Morris, Biology for the AP Course 1e - Mod 3
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
ribose
A pentose sugar commonly found in RNA.
functional group
A group of one or more atoms that has a particular chemical property on its own, regardless of what it is attached to.
deoxyribose
The pentose sugar component of DNA.
disaccharide
Two simple sugars joined by a covalent bond; an example is sucrose.
polysaccharide
A polymer of simple sugars. Polysaccharides provide long-term energy storage or structural support.
complex carbohydrate
A long, branched chain of monosaccharides.
cell membrane
The membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm of the cell, separating the inside of the cell from the outside of the cell; also known as plasma membrane.
triacylglycerol
A lipid composed of a glycerol backbone and three fatty acids.
glycerol
A 3-carbon molecule with hydroxyl groups attached to each carbon; a component of triacylglycerol.
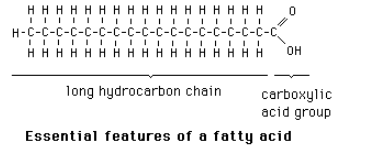
fatty acid
A long chain of carbons attached to a carboxyl group; three fatty acid chains attached to glycerol form a triacylglycerol, a lipid used for energy storage.
saturated
Describes fatty acids that do not contain double bonds; the maximum number of hydrogen atoms is attached to each carbon atom, "saturating" the carbons with hydrogen atoms.
unsaturated
Describes fatty acids that contain carbon-carbon double bonds.
van der Waals force
An interaction of temporarily polarized molecules because of the attraction of opposite charges.
steroid
A type of lipid; the precursor molecule for cholesterol and steroid hormones.
phospholipid
A type of lipid and a major component of the cell membrane.