Meiosis and Mendelian Genetics: Key Concepts and Crosses
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Diploid
Cells that contain two copies of each chromosome.
Gametes
Egg and sperm cells.
Gene
Section of DNA that provides the instructions for making a protein.
Alleles
Different versions of the same gene.
Homologous Chromosomes
Matching chromosomes from mom and dad that contain the same genes in the same locations but may have different alleles.
Law of Dominance
A dominant allele will express itself over a recessive allele.
Law of Segregation
The two alleles for a trait segregate during gamete formation.
Law of Independent Assortment
Genes for different traits are inherited independently of each other.
Purebred
Type of organism whose ancestors are genetically uniform.
Genetic Cross
The mating of two individuals.
P Generation
Parental generation in a genetic cross.
F1 Generation
First generation of offspring from a genetic cross.
F2 Generation
Second generation of offspring from a genetic cross.
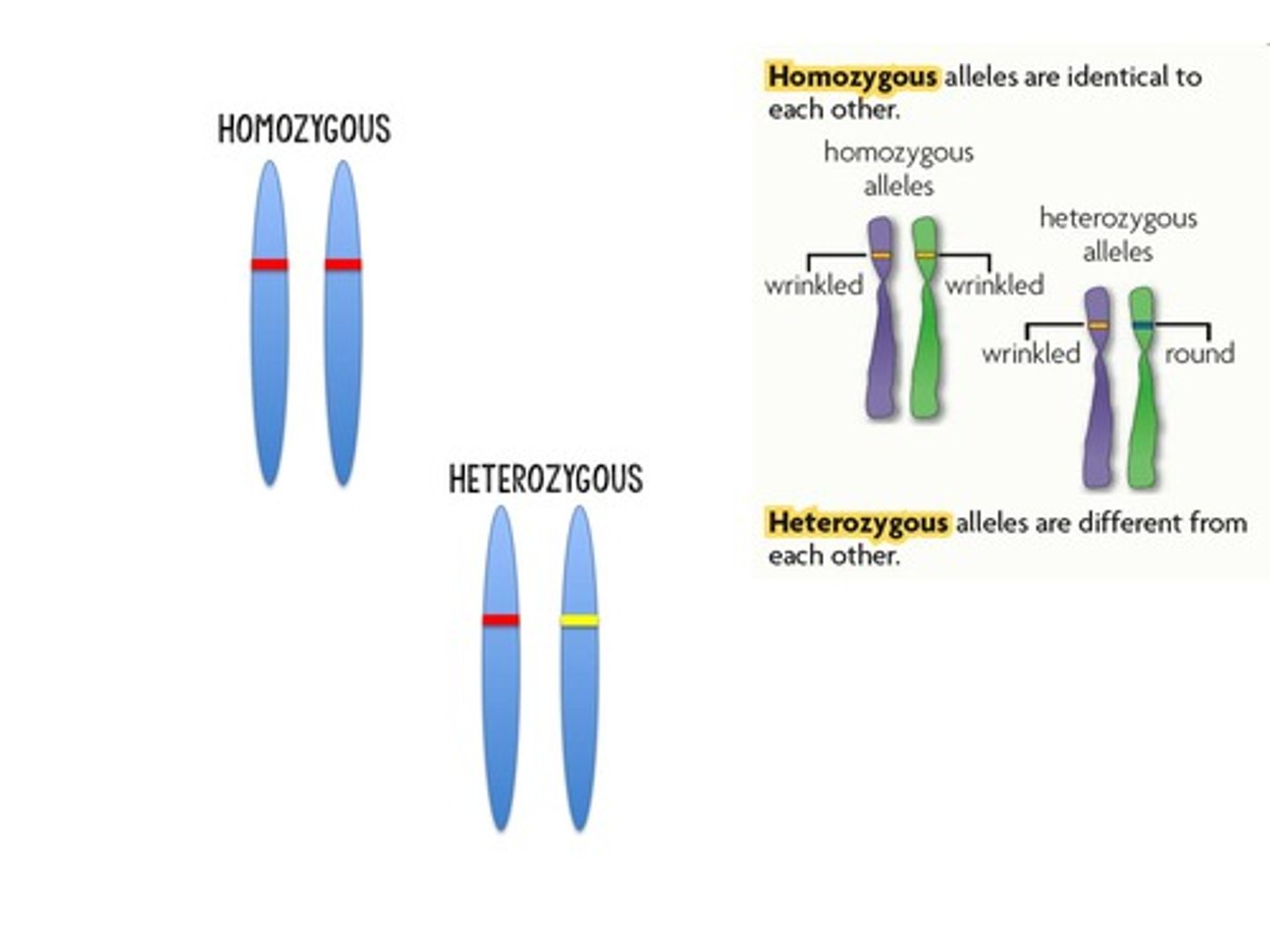
Homozygous
Having two of the same alleles for a gene.
Heterozygous
Having two different alleles for a gene.
Dominant Allele
An allele that expresses its trait even in the presence of a recessive allele.
Recessive Allele
An allele that only expresses its trait when the dominant allele is not present.
Genotype
The actual alleles inherited from parents.
