lecture 3 & 4 - Microbial Life I & ll
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Earth’s Timeline
Earth formed ~4.5 bya
Liquid water ~4.3 bya
Life ~4 bya
What is needed to make a primitive cell?
Container
Mechanism of self replication/catalysis
What are the requirements for life?
Heredity
Reproduction
Growth
Development
Metabolism
Responsiveness
Metabolism
Transport
Archean Era
4.25 bya
3.8 bya Bacteria & Archaea diverge
3.4 bya Orgin of photosynthesis
2.5 bya Ends with Great Oxygenation Event
Proterozoic Era
2.5 bya Great oxygenation event
1.7 bya Eukaryotes emerge
0.6 bya Cambrian Explosion
Macromolecules
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Protein
Nucleic Acids
Carbohydrates
Organic compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen atoms
(CH2O)n
→ Resembles carbon + water
→ N=Number of units that combine to make the finished carbohydrate
Saccharide
Simple carbohydrate
Monosaccharide
Simple polyhydroxy aldehyde/ketone containing 3-7 carbons
Disaccharide
Combination of two monosaccharides
Polysaccharide
Polymer of 5 or more monosaccharides, can be branced or linear
Role of Carbohydrates
Provide structural support, nutrient and energy storage, adhesion
Celluose
Carbohydrate
Rigid polymer that provides cell wall support in plants and algae
Only a few bacteria can break down cellose
Peptidoglycen
Structural support in bacterial cell walls
Form of carbs in plants and
Starch ( plants, algae, fungi )
Glycogen ( animals, bacteria, protozoa)
Hydrolysis
breaking down large molecules
Lipids
Not soluble
Long hydrocarbon chains that are hydrophobic
Function of Lipids
Storage and structue
Storage: Triglycerides
Cell membrane structure: Phospholipids
Cell membrane components: Sterols and steroids
Waterproofing: Wax
Triglycerides
Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids
Building blocks of proteins
Amino acids
Peptide bonds
Bonds between amino acidsP
Peptide
Short amino acids
Polypeptide
Long amino acid chain (20+)
Primary Protein Structure
Amino acid sequence
Secondary protein structure
Hydrogen bonds between amino acids located near each other
a helix or B sheet
Tertiary
Complex 3D structure of a protein
Quartnary
2 or more polypeptides form a protein complex
DNA
Genetic info
RNA
Carries the instructions stored in DNA
Components of nucleotides
Nitrogenous Base
Pentose
Phosphate
Purine
A and G{
Pyrimideine
T C and U
Phylogeny
Evolutionary history and relationships between organisms
Taxonomy
Organization and classification of organism
3 domains of life
Bacteria
Eukarya
Archaea
What is the classification naming system for organisms?
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
External Bacterial Cell Structure
Locomotor Appendages
Attachment Appendages
Glycocalyx
Capsules
Slimes
Appendages of a bacterial cell
Locomotor Appendages
Attachment Appendages
Locomotor / Motility appendages
Flagella
Propellor like action
Gives cells the ability to move in aq. environments
Attachment appendages
Fimbriae
Short bristles
Gives the cell the ability to attach to surfaces and host cells
Pilli
Longer
Gives the cell the ability to attach to surfaces and cells
Can have a specific function like transferring DNA between cells
3 types of bacterial motility
Phototaxis
Magnetotaxis
Chemotaxis
Phototaxis
Movement response to a light signal
Magnetotaxis
Movement response to a magnetic field
Chemotaxis
Movement in response to a chemical signal
How does a flagella move
Run: counterclockwise
Tumble: Flagella move clockwise
Bacterial glycocalyx
Coating of macromolecules that provides protection for the cell
Slime layer: Loose shield protects from dehydration and allows adhesion
Capsule: Tightly bounded
Encapsulated cells have an increased pathogenicity. Why?
Cell Wall
Provides cell shape and structural support
Composed of Peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan
Composed of glycan chains crosslinked by peptide fragments
Peptidoglycan amount varies among different bacteria
Peptidoglycan is needed to prevent cell lysis
Lysozyme
Breaks bonds in glycan chains resulting into bacterial cell walls down
Located in tear, saliva, sinus and nasal fluids
Gram positive cell walls
Thick peptidoglycan layer
Teichoic acids
Loosely bounded to cell membrae
Periplasmic space
Gram Negative Cell wall
•Comprised of a thinner layer of peptidoglycan + an outer membrane
•Lipopolysaccharides (LPS)
•Outer membrane proteins
•Porins- Control transport in/out of cell
•Structural proteins
•Thinner layer of peptidoglycan makes Gram – cells much more flexible than Gram + cells
Cell membrane components
Phospholipid bilayer
Selective permeability
Fluid mosaic model
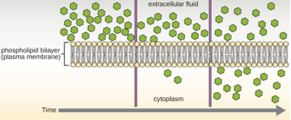
Simple diffusion
Molecules move down a concentration gradient down the phospholipid bilayer
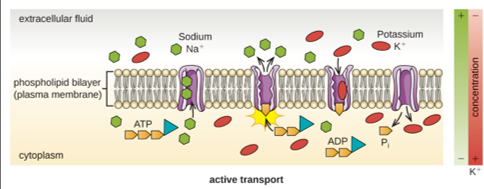
Active transport
Energy dependent movement against a concentration gradient through a pump
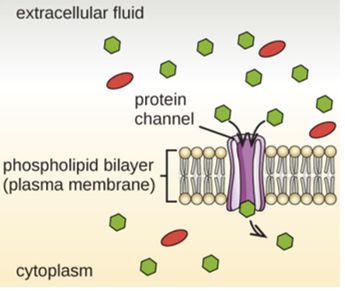
Facilitated Transport
Movement down a concentration gradient through a membrane protein
Nucleoid & DNA
Chromosome location
Prokaryotic cells have a circular chromosomes and there is one
Plasmids
•small, extrachromosomal, circular pieces of DNA
•Not all cells of a species (or a population) will have these plasmids
•Contain genes that are NOT necessary for cellular function
Ribosomes
Protein synthesis
Composed of individual subunits: proteins and subunits
Smaller than eukaryotic ribosomes
Gram stain steps