PSYC-2900 Chapter 2.1
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
central nervous system (CNS)
a division of the nervous system comprised of the brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
a division of the nervous system comprised of all of the nerves that receives external information/stimuli and directs it between the central nervous system and the rest of the body
nerves
composed of a membrane sheath, bundles of axons, and small blood vessels
neurons
the information-processor/transmitter of the nervous system. includes 3 types: sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons
soma
the cell body of the neuron containing the nucleus (DNA) and cellular machinery. the shape will differ depending on the type of neuron
dendrites
tree-like branches attached to the soma that receive signals using their receptors (receptor sites) on which substances bind to
axons
thin, cylindrical structures extending from the soma that carries action potentials to the terminal buttons of the neuron. depending on the type of neuron, it may be surrounded by a myelin sheath. running on the inner length of it, microtubules move substances between the soma and terminal buttons
myelin sheath
a fatty substance found surrounding the axons of some neurons, giving a lighter appearance. (i.e. the white matter of the brain) it provides insulation to the neuron, and speeds the movement of neural messages within the axon
terminal buttons
bud-like structures at the end of an axon’s branch. they form synapses with other neurons and release neurotransmitters into the synapse
synapse
a junction in between the terminal buttons of one neuron and dendritic/somatic membrane of another neuron
neurotransmitters
molecules/chemicals that are sent between synapses
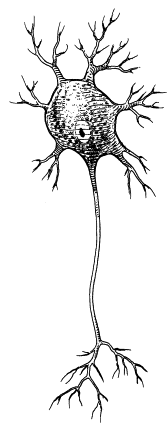
multipolar neurons
a shape-classified neuron that has multiple dendritic branches and multiple axon branches. unless the neuron is specified to be uni/bipolar, all other neurons are considered to be under this class
unipolar neurons
a shape-classified neuron that has one process (axon) extending from the soma that serves both functions of the dendrites and axons. they are common in invertebrates, and are not present in humans

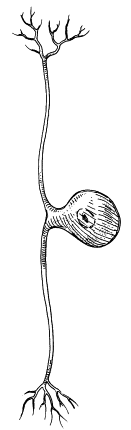
pseudounipolar neurons
a shape-classified neuron that has that has one process (axon) extending from the side of the soma, which then splits into two branches, one extending into the PNS and one to the CNS. the process serves functions of the dendrites and axons. they play a role in transmitting information related to touch, proprioception, pain, and temperature
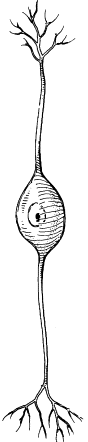
bipolar neurons
a shape-classified neuron that has one axon and one dendritic branch extending from the soma. they play a role in transmitting information related to sight, smell, and hearing
proprioception
the sense of the body’s position and movement
anaxonic neurons
a type of neuron that lacks an axon, and can therefore only receive signals, and cannot send signals, and instead communicate through their dendrites. they are found in the retina and the brain
membrane
the outer layer of a neuron
cytoskeleton
a layer within the neuron that extends throughout the cell to transport materials and maintain shape. it is made of 3 kinds of protein strands, including microtubules
microtubules
strands of proteins found within a neuron that act as conveyer belt between the soma and terminal buttons of the axon
cytoplasm
a clear, viscous fluid within the cell body of a neuron that holds organelles and molecules. it is the site of most chemical activities in the cell, including protein synthesis
mitochrondria
a cell organelle within the cytoplasm that produces adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
nucleus
a cell organelle within the cytoplasm that contains genetic material, such as chromosomes made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
protein synthesis
initiated by genes, it consists of 2 steps:
transcription from DNA to messenger RNA (mRNA) within the nucleus
mRNA leaves the nucleus, attaches to ribosomes in the soma/cell body where it is translated into a protein
enzymes
proteins that control chemical reactions for the cell
(the construction & demolition crew of the cell)
axoplasmic transport
a process that moves materials between the soma and terminal buttons of the axon. small vesicles hold the materials being moved, attach onto microtubules, and are carried to their destination
anterograde axon transport
axon transport in which vesicles holding materials are carried towards the terminal buttons of the axon
retrograde axon transport
axon transport in which vesicles holding materials are carried towards the soma
glial cells
cells that support and protect other cells in many different functions depending on the type. 3 types include astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglia
astrocytes
a type of star-shaped glial cell found in the CNS that sends branches with u-shaped buttons to the soma of neurons and to capillaries. they use phagocytosis to digest debris (i.e. waste/dead cells) and send it to the vascular system
oligodendrocytes
a type of tube-shaped glial cell found in the CNS that provide support to axons by producing myelin sheaths
nodes of ranvier
exposed parts of the axon between sections of myelin, that allow ions to diffuse in and out of the neuron, propagating action potentials
microglia
the smallest type of glial cell that act as phagocytes, and serve as part of the immune system. they are responsible for inflammatory reaction to damage by cleaning dead cells, and may have a constructive role during development
schwann cells
a type of supporting cell found in the PNS that provide one segment of myelin sheath by surrounding its’ entirety around an axon
blood brain barrier (BBB)
a protective layer found in the CNS that is produced by the cells in walls of the brain’s capillaries, and reinforced by astrocytes. it is selectively permeable, allowing water and small, neutrally-charged molecules in/out, however, larger substances require active transport to enter/exit, using ATP. it regulates the composition of extracellular fluid by protecting the brain from harmful substances, and allowing nutrients to reach the brain
(e.g. can detect toxic substances entering blood and induce vomiting)
area postrema
a weak region of the blood brain barrier