scanning probe microscopy part II - imaging modes
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
imaging modes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Imaging modes
Atomic Force Microscopy
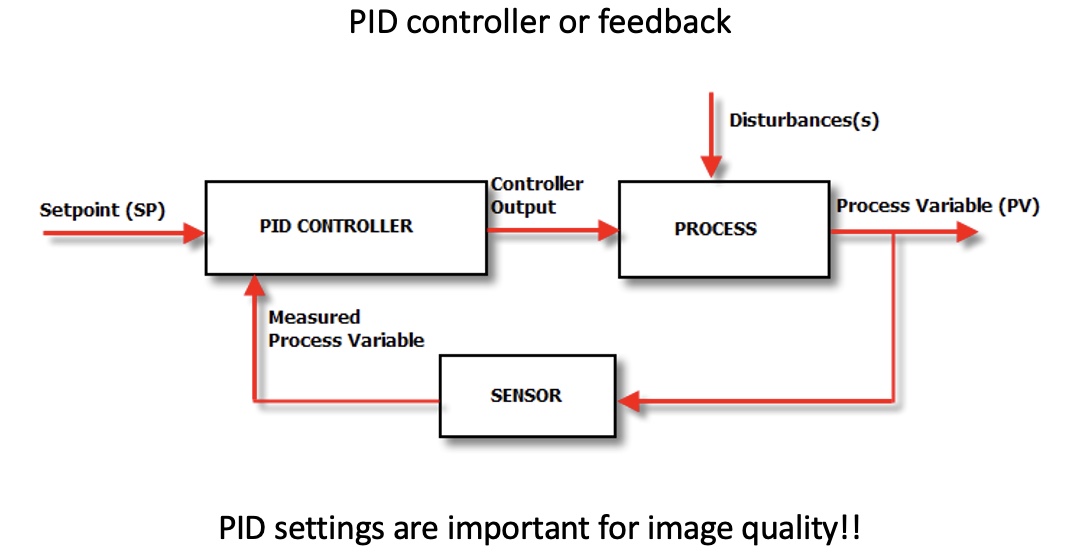
Modes of operation
The interatomic interaction between sample and tip involves van der Waals’ forces:
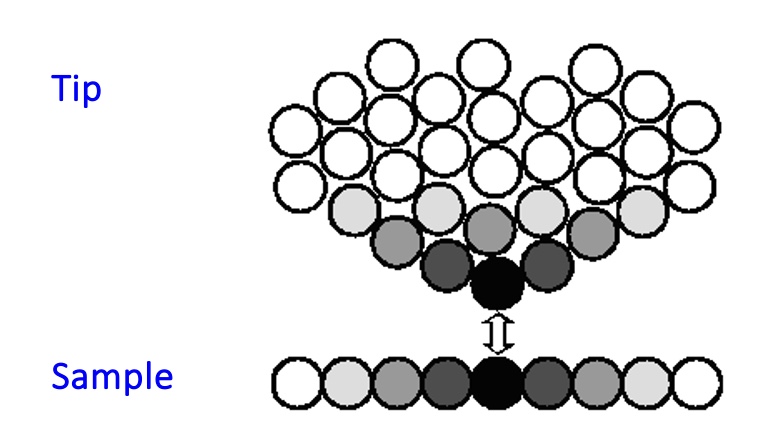
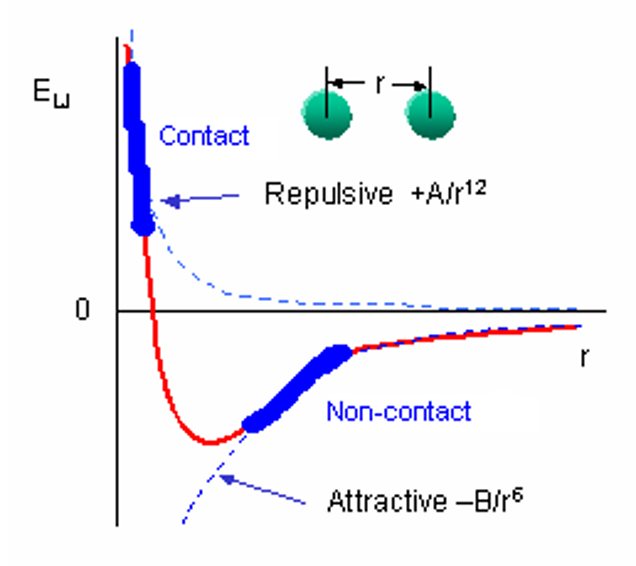
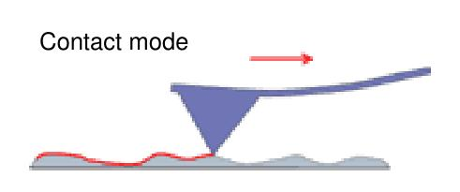
Contact mode
In contact AFM method, the probe tip scans across the sample surface, coming into direct physical contact with the sample.

