4. Pharmacokinetics I
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
60/40/20 Rule
Estimates the volume of fluid in each body compartment based on total body weight
60% of total weight → total body water
40% of total weight → intracellular fluid (ICF)
20% of total weight → Extracellular fluid (ECF) → 75% interstitial and 25% intravascular
Drugs are absorbed faster from organs with large ______ _____ and ________ membranes
Drugs are absorbed faster from organs with large surface areas and thinner membranes
1st Pass or Pre-systemic Metabolism
Process through which ORAL drugs lose most of their bioavailability due to pre-systemic metabolism by the gut wall or liver
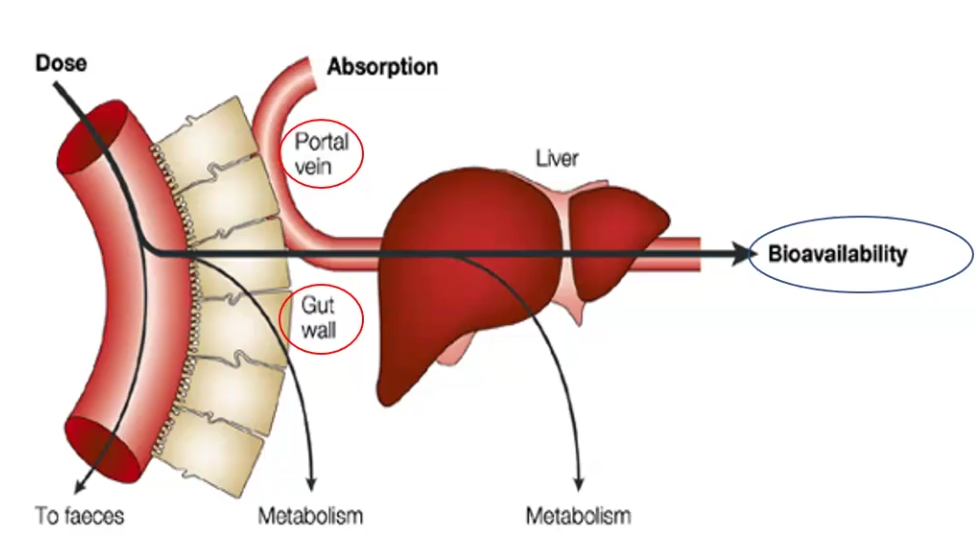
Bioavailability
The fraction of the given dose that reaches the systemic circulation following administration by any route
Bioavailability of Major Routes of Administration
Intravenous
Intramuscular
Subcutaneous
Oral
Mucous membranes
Rectal
Inhalation
Transdermal
Sublingual
Intravenous 100%
Intramuscular 75-99%
Subcutaneous 75%-99%
Oral 5-99%
Mucous membranes ECTREMELY LOW
Rectal 30-99%
Inhalation 5-99%
Transdermal 80-100%
Sublingual EXCELLENT
Factors Affecting Oral Drug Absorption
Blood flow to the area, the more the better absorption
Gastric emptying time; can be increased by gastric stimulants, fatty foods, anticholinergic drugs and pyloric stenosis
pH of gut: affects ionization and stability of drug
Food particles that trap drug molecules
Surface area and thinness of area increases absorption
Factors Affecting Drug Distribution
Drug binding to plasma or tissue proteins decreases distribution and excretion