Phenotype
The observable traits of an organism.
Traits
Characteristics that are observed in organisms.
Allele Notation
Uppercase for dominant alleles (e.g., A) and lowercase for recessive alleles (e.g., a).
Punnett Square
a diagram that shows the probability of inheriting traits from parents with certain genes.
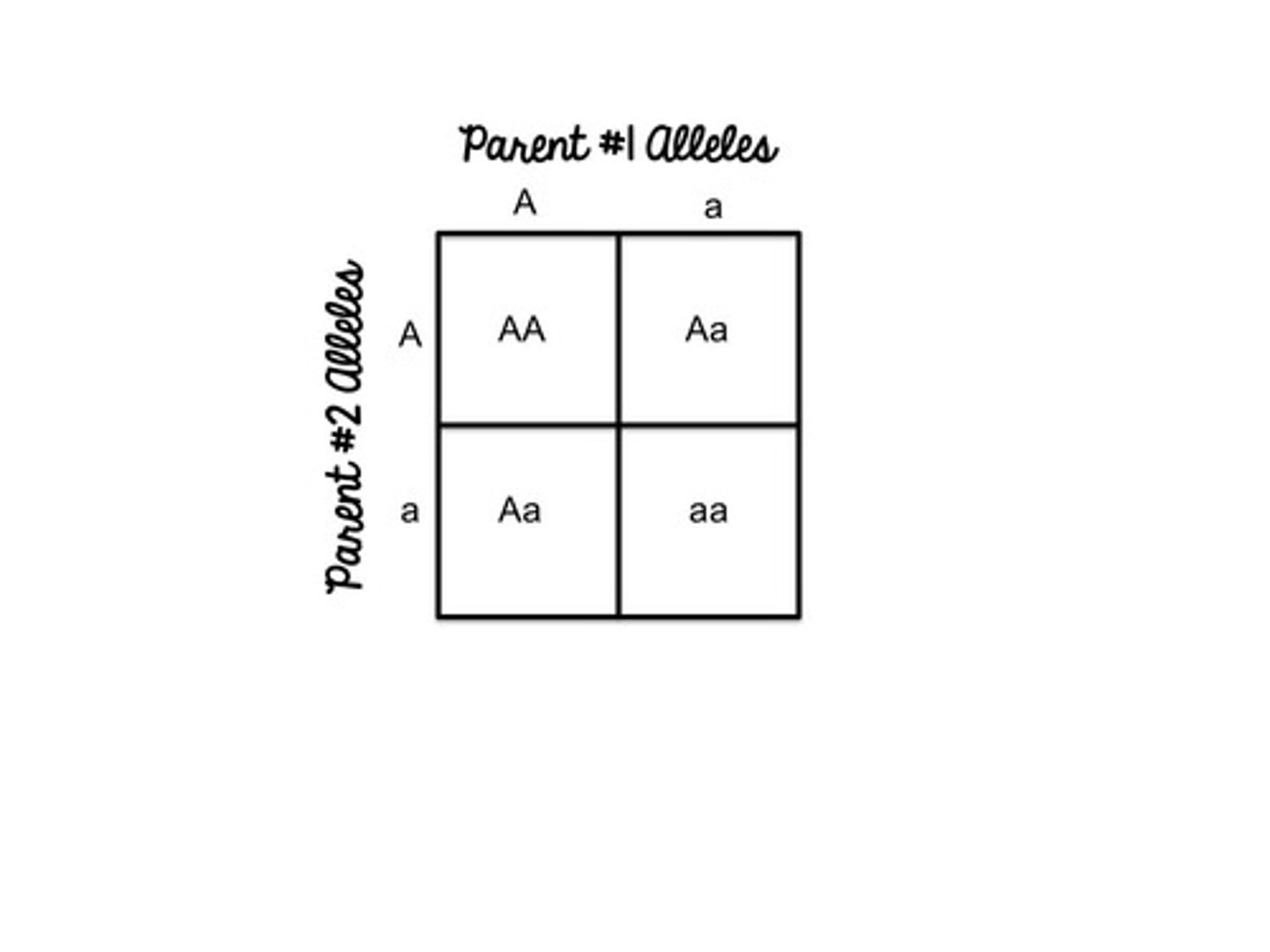
Monohybrid Cross
a cross between two organisms looking at one trait, with both parents being a hybrid for that trait. Resulting Phenotypic Ratio (3:1).
Genotypic Ratio
the ratio of different genotypes produced in a genetic cross.
Dihybrid Cross
Used when finding the possible genotypes for offspring when considering two traits at the same time. Both parents are hybrids for both traits. Resulting phenotypic ratio: 9:3:3:1
Dominant Trait
a trait that is expressed in the phenotype even when only one allele is present.
Recessive Trait
a trait that is only expressed in the phenotype when two copies of the allele are present.
Phenotypic Ratio
the ratio of different phenotypes produced in a genetic cross.
Cross
the mating of two organisms to produce offspring.
75% Round, 25% Wrinkled
the expected phenotypic ratio from a monohybrid cross of round and wrinkled seeds.
1RR:2Rr:1rr
the genotypical ratio from a monohybrid cross.