contact mode
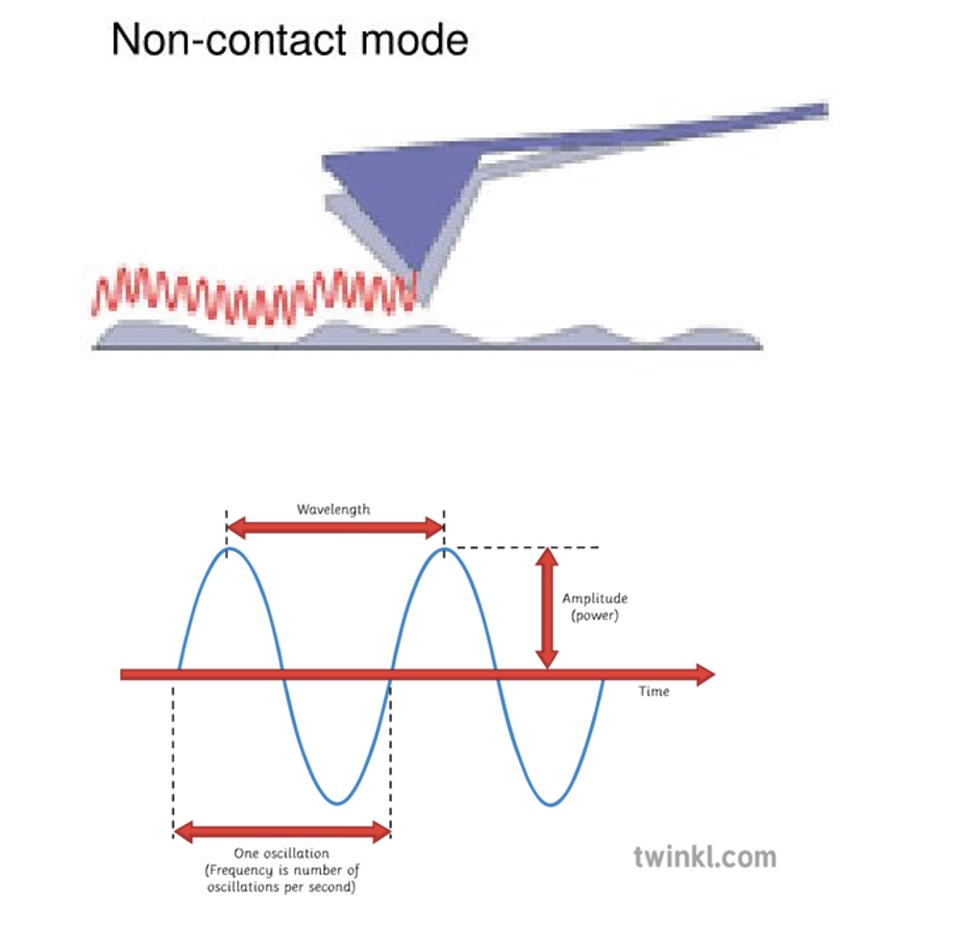
non-contact mode
In Non-Contact Mode AFM the cantilever oscillates at a frequency slightly above its resonance frequency (amplitude <10nm) in order to obtain an AC signal from the cantilever.
The cantilever's resonant frequency decreases by the van der Waals’ force and by other long range forces extending above the surface.
The system detects variations in the resonant frequency or vibration amplitude.
This mode is ideal for studying soft or elastic samples because the total force between the tip and sample is very low (about 10-12 N).
The force in the non-contact regime is low, making it more difficult to measure than that of contact mode.
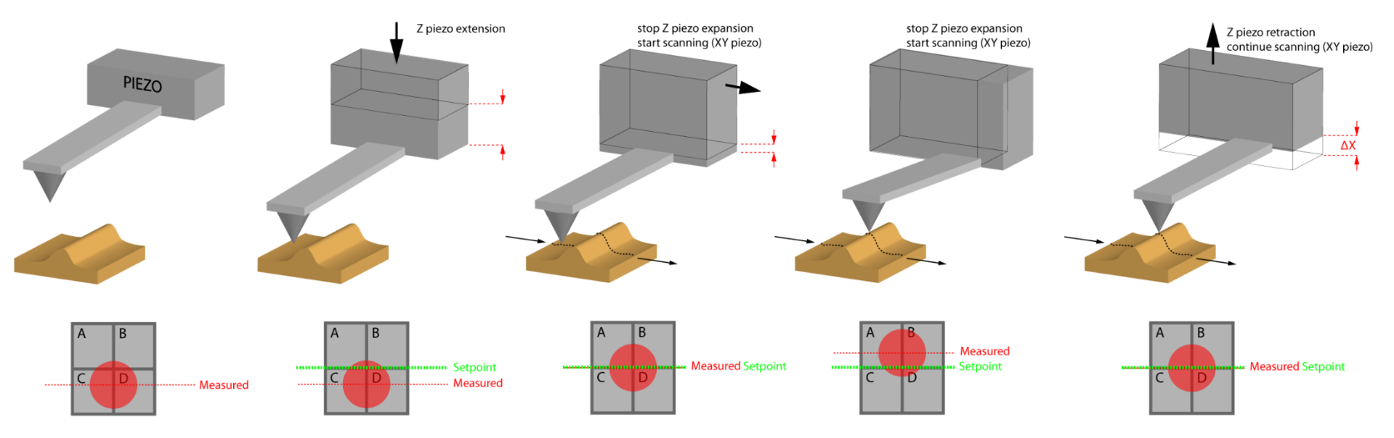
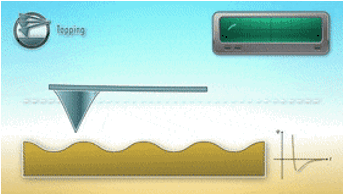
OSCILLATING MODE (TappingMode™)
Oscillating the probe cantilever while scanning avoids lateral or shear forces between the probe and sample during imaging.
