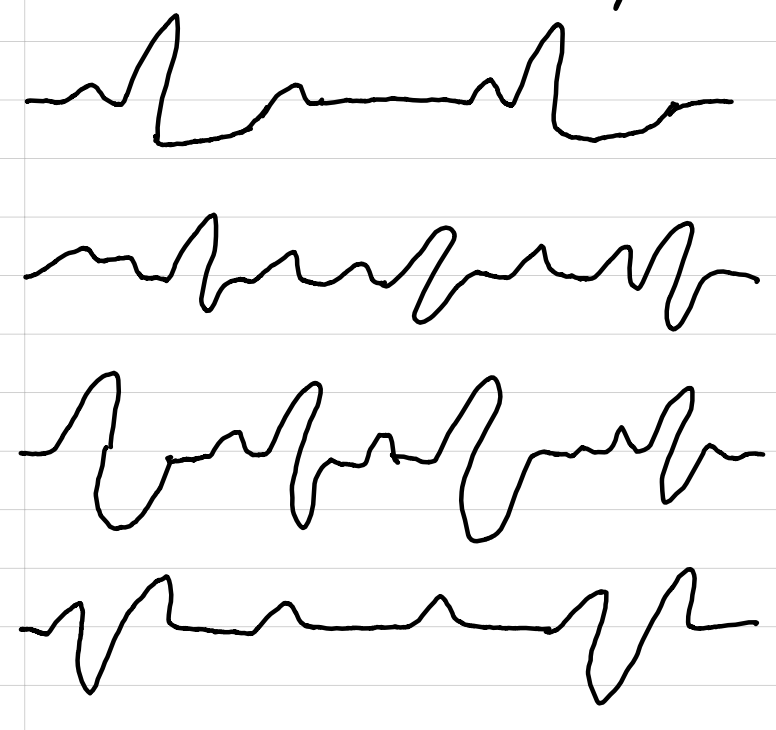
pulseless electrical activity (PEA)
“H” causes
hypovolemia
H+ (acidosis)
hypoxia
hypo-/hyperkalemia
hypothermia
pulseless electrical activity (PEA)
“T” causes
tension pneumothorax
tamponade (cardiac)
toxins
thrombosis
medications for resuscitation
drugs given during CPR immediately after rhythm is checked
CPR continues during admin
admin by bolus injection → 20 mL bolus IV, elevation of extremity
intraosseous (IO) or endotracheal admin if IV not available
ACLS drugs
cardiovascular support
ACLS drugs that alter C.O., rate, and PVR
examples:
epinephrine
vasopressin
norepinephrine
dobutamine
dopamine
digoxin
milrinone
nitroglycerin
sodium nitroprusside
ACLS drugs
arrest rhythms
ACLS drugs that control heart rate and rhythm
examples:
lidocaine
-lol drugs
verapamil
atropine
magnesium
dopamine
oxygen
dosage
22-100% FiO2 via positive pressure ventilation or manual resuscitation bag
oxygen
precautions
watch concentration and duration of exposure
nitrogen washout
radicals
epinephrine
mechanism of action
α and β effects
peripheral vasoconstriction
increased rate and force of contractions
epinephrine
dosage
1 mg IV every 3-5 minutes
epinephrine
precautions
don’t mix with alkaline solutions
can cause hypertension if patient is not in cardiac arrest
norepinephrine
mechanism of action
α vasocontriction
β1 inotropic effect
norepinephrine
indications
severe hypotension
low PVR refractory to other sympathomimetics
norepinephrine
dosage
0.50-1 mcg/min
titrate so SBP ≥ 90
sodium bicarbonate
mechanism of action
buffer base that neutralizes acid
sodium bicarbonate
indications
metabolic acidosis prior to cardiac arrest
hyperkalemia
drug overdose
sodium bicarbonate
precautions
can cause respiratory acidosis
sodium bicarbonate
dosage
1 mEq/kg IV bolus
0.5 mEq/kg IV every 10 minutes
positive inotropic drugs
digoxin
inamrinone
dopamine
dobutamine
digoxin
indications
atrial fibrillation
atrial flutter
slow ventricular response
digoxin
dosage
10-15 mcg/kg lean body weight IV
based on body size and renal function
digoxin
precautions
can cause arrhythmias
inamrinone
mechanism of action
inhibits phosphodiesterase
causes increased C.O. via positive inotropic effect and vasodilation
inamrinone
indications
heart failure refractory to diuretics, vasodilators, and other inotropics
inamrinone
dosage
IV load of 0.75 mg/kg
IV infusion of 5-15 mcg/kg/min
inamrinone
precautions
can cause tachyarrhythmias, hypotension, and thrombocytopenia
dopamine
indications
symptomatic bradycardia
hypotension (SBP 70-100) with signs of shock
dopamine
dosage (low)
1-2 mcg/kg/min
cerebral, renal, and mesenteric vasodilation
dopamine
dosage (medium)
5-20 mcg/kg/min
stimulates β1 and α receptors, increases C.O.
