Business Test Chapter 1
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
business
organization that provides goods or services to earn profits
EX: Smucker's
profits
a business's revenue minus expenses
what is the lure of profits?
the lure of profits leads some people to abandon the security of working for someone else and assume the risks of entrepreneurship
revenue
price x quantity
expenses
bills, cost of materials, wages, and capital
EX: grapes, machinery
STEEPLE analysis
a way to analyze external environmental factors affecting business objectives and strategies
what are the factors of STEEPLE?
Social, Technological, Economic, Environmental, Political, Legal, Ethics
environmental environment
weather, climate, flora & fauna, and pressure from environmental groups & activists
EX: heat wave where grapes are produced
external environment
everything outside an organization's boundaries that might affect it
domestic business environment
the environment in which a firm conducts its operations and derives its revenues
EX: Smucker's store in NYC
global business environment
The international forces that affect a business
EX: political unrest where hazelnuts are produced
technological environment
all the ways by which firms create value for their constituents, including the state of tech advancement & introduction to new technology
EX: new jam-making machines
political environment
government (stability, ideologies, type), attitude to free markets, incentives, and tariffs
EX: new tariff on grapes
legal environment
law influencing business activity (competition, health & safety, employee protection, consumer protection)
EX: animal welfare statement from Smucker's
sociocultural environment
the customs, mores, values, and demographic characteristics of the society in which an organization functions
EX: eating jam becomes frowned upon as unhealthy
economic environment
relevant conditions that exist in the economic system in which a company operates (such as GDP growth, inflation, exchange rates, interest rates, and unemployment rates)
EX: unemployment gets so low that Smucker's raises their wages
ethic environment
a general code of ethics followed by most people in the country & a tendency of people to be ethical
EX: Smucker's unfairly treats its workers so it has to shut down
code of ethics
a company's formal statement of ethical principles and rules of conduct
economic system
a nation's system for allocating its resources among its citizens
factors of production
resources used in the production of goods and services—labor, capital, entrepreneurs, physical resources, and information resources
labor (human resources)
the physical & intellectual contributions people make while engaged in economic production
EX: Smucker's factory workers
capital
financial resources needed to create and operate a business enterprise
EX: funds that Smucker's needed to start operating and manufacturing
entrepreneur
individual who accepts the risks and opportunities involved in creating and operating a new business venture
EX: Jerome Monroe Smucker, who created Smucker's
physical resources
tangible items that organizations use in the conduct of their businesses, including natural resources & raw materials
EX: coal used to power jam-making machines
information resources
data and other information used by businesses, including market forecasts, the specialized knowledge of people, & economic data
EX: Smucker's price forecasts
planned economy
