Anxiety - biochemistry and pharmacology
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What is adaptive anxiety?
A normal response to everyday danger that prepares the body for fight‑or‑flight and can be beneficial
What is maladaptive anxiety?
An exaggerated or inappropriate anxiety response occurring in non‑dangerous situations
What happened to OCD and PTSD in diagnostic manuals?
They were moved out of anxiety disorders into adjoining chapters in DSM‑5
What are the core diagnostic requirements for GAD?
Excessive anxiety and worry plus difficulty controlling the worry for at least 6 months
How many symptoms are required for an anxiety disorder diagnosis?
Five or more symptoms during a 6‑month period
What gender pattern and family history is seen in anxiety disorders?
Females have approximately double the risk compared to males
A family history of anxiety, depression, or other psychiatric disorders increases risk
How does drug misuse relate to anxiety disorders?
Drug misuse is a key risk factor for developing anxiety disorders
How common is comorbidity between anxiety and depression?
Very common; anxiety increases risk of later depression and vice versa
What is the estimated heritability of anxiety disorders?
Between 30–50%
How do autoreceptors affect serotonin release?
More 5‑HT autoreceptors lead to reduced serotonin release
What is the effect of the MAOA G‑allele?
It increases breakdown of monoamines, raising vulnerability to anxiety and mood disorders
What does COMT do?
It breaks down dopamine and noradrenaline, influencing stress and anxiety regulation
What does the 5‑HTTLPR short allele increase risk for?
Depression and anxiety disorders due to reduced serotonin transporter function
What does the 5‑HTTLPR long allele increase risk for?
Obsessive‑Compulsive Disorder
What do transporter‑knockout mice show?
Removing serotonin transporter genes increases anxiety‑like behaviour
mice like to be in enclosed spaces (there are two closed arms and two open arms)→ so they hide in these spaces when expericing more anxiety → when have the shorter form of the transporter protein
How does stress interact with genetics in PTSD?
Stress activates the HPA axis; genetic differences increase vulnerability
What HPA axis abnormalities occur in PTSD?
Low baseline cortisol and hypersensitive glucocorticoid receptors
the peak of cortisol levels is not as high as expected in controls
What is the role of the amygdala in anxiety?
It processes emotional responses, especially fear and threat
What role does the insular cortex play in anxiety?
It contributes to emotional awareness and disgust processing
What does the hippocampus do in anxiety?
Supports memory and contextual processing, linking memories with fear
What is the function of the vmPFC (ventromedial prefrontal cortex) in anxiety regulation?
Decision‑making and inhibiting fear responses
What role does the anterior cingulate cortex play?
Attention, conflict monitoring, and inhibition control
What happens when the amygdala is removed in animal studies?
Rats fail to form fear associations with aversive stimuli
What amygdala activity pattern is found in GAD?
Increased anticipatory amygdala activity to both aversive and neutral cues
What did the fear‑conditioning study show about anxiety disorders?
People with anxiety disorders show stronger amygdala reactions to fearful faces than happy faces and learn fear too easily; they treat safe cues (CS–) as dangerous and keep feeling fear even after the danger is gone.
Meta analysis - Kausche et al 2015
What neural pattern appears in anxiety disorders?
Amygdala hyperactivation combined with reduced vmPFC regulation
there is reduced connection between fear alarm (amygdala) and calm down (PFC)
so the PFC cannot regulate amygdala → fear responses are too strong in GAD
How does CBT affect anxiety‑related brain circuits?
It increases functional connectivity between the amygdala and frontoparietal regions
What is fear generalisation in GAD?
Associating fear with CS– (non‑threat cues) showing over‑generalised anxiety
What connectivity abnormality is found in social anxiety disorder?
Reduced connectivity between left amygdala and medial orbitofrontal cortex
what are some environmental biomarkers from GAD
Childhood emotional maltreatment leads to overactive amygdala responses to emotional faces, underactive vmPFC,
Teicher et al 2016
What were early treatments for anxiety?
Non‑specific CNS depressants such as barbiturates
just supressed the nervous system
barbituates have a low theraputic index (beneficial effect vs harmful effect is a low gap)
Why are benzodiazepines safer than barbiturates?
They have a wider therapeutic index and lower overdose lethality
What are examples of benzodiazepines?
Diazepam, lorazepam, alprazolam (Xanax)
How do benzodiazepines reduce anxiety?
They enhance GABA activity in the brain, increasing inhibitory signalling
What type of receptor is GABA‑A?
A ligand‑gated chloride ion channel made of 5 protein subunits
GABA binds to receptor and allows the ion channel to open → chloride enters the cell and makes it more harder for hyperpolarisation to reach action potential
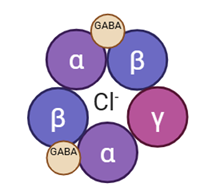
How do benzodiazepines act at the GABA‑A receptor?
They allosterically increase GABA binding affinity, enhancing inhibition
means they bind to receptor and change the receptors response
Bind to benzodiazepine recognitions of GABA receptors -> causing a structural change -> increasing affinity for GABA -> more likely for chloride to come into cell -> increases the function of GABA
Example study on benzodiazepines and anxiety
Lorazepam in healthy controls reduced amygdala and insula activity when looking at emotional faces
Paulus 2005
What are common benzodiazepine side effects?
Ataxia (loose muscle control), sedation, anterograde amnesia, and dependence (17.2% develop drug addiction)
What are full agonists at GABA‑A receptors?
Drugs that maximally increase GABA‑A mediated inhibition
What are partial agonists at GABA‑A receptors?
Drugs that increase GABA‑A function but to a lesser degree
What are benzodiazepine antagonists?
Drugs that block benzodiazepine effects without changing GABA affinity, used for overdose management
What are inverse agonists at GABA‑A receptors?
Drugs that reduce GABA‑A receptor activity, decreasing chloride channel opening
summary of Costa et al 1996 study on partial agonist
retain effects but with reduced side effects
however this is less proved by following studies
How does GABA‑A receptor composition influence drug effects?
Different subunits produce different behavioural actions
there are 6 different alpha proteins, 3 x beta proteins, 3 x gammar proteins
Which subunits are common in limbic regions like the amygdala?
Alpha‑2 and alpha‑3
Which GABA‑A subunit mediates sedation?
Alpha‑1
Which GABA‑A subunit mediates anxiolytic effects?
Alpha‑2
What is the first‑line pharmacological treatment for anxiety?
SSRIs
How does buspirone work?
As a full agonist at presynaptic 5‑HT1A autoreceptors, reducing their sensitivity and increasing serotonin availability
How do beta‑adrenergic blockers help anxiety?
They reduce physical symptoms like rapid heart rate by blocking noradrenaline receptors
How is MDMA being used clinically?
As an adjunct treatment for PTSD in controlled therapeutic settings
breakthrough therapy by FDA
Smith et al 2022