Neuroscience exam 1 Indiana university Dr. Deboeuf
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What did Aristotle say the brain did?
believed the heart was the source of intelligence
What about Hippocrates
Brain was source of sensation and intelligence
• What is the fluids hypothesis of neural function? How long did this idea persist?
Galen believed that neuronal transduction was done via fluids that flow through neurons. lasted about 1200 years
• What caused the downfall of the fluids hypothesis? Who was responsible?
electricity By Luigi Galvani.
• What replaced the fluids hypothesis?
electricity ran through neurons
• Where did Descartes believe the mind resided?
pineal glad
What was the debate between Golgi and Cajal about? Who "won?
Recticular theory (Golgi): nervous tissue is continuous network. Neuron theory(Cajal) neurons are discrete entities. Cajal won
• What does a molecular neuroscientist study? How is this different than what a cellular neuroscientist studies? A systems neuroscientist? Etc.
Molecular neuro: study of molecules
Cellular: how cells operate
• What is a synapse?
the space in which two neurons interact
• Could you identify a bipolar cell? A multipolar cell?
bi polar one dendrite one axon. multipolar: one axon multiple dendrites
• What makes neurons different from other cells?
They have dendrites and axons
• Is there more K+ inside or outside the cell? What about Na+?
more potassium inside the cell. less na inside the cell
What is the resting membrane potential of a typical neuron
-65
• What is the universal energy currency of a cell?
ATP
• What are the 2 forces that act on an ion? What is the term for the membrane potential at which these 2 forces are in equilibrium?
Diffusion: high to low concentration.
Electricity: charge particle movement.
Equilibrium potential: no net movement or equilibrium
• Provided with the equation, could you use the Nernst equation? Goldman equation? Why aren't these values the same?
They are different because the nernst is for one ion. while the goldman is for multiple
• How are the concentration gradients maintained?
Sodium potassium pump
• What part of the membrane phospholipids is hydrophilic, and which is hydrophobic?
hydrophillic head
hydrophobic tail
• What is conduction? What is its relationship to resistance?
• What is referred to by 'all-or-none' property of an action potential?
once depolarization crosses the threshold.
• Could you identify a Na+ channel from its single channel properties? K+?
voltage gated channels for NA+. they use the ball and chain method.
K+ channels are cylinder like
• What are the phases of an action potential? Movement of which ion is responsible for each phase?
threshold: VG sodium channels open
Rising phase: sodium increase
overshoot: membrane potential =
Falling phase: sodium gates inactivate. K opens
ARP: sodium channels inactive for some time
• What are nodes of Ranvier? What purpose do they serve? Why is myelin important?
nodes of raniver are the gapes between myelin.
• What is tetrodotoxin, and how is it toxic?
is a sodium blocker. blocks action potentials
• What is an absolute refractory period? Which ion mostly determines this?
