BIO 107 LAB - FINAL WRITTEN - CSUN
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
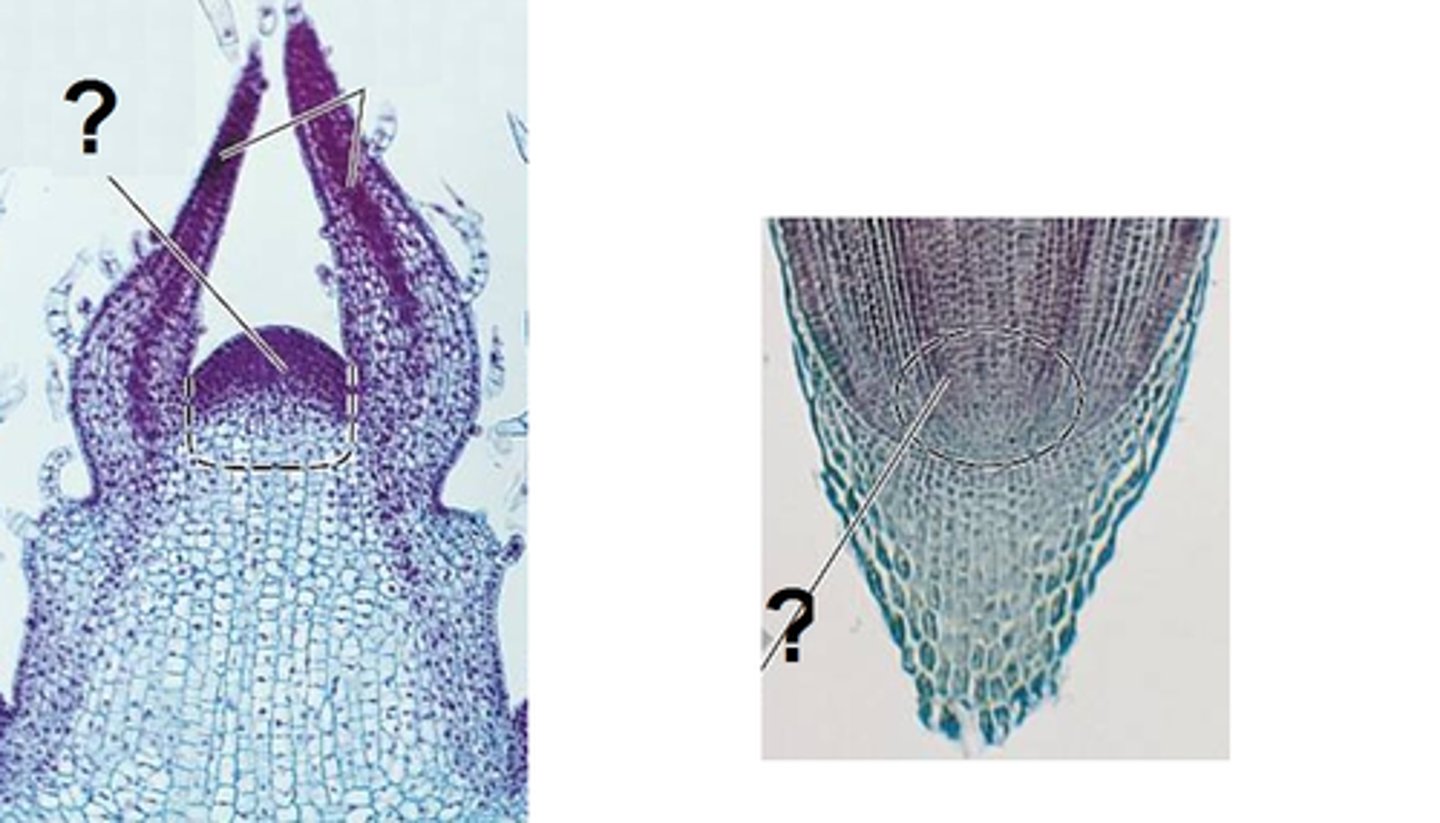
Apical Meristem
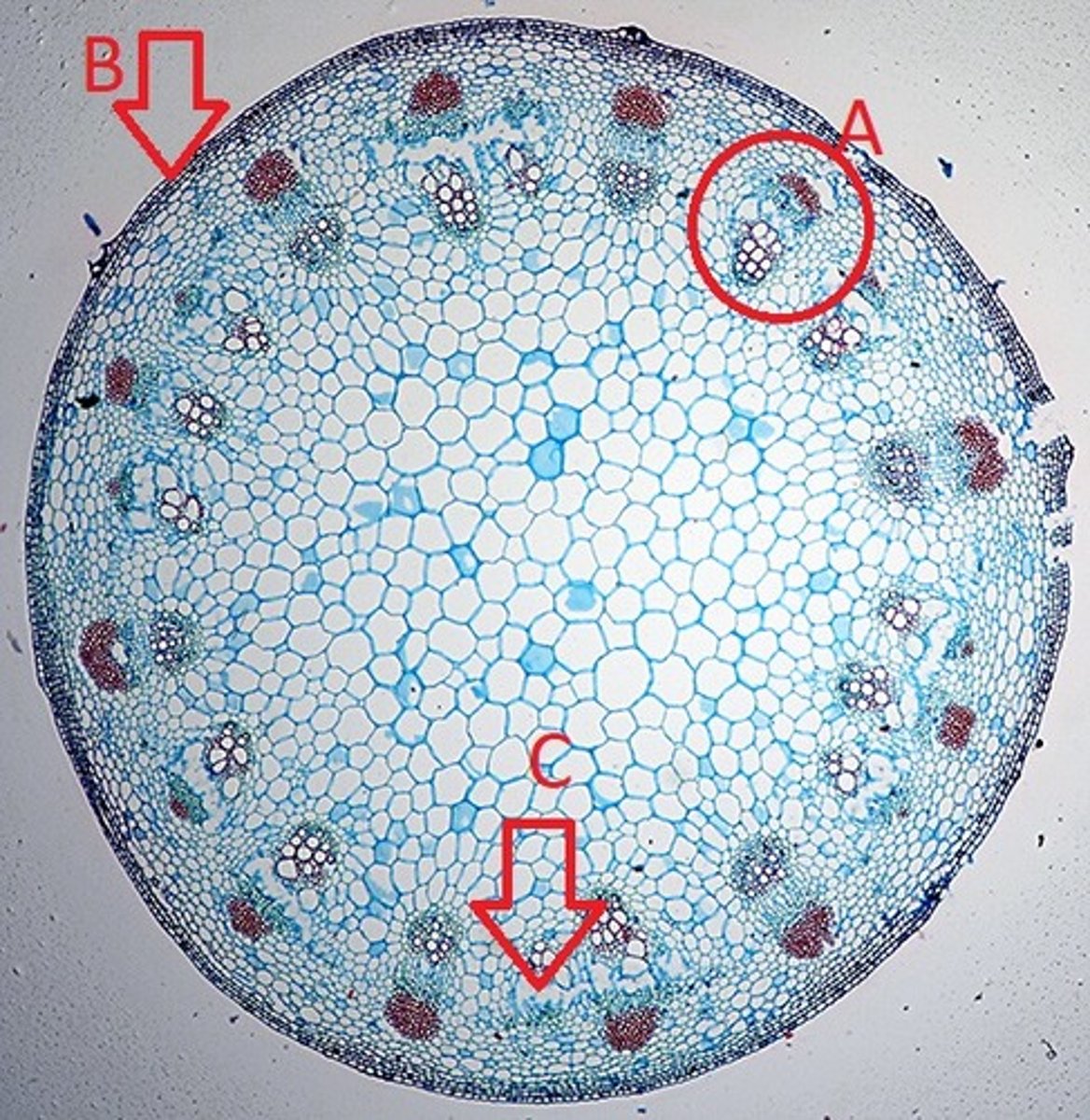
A = Vascular Bundle
B = Epidermis