Typically, probe cantilever oscillation is at the cantilever resonance frequency, and a relatively stiff cantilever is used.
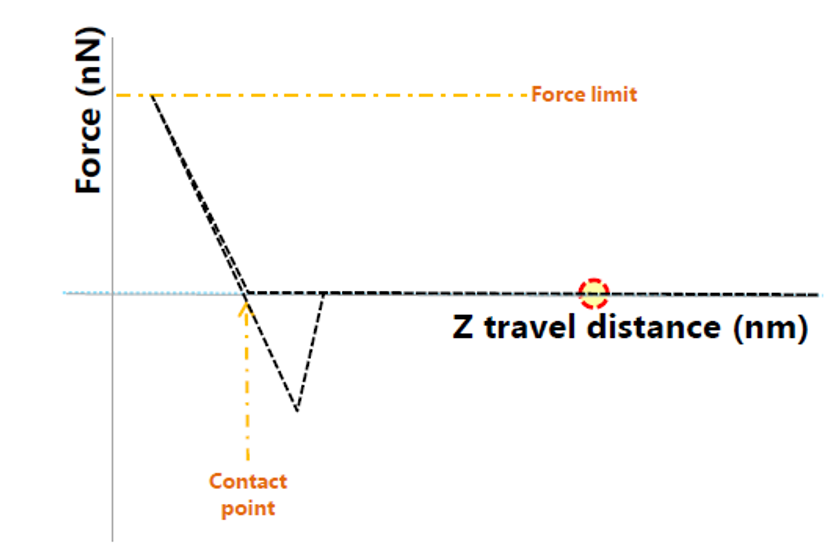
When large amplitude oscillations are used, the probe might crash