economy that relies on a centralized government to control all or most factors of production and to make all or most production and allocation decisions
EX: communism, socialism
market economy
economy in which individuals control production and allocation decisions through supply and demand
EX: capitalism
communism
political system in which the government owns and operates all factors of production
EX: North Korea
market
mechanism for exchange between buyers and sellers of a particular good or service
supply & demand
free to buy/sell what you want (work wherever you want)
capitalism
system that sanctions the private ownership of the factors of production and encourages entrepreneurship by offering profits as an incentive
EX: United States
mixed market economy
economic system featuring characteristics of both planned and market economies
privatization
process of converting government enterprises into privately owned companies
socialism
planned economic system in which the government owns and operates only selected major sources of production
demand
the willingness and ability of buyers to purchase a good or service
supply
the willingness and ability of producers to offer a good or service for sale
law of demand
principle that buyers will purchase (demand) more of a product as its price drops and less as its price increases
EX: Smucker's sees people buying less, so they lower the prices on their jam. Then, people buy more jam
law of supply
principle that producers will offer (supply) more of a product for sale as its price rises and less as its price drops
EX: Smucker's sees people buying more, so they raise the prices on their jam. Then, people buy less jam
demand and supply schedule
assessment of the relationships among different levels of demand and supply at different price levels
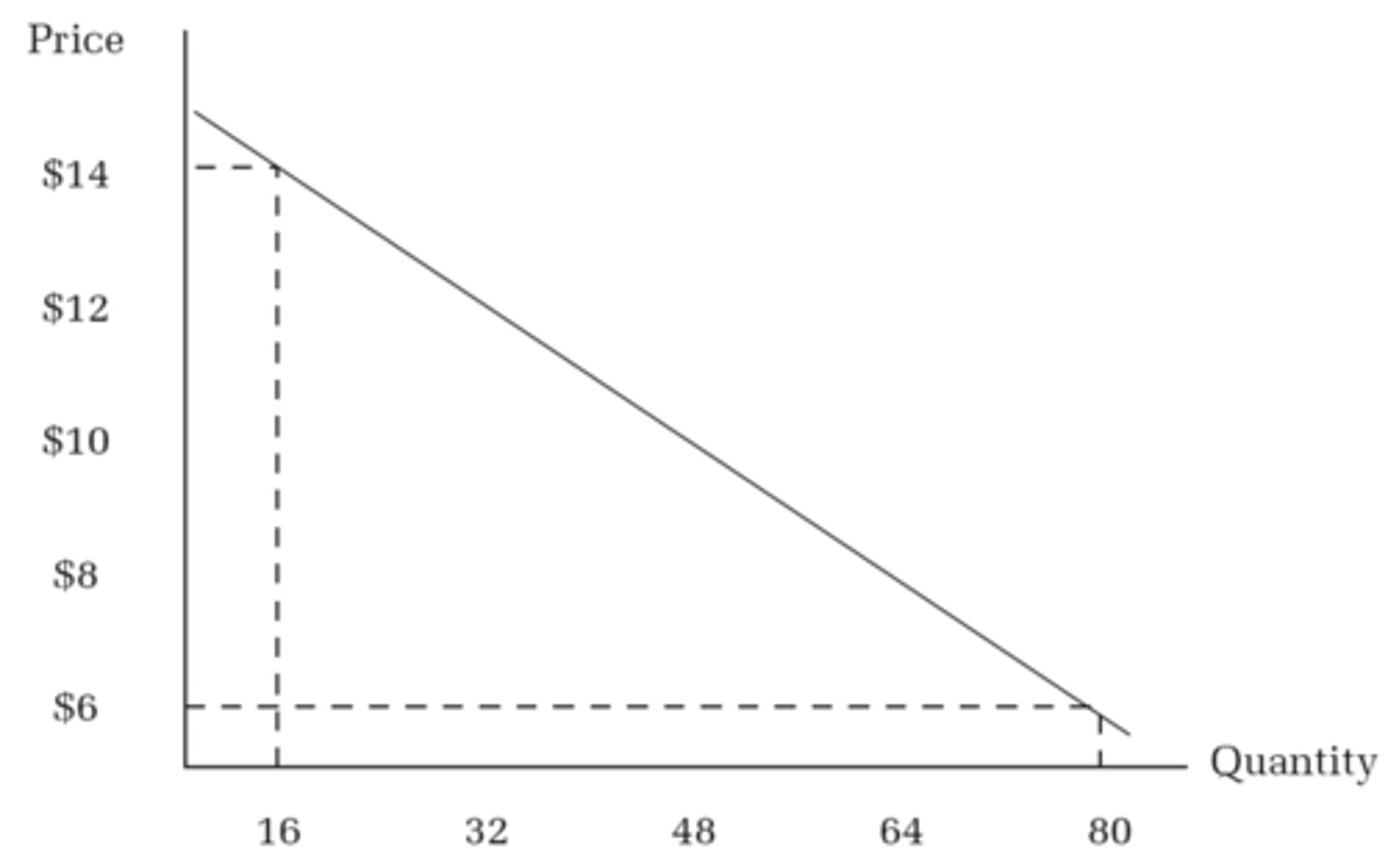
demand curve
graph showing how many units of a product will be demanded (bought) at different prices
supply curve
graph showing how many units of a product will be supplied (offered for sale) at different prices
market price (equilibrium price)
profit-maximizing price at which the quantity of goods demanded and the quantity of goods supplied are equal
surplus
situation in which quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded
EX: Smucker's has produced too much jam and cannot sell all of it
shortage
situation in which quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied
EX: Thanks to a trend, everyone rushes to buy Smucker's but there is not enough
determinants of demand
- Consumer tastes & preferences (EX: Smucker's vs Welch's)
- Consumer expectations (concern = less buying to preserve wealth) (EX: expect reopenings)
- # of buyers (EX: low birth rate)
- Income (EX: lottery)
- Prices of related goods (EX: Jif lowers prices)
complementary/substitute good
two or more products that go very well together
EX: Jam and peanut butter
determinants of supply
- # of sellers (EX: more competitors -> more suppliers)
- Prices of other goods (EX: welch's lowers prices)
- Producer expectations (EX: worried about Covid -> less supply)
- Resource prices (EX: grapes $ go up, less jelly can be made)
- Technology (EX: automatic Jam robot)
- Tax & subsidies (EX: tax lifted from jam -> more supply)
private enterprise
economic system that allows individuals to pursue their own interests without undue governmental restriction
EX: United States
what are the four elements required in a private enterprise?