C = Cortex
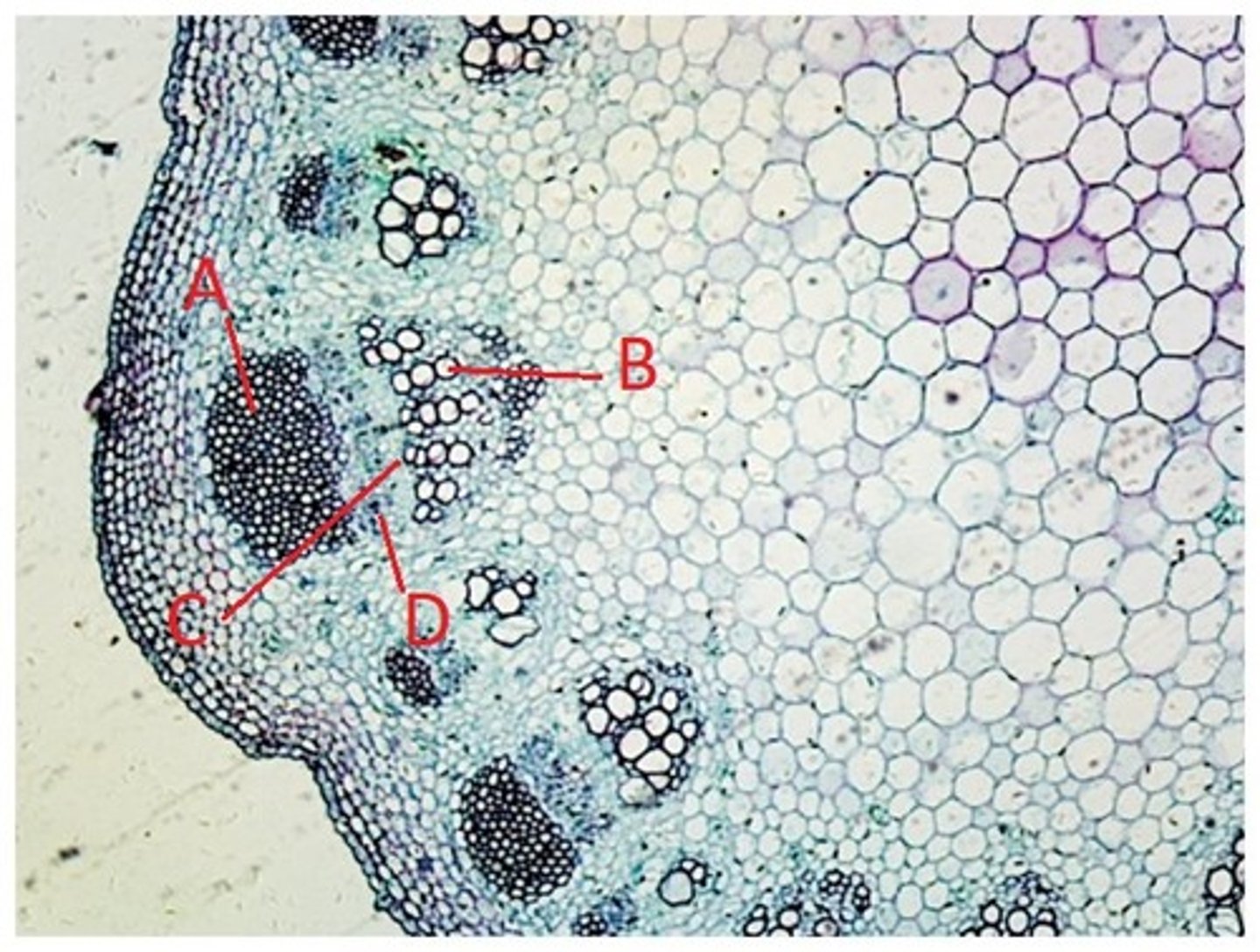
A = Bundle Cap
B = Xylem
C = Cambium
D = Phloem
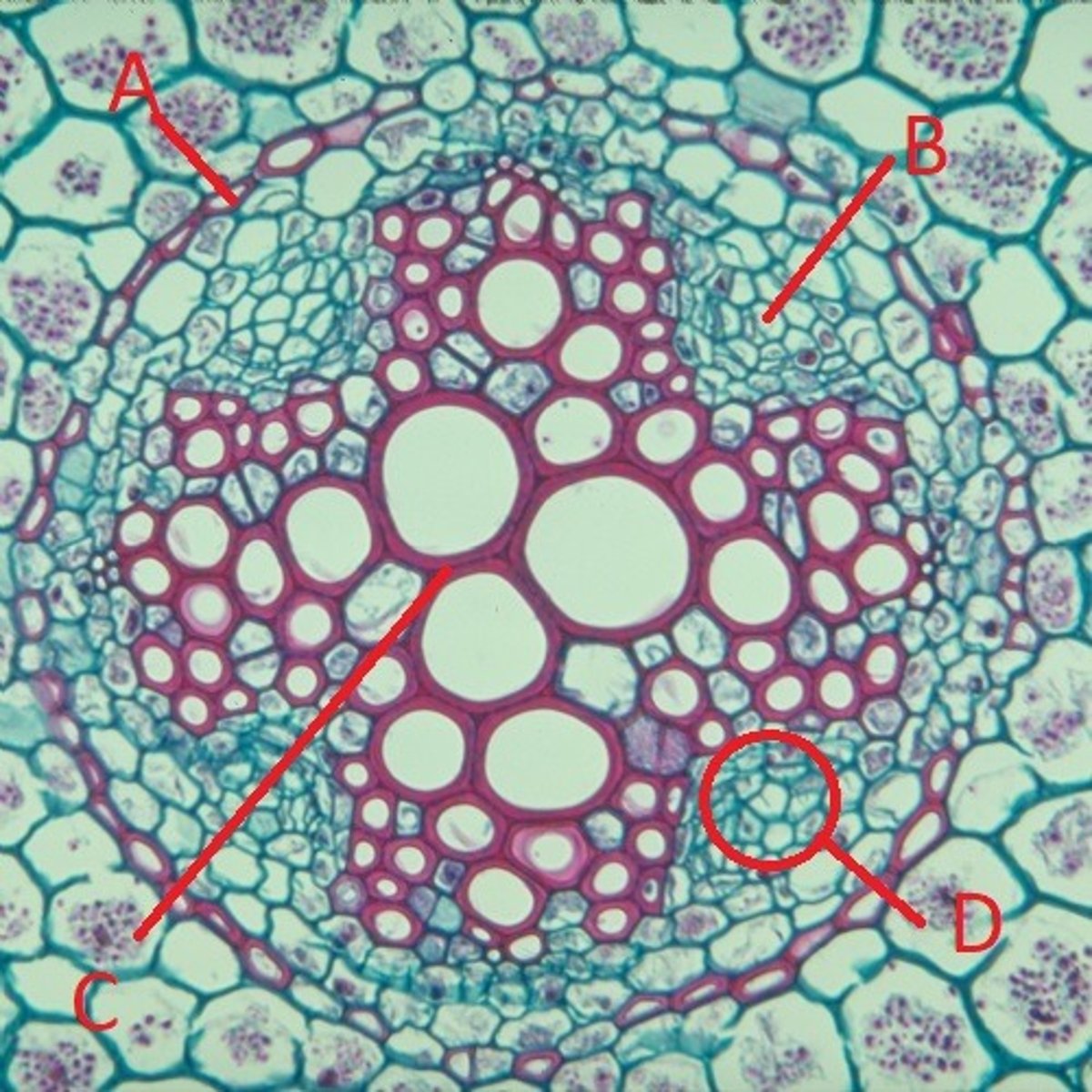
A = endodermis
B = pericycle
C = Xylem
D = Phloem
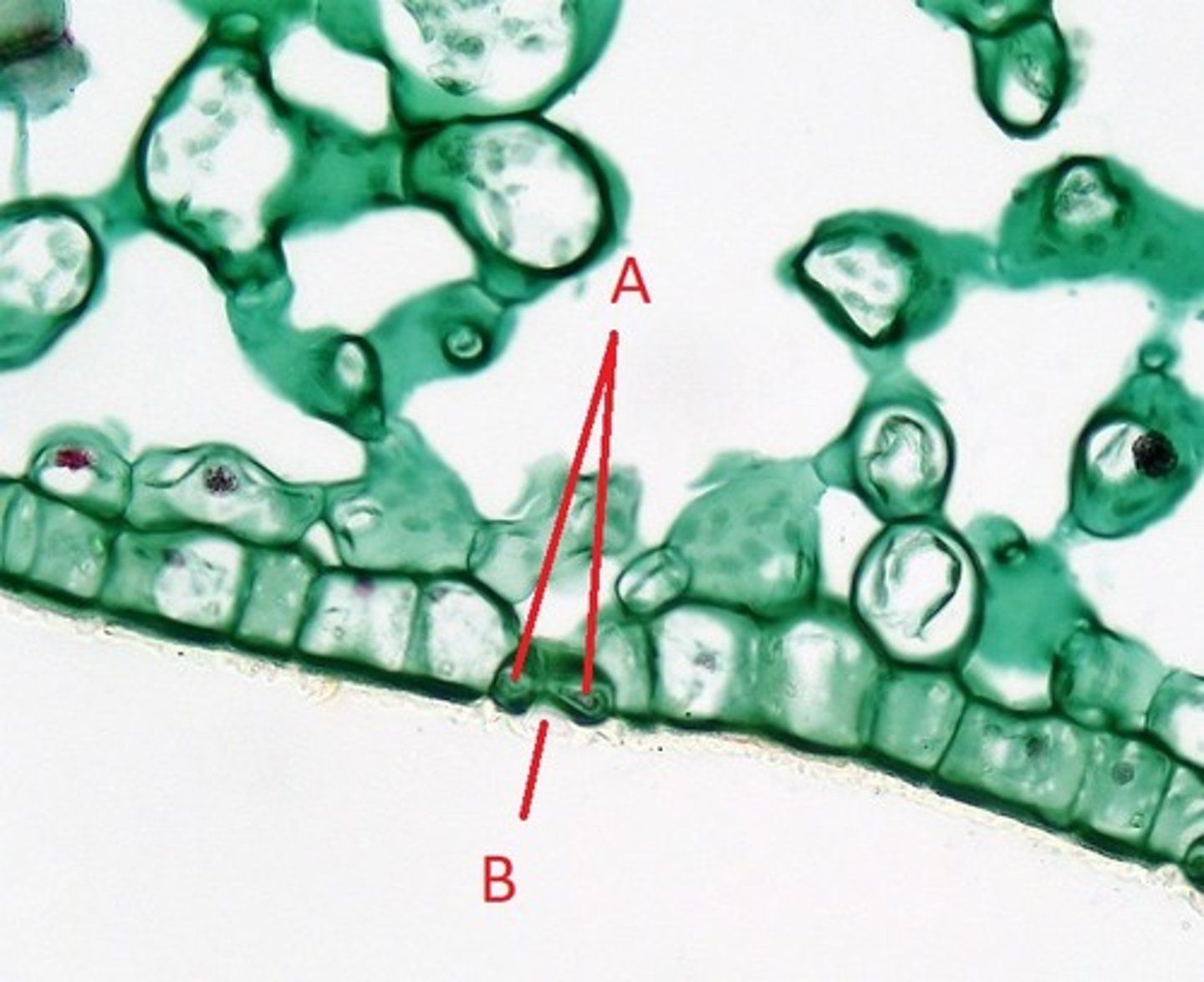
A = Guard Cells
B = Stoma
Nodes, Stem, Shoot apical meristem
Which of the following is part of the shoot of the plant?
Nodes
Stem
Shoot apical meristem
root apical meristem
none
Apoplastic , Symplastic
There are two types of pathways in roots by which surrounding materials from the environment can get transported into plants. the _______ pathways involves materials being transported in-between cells while the _______ pathways involves materials being transported inside of cells.
Guttation
Which of the following describes the name of the process in which plants secrete water and other molecules through their stoma, with the asssitance of guard cells?