and cause damage to tip and sample.

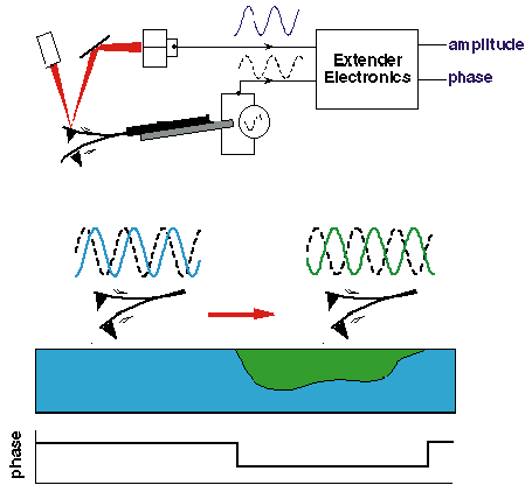
Phase imaging
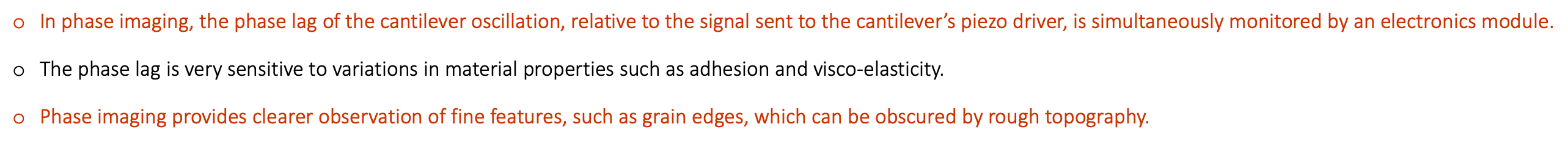
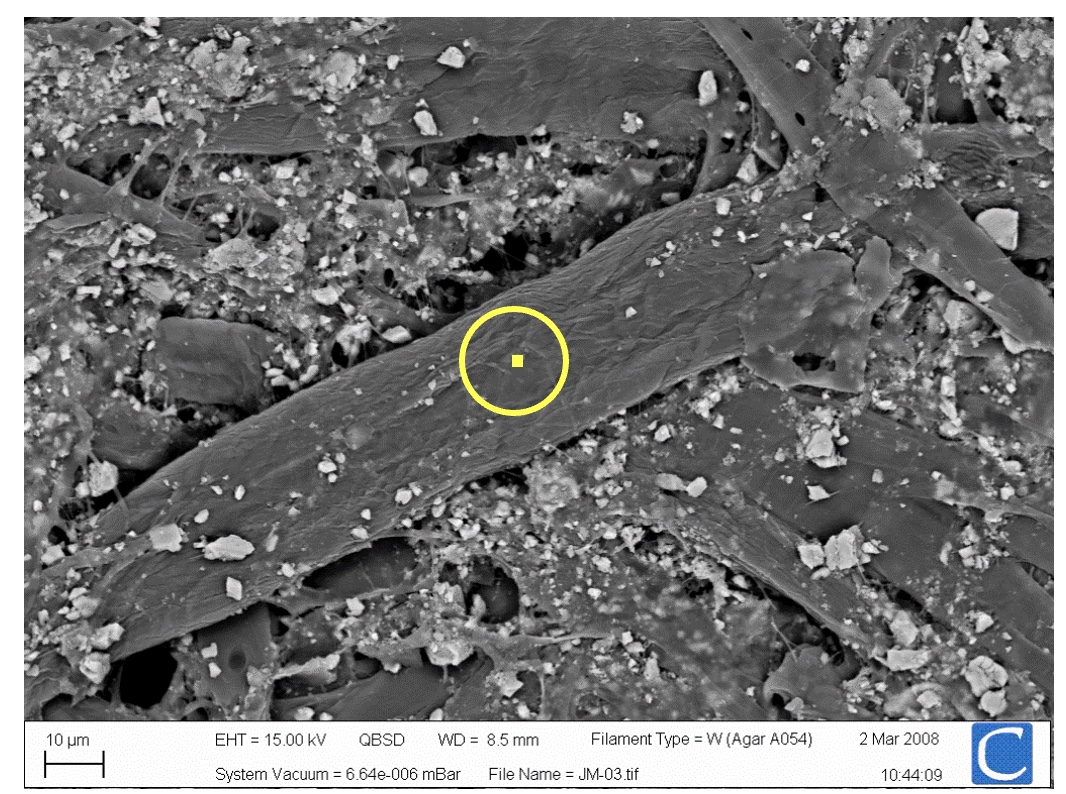
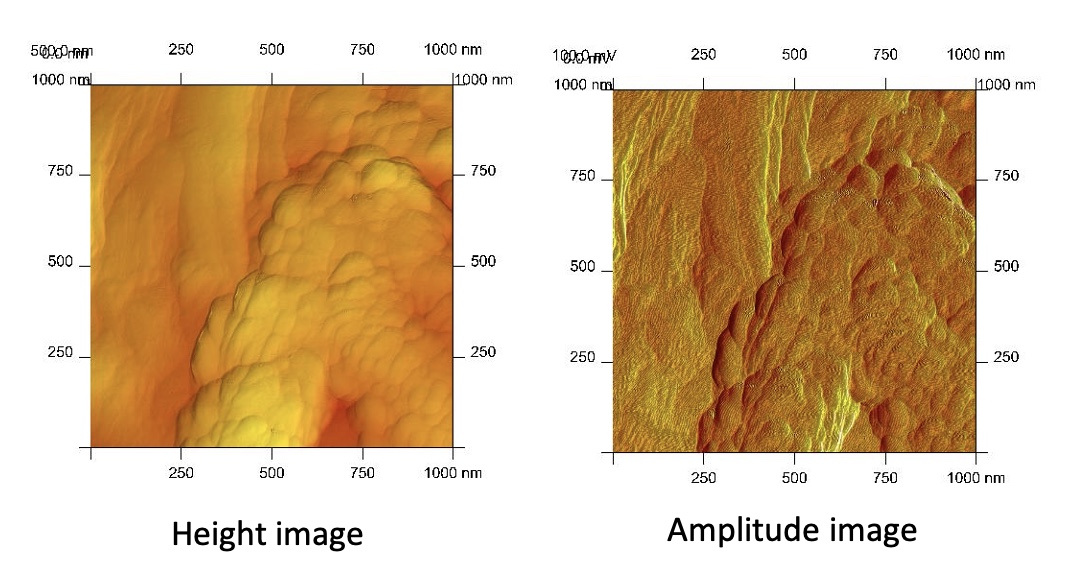