when sodium channels are inactive do to ball and chain.
• What is happening in multiple sclerosis (MS)?
The immune system is attacking the myelin
• What are chemical synapses? How do they differ from electrical synapses?
chemical synapses use NT
• What are the steps involved in synaptic transmission?
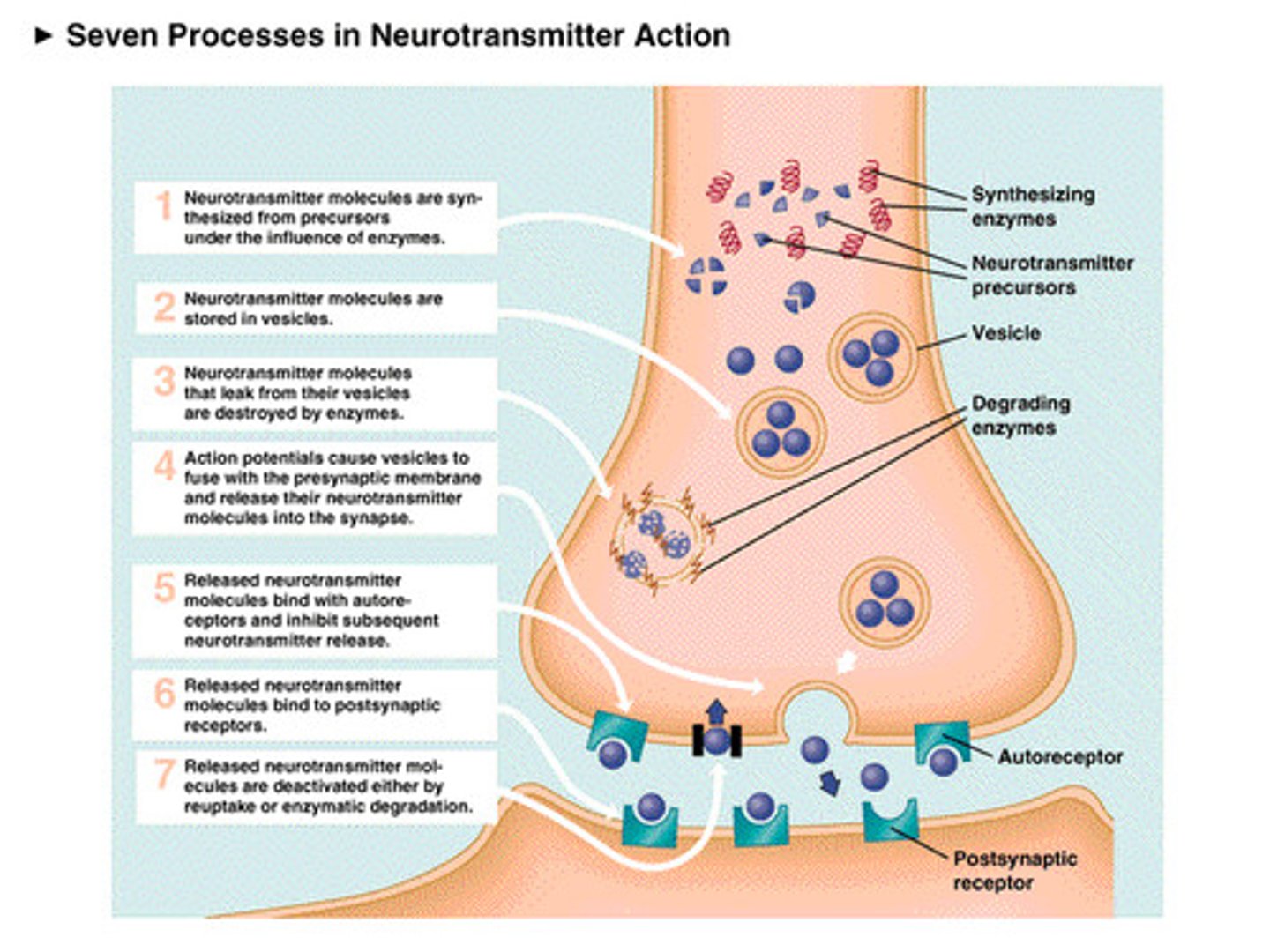
• What is a neurotransmitter (NT)?
they are a chemical that is released on the presynaptic side and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic side
• What is the primary excitatory NT? What type of ion channel does it open?
Glutamate: opens Na+ channels
• What is the primary inhibitory NT? What type of ion channel does it open?
GABA it opens Cl- channels
• What are IPSPs and EPSPs, and what ions primarily determine each?
IPSP = inhibitory post synaptic potential: Ligand channel, uses Cl-
EPSP: excitatory postsynapic potential: uses Na+ depolarizes
• What is the role of Ca2+ in an action potential?
It causes vesicles to fuse with presynaptic membrane
• What characteristics define a neurotransmitter?
it is present: it is then released: and it activates receptors on a postsynaptic membrane
• How is excess neurotransmitter removed from the synapse?
microglial cells: diffusion: or reuptake: or enzymatic breakdown
• What is the protein complex that helps fuse a synaptic vesicle with the membrane? (What does Botulinum and tetanus toxins do?)
The T-snare complex is responsible for fission. These toxins interupt the t-snare processes. thus preventing release of NT
• What are the major hemispheres of the brain?
Dorsal: top
Ventral: belly
Rostral: front
Caudal: back
• What is dark matter? White matter?
Dark matter is somas:
white matter is axons
• What is CSF and how is it made? What disorder is caused from a build-up of CSF?
CSF is cerebrospinal fluid: which is produced in the ventricles. Hydrocephalus
What brain imaging techniques are used to look at brain structure? Function?
CT and MRI are structure techniques.
PET and fMRI are functional
• What area do all major sensory inputs pass through?
The thalamus
• How do NMDA receptors differ from AMPA receptors?
AMPA are fast and use Na and K needs glutamate.
NMDA are slow use Ca2+ need glutamate and depolarization
• What is an ionotropic receptor? How does it differ from a metabotropic receptor? When is each important?
Ionotropic are ligand-gated and.
G-protein are metatropic andd cause activation of g-proteins in the cell, which are secondary messangers. think signal amplification
• Why are unconventional neurotransmitters considered unconventional? (What is retrograde signaling?)
They travel from post to pre. example: endocannabinoids released because of too much postsynaptic activity. which modulates presynaptic NT release
• What are transporters? What do selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors do (SSRI's such as Prozac) do?
they recycle released NT back into the cell. block this process and allow NT to stay in synapse
• What is an agonist? Antagonist?
agonist: action of NT
Antagonist: block NT action
• Why is taking alcohol and benzodiazepines a potentially lethal combination?
too many positive allosteric modulators increase the sensitivity to GABA. can stop breathing/heart