Gastrulation
Cytokinesis
Photosynthesis
Guttation
they exert pressure to assist in driving fluid upwards to the top of the plants to transfer nutrients
What is the reason that the roots in a plant exert pressure?
A = Longitudinal Section
B = Cross Section

Plastic refers to the plants plasticity within its environment. This means a plant is capable and often very good at adjusting to and conforming to its given environment.
In pre-lab handout and control, it was stated that plants are both highly organized and that this organization is plastic. please describe what plastic refers to.
Stress tolerance, flowering, branching
Which of the following are examples listed in the pre-lab of plant mechanisms that are regualted by hormones.
Auxinization
stress tolerance
flowering
branching
none
Cytokinins
Absciscic acid
Auxins
Which of the following are examples of plant hormones ?
Cytokinins
Absciscic acid
auxins
carbon dioxide
glucose
Fruits
What is the source of ethylene mentioned in the pre-lab?
shoot apical meristem
According to the pre-lab, where is the plant hormones auxin produced in plants?
Cytokinin
Which of the following is NOT a hormone we worked with in one of our labs?
Gibberellic acid
Cytokinin
Auxin
Abscisic Acid
Ethylene
_______ is given off by many fruits and can cause epinastic growth of shoots.
We tested these with the mutant and nonmutant pea plants that had the auxins on them. We wanted to measure mutant growth and wild growth with and without auxins.
For the experiment in lab that tested auxin, what were the three treatment conditions we tested?
Gibberellic Acid
Which hormone was responsible for germination and stem elongation?
Absciscic Acid
Which of the following hormones was states to casue the stomata of the plant to close?
Ethylene
Gibberellic Acid
Absciscic Acid
Auxin
pig
What animal did we disect in vertebrate labs?
Epithelial, Connective, Nervous
We were briefly surveying four major categories of tissues. Which tissues does this include?
Pepsin, Acids
The digestion system mentioned two compounds with the stomach that aid in breaking down food, which of the following were tehse?
Sugar
Pepsin
Acid
Amino Acids
Fatty Acids
Liver
Which organ in the lab possesses the function of regulating levels of blood sugar?
Origenital opening, Genital papilla
When sexing your pigs, the _______ and _______ are the most indicative areas for this determination
None
According to the cheek dissection figure in the pre-lab, there were four key structures that you needed to identify. Which of the following is NOT one of these four structures, if none, select none
Salivary gland
Masseter muscle
facial nerve
salivary duct
none
Diaphragm
In figure 12.1 of the pre-lab, the image shows the part of the dissection where you needed to identify the air and food passages. there were six structures that you needed to be able to identify, which of the following is NOT one of these six structures?
Esophagus
Diaphram
Nasopharynx
Palate
None
Blue, red
The veins in the pig were stained with a ______ color while the arteries in the pig were stained with a _______ color
Liver
The _______ organ is the largest organ in the abdominal cavity and is responsible for storing glycogen
Nasal Passage
Lungs
Trachea
Name the three parts of the pig that constitute the pigs respiratory system.
Nasal Passage
Lungs
Thymus Gland
Trachea
None
Esophagus
Which structure in the pig body connects the mouth to the stomach?
heart, lungs
Blood enters through the _______ and is pumped through the pulmonary circuit to the _______ where it takes on oxygen and gives off carbon dioxide
Stethoscope
Which of the following instruments is used to hear the sound of a beating heart, letting your doctor indicate the health of your heart?
Hypodermic needle
sphygmomanometer
stethoscope
none
Systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure
The _______ is the pressure produced by the contraction of the ventricles of the heart while the _______ is the pressure that measures arterial pressure during the relaxation of the ventricles
striped
Striated muscle is so named because it has a _______ appearance
True
(T/F) smooth muscle normally lacks striation
Heart
Which major organ in the body contains cardiac muscle?
thick, thin
Arteries tend to have ______ walls while veins tend to have _______ walls
Urethra
which structure in the urinary tract aids in releasing urine contents from the body?
Central Nervous system, peripheral nervous system
The nervous system is often divided into the _______ consisting of the brain and spinal cord, and the _______ which radiates out to all parts of the body.