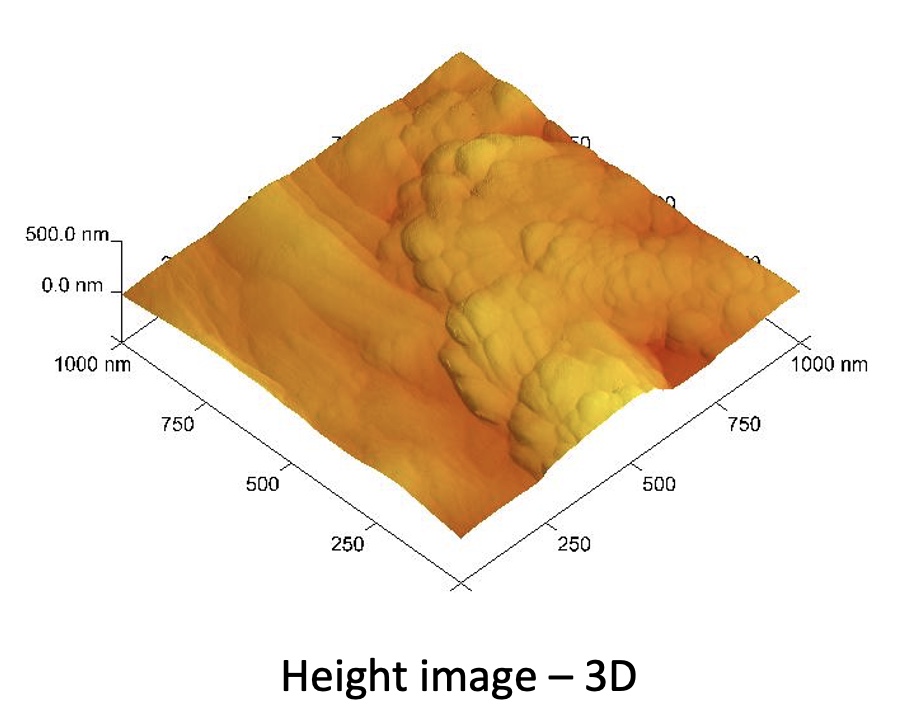
Imaging - paper fibres

imaging-paper fibres
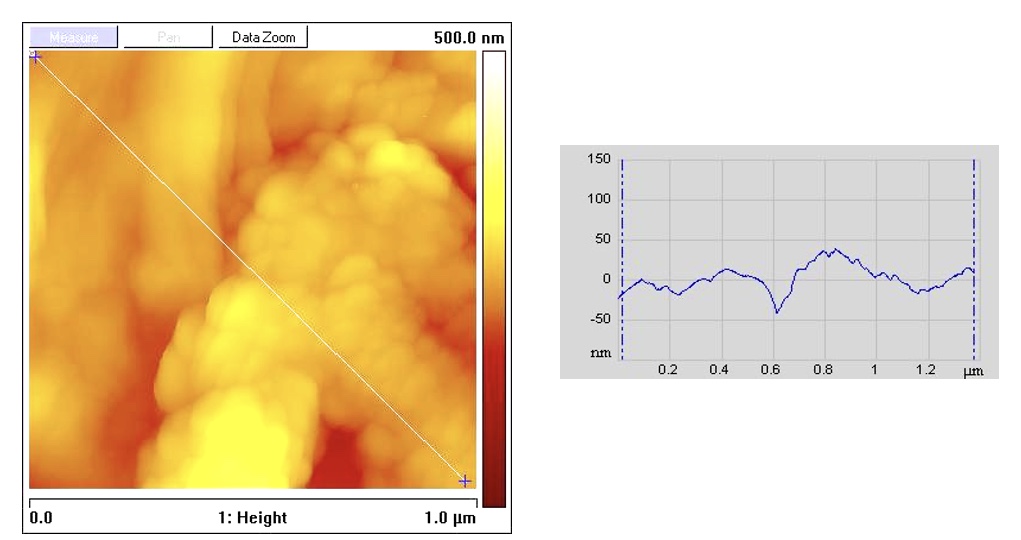
AFM IMAGES OF COTTON WEAVE
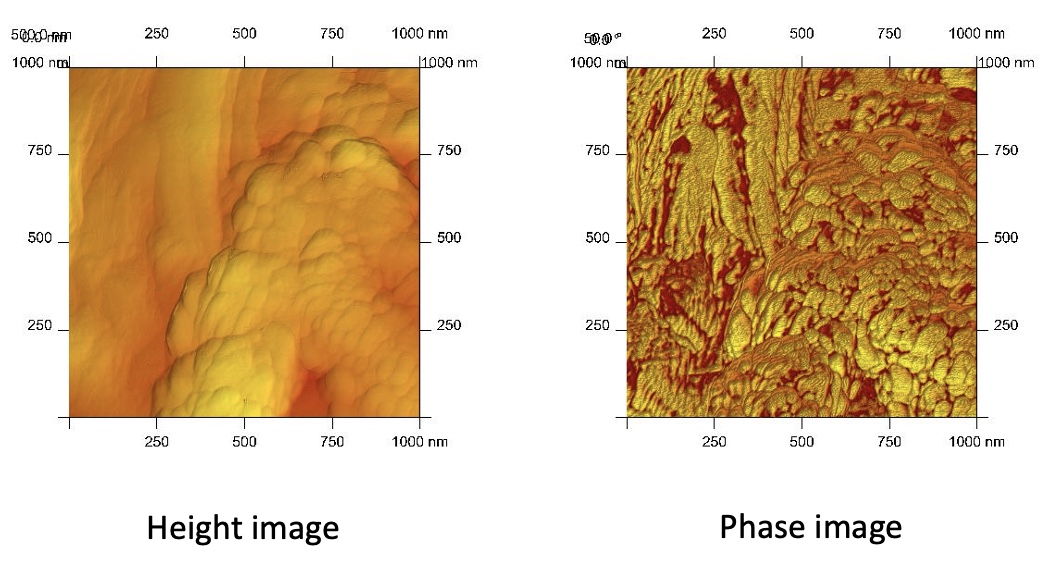
AFM PHASE IMAGES OF COTTON WEAVE
AFM images of cotton cross section