1) private property rights
2) freedom of choice (supply + demand)
3) profits
4) competition
private property rights
ownership of resources used to create wealth is individually owned
competition
vying among businesses for the same resources or customers
do consumers benefit more from high or low competition?
high competition
perfect competition
market or industry characterized by numerous small firms producing an identical product
EX: wheat farmers
monopolistic competition
market or industry characterized by numerous buyers and relatively numerous sellers trying to differentiate their products from those of competitors
EX: stationery store
oligopoly
market or industry characterized by a handful of (generally large) sellers with the power to influence the prices of their products
EX: car industry
monopoly
market or industry in which there is only one producer that can therefore set the prices of its products
EX: PSE&G
natural monopoly
industry in which one company can most efficiently supply all needed goods or services
EX: PSE&G
economic indicators
statistics in context of time that help assess the performance of an economy (whether an economic system is strengthening, weakening, or remaining stable)
business cycle
short-term pattern of economic expansions and contractions
aggregate output
the total quantity of goods and services produced by an economic system during a given period
what happens when aggregate output increases?
output per capita increases
what is the primary measure of growth in a business cycle?
aggregate output
standard of living
the total quantity and quality of goods and services people can purchase with the currency used in their economic system
gross domestic product (GDP)
total value of all final goods and services produced within a given period by a national economy through domestic factors of productio
(a measure of aggregate output)
(outflow)
what happens if GDP increases?
there is economic growth
gross national product (GNP)
total value of all final goods and services produced by a national economy within a given period regardless of where the factors of production are located (domestic or global)
(inflow)
GDP per capita
gross domestic product divided by total population
real GDP
GDP adjusted to account for changes in currency values and price changes
nominal GDP
GDP measured in current dollars or with all components valued at current prices
purchasing power parity
the principle that exchange rates are set so that the prices of similar products in different countries are about the same
(stability, quantity able to purchase)
what happens if there is less purchasing power parity?
a lower standard of living
productivity
a measure of economic growth that compares how much a system produces with the resources needed to produce it
how does the standard of living improve?
only through increases in productivity
balance of trade
the economic value of all the products that a country exports minus the economic value of all the products it imports
(factors into economic growth)
trade deficit
when a country imports more than it exports
national debt
the amount of money the government owes its creditors
stability
condition in which the amount of money available in an economic system and the quantity of goods and services produced in it are growing at about the same rate
what is the chief goal of an economic system?
economic stability
what is a stable growth rate?
2 to 5%
inflation
occurs when widespread price increases occur throughout an economic system
(more $ to spend but same # of products to buy)
(threatens stability, purchasing power declines)
(better than deflation)
BLS
Bureau of Labor Statistics
FRED
Federal Reserve Economic Data
deflation
when prices go down
(shrinking economy)
how would you correct unemployment?
inject more money into an economy
(EX: Economic Recovery Act of 2009)
unemployment
the level of joblessness among people actively seeking work in an economic system
what happens if there is low unemployment?
low unemployment -> shortage of labor -> raise wages -> raise price of products -> reduced sales -> cut back on hiring -> high unemployment
consumer price index (CPI)
a measure of the average change of prices of typical goods/services (market basket) from the prior period (previous month) purchased by consumers living in urban areas
how did the 2009 recession occur?
housing market was big -> people buy things with money they don't have -> loose credit -> banks sell structure notes (collected credit) -> people can't pay it back
(snowball effect)
recession
a period during which aggregate output, as measured by GDP, declines
(2 quarters)
depression
a prolonged and deep recession
fiscal policies
policies used by a government regarding how it collects and spends revenue
monetary policies
policies used by a government to control the size of its money supply
stabilization policy
government economic policy intended to smooth out fluctuations in output and unemployment and to stabilize prices
what causes a recession?
1) a shock
2) a bursting bubble
3) federal reserve bank meddling
4) fear
what stops a recession?
confidence
employed
currently has a job
out of the labor force
a person with no job and not actively looking for one
unemployed
no job and actively looking for one
(must be 16+, looked for work in the previous 4 weeks, currently available for work)
underemployed
working part time and would want to work full time OR overqualified for their job
unemployment rate
percentage of labor force that are unemployed
(# unemployed)/(# people in labor force) x 100