Storage of lipophilic drugs in ADIPOSE TISSUE
Blood flow to tissues and organs
Physical properties
Chemical properties: hydrophilic vs lipophilic
Capillary permeability
Ionization
Describe how plasma protein binding affects distribution
Why is this no longer an issue in MOST cases
Plasma protein binding such as albumin traps drug molecules in the vascular space and prevents them from reaching the site of pharmacologic action, as well as decreases clearance
Not an issue anymore because plasma protein # far exceeds #drug molecules → also as free drug increases so does clearance
Only a problem if drug clearance is greatly decreased due to kidney or liver disease OR if displaced drug has low TI
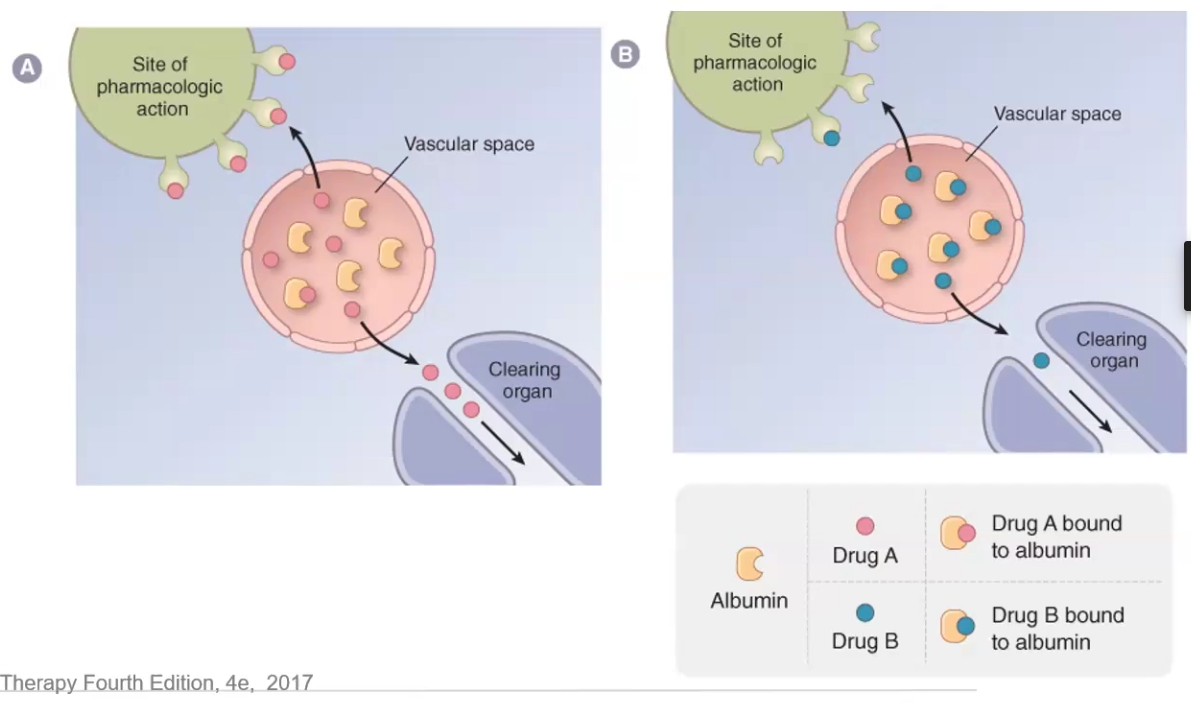
Describe Capillary Permeability in terms of drug acess
Endothelial cells lining blood vessels in the liver have large fenestrations that allow free movement of substances between the blood and the interstitium
Blood vessels in the brain have endothelial cells with very tight junctions that only allow high lipid solubility substances to pass the BBB
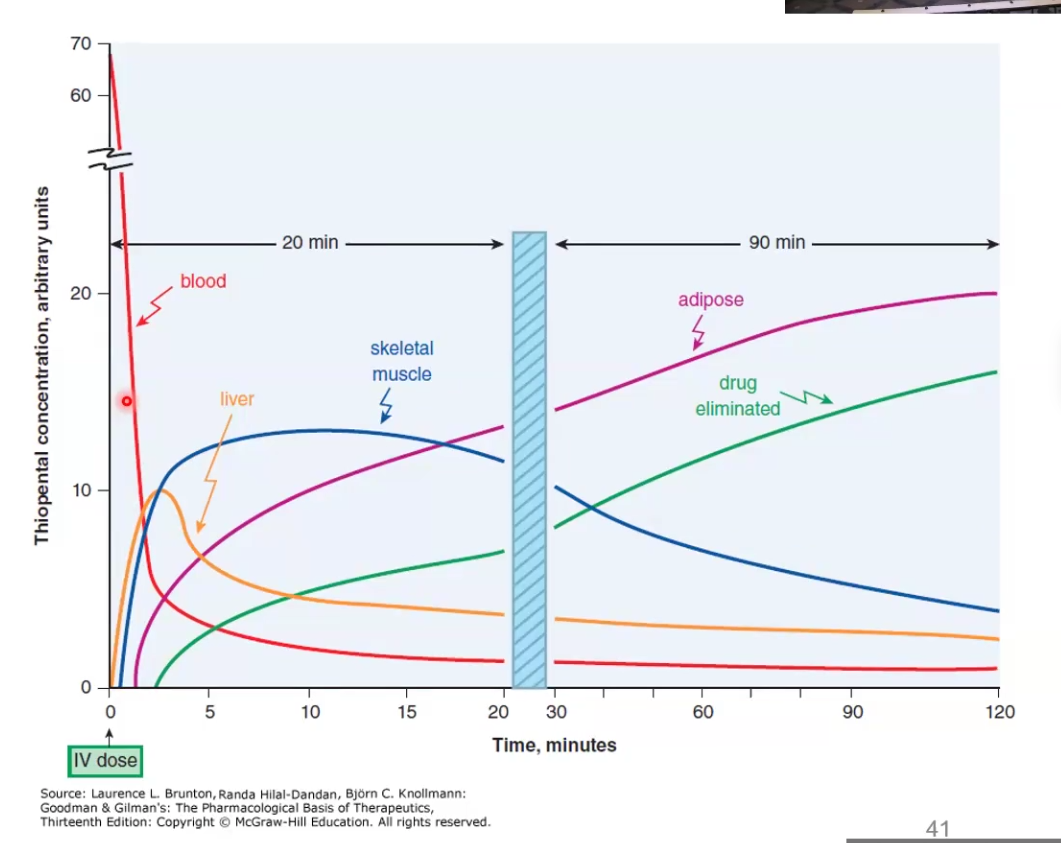
Explain how redistribution terminates drug action
While the drug may distribute initially to one place to have a pharmacological effect, redistribution to other tissues can terminate the effect
Ex. Thiopental acts rapidly crossing the BBB and causes anesthetic effect, but then it redistributes to muscle, fat, etc and the patient wakes up because the brain concentration decreased
Volume of Distribution formula
Volume of Distribution (Vd) = Dose (D) / Plasma Concentration (Cp)