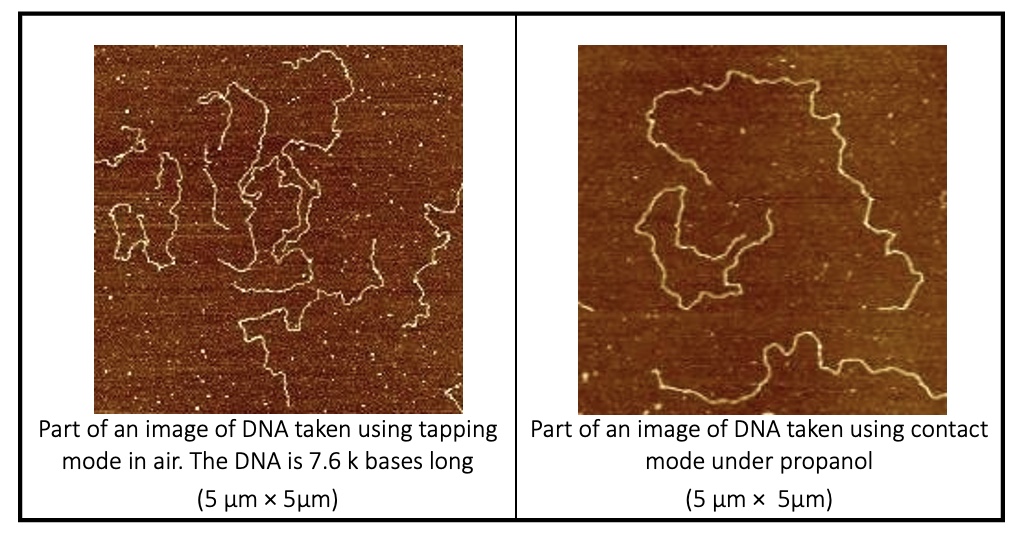
AFM IMAGES OF DNA

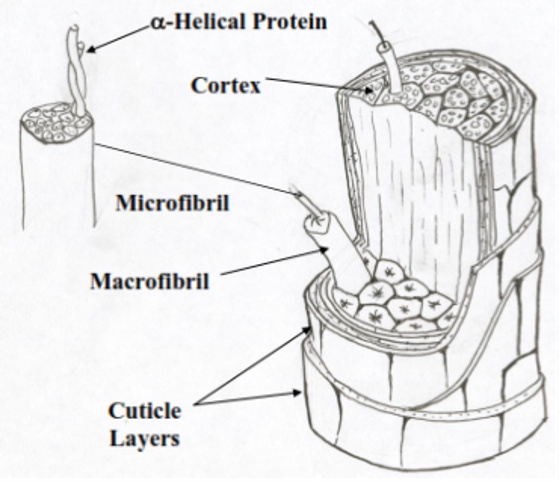
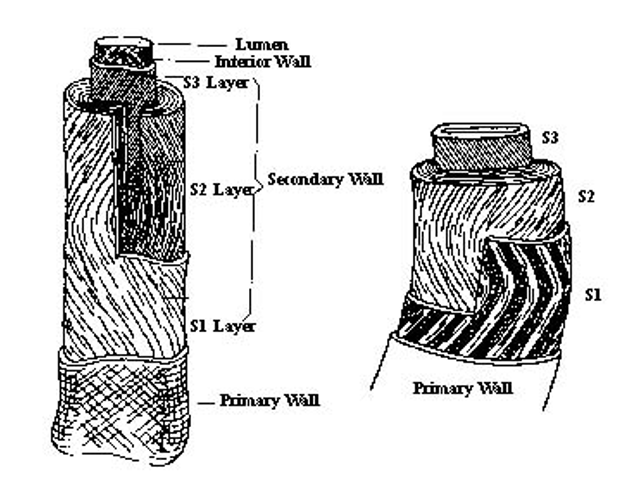
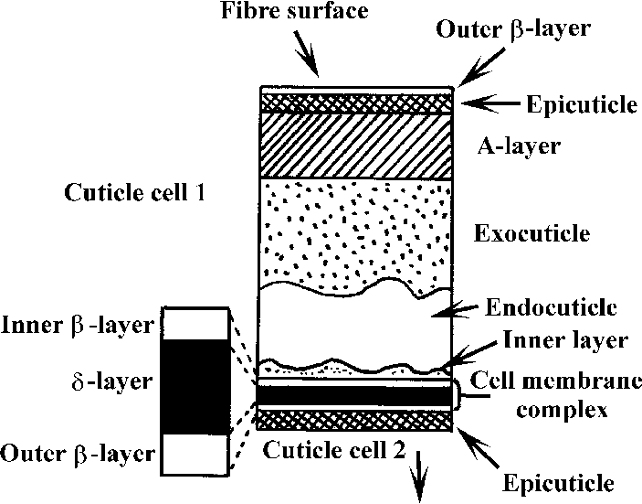
Human Hair
Brightfield microscopy