dopamine
dosage (high)
> 10 mcg/kg/min
α-adrenergic effects
dobutamine (Dobutrex)
mechanism of action
stimulates α1 receptors
dobutamine (Dobutrex)
indications
CHF
pulmonary congestion with SBP 70-100 without signs of shock
dobutamine (Dobutrex)
dosage
2-20 mcg/kg/min
HR should not increase >10% of baseline
atropine
mechanism of action
parasympatholytic; increases HR
atropine
indications
increased parasympathetic tone due to advanced heart disease
bradycardia
atropine
dosage
IV bolus 1 mg every 3-5 minutes until HR is 60 bpm
max dose: 3 mg
lidocaine (Xylocaine)
substitution
can be used instead of amiodarone
lidocaine (Xylocaine)
mechanism of action
makes heart more responsive to defibrillation
lidocaine (Xylocaine)
indication
no response to epinephrine or defibrillation
lidocaine (Xylocaine)
dosage
1-1.5 mg/kg every 3-5 minutes until 3 mg/kg
lidocaine (Xylocaine)
precautions
can cause toxicity due to prolonged administration
amiodarone (Cordarone)
indications
SVT
ventricular tachycardia
v-fib
amiodarone (Cordarone)
dosage
1 dose:
300 mg IV/IO bolus
2nd dose (if v-fib or pulseless VT):
150 mg every 3-5 minutes
3rd dose (if tachycardias):
150 mg in 10 minutes
repeat for every VT
1 mg/min infusion for 6 hours
amiodarone (Cordarone)
side effects
hypotension
bradycardia
procainamide (Pronestyl)
mechanism of action
decreases automaticity in Purkinje fibers
procainamide (Pronestyl)
dosage
IV infusion 1-4 mg/min
procainamide (Pronestyl)
precautions
if given too fast or blood volume is too high, hypotension can occur
magnesium sulfate
mechanism of action
affects sodium-potassium pump, calcium-channel blocker
treats Torsades de Pointes
magnesium sulfate
dosage
arrest:
1-2 g in 10 mL of 5% dextrose over 5-20 minutes
no arrest
1-2 g in 50-100 mL of 5% dextrose over 5-60 minutes
verapamil (Calan, Isoptin)
mechanism of action
negative chronotropic and inotropic effects
verapamil (Calan, Isoptin)
dosage
2.5-5 mg IV bolus over 1-2 minutes
max dose: 20 mg
verapamil (Calan, Isoptin)
precautions
may cause severe hypotension and v-fib
diltiazem (Cardizem)
mechanism of action
negative chronotropic and inotropic effects
controls ventricular response in patients with a-fib
diltiazem (Cardizem)
dosage
IV bolus 0.25 mg/kg → infusion
diltiazem (Cardizem)
precautions
pretreat with calcium, or hypotension can occur
adenosine (Adenocard)
mechanism of action
treats SVT
does not treat a-fib, a-flutter, or VT
half-life: 10 seconds
adenosine (Adenocard)
dosage
1st dose:
6 mg bolus given over 1-3 seconds
(temporary pause of HR after admin)
2nd dose:
12 mg if no response within 1-2 minutes
(each admin MUST have saline flush!)
beta-blockers
indications
angina
v-fib
beta-blockers
mechanism of action
causes decreased HR and contractions, hypotension, and reduced O2 consumption
beta-blockers
contraindications
bradycardia
AV heart blocks
beta-blockers
precautions
side effects increase when added to calcium-channel blockers, antihypertensives, and antiarrhythmics