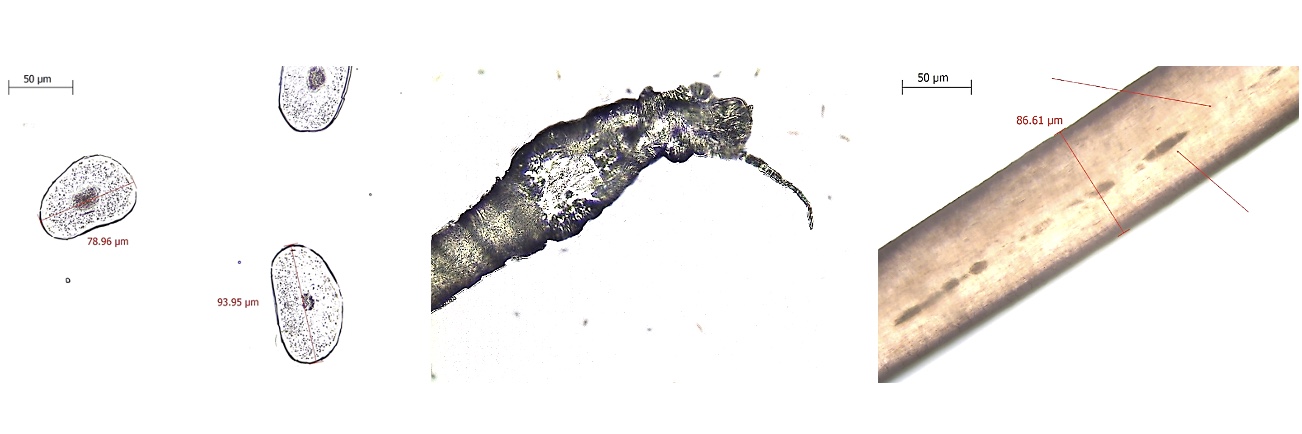
Darkfield Microscopy
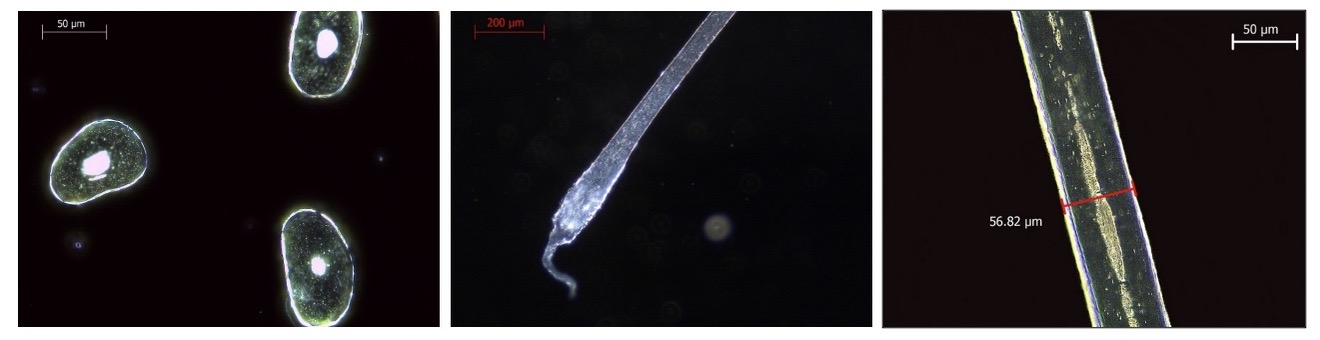
polarised light microscopy
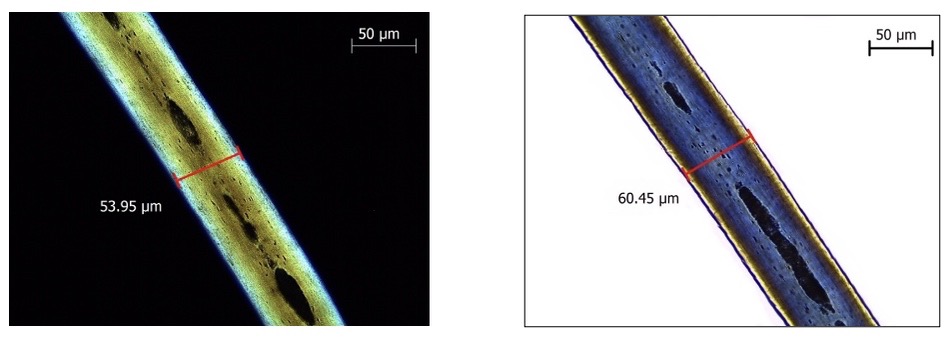
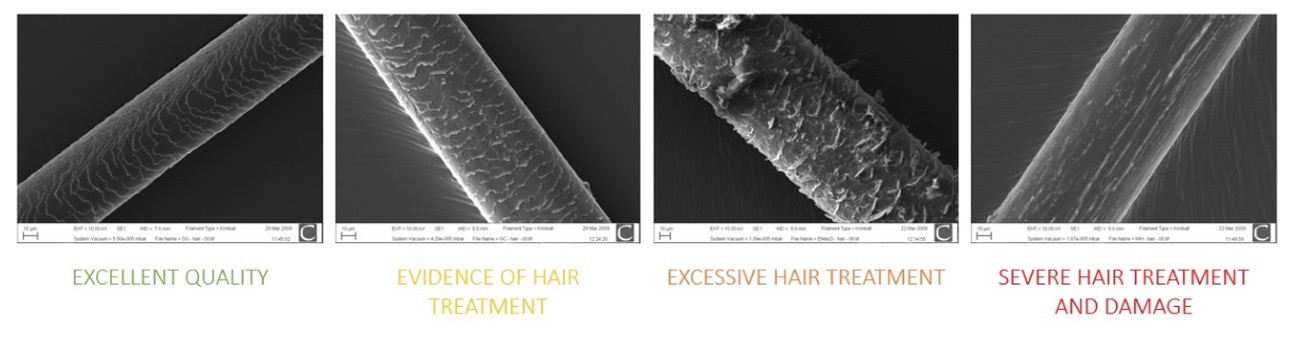
Electron micrographs of human hair
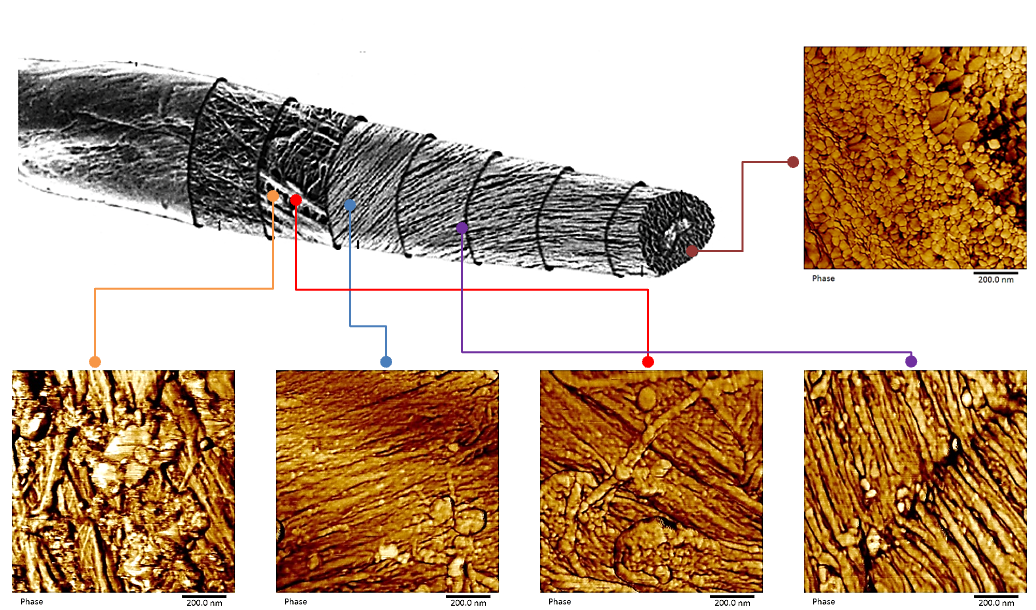
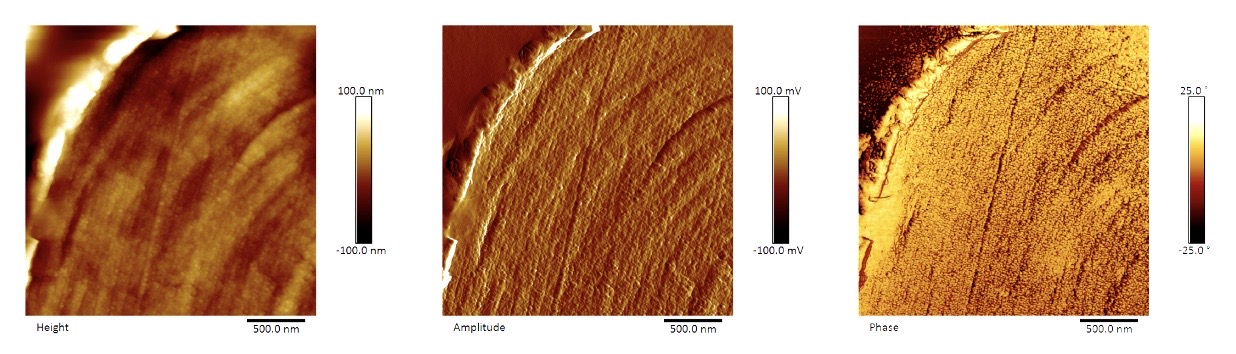
AFM images of Human Hair
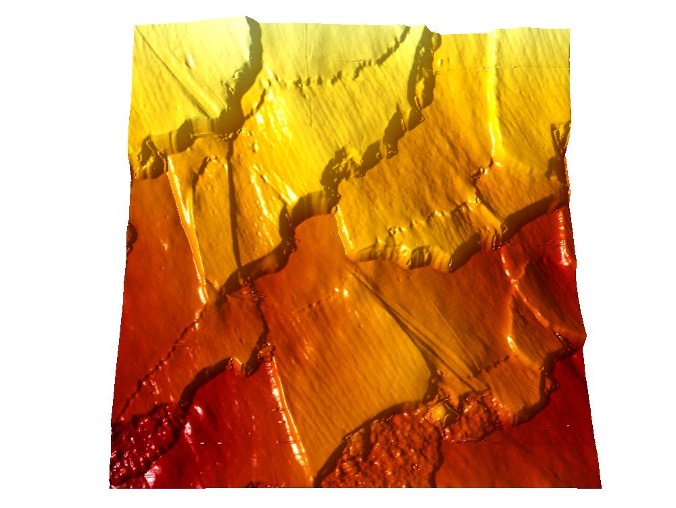
AFM images of human hair
AFM images of Human Hair

AFM Images